The Endocrine System (OB1)
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
protein and amine hormones
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment for cell function, endocrine system controls through chemical messengers
Endocrine System
Glands secreting hormones into the bloodstream.
Nervous System
exerts control by transmission of nerve impulses to and from the various tissues.
Endocrine Glands
secrete hormones into the extracellular fluid that surrounds the cells that make up the gland.
secretions passed into the capillaries transported in blood. ductless gland
Exocrine Glands
secrete substances into a duct that carries the secretion to the body surface or to one of the body cavities. e.g. sweat and mucuos glands
Hormones
Chemical messengers affecting cell functions, secreted by endocrine system
influence by: changing type/activties/ quantities of enzymes produced. not enzymes,
exert influencing by changing activity of enzymes or their conc by: activating genes in nucleus so proteins produced, changing shape/ structure of enzymes, changing rate of production increasing/ decreasing (transcription and translation)
Lipid Soluble Hormones
the ability to dissolve through the lipid (fat) portion of a membrane;
Water Soluble Hormones
Hormones unable to diffuse, act via receptors.
Saturation
All receptors occupied; no increased cell activity, the addition of hormones will not have a further effect. different cells have diff number and types of receptors, variation in sensitivities of cells to hormones
Steroid Hormones
Lipid-soluble, Slow to have effect but long-lasting effects
how to steroid hormones work
Once released into blood, bind to a transport protein enabling them to travel in blood.
then seperation from transport protein when at target cell
Diffuse across cell membrane and combine with a receptor protein inside the cytoplasm/nucleus.
Hormone-receptor complex binds to promoter region of gene to stimulate/inhibit transcription and therefore control protein synthesis for particular proteins.
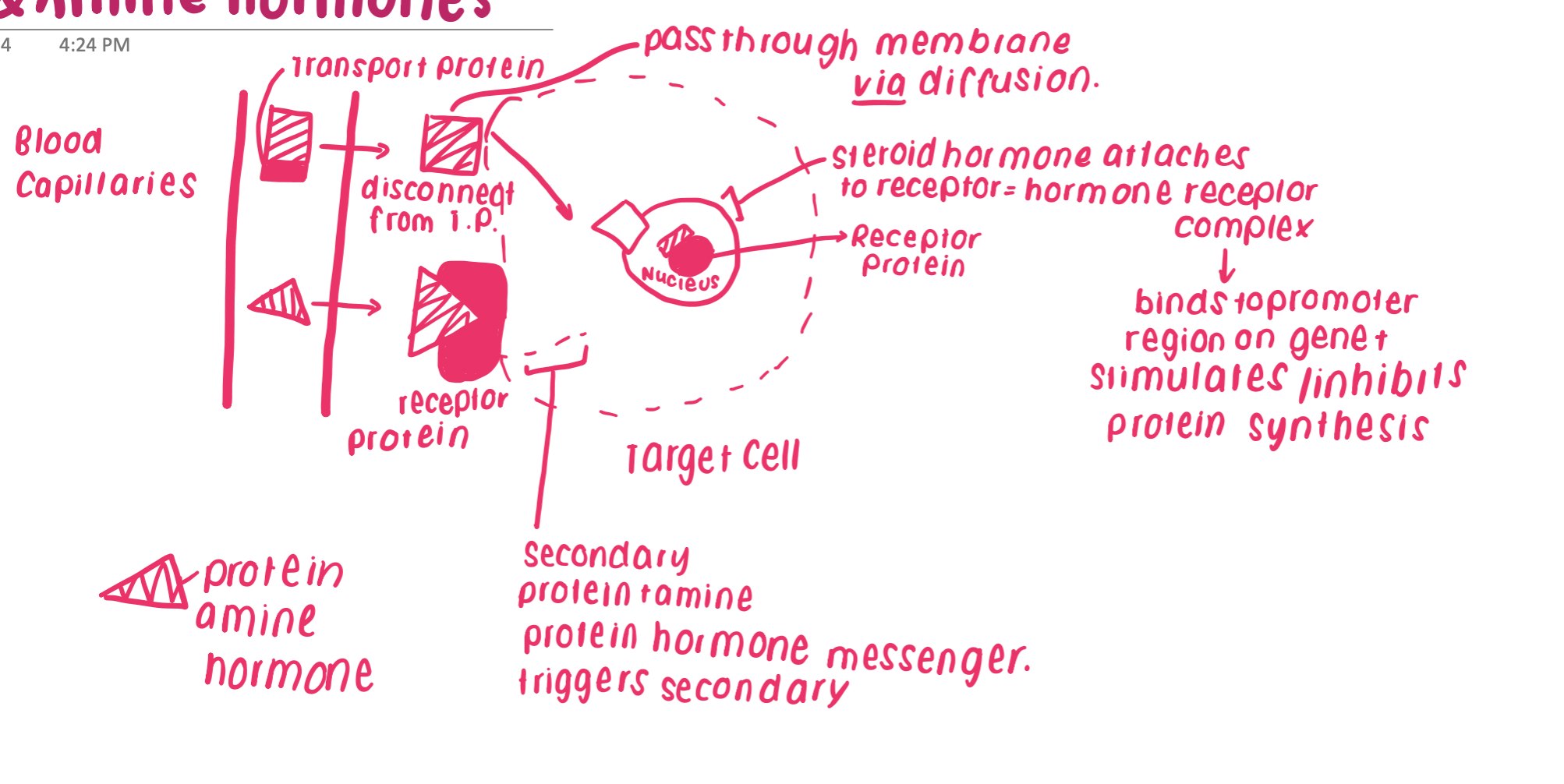
Protein and amine Hormones
Water-soluble -Result in quick response by effects are short-lasting.
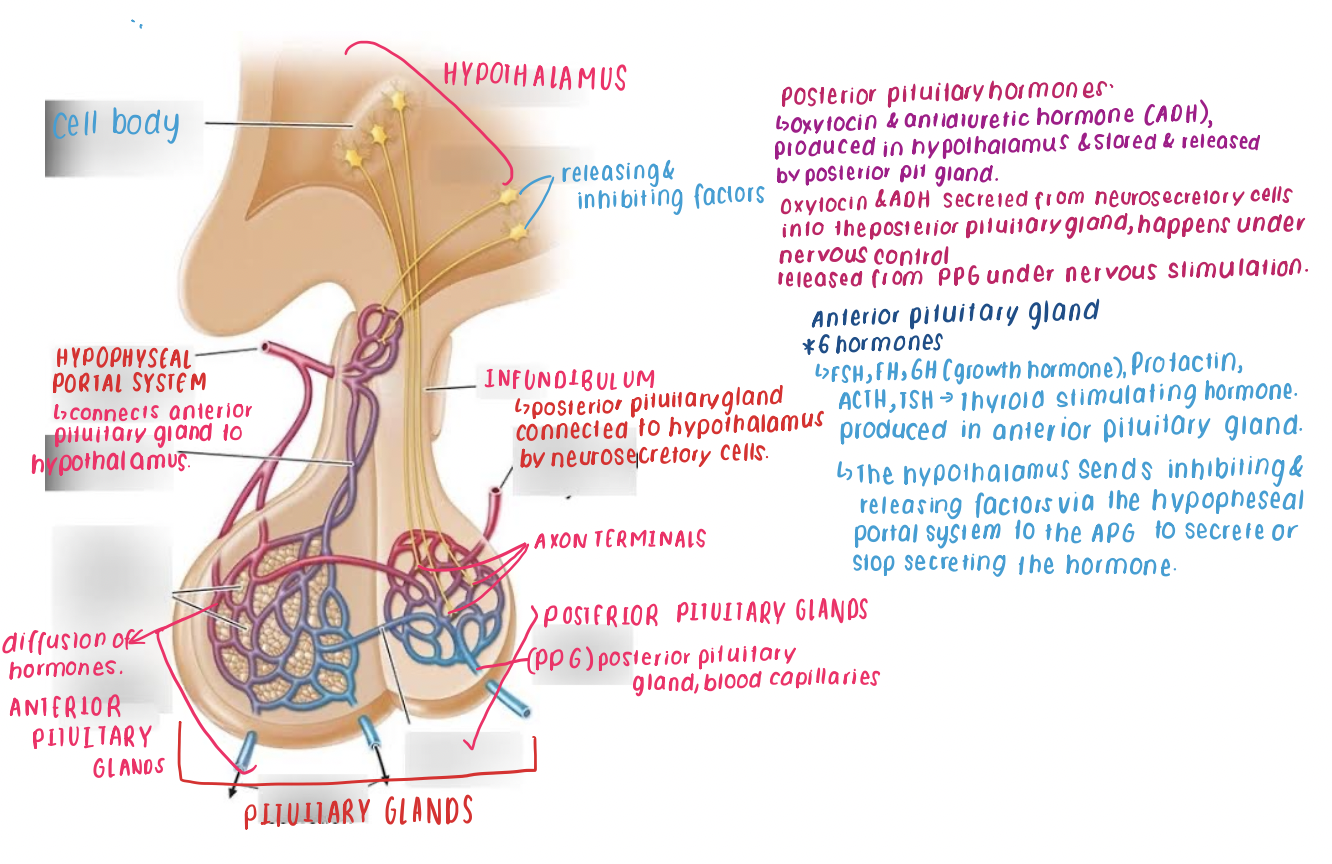
diagram of a pituitary gland
how do protein and amine hormones work
Attach to receptor proteins in the membrane of the target cell.
Combination of hormone and receptor results in a secondary messenger substance to diffuse through the cell and activate particular enzymes.
how hormones affect target cells/ organs
Hormones travel through the bloodstream to their target organs
target cell has specific receptor only bind to a specific hormone, which will only respond to that particular hormone, making the action specific.
hormones moving through the cell membrane diagram
Negative Feedback
maintains homeostasis.
a stimulus must trigger a change in the internal environment
Releasing Factors
Hormones stimulating secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary.
Inhibiting Factors
Hormones reducing secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary.
State where the hormones that are released from the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary are made

how is the hypothalamus connected to PPG
nuerosecretory cells in the infundibilum
how is the hypothalamus connected to APG
Hypopheseal portal system in the infundibulum
How do releasing and inhibiting factors work
The hypothalamus sends inhibiting and releasing factors via the hypophyseal portal system to the APG to secrete or stop secreting the hormone.
hypothalamus
serves as a connection between both the nervous and endocrine systems.
Regulates the main functions of the body, such as body temperature, water balance and heart rate, increasing and decreasing the secretions of the glands.
stimulates release of hormones from posterior and anterior
Posterior- Nervous control that causes the release. Occurs as they are connected by Neurosecretory cells
Anterior- released and stimulated by inhibiting and releasing factors
How are the hypothalamus and anterior and posterior glands connected
Anterior pituitary gland- connected to the hypothalamus via the blood vessels (hypophyseal portal system)
Posterior pituitary gland connected to hypothalamus by neurosecretory cells.
Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3)
Production: Thyroid gland
Target: all cells
Effect: Controls/ Increases body metabolism by regulating catabolic reactions to release energy/ heat. Secreted in response TSH from APG
Calcitonin
Production: thyroid gland
Target: kidneys and bones
Effect: Decreases calcium and phosphate levels in blood by reducing reabsorption in the kidney, and decreasing breakdown of bone (bone releases calcium)
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Production: parathyroid gland
Target: Bones, kidneys + intestines
Effect: Increases calcium and phosphate levels in blood
Thymosin
Production: Thymus
Target: T- lymphocytes, Targets immune system
Effect: Influence maturation of T- lymphocytes.
Cortisol
Production: Adrenal cortex, (Adrenal glands)
Target: Most body cells
Effect: Promotes normal metabolism, helps body adapt to stress and repair damages tissues.
Aldosterone
Production: Adrenal cortex, (Adrenal glands)
Target: kidneys
Effect: Reduces NA+ and increase K+ in urine
Adrenaline (epinephrine)
Production: Adrenal medulla, (adrenal glands)
Target: Most cells/ tissues
Effect:Fight or flight responses (prepares body for threatening situation) e.g. increase heart rate, metabolic rate, blood pressure.
Noradrenaline (norepinephrine)
Production: Adrenal medulla, (adrenal glands)
Target: Most cells/ Tissues
Effect: Similar effect to adrenaline particularly increasing rate and force of heartbeat.
function of pancreas in terms of production of hormones
As well as hormones produced in cluster of cells called islets of Langerhans, the pancreas also produces enzymes (exocrine function)
Insulin
Production: pancreas
Target: Liver, muscles cells + fat storage, Produced by beta cells
Effect: Decrease blood sugar by:
Increasing glucose uptake by cells (particularly muscle), promoting glucose
Promotes glucose conversion to glycogen (fat), happens in liver and muscles.
Glucagon
Production: pancreas
Target: Liver, Produced by alpha cells
Effect: Increases blood sugar mainly by stimulating the breakdown of glycogen to glucose (liver), also breakdown of fats in liver and fat stores.
Androgens (testosterone)
Production: testes
Target: Many tissues
Effect: Stimulates sperm production
Growth of skeletal muscles
Development and maintenance of male sex characteristics
Oestrogen
Production: Ovaries
Target: Many tissues
Effect: Stimulates development of female characteristics, Regulates menstrual cycle
Progesterone
Production: Ovaries
Target: Uterus + mammary glands
Effect: Regulate menstrual cycle and pregnancy
Prepares mammary glands for milk secretion.
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) gonadadropin
Production: anterior pituitary gland
Target- ovaries and testes
Effect: Stimulates development/ growth of follicles
Stimulates production + maturation of sperm
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Production: apg
Target: ovaries and testes
Effect: Triggers ovulation, formation of corpus luteum, Stimulates intestinal cells in testes to secrete male sex hormones (e.g. testosterone).
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Production: APG
Target: adrenal cortex
Effect: Controls production + release of some hormones from the adrenal cortex.
(e.g. cortisol)
Growth hormone (GH)
Production: APG
Target: all cells
Effect:Stimulates body growth, particularly of Skeleton.
And protein synthesis. Maintains organ size, once mature.
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Production: APG
Target: thyroid gland
Effect: Production + release of thyroid hormones (thyroxine)
Prolactin
Production: APG
Target: Mammary glands
Effect: Works with other hormones to initiate and maintain milk secretion in females.
Oxytocin
Production: PPG
Targets: uterus and mammary glands
Effect: Stimulates contraction of uterine muscles., Stimulates contraction of cells in mammary glands. Resulting in release of milk in breastfeeding.
Antidiuretic hormone
Production: PPG
Targets: Kidneys
Effects: Causes kidney to remove water from urine and return to blood (fluid retention), at high conc, also constricts small arteries.
Melatonin
Production: pineal gland
Target: most cells
Effect: regulates sleep cycle, circadian rhythm
Master gland
Pituitary gland- control the functioning of many other glands.
hyperthyroidism symptoms

symptoms of hypothyroidism
Goitre- enlargement of the thyroid gland, lump on neck.
Thyroid gland- due to thyroid gland working extremely hard to produce thyroid hormone.
Unexplained weight gain,
Fatigue
Emotional mood changes
Constipation
Swollen ankles,
Joint pain
causes of hypothyroidism
insufficient amount of thyroid hormone (thyroxine) being produced

treatments of hypothyroidism
pituitary surgery, increase iodine, thyroxine tablets.
what causes hyperthyroidism

treatments of hyperthyroidism
