Data Analysis
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Formula For calculating Z-Scores
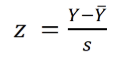
Two most common forms of analysis used for two variables
Cross-tabs and Chi-Square
Steps to calculate percentage
First, choose the variable for which you are creating a percentage, deciding the part and whole you are comparing
Then, divide the smaller number (the part) by the larger number (the whole)
Finally, you multiply that proportion by 100
What does the symbol “fₑ” mean
Expected frequency
Four measures of variability
Standard deviation
Interquartile Range
Range
Variance
What type of data can be tested with Chi-Square
Significant relationship between two nominal or ordinal variables
What data is used to analysis a Likert Scale
Ordinal
How do you calculate the Interquartile Range?
First, place all data points in order from least to greatest
Then, divide the data into 4 equal groups
Focusing on the data on the second and third groups (The inner 50%) calculate the range from the lowest and highest numbers in the inner 50%
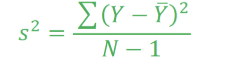
What is the formula used to calculate?
Variance
What is meant by the term control variable?
An additional variable in a bivariate relationship that is controlled for when we take into account its effect on the variables in the relationship.
What is meant by the term p-value
The probability that an obtained value was obtained due to random chance or error
Define the Central Limit Theorem
The Central Limit Theorem states that if all possible random samples of size N are drawn from a population with mean 𝝻y and standard deviation σy , then as N becomes larger the sampling distribution of samples means becomes approximately normal
Three different symbols used in SPSS to denote the types of data being used
Nominal data is represented by the three separate blue, red, and green circles.
Ordinal data is represented by the histogram of blue, green, and red bars.
Ratio/Interval data is represented by the ruler.
Bivariant Table
