Psychology from inquiry to understanding: Chapter 11
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
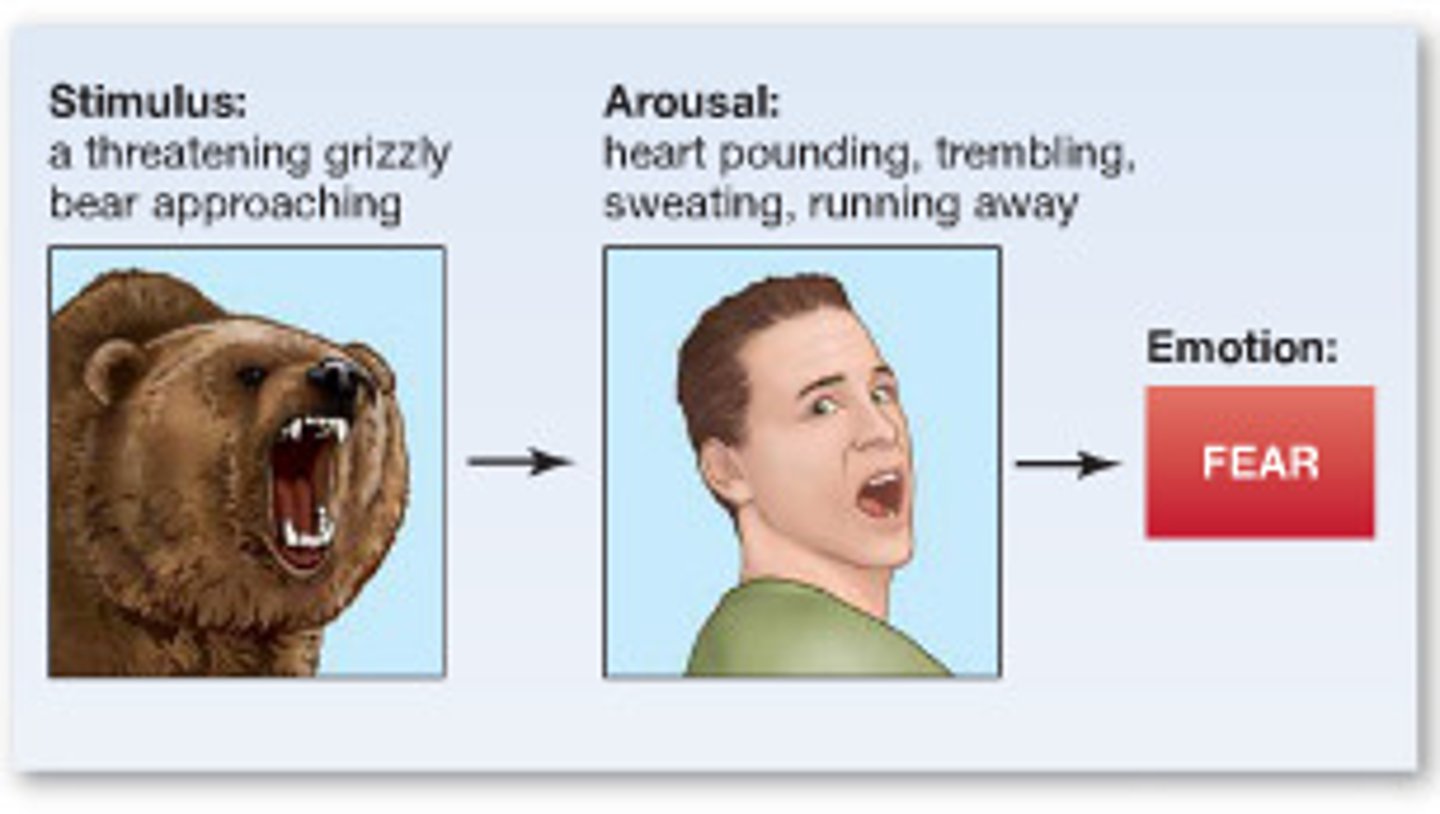
Emotion
... is the servant of reason. Without feelings, we have scant basis for rational decisions.
Emotions
mental states or feelings associated.
Discrete emotions theory
theory that humans experience a small number of distinct emotions that are rooted in our biology.
Motor program
Each emotion (Discrete emotions theory) is associated with a distinct "...": a set of genetically influenced physiological responses that are essentially the same in all of us.
Evolutionary basis
The fact that some emotional expressions emerge even without direct reinforcement suggests that they have an ...
Universality
Discrete emotions are products of evolution because across cultures there is an ... of emotions.
Primary emotions
Ekman concluded seven ... are cross-culturally universal.
Secondary emotions
Our brains 'create' an enormous array of ... from a small number of primary emotions.
Leedvermaak
Some of these complex emotion blends (secondary emotions) have names in one language but not in another e.g. Schadenfreude = ...
Display rules
... are societal guidelines for how and when to express emotions. Culture doesn't influence the emotion itself; but its overt expression.
Facial expressions
(Discrete emotions theory) Each primary emotion is associated with a distintive constellation of ...
Brain activation
... is surprisingly similar with happiness and sadness. Which makes it hard to distinguish emotions by means of their physiology.
Duchenne smile
Genuine expression of emotion: Genuine happiness = entire face expression.
Pan Am smile
fake smile: movement of mouth but not the eyes
Cognitive theories of emotion
theories proposing that emotions are products of thinking. No discrete emotions, rather fuzzy and as many different emotions as there are kinds of thought.
James-Lange
... theory of emotion: proposes that emotions result from our interpretations of our bodily reactions to stimuli.
Somatic marker theory
theory proposes that we use our "gut reactions" to help us determine how we should act. But they only help us, they are not necessary to make wise choices.
Pure Autonomic Failure
(PAF) is a rare condition marked by a deterioration of the automatic nervous system neurons beginning in middle age.
Cannon-bard
... theory of emotion: proposes that an emotion-provoking event leads simultaneously to an emotion and to bodily reactions.
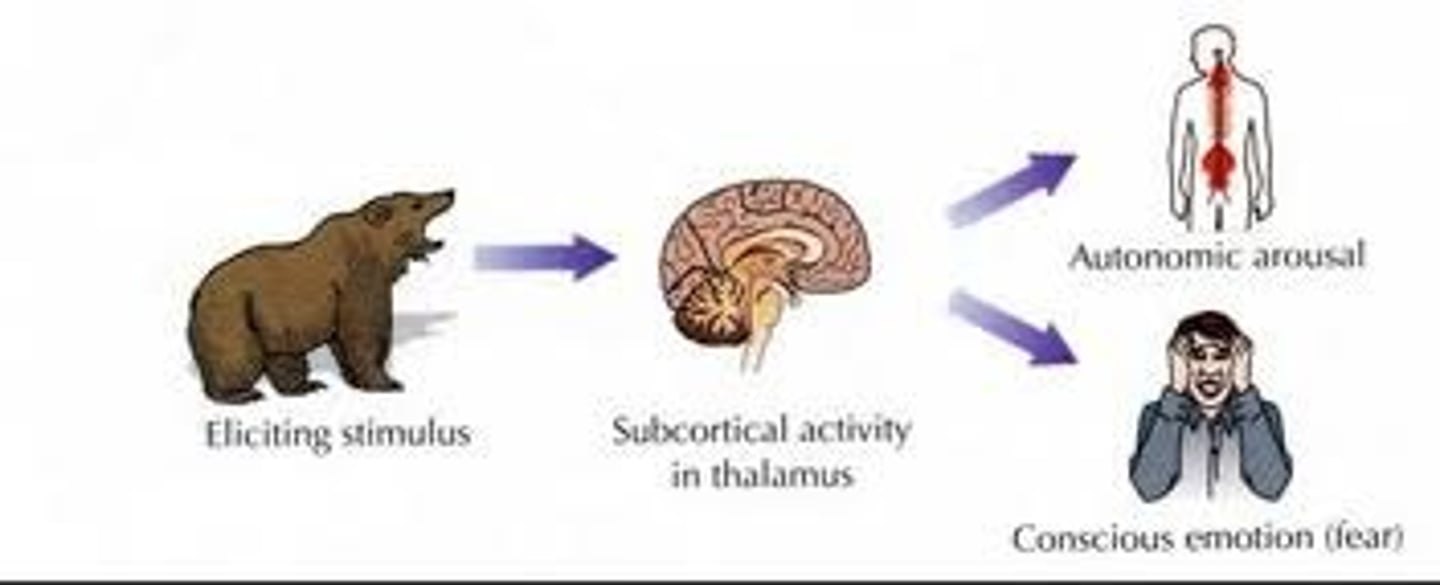
Two-factor
... theory of emotion: proposes that emotions are produced by an undifferentiated state of arousal along with an attribution (explanation) of that arousal. -> But arousal isn't necessary for all emotional experiences.
Labeling process
(Two factor theory) We explain the source of autonomic arousal by attributing it to an occurence (internal or external).
Unconscious
... influences on emotion: variables outside our awareness that can affect our feelings. (Automatic behaviors)
Automatic
Many emotional reactions may seem intentional but could be ... (Test with subliminal stimuli)
Subliminal
... stimuli = below the threshold for awareness.
Mere exposure effect
phenomenon in which repeated exposure to a stimulus makes us more likely to feel favorably toward it. (Familiarity breeds comfort)

cognitive misers
we are ... ...: We prefer less mental work to more. (Supports mere exposure effect because the more often we experience something the less effort it takes us to comprehend it.)
facial feedback hypothesis
theory that blood vessels in the face feed back temperature information in the brain, altering our experience of emotions. (Your emotions correspond to your facial features.)
Nonverbal leakage
unconscious spillover of emotions into nonverbal behavior. (is often a powerful cue that we're trying to hide an emotion.)
Curse of knowledge
When we know something, we often make the mistake of assuming others know it too. (misinterpretations on whatsapp because there is no nonverbal behavior)
Illustrators
gestures that highlight or accentuate speech. (e.g. forcefully moving hands forward to make an important point.)
Manipulators
When stressed out, we use ... (= gestures in which one body part strokes, presses, bites, or otherwise touches another body part.) e.g. twirling hair or biting fingernails.
Emblems
gestures that convey conventional meanings recognized by members of a culture. (e.g. hand wave, nodding the head, crossing fingers)
Proxemics
the study of personal space. Personal distance is correlated positively with emotional distance.
Public, social, personal, intimate
4 levels of personal space. ... distance. -> BUT there are cultural and gender differences.
Pinocchio response
supposedly perfect physiological or behavioural indicator of lying.
Modern polygraph test
"lie detector" that measures several physiological signals that often reflect anxiety. Is based on the assumption of the pinocchio response.
Controlled question test
(CQT) most widely administered version of the polyagraph test measures suspect's physiological responses following three major types of yes-no questions.
Relevant, irrelevant, control
3 major types of yes-no questions asked during a controlled question test with a polyagraph machine.
False positives
innocent individuals whom the test labels incorrectly as guilty. (high rate of ... with the polyagraph, which is why it's not used in court)
Voice stress analysis
a method of detecting lies on the basis of findings that people's voices increase in pitch when they lie. -> BUT people's voices also go up in pitch when they're stressed out.
False negatives
guilty individuals whom the test incorrectly labels innocent. (People who use countermeasures or psychopaths)
Countermeasures
Properly trained subjects can "beat" the polygraph test by using ... (= methods designed to alter their responses to control questions.)
Guilty knowledge test
(GKT) is an alternative lie detecting test that relies on the premise that criminals harbor concealed knowledge about the crime that innocent people don't. (High FP & high FN)
Brain fingerprinting
Sensitive measure for the GKT that uses brain waves for the recognition of concealed knowledge. -> BUT brain activation may be similar when only merely thinking about lying.
Truth serum
... a term for a broad class of drugs called barbiturates, which typically relax people. Was a popular tool in psychotherapy & in military/police operations in the hope of dredging up concealed information.
-> BUT has only the same effect as alcohol and is scientifically proven as false.
Integrity tests
questionnaire that presumably assesses workers' tendency to steal or cheat. (High False positive rate, so may be biased against the innocent.)
Positive psychology
discipline that has sought to change the state of neglect by emphasizing human strengths, such as resilience, coping, life satisfaction, love, and happiness.
Defensive pessismism
strategy of anticipating failure and compensating for this expectation by mentally overpreparing for negative outcomes. Serves a valuable function for many anxious people.
Happiness
... - generally defined as people's subjective sense of how satisfied they are with life- may produce enduring psychological and physical benefits.
Broaden and build theory
(Barbara Fredrickson) theory proposing that happiness predisposes us to think more openly, allowing us to see the "big picture" & seek out more opportunities.
optimists
life is easier for those of us who are ...
What happens to us
(MYTH 1 what makes us happy) - the prime determinant of happiness is ...
Money
(MYTH 2 ) ... makes us happy.
declines in old age
(MYTH 3 what makes us happy) - happiness ...
positivity effect
the tendency for individuals to remember more positive than negative information with age.
amygdala
The positivity effect is accompanied by diminished activity of the ... which plays a key role in the processing of negative emotions.
Marriage, Friendships, College, Religion, Exercise, gratitude & giving
What makes us happy: MFC, REG & G.
Flow
(what makes us happy) a mental state in which we're completely immersed in what we're doing.
Affective forecasting
we are incredibly poor at ..., which is our ability to predict our own and others' happiness.
Durability bias
... = belief both our good and bad moods will last longer than they do. Which makes us especially bad at affective forecasting.
Hedonic treadmill
tendency for our moods to adapt to external influences. Our levels of happiness adjust quickly to ongoing life situations bringing us back to emotional square 1.
Self-esteem
evaluation of our worth. is correlated positively with happiness (BUT does not cause it), and negatively with loneliness.
narcissism
extreme self-centeredness
positive illusions
tendencies to perceive ourselves more favourably than others do. ( can be healthy in moderation)
Motivation
the drives - especially our wants and needs - that propel us in specific directions.
Drive reduction theory
theory proposing that certain drives, like hunger, thirst, and sexual frustration motivate us to act in ways that minimize bad states.
Homeostasis
equilibrium or balance of our mind and body.
Yerkes-dodson law
inverted U-shaped relation between arousal on the one hand, and mood and performance on the other.
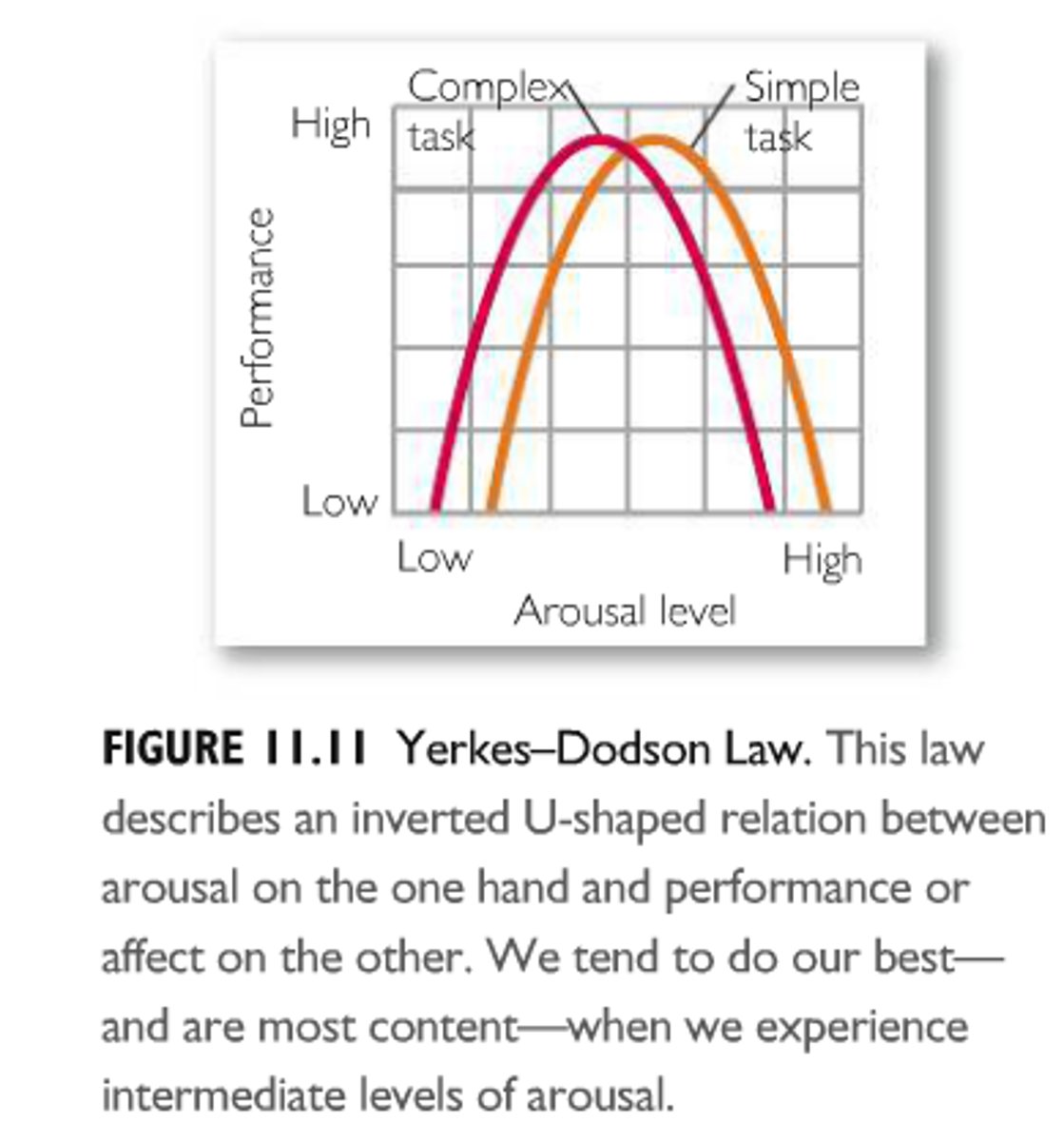
Sensory deprivation
under-arousal of our senses.
Approach
certain drives generate tendencies toward ..., a predisposition toward certain stimuli (food/objects of sexual desire)
Avoidance
Tendencies towards ..., a disposition away from certain stimuli (rude people / frightening animals )
Incentive theories
theories proposing that we're often motivated by positive goals. (intrinsic motivation & extrinsic motivation)
Contrast effect
Once we receive reinforcement for performing a behavior, we anticipate that reinforcement again. So if the reinforcement is suddenly withdrawn, we're less likely to perform the behavior.
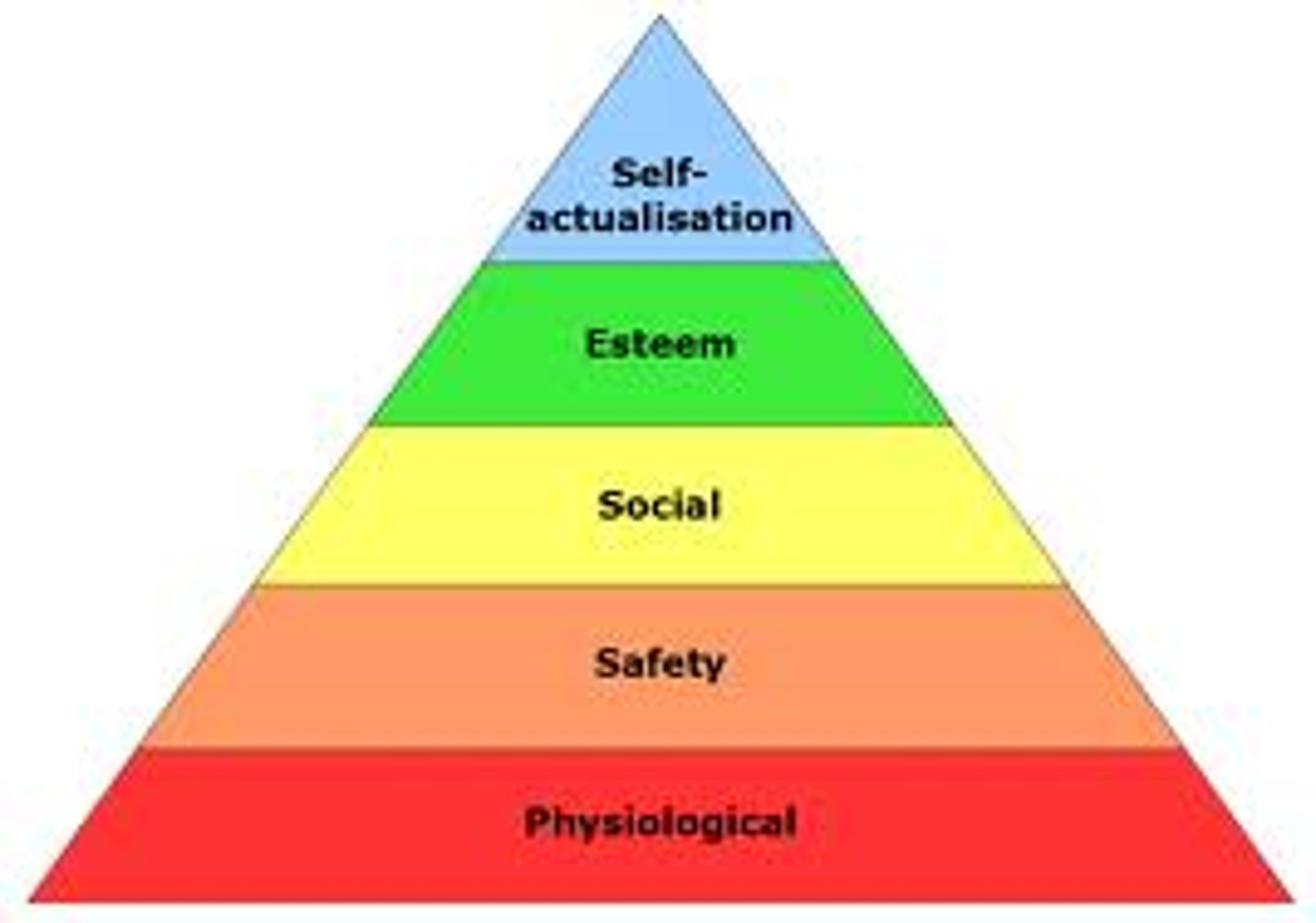
Hierarchy of needs
(Maslow) model proposing that we must satisfy primary/physiological needs and needs for safety and security before progressing to more complex needs. (Should not be taken literally)
stomach contraction theory
theory that hunger is measured by muscle contractions in the stomach. (Falsified by the report of hunger even when stomach is removed.)
lateral hypothalamus
part of brain that functions as a control centre for food cravings. Plays a key role in initiating eating.
Ventromedial
lower middle part of rats' hypothalamus. When stimulated rats eat very little or stop eating entirely -> lets rats know when to stop eating.
glucostatic theory
theory that when out blood glucose levels drop, hunger creates a drive to eat to restore the proper level of glucose. (to achieve homeostasis)
Leptin
hormone that signals the hypothalamus and brain stem to reduce appetite and increase the amount of energy used.
obesity
A lack of or being resistant to the gene for leptin results in ...
set point
a genetically predisposed value that establishes a range of body and muscle mass we tend to maintain.
Regulatory mechanisms
... kick in when we eat too little and drop below our set point, to increase our appetite or decrease our metabolism. Defense against weight loss.
Melanocortin-4 receptor gene
a mutation in the MC-4 RG is responsible for some cases of severe obesity. Makes people inable to feel satiated.
portion distortion
(Cause of high levels of obesity) The super sizing of portions in america.
Unit bias
Heuristic of thinking in terms of 'units' of things as the optimal amount.
Internal-external theory
theory holding that obese people are motivated to eat more by external cues than internal cues. (Critics say it could be a consequence of eating patterns rather than a cause.)
Bulimia nervosa
eating disorder associated with a pattern of bingeing and purging in an effort to lose or maintain weight. Vicious cycle.
Bingeing
eating large amounts of highly caloric foods in brief periods of time
purging
vomiting or other means of drastic weight loss, like excercise or extreme dieting.
Anorexia nervosa
eating disorder associated with excessive weight loss and the irrational perception that one is overweight.
Body image distortion
People with anorexia nervosa often suffer from ... which contributes to their irrational fear of being fat despite being severely underweight.
libido
Sexual desire
testosterone
sex hormone that can enhance sexual interest in the short-term.
Sexual response cycle
4 phases of sexual response: 1) Excitement, 2) plateau 3)orgasm 4) resolution
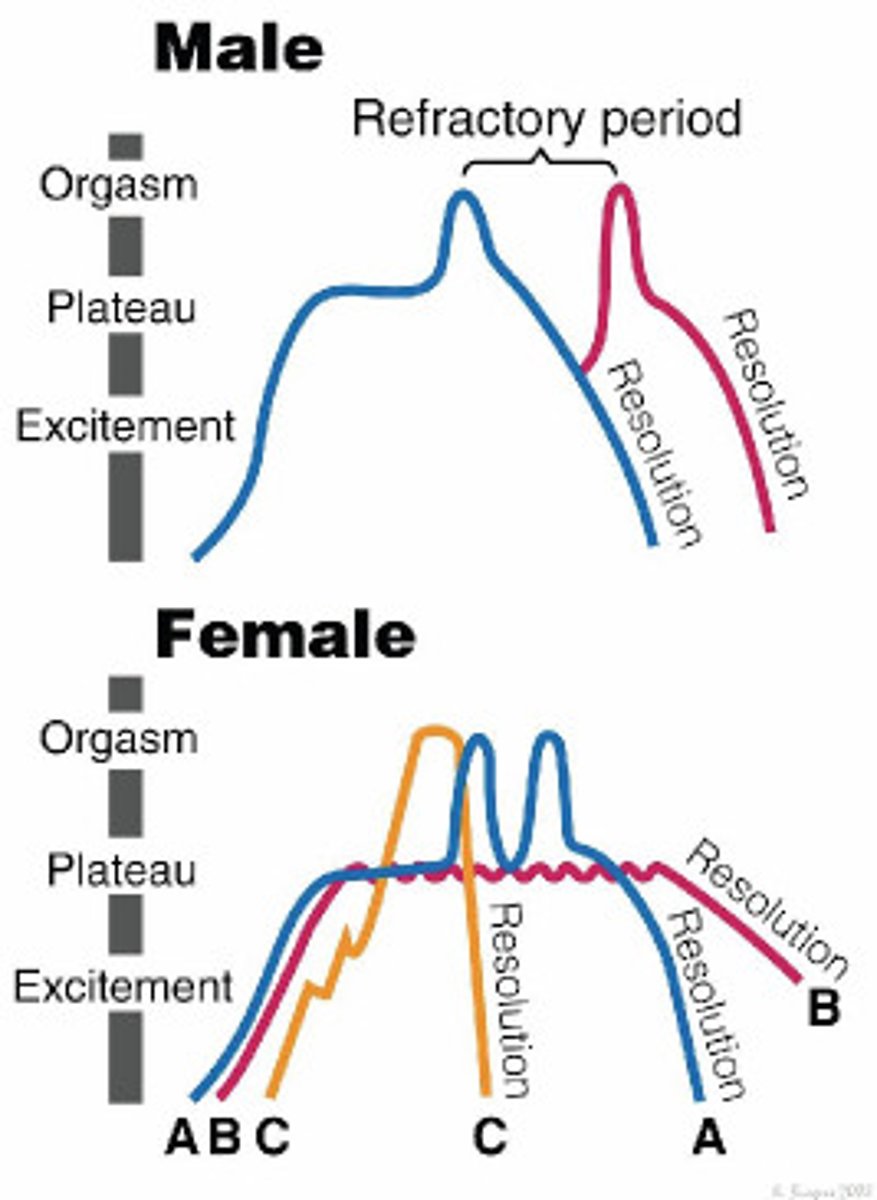
Excitement phase
(sexual response cycle 1) people experience sexual pleasure and notice physiological changes associated with it.
Plateau phase
(sexual response cycle 2) sexual tension builds
orgasm phase
(sexual response cycle 3) climax: involuntary rhythmic contractions in the muscles of genitals in both men and women.
resolution phase
(sexual response cycle 4) following orgasm, relaxation and a sense of well-being.
same-sex
... sexual and romantic attractions are normal variations of human sexuality - no need for psychological interventions to change sexual orientation. (APA 2009)
concordance
the proportion of co-twins who exhibit a characteristic when the other twin also exhibits this characteristic.