ATC 420 - Research Designs
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
validity
accuracy
reliability
repeatability
validity and reliability
study can be valid but not reliable
VICE VERSA
generalizability
large enough sample so results can apply to broader/more general population
5 steps of evidence based practice
1. ask
2. acquire
3. appraise
4. apply
5. audit
ask
convert information need into an answerable clinical question
acquire
to obtain
appraise
critically appraise the evidence for validity, impact, and applicability
apply
integrate the evidence into your clinical decision making
audit
evaluate steps 1-4 and seeks ways to improve
scientific method
1. make observation
2. review of literature
3 state problem
4. ID variables
5. hypothesis
6. research design
7. IRB approval
8. collect data
9 statistic analysis
10. conclusions
11. apply findings
12. assess application
ID variables
independent
dependent
control
independent variable
manipulated in experiment
dependent variable
outcome on manipulated variable
control variable
the equalizer and delimitation
IRB approval
institutional review board approval
null hypothesis
statement of no difference
A = B in study (statistical)
alternate hypothesis
statement predicting what will happen
qualitative research designs
1. case report
2. case series
3. cross sectional
4. case-control
5. cohort studies
qualitative
"why"
observation, words, symbols, etc.
quantitative
"how many/much"
always a number result
measurable and testable
statistical analysis
mixed methods
combination of qualitative and quantitative
take quantitative date and ask qualitative questions
non-experimental
no comparison group
quasi-experimental
control group to be compared
experimental
measures outcomes for both groups
explicit comparison group
relationship
correlation
cause and effect
t test
prevalence
frequency (observation)
compare
pre vs post
A vs B
regression analysis
predict
randomization
increases level of evidence
recall/memory
decreases level of evidence
large n
larger population is better for study
clinical research
may be unethical (placebo)
weakness of research designs
subjects representative of whole target population
qualitative factors
no cause and effect
no randomization
no equal start
quantitative research designs
1. simple RCT
2. between subject RCT
3. between subject pre-post RCT
4. within subject RCT
5. within subject pre-post RCT
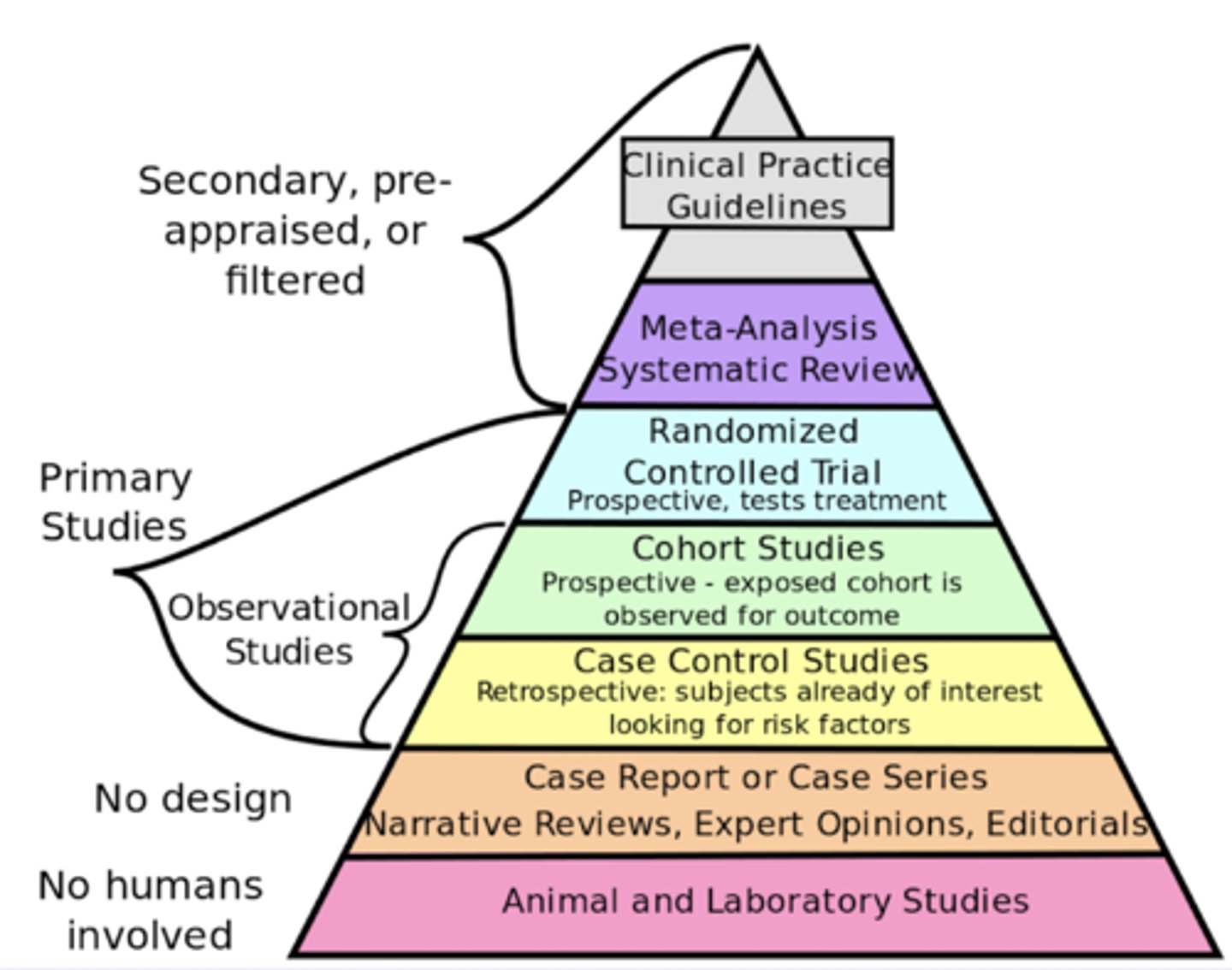
levels of evidence
the LOWER the number the BETTER the quality of evidence
bench/expert
neither qualitative or quantitative
bench
lab study done on animals or cells
(unreliable since not done on humans)
expert
presentation from an specialist in the field
(no study, just facts from an expert, neglects conflict of interest)
case report
observational
qualitative
one subject
case series
case report with more people
qualitative
no control group (everyone receives manipulated variable)
cross sectional
observational
qualitative
to understand prevalence
snapshot of a particular period of time
case-control
observational
qualitative
outcome is already known
compares subjects with and without (control group)
looks in past
relies on recall/memory
confounding variables not considered
ONLY QUALITATIVE WITH CONTROL GROUP
cohort studies
prospective and retrospective
observational
qualitative
may rely on recall/memory
difficult to populate
needs larger subject size
confounding variables not considered
prospective cohort
observes a population and what things influence outcomes
(conducted presently and looking at future)
retrospective cohort
takes a group and sees if there are any trends from the past that would cause ______
(conducted after and looks into the past)
simple RCT
experimental research design
quantitative
researchers manipulate independent and observe dependent
control group vs treatment group
simple RCT disadvantages
clinically preventing someone from getting something they need
OR
giving something that results in bad outcomes
improve simple RCT
add a control group as a baseline
between subject RCT
compares control vs experiment group
between subject pre-post RCT
testing before and after manipulation
pre acts as control (baseline)
between subject threats
boredom
crossover
fatigue
within subject RCT
subject is being compared to oneself
within subject pre-post RCT
crossover study
everyone serves as own control group
washout period
both groups doing the same thing
within subject threats
order effect (learning effect and randomization)
clinically have to give something up thats potentially working to do the other part of study
any learning
cannot be unlearned
meta-anaylsis
makes any research design stronger
(one step up)
strongest research design
meta-analysis of RCT
research design order
FINER
Feasible
Interesting
Novel
Ethical
Relevant
feasible
possible, able to be done
interesting
for researcher to study/to read
novel
new and different
ethical
morally right
relevant
important or pertinent
p levels
statistical significance
sound be set to <0.05 (95%)
probability results would occur if null hypothesis is true