Definitions of Enthalpy change (Year 13)
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
ΔatHθ (Enthalpy of Atomisation)
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous atoms is formed from the element in its standard state
ΔrHθ (The standard enthalpy change of reaction)
The enthalpy change when a reaction occurs in the molar quantities shown in the chemical equation
With all reactants and products in their standard states
ΔcHθ (The standard enthalpy of combustion)
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is completely burned in oxygen,
under standard conditions with all reactants and products in their standard states
ΔfHθ (The standard enthalpy of formation)
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions
ΔneutHθ (The standard enthalpy of neutralisation)
The enthalpy change when solutions of an acid and alkali react together to form 1 mole of water, under standard conditions
ΔIE1Hθ (The first ionisation energy)
The energy needed to form 1 mole of gaseous unipositive ions from 1 mole of gaseous atoms
ΔIE2Hθ (The second ionisation energy)
The energy needed to form 1 mole of gaseous dipositive ions from 1 mole of gaseous unipositive ions
ΔEA1Hθ (The first enthalpy of electron affinity)
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous atoms each gain an electron to form 1 mole of gaseous uninegative ions
ΔEA2Hθ (The second enthalpy of electron affinity)
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous uninegative ions each gain an electron to form 1 mole of gaseous dinegative ions
ΔhydHθ (The enthalpy change of hydration)
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous ions are dissolved in water to form hydrated ions
ΔsolHθ (The enthalpy change of solution)
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of solute is dissolved by a solvent
(The Solvent is nearly always water)
ΔLEFHθ (The enthalpy of lattice formation/Lattice Enthalpy)
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound is formed from its gaseous ions
ΔLEDHθ (The enthalpy of lattice dissociation)
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound is broken up into its constituent ions in the gas phase
ΔDISHθ (The enthalpy of bond dissociation)
The enthalpy change when one mole of covalent bonds is broken in the gaseous state
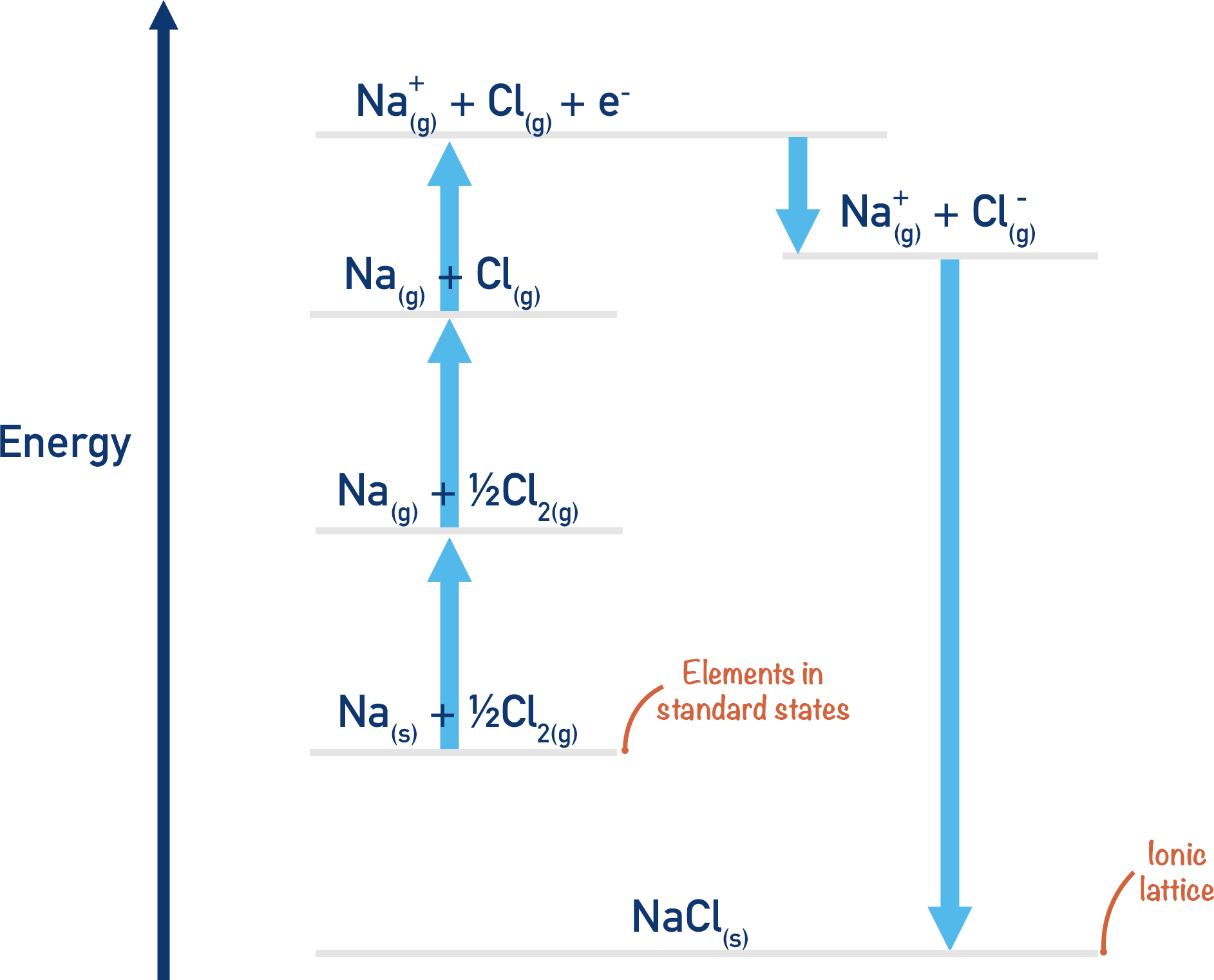
Born Haber Cycle
The conversion of enthalpy of atomisation to bond dissociation enthalpy
Double it
The Perfect ionic model
All ions are completely spherical
all ions have an even charge distribution
The attractions are purely electrostatic
There is no covalent character in the bonds (Purely ionic)
ΔLEFHθ trends within periodic table
Decreases going down the group
increases going across the period