Session 9: Molecular Techniques and Diagnosis
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Name some molecular techniques for analysis of DNA/RNA
PCR
DNA/RNA electrophoresis
Restriction analysis
DNA sequencing
Karyotyping
FISH
DNA hybridization
Name some molecular techniques for analysis of protein
Protein electrophoresis
Immunoassays
Enzyme assays
Mass spectrometry
Describe steps of PCR
1) Denaturation - use heat to separate the strands
2) Annealing - cooling and adding primers
3) Elongation - add heat-stable DNA polymerase
This process is repeated 20-30x until the specific sequence is present at 10^6 copies
Components of PCR reaction
DNA template
DNA primers
DNA polymerase enzymes (taq*
dNTPs
Buffer
Clinical application of PCR
1) Forensic medicine (from small sample of hair, single cell)
2) Detection of viral, bacterial and protozoal agents
3) Diagnosis and genetic analysis of inherited disease
4) Diagnosis and analysis of neoplastic disorders
5) Prenatal and pre-implantation diagnosis

Examples of clinical application of PCR: inherited diseases
- Beta-thalassemia
- Sickle cell disease
- Hemophilia
- Tay-Sachs disease
Examples of clinical application of PCR: neoplastic disorders
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
- Follicular lymphomas
- Various other cancers
- Detecting activated oncogenes
Example of application of multiplex PCR
Cystic fibrosis (CF)
Multiplex PCR
Multiple primers for multiple targets - good for analysing diseases which are associated with multiple alleles e.g., CF
DNA/RNA gel electrophoresis is used to separate...
Charged molecules such as DNA, RNA and proteins according to their size
When electric current is passed through the DNA/RNA gel during electrophoresis - what happens?
Charged molecules move through the permeable gel matrix when electric current passes through it.
- Smaller molecules migrate through gel quickly - travel further
- Larger molecules migrate through gel slowly - travel shorter distance
Restriction analysis is based on ___ ___ enzymes produced by bacteria
restriction endonucleases (RE)
Restriction endonucleases recognise and cut specific DNA sequences called '___ ___' (in restriction analysis)
restriction site
Restriction analysis is used alongside DNA gel electrophoresis to...
- Investigate mutations
- Investigate DNA variation
- Clone DNA
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
Differences in DNA sequence on homologous chromosomes that can result in different patterns of restriction fragment lengths (DNA segments resulting from treatment with restriction enzymes).
Two examples of diseases which have clinical use for Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
1) Sickle cell anemia = single base mutation removes restriction site within a gene
2) Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB) = single base mutation creates restriction site within a gene
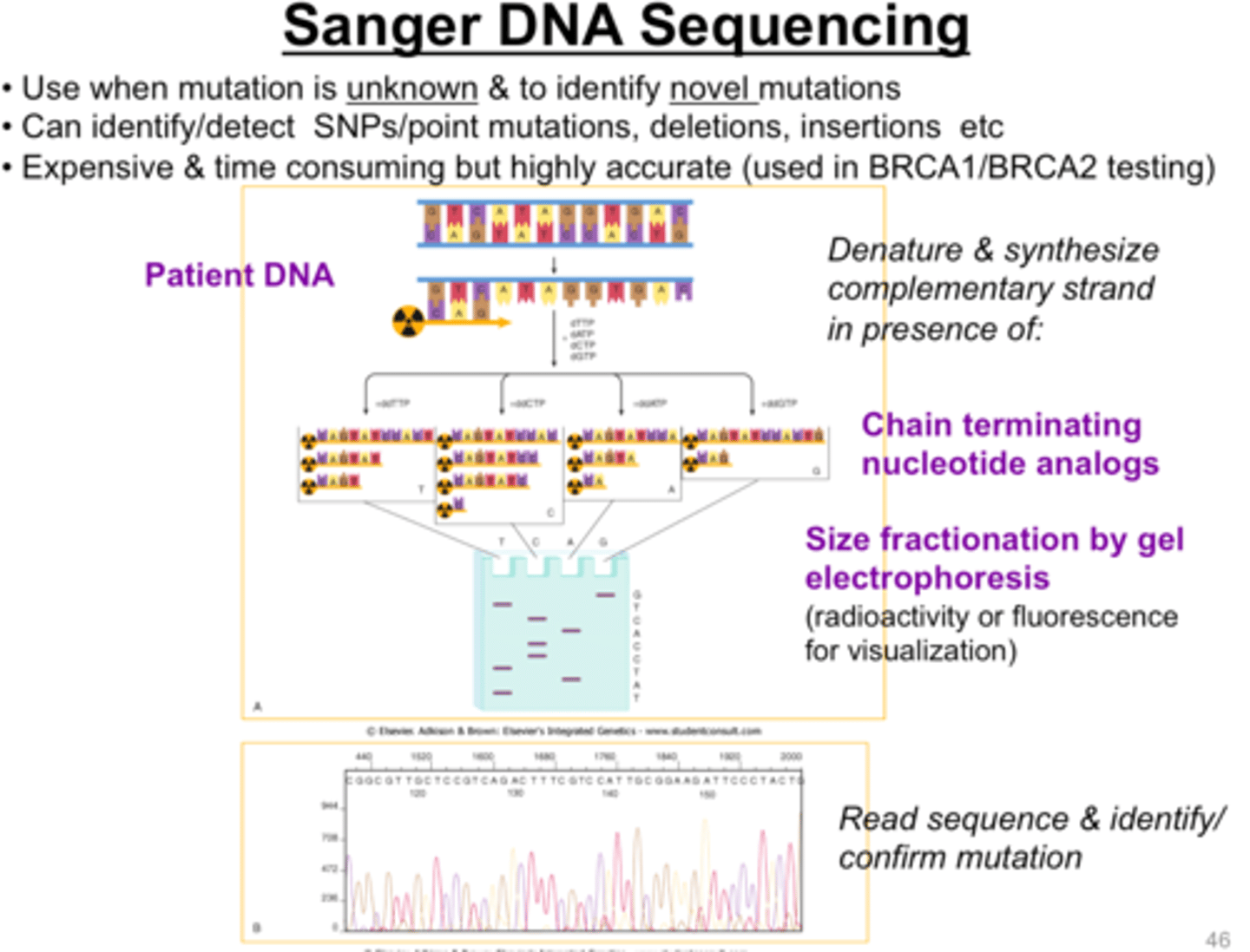
Sanger DNA sequencing
- Dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs) halt DNA polymerization at each base
- Generates sequences of various lengths that encompass the entire original sequence.
- Terminated fragments are electrophoresed and the original sequence can be deduced
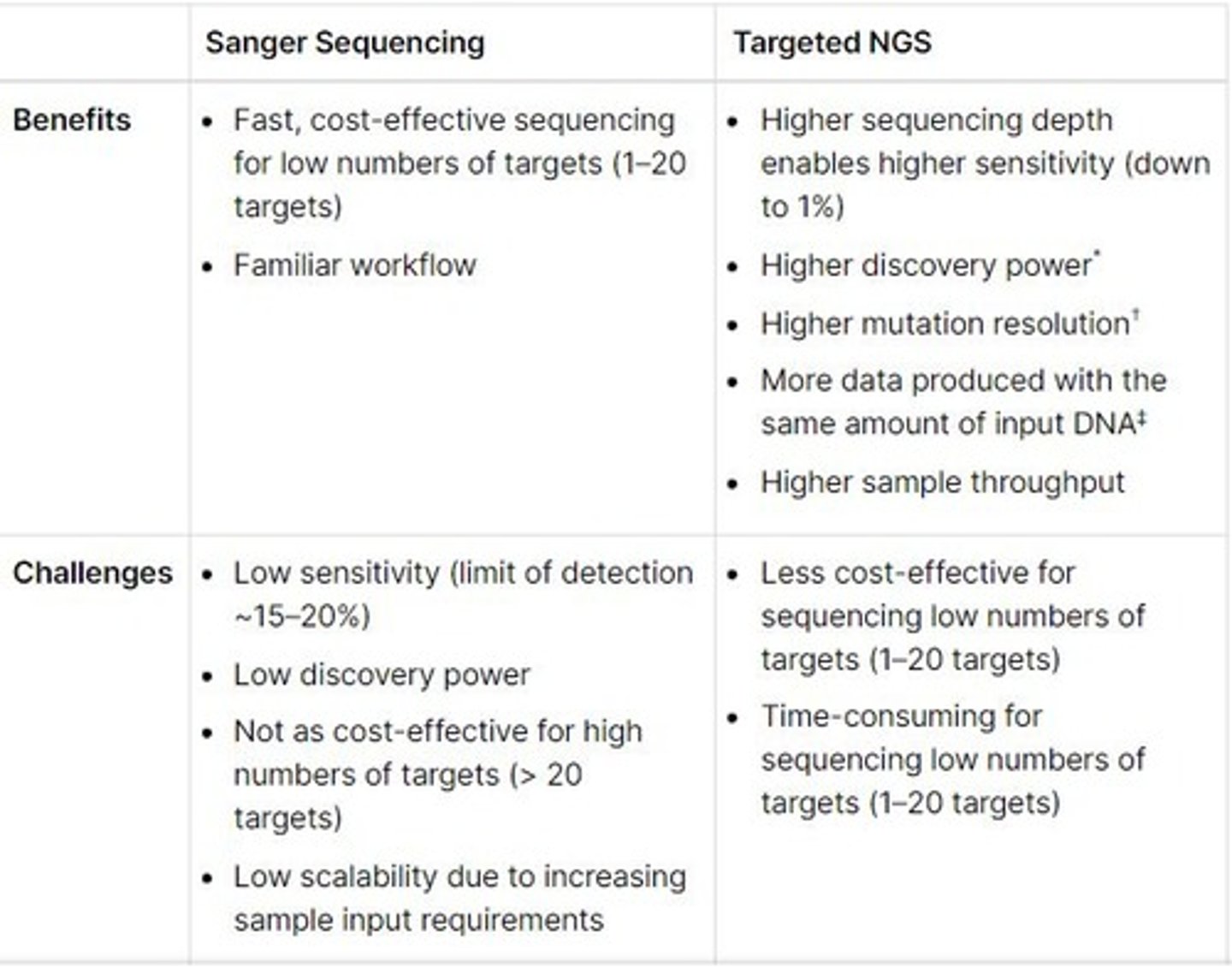
Benefits of Sanger DNA sequencing
- Cost-effective for sequencing single genes (99.99% accuracy)
- Works best for determining sequence of nucleotide bases in piece of DNA (less than 1,000 bp in length)
Components of a Sanger sequencing reaction
1) Thermostable DNA Polymerase
2) ddNTPs - dideoxynucleotides
3) dNTPs - nucleotides
4) Buffer
Three main steps for Sanger sequencing process
1) Chain-termination PCR with fluorescent, chain-terminating ddNTPs
2) Size separation by capillary gel electrophoresis
3) Laser excitation and detection by sequencing machine to produce output chromatogram
Human Genome Sequencing
The sequencing of the first human genome.
Composite "everyman" was assembled from the DNA of several volunteers
Becoming more common now - cheaper and more accessible
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Any of the high throughput approaches to DNA sequencing using the concept of 'massively parallel processing'
Benefits of NGS vs Sanger
Advantages of NGS include...
- Higher sensitivity to detect low-frequency variants
- Faster turnaround time for high sample volume
- Comprehensive genomic coverage
- Ability to sequence hundreds-thousands of genes or gene regions simulataneously
1,000 Genomes Project
2008
- International effort to catalogue 'common' human genetic variation
- Sequence 1,000 genomes from people who declared themselves to be healthy
The goal of the 1,000 Genomes Project
Find common genetic variants with frequencies of at least 1% in populations studied
10,000 Genomes Project
2010
- International effort to catalogue 10,000 genomes (4000 healthy; 6000 diseased)
- Included rare inherited disorders
- Included more common disorders - obesity, autism, schizophrenia
- Showed contribution of rare variants to range of diseases
- Discovered new genetic variants and genes underpinning disease risk
100,000 Genomes Project
2012
- 100,000 genomes sequenced from 85,000 people
- Participants = NHS patients with rare diseases, their families and patients with cancer
Karyotyping
The process of pairing and ordering all the chromosomes of an organism
What is karyotyping used to detect?
- Changes in chromosome number
- Changes in chromosome structure e.g., chromosomal deletion, duplication, translocation, inversions
Karyotypes are prepared from mitotic cells that have been arrested in ___ or ___ of the cell cycle
metaphase or prometaphase
Why do karyotypes use cells that have been arrested specifically within metaphase or prometaphase?
Chromosome are in their most condensed form
Variety of tissue types can be used as a source of these mitotic chromosomes for karyotyping - name some
- Peripheral skin
- Skin biopsy
- Tumor biopsies
- Bone marrow biopsy (cancer)
For prenatal diagnosis, the source of mitotic cells (chromosomes) for karyotyping can be obtained by - what two procedures?
1) Amniotic fluid = amniocentesis
2) Chorionic villus biopsy
Two types of banding used for karyotyping which produce visible karyotype by staining the condensed chromosomes?
1) Giemsa banding = using giemsa stain
2) Quinacrine banding = fluorescent staining using quinacrine
Most common chromosome banding method for karyotyping?
Giemsa banding
What is the purpose of FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridization)?
FISH detects and localizes specific DNA sequences using fluorescently labeled complementary DNA probes
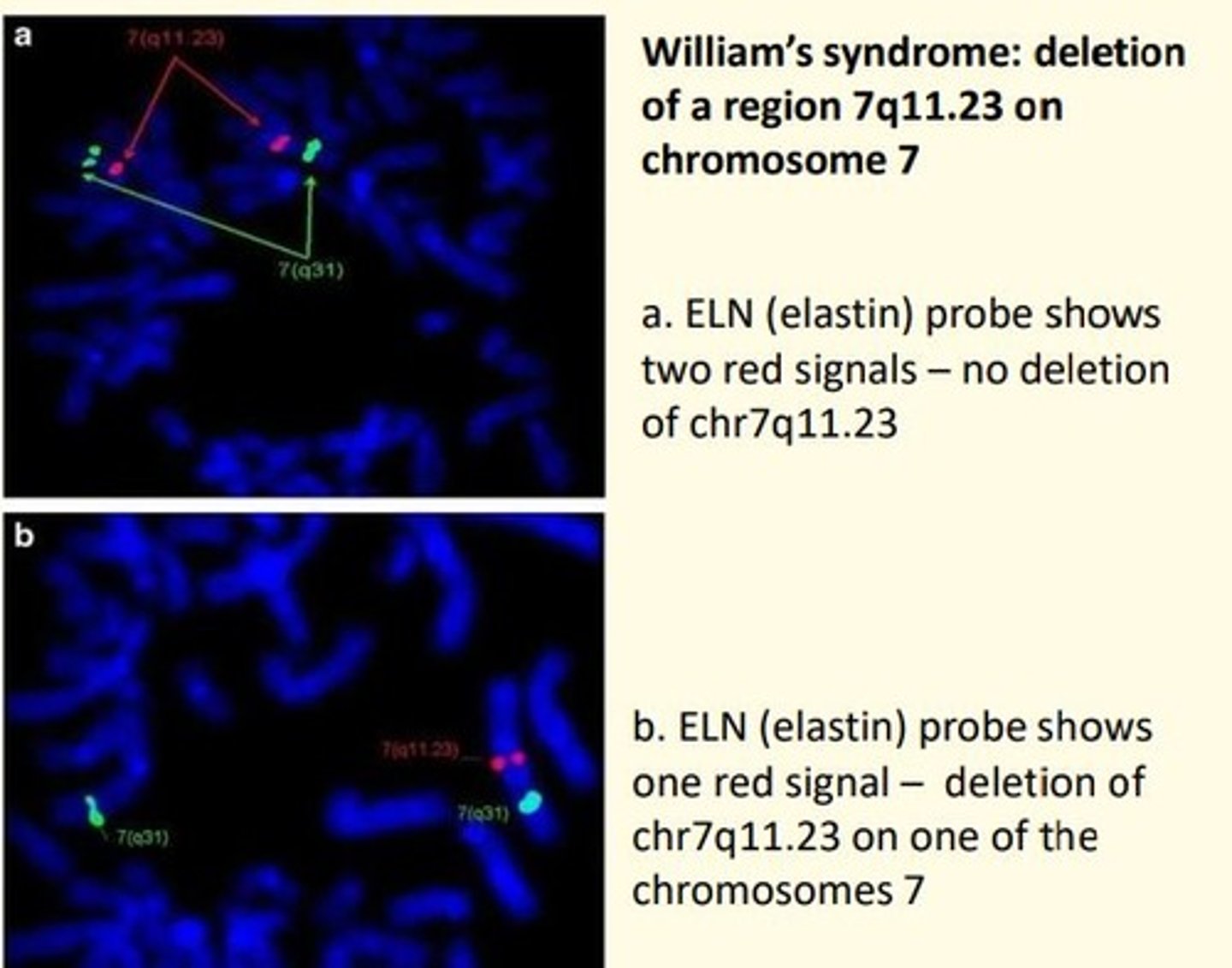
Steps of FISH
1) Target DNA = fluorescently labeled probe DNA
2) Denature = separate DNA strand (allow probe access)
3) Hybridize = bind probe to target
4) Analyze = analyze probe signals using fluorescent microscopy
Why is denaturation important step in FISH?
Allow the probe access to the target DNA to hybridize
What is the purpose of FISH? What does it investigate?
1) Investigate genes in situ e.g., deletion, duplication, amplification
2) Investigate chromosome structure e.g., deletions, duplications, translocations
3) Investigate chromosome number e.g., trisomy 21
DNA microarray
Research tool used to study gene expression
- Resulting grid of probes can hybridize to complementary 'target' sequences derived from samples to determine the expression level of specific m-RNAs in a sample
DNA microarray technology
Collection of synthetic DNA sequences (probes) attached to a spot, on a solid surface - research tool used to study gene expression
Applications of DNA microarray technology
- Investigate disease associated SNPs (SNP arrays)
- Investigate chromosome deletions/duplications (comparative genome hybridization assay)
- Investigate conditional gene expression e.g., compare gene expression in healthy tissue vs tumor
Name some molecular techniques used for the analysis of proteins
1) Protein electrophoresis
2) Immunoassays
3) Enzyme assays
4) Mass spectrometry
SDS-PAGE
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
What does SDS-PAGE do?
Analytical technique used to separate proteins based on their molecular weight
Some applications of SDS-PAGE
1) Estimate relative molecular mass = determine relative abundance of major proteins in a sample
2) Assess purity of protein samples
3) Detecting rare proteins
4) Specialized staining methods (e.g., western blotting, 2D-electrophoresis and peptide mapping) can be used to detect scarce gene products and detect/separate isozymes of proteins
Specialized staining methods of SDS-PAGE such as western blotting, 2D-electrophoresis and peptide mapping are valuable as they can be used to...
1) Detect extremely scarce gene products
2) Detect and separate isozymes of proteins
Protein Gel Electrophoresis importance in sickle cell anaemia
Used to detect alloenzyme variation e.g., Sickle Cell Anemia
- Hemoglobin replacement of negatively-charged Glu in normal HbA beta-globin to a → neutral valine in HbS
- This change results in a protein with a slightly reduced negative charge
Antibody (immunoglobulin)
Y-shaped protein produced by B cells of the immune system in response to the presence of antigens on foreign body invaders e.g., viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites
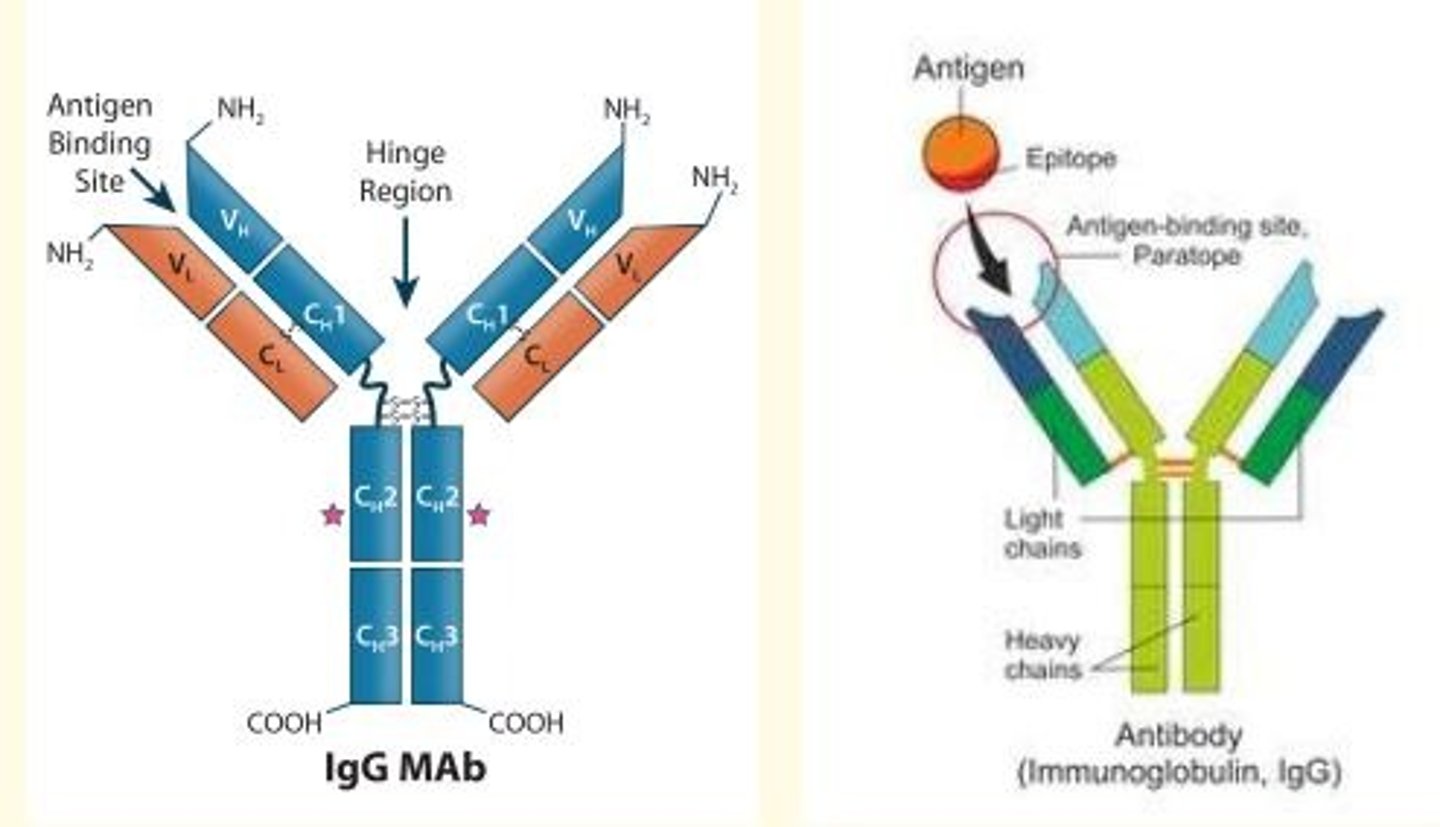
Antibodies are used in...
1) Diagnostic tests e.g., autoimmune disorders, infectious/metabolic diseases
2) Therapies e.g., recombinant antibody therapy for MS
ELISA
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
What is ELISA?
Plate-based assay technique used for detecting and quantifying soluble substances such as peptides, proteins, antibodies and hormones
Brief description of how ELISA is carried out
1) Antigen immobilized on solid surface (microplate)
2) Immobilized antigen is then complexed with an antibody that is linked to a reporter enzyme in DIRECT ELISA
3) Activity of reporter enzyme is measured via incubation with appropriate substrate to produce measurable product
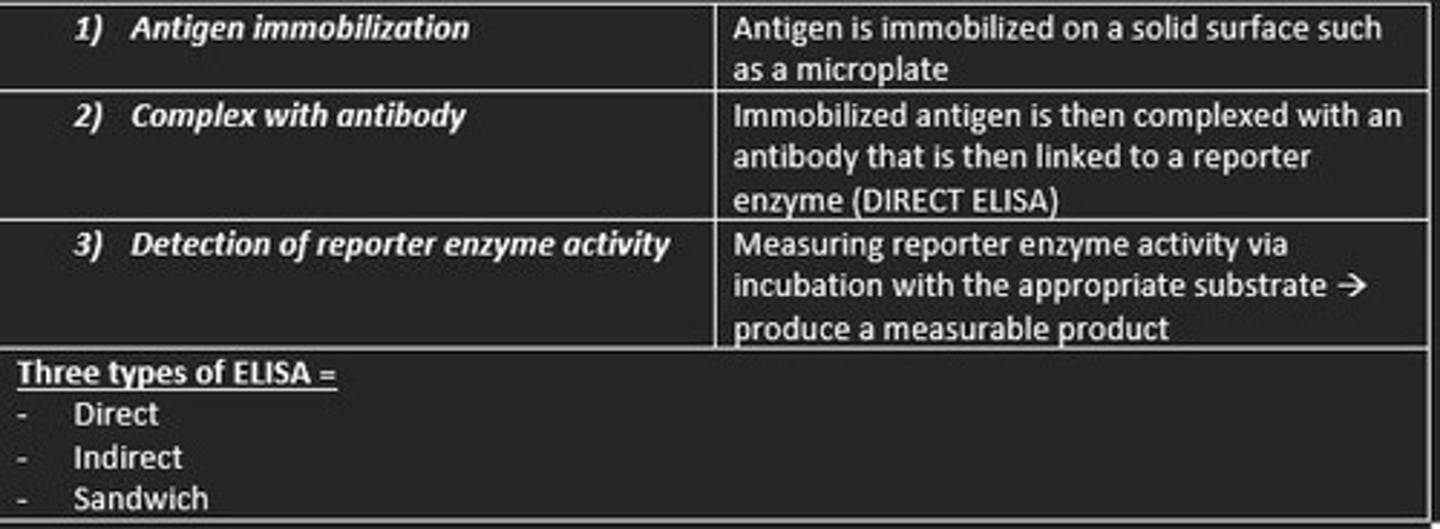
Three types of ELISA
1) Direct
2) Indirect
3) Sandwich
Some examples of the clinical applications of ELISA
1) Identification of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura = detection of platelet antibodies in serum
2) Identification of systemic lupus (SLE) = detection of platelet antibodies in serum
3) HIV testing
4) Pregnancy testing (hCG in urine)
Enzyme Assays
Measure the activity of clinically useful enzymes
- Need high concentration substrate
- Amount of enzymatic reaction product is measured
In enzyme assays - the measurable product is the...
Amount of enzymatic reaction product
Example of enzyme assays in medicine
Liver Function Tests (LFT)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- AST/ALT ratio
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)

Other enzyme assays used in medicine
- Amylase/lipase = marker for pancreatitis
- G-Glutamyl transferase = markers for liver
- Acid phosphatase = marker for prostate cancer
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
Analytical technique used to measure mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of one or more proteins in a sample
What does a mass spectrum plot show?
The mass-to-charge (m/z) ratio of ions present in a protein sample
Each peak in a mass spectrum shows
Component of unique mass/charge ratio in sample
Height of peaks in mass spectrum shows
Abundance of various components in sample
Mass spectrum plots are plotted against ___
intensities
Mass spectrophotogemtry can be used to identify...
1) Molecular weight
3) Quantity of known compounds
4) Determine structure and chemical properties of molecules
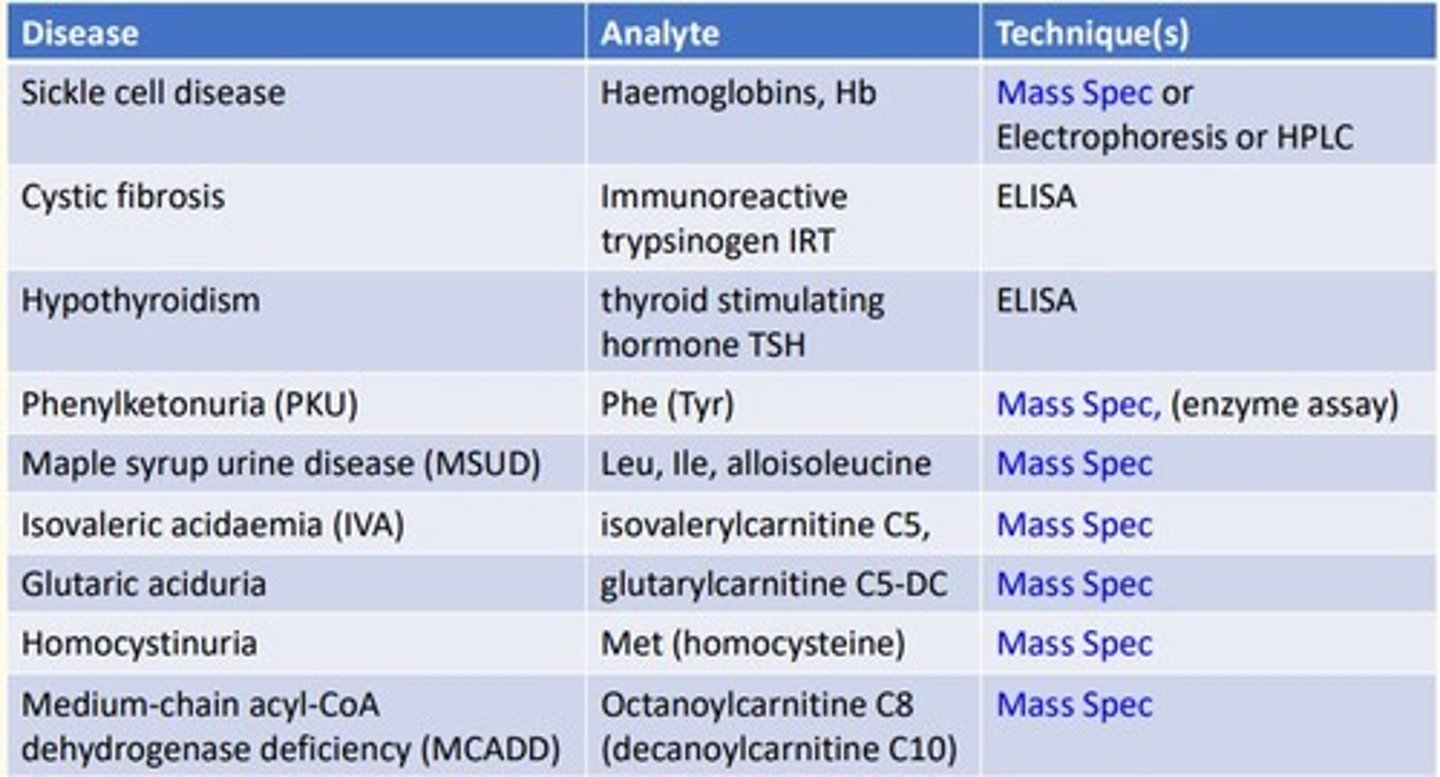
Sickle cell disease analytical technique
Sickle cell is looking at the analyte hemoglobins (Hb) which is a protein...
- Mass spectrometry
- Electrophoresis
- High-performance liquid chromatography (HLPC)
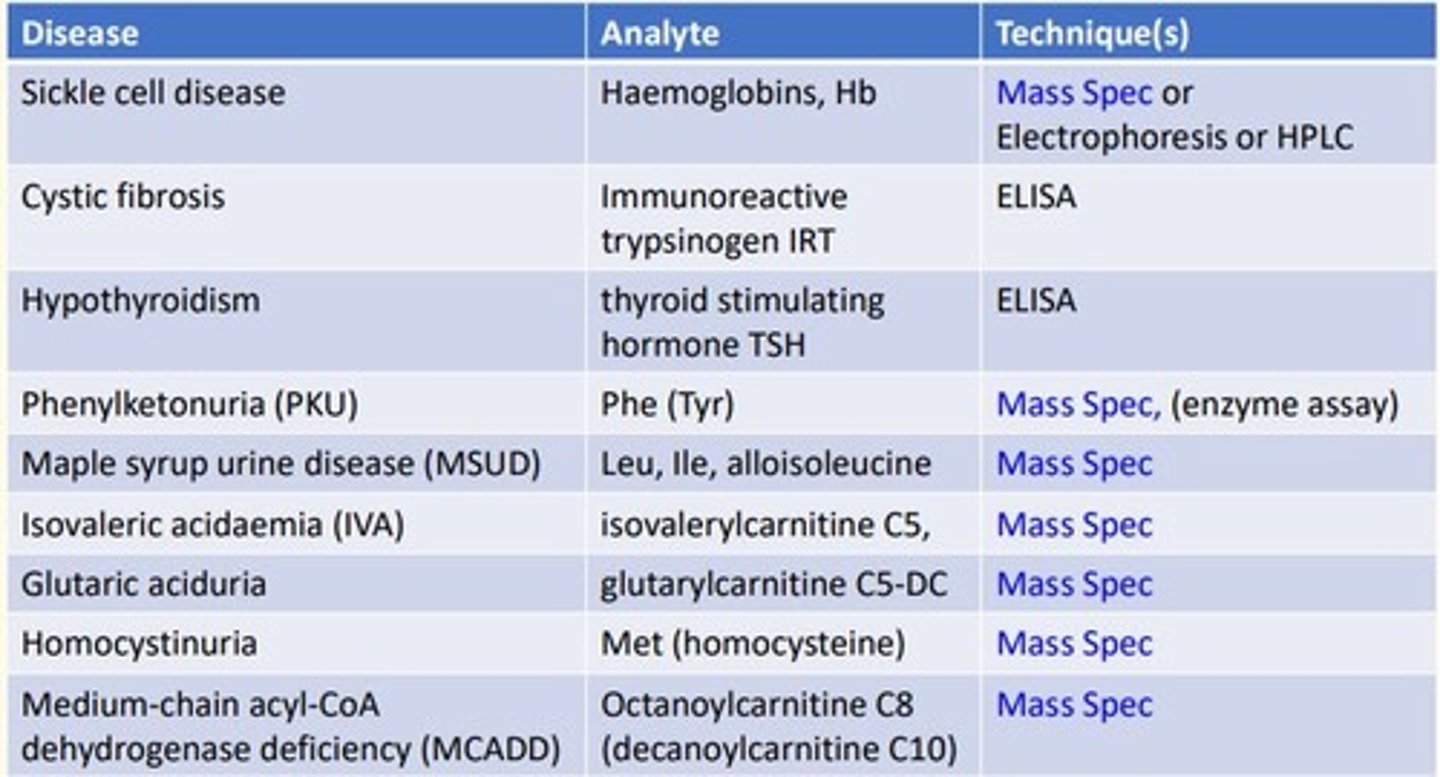
Cystic fibrosis (CF) disease analytical technique
Cystic fibrosis is looking at the analyte immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT)...
- ELISA
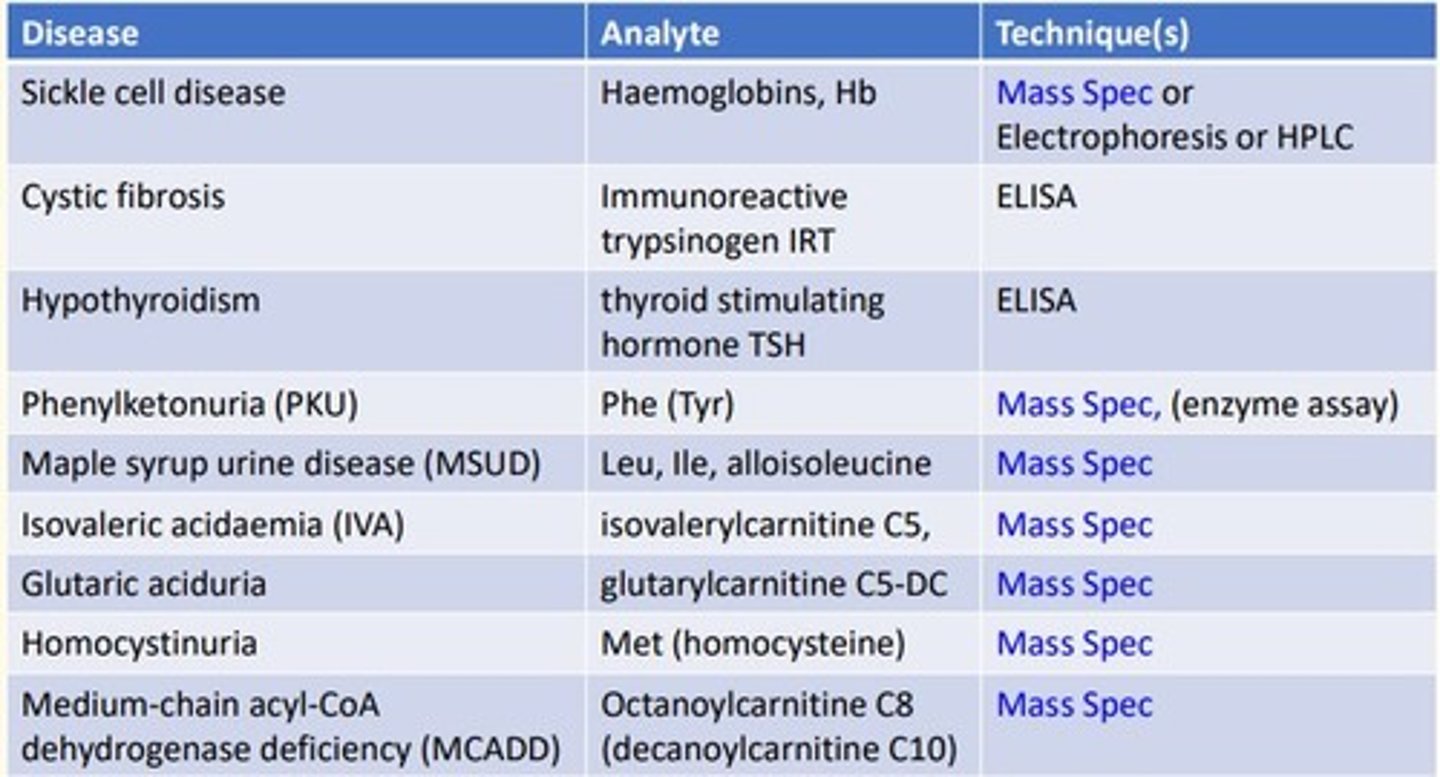
Hypothyroidism disease analytical technique
Hypothyroidism is looking at the analyte thyroid-stimulating-hormone (TSH)...
- ELISA
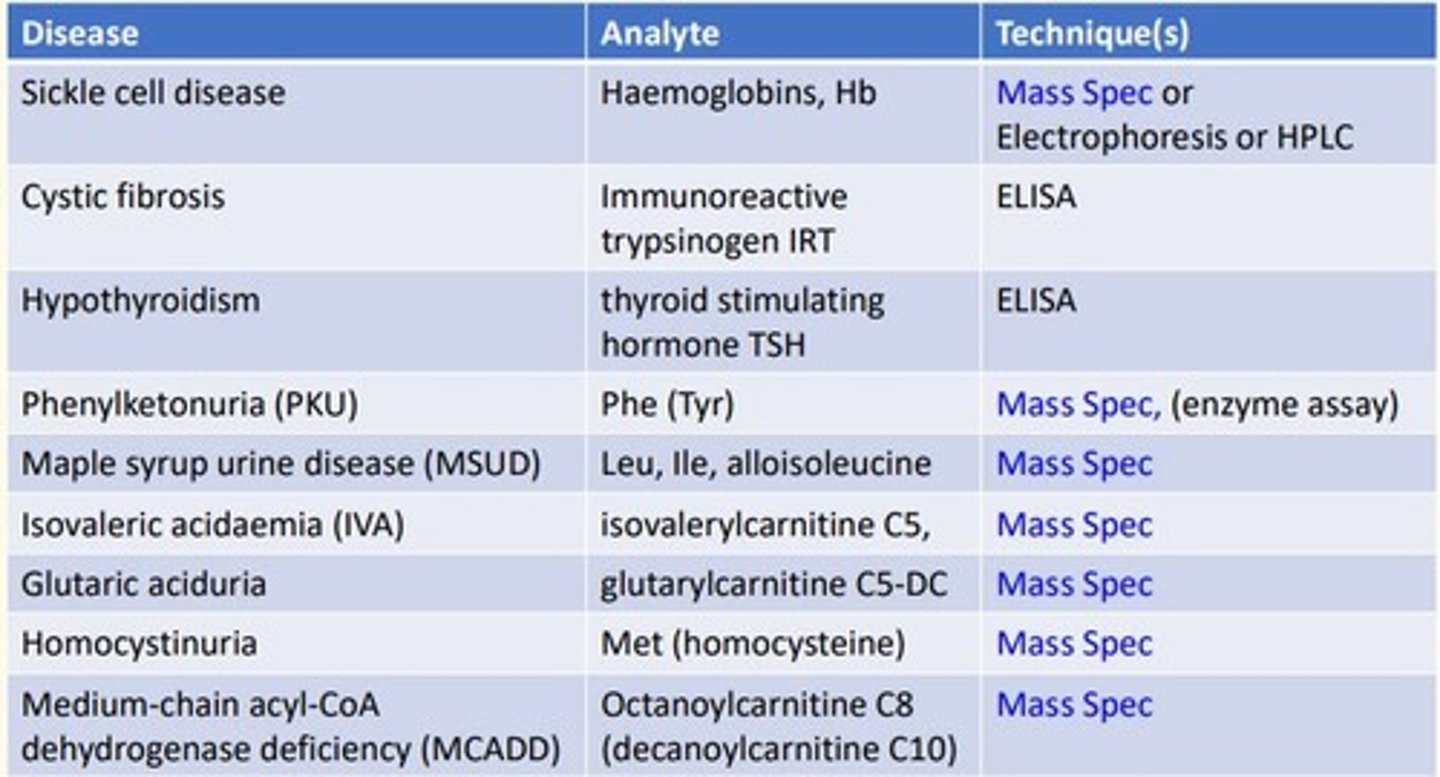
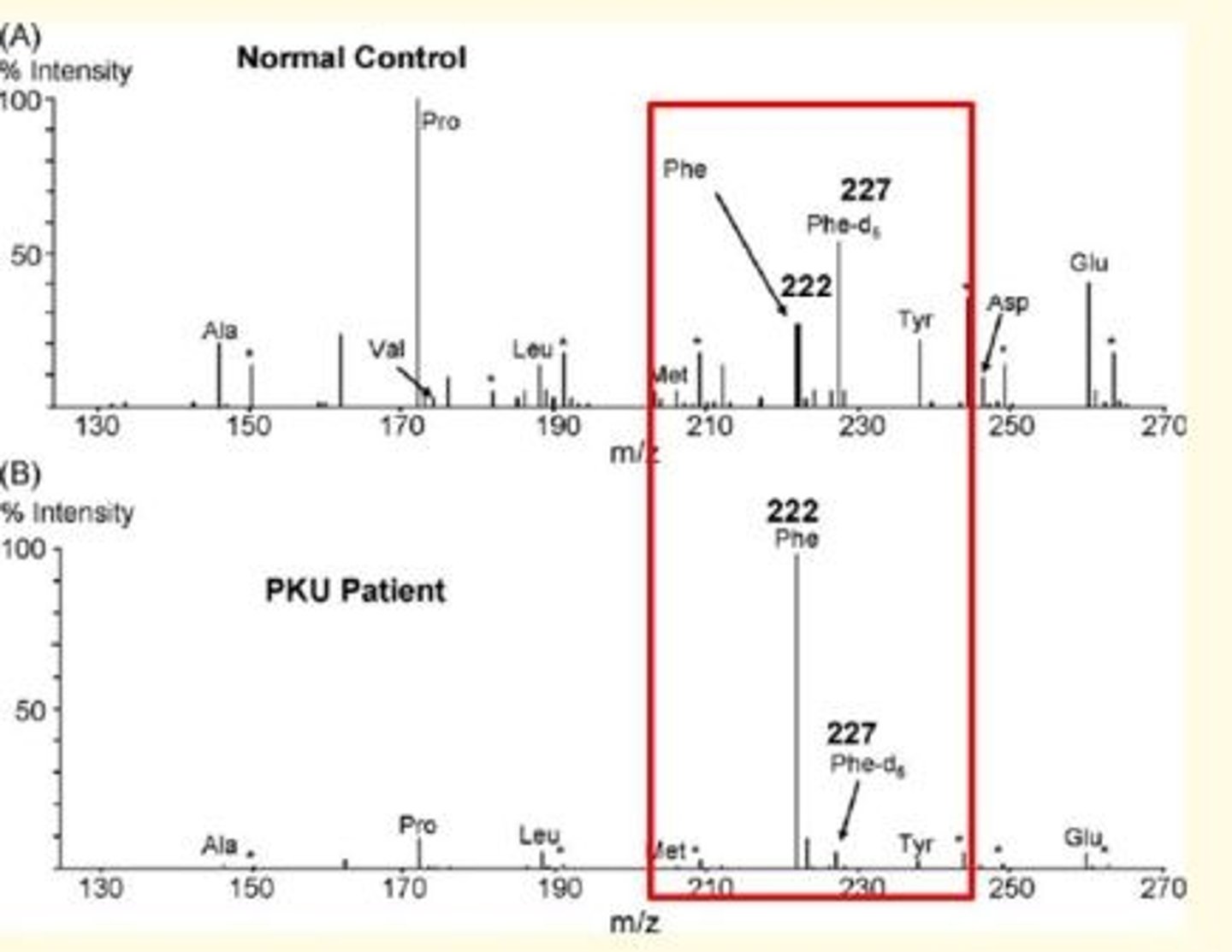
Phenylketonuria (PKU) disease analytical technique
Phenylketonuria is looking at the analyte Phenylalanine (Tyrosine)...
- Mass spectrometry
- Enzyme assay
Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) analytical technique
MSUD is looking at the analyte Leucine, Isoleucine, alloisoleucine
- Mass spectrometry
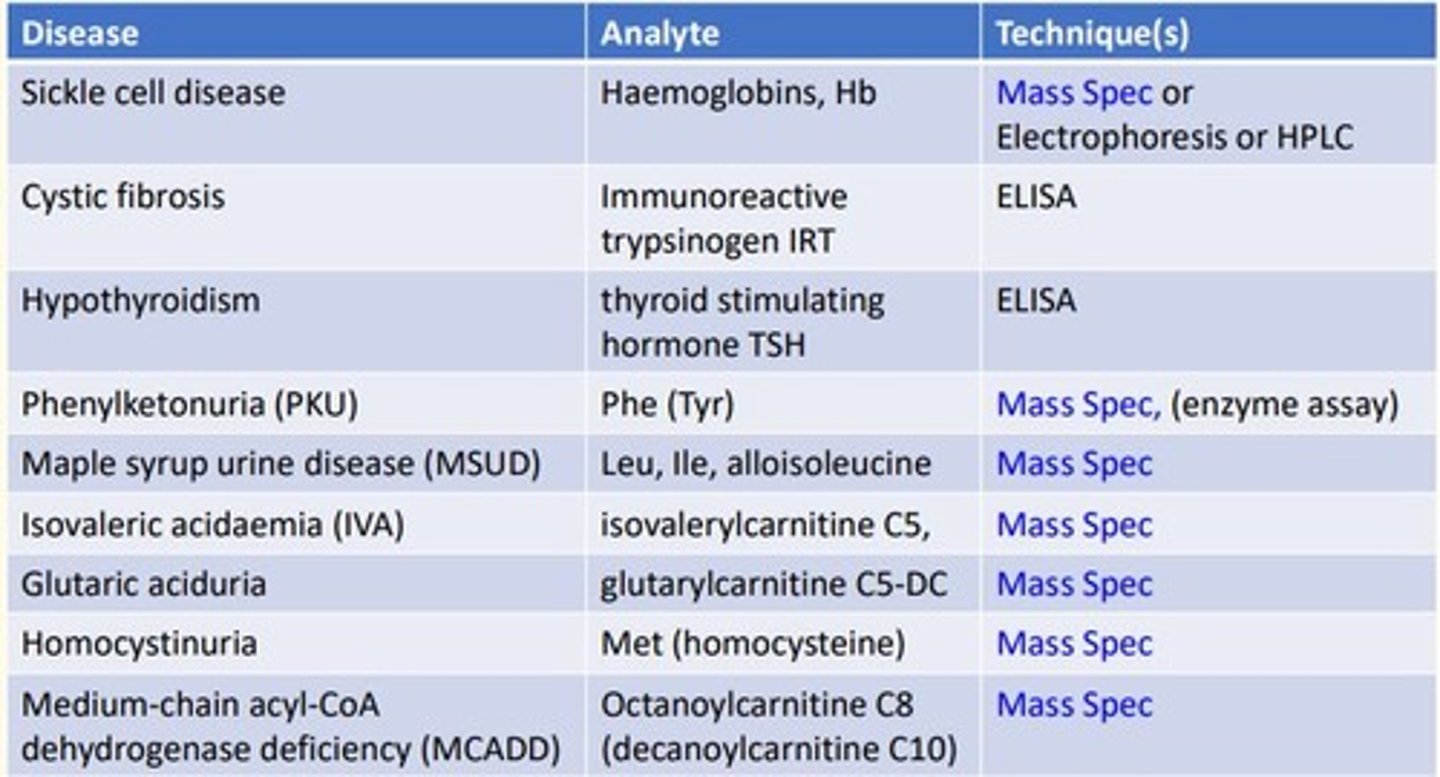
Isovaleric acidaemia (IVA) analytical technique
IVA is looking at the analyte Isovalerylcarnitine C5
- Mass spectrometry
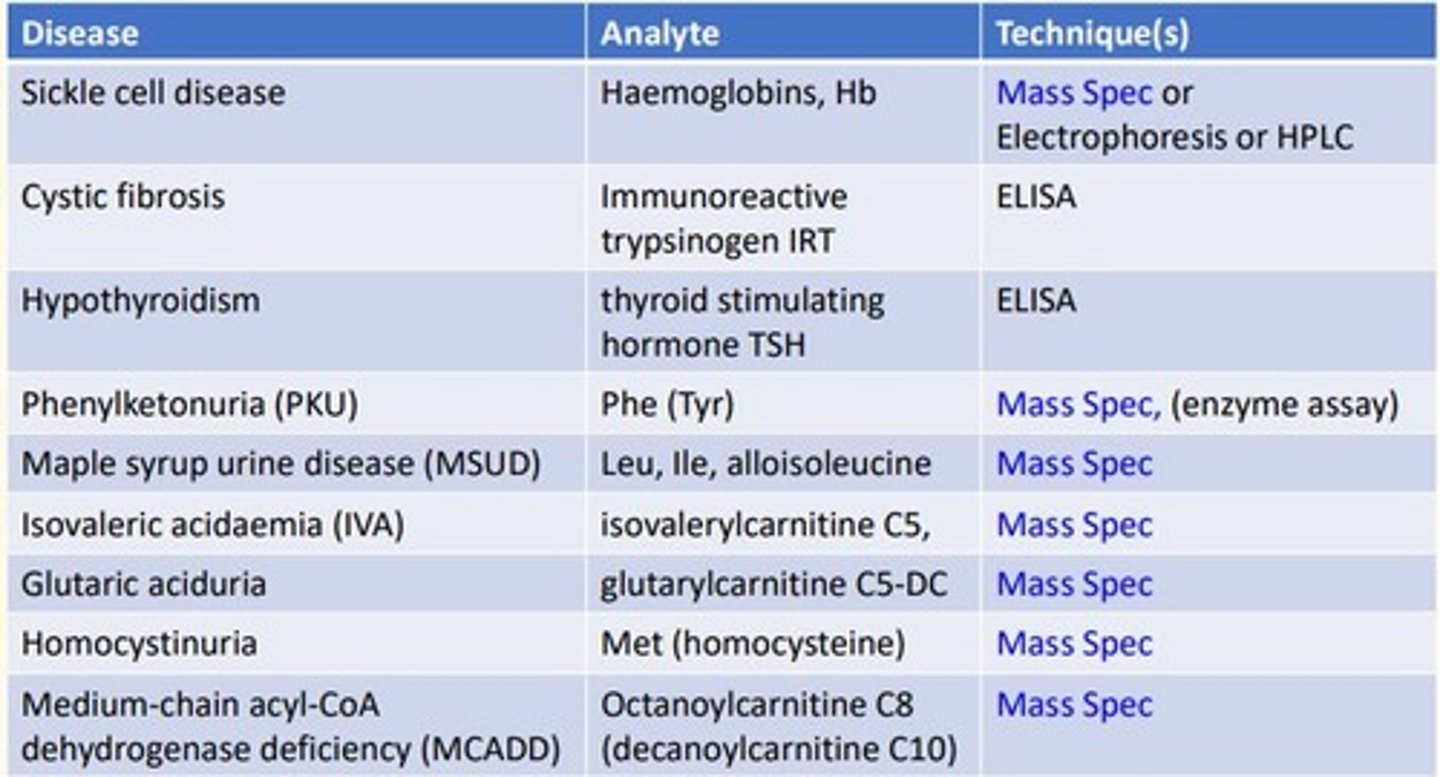
Glutaric aciduria analytical technique
Glutaric aciduria is looking at the analyte glutarylcarnitine C5-DC
- Mass spectrometry
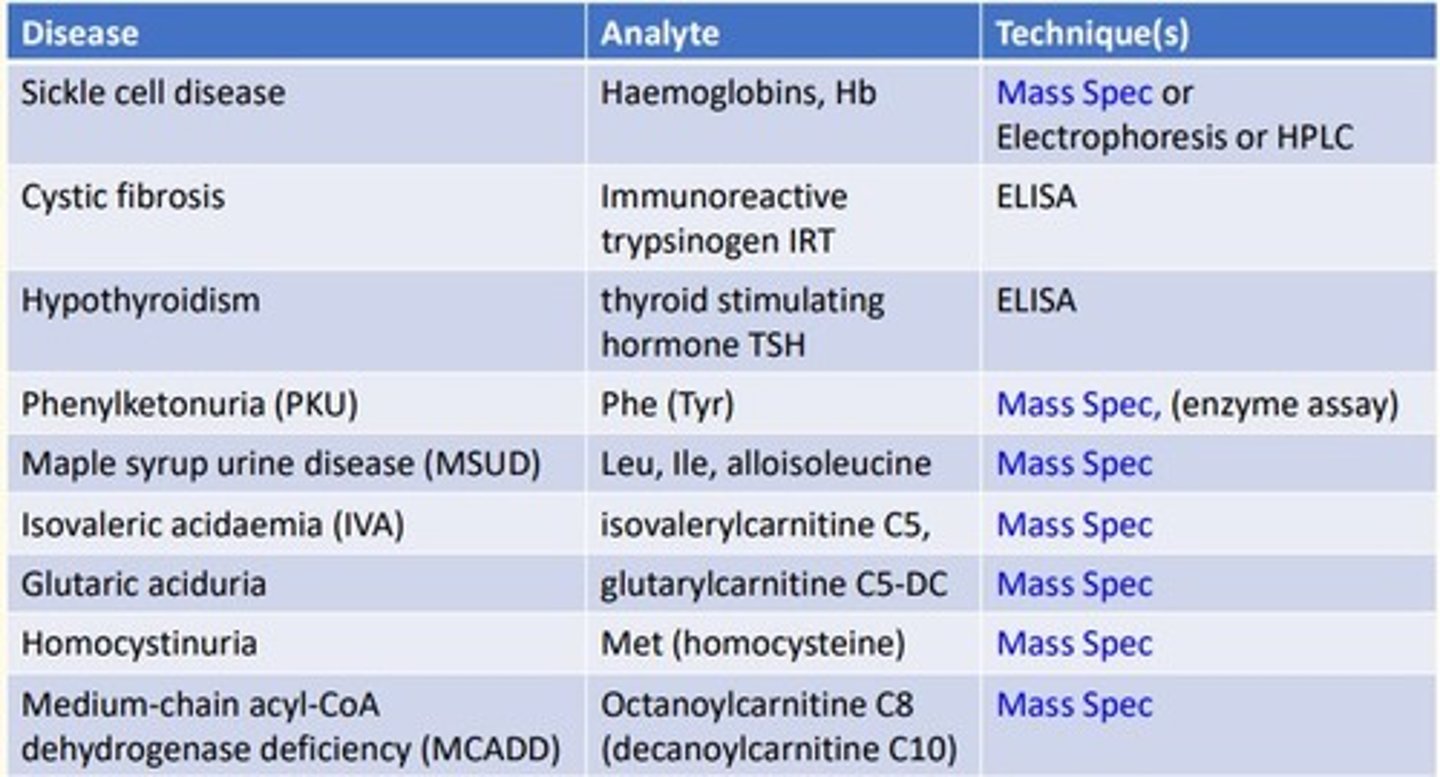
Homocystinuria analytical technique
Homocystinuria is looking at the analyte Methionine (homocysteine)...
- Mass spectrometry
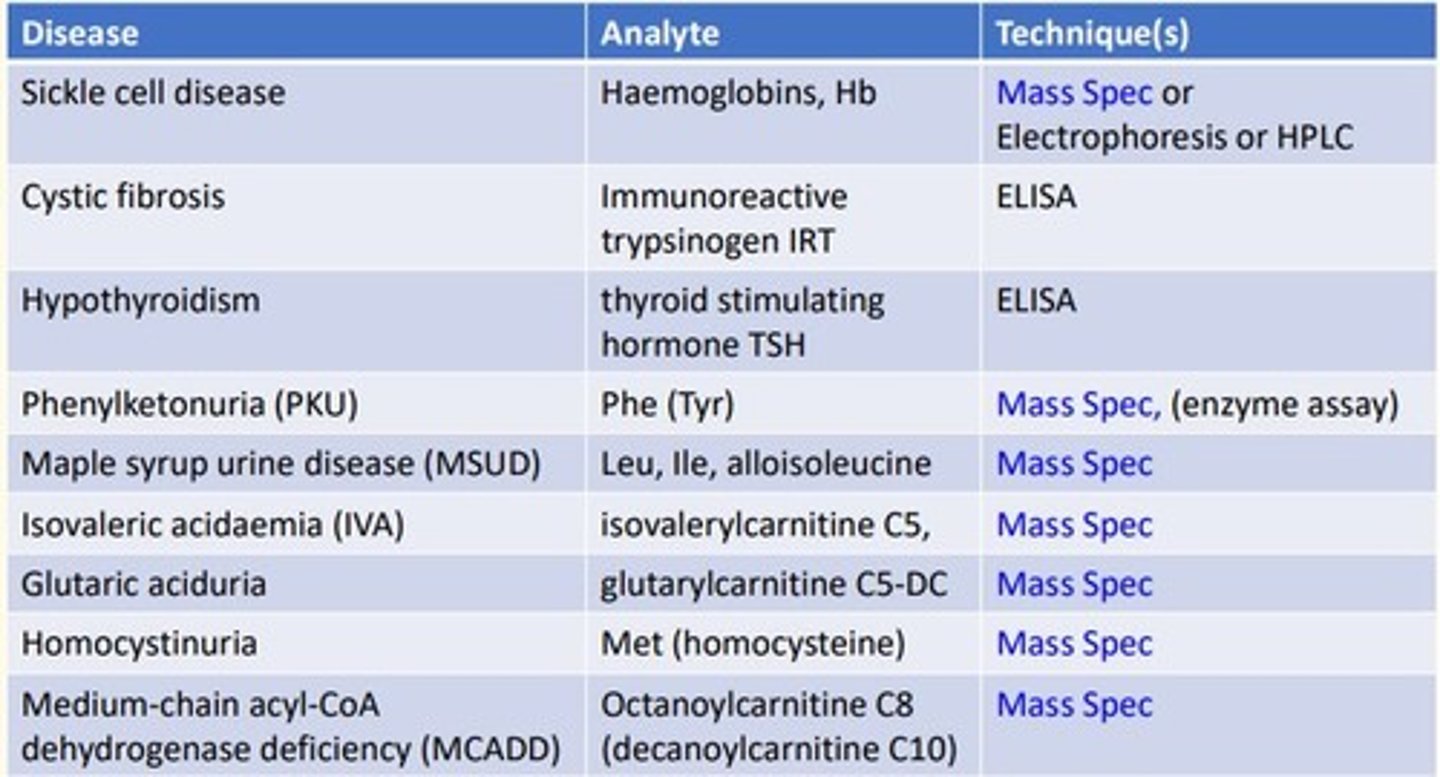
Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (MCADD) analytical technique
MCADD is looking at the analyte Octanoylcarnitine C8 (decanoylcarnitine C10)...
- Mass spectrometry