A&P - 3.2 The Cytoplasm and Cellular organization (non-membranous organelles)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
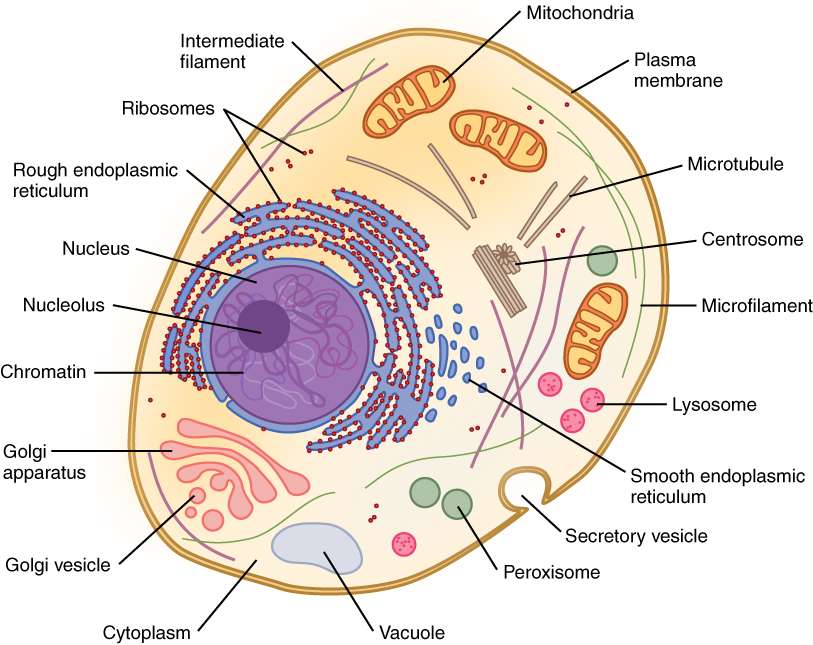
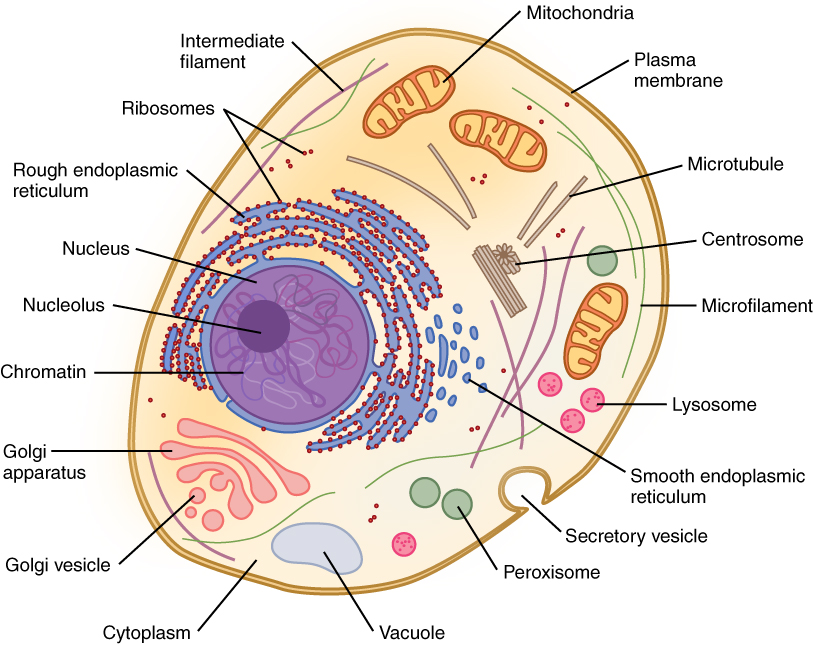
non-membranous organelles
not completely enclosed by membrane so that all of their components are in direct contact with the cytosol
includes: cytoskeleton, microvilli, cilia, ribosomes
cytoskeleton
formed by rod-like proteins that have an important role in maintaining cell shape and structure and cellular movement
consists of: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments
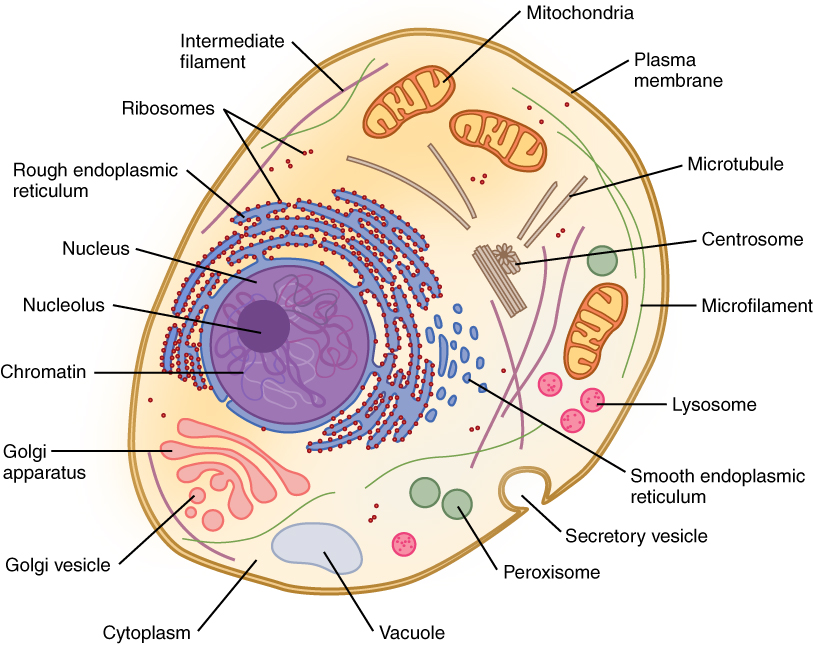
microtubules
thickest of the cytoskeletal filaments, composed of tubulin subunits that function in cellular movement and structural support, resist compression
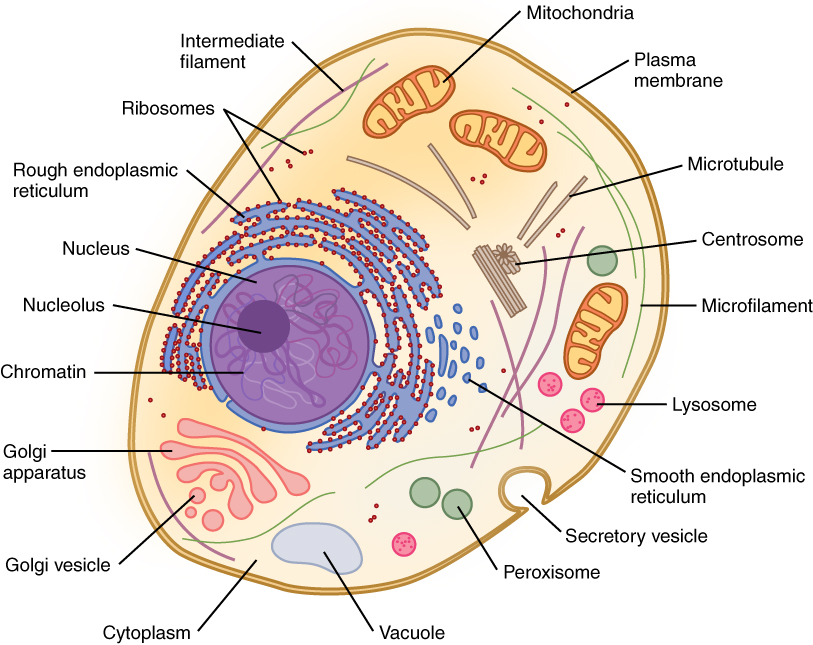
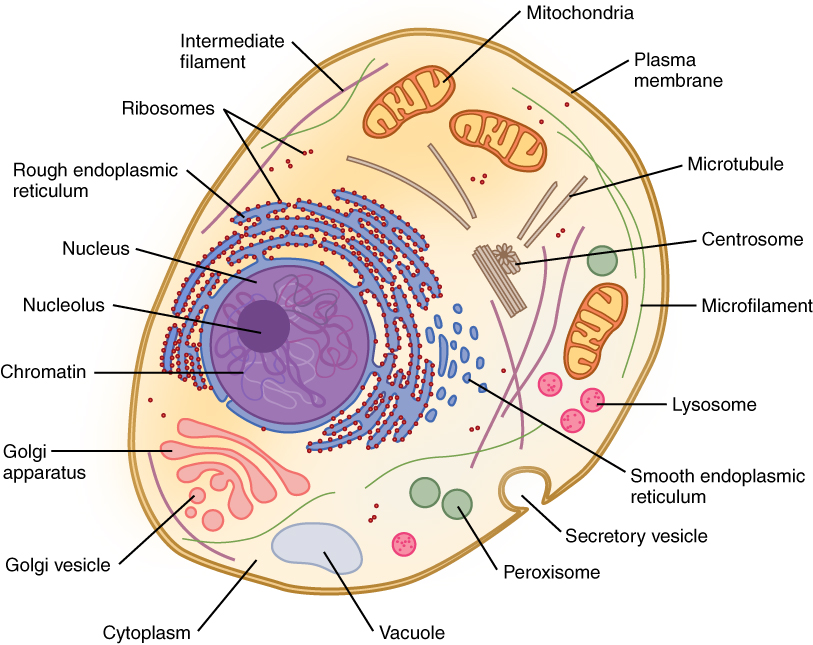
centrosome
region near the nucleus
organizes microtubules during cell division
centrioles
cylindrical structures composed of short microtubules - provides the origin for microtubule growth
two centrioles are located at the centrosomes
during cell division centrioles are associated with the formation of spindle fibers which move the strands of DNA to the poles
microfilaments
smallest of the cytoskeleton elements, composed of the protein actin that forms chains, common in the periphery of the cell, provides cellular structural support, large component of muscle tissue and muscle contraction
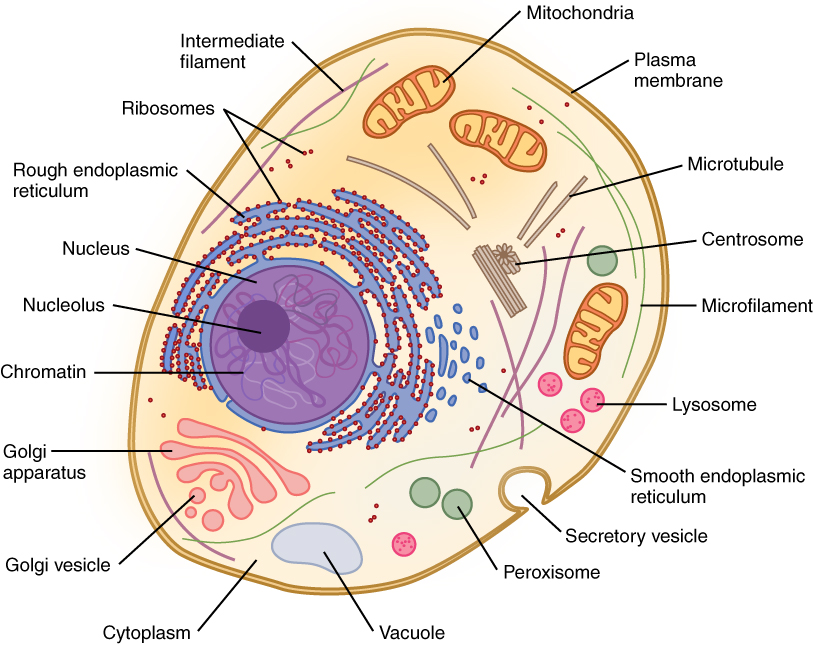
intermediate filaments
strongest and most durable of the cytoskeleton elements, made up of subunits of a protein called keratin that would together like the threads of a rope, resist tension
microvilli
finger-shaped extension of the plasma membrane
greatly increase surface area of the cell and enhance its ability to absorb nutrients from the extracellular fluid
cilia
long slender extensions (hair like) of microtubules and modified for movement of materials across the cellular surface
ribosomes
cellular organelle that functions in protein synthesis and often attached to endoplasmic reticulum
the more protein a cell synthesizes the more ribosomes it has