12) Environment, Health & Wellbeing: Malaria
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Malaria
"a life-threatening disease spread to humans by mosquitoes"
... caused by a parasite
... vector borne disease
How is malaria contracted?
Female mosquitos feed on human blood, and their bite injects the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into the person's bloodstream
Parasite = Plasmodium
(invades red blood cells and liver cells)

Global Malaria cases + deaths
Globally an estimated 249 million malaria cases and 608,000 malaria deaths in 85 countries (2022)
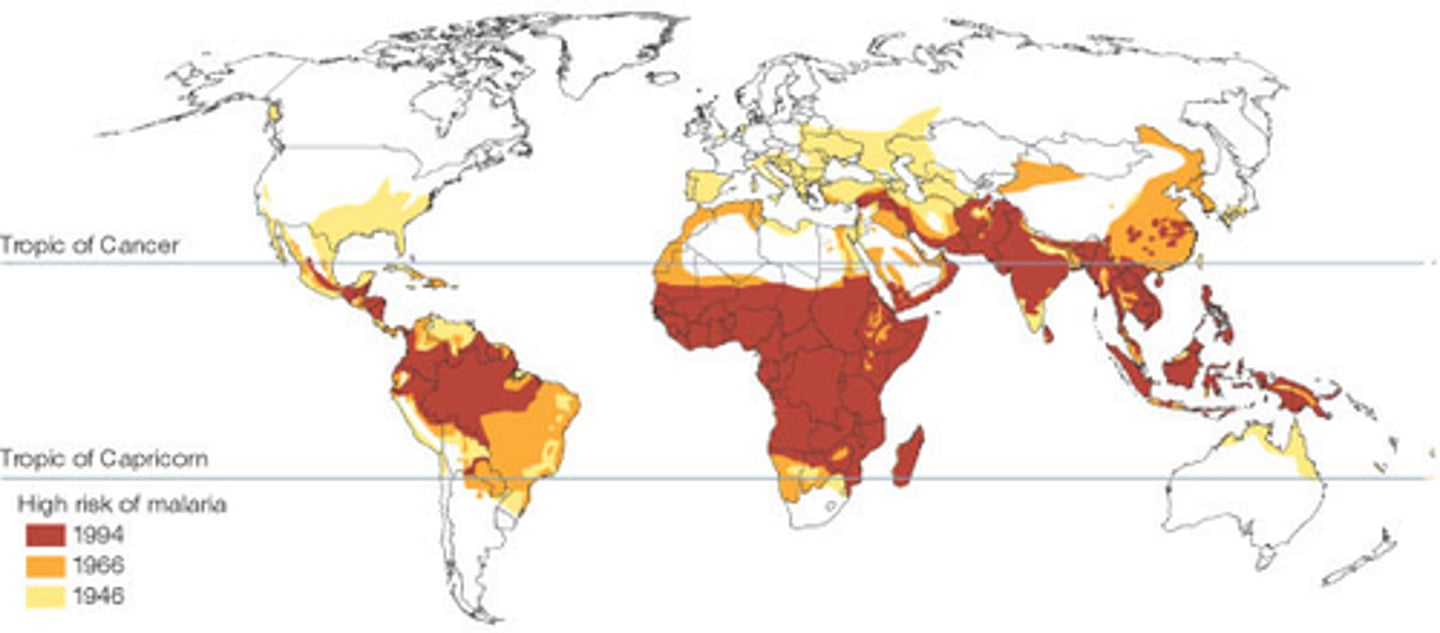
Global malaria burden
WHO African Region carries a disproportionally high share of the global malaria burden
=> region was home to 94% of malaria cases (233 million) and 95% (580,000) malaria deaths
=> children under 5 accounted for about 80% of all malaria deaths in the region
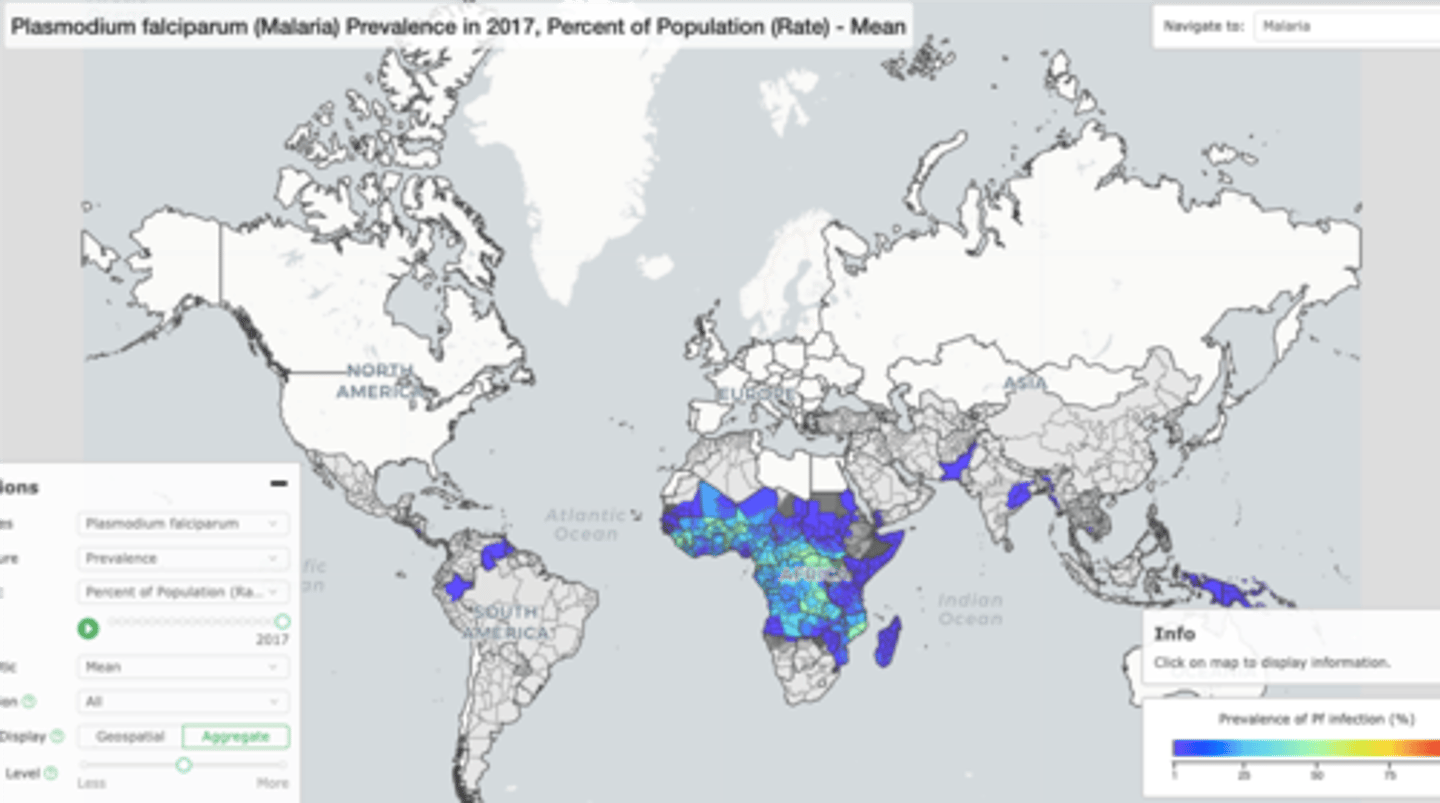
4 African Countries that account for over half of all malaria deaths worldwide
1. Nigeria (26.8%)
2.Democratic Republic of the Congo (12.3%)
3. Uganda (5.1%)
4. Mozambique (4.2%)
account for just over half of all malaria deaths worldwide:
Malaria + the Physical Environment
warmer temperature
frequent, moderate rainfall
hydrography, hydrology, and topography
humidity
Warmer Temperatures
... speed up the growth cycle of the malaria parasite in mosquitos, enabling it to develop faster for transmission
=> temperature range between 16 degrees C and 34 degrees C, with optimal transmission at 25 degrees C
Frequent and Moderate Rainfall
...creates large bodies of water which are "breeding grounds" for mosquitos, eggs can only hatch in water
Hydrography, Hydrology, and Topography
... hills, irregular land often creates pools of stagnant water when it floods
... rivers make flooding more likely
e.g., Amazon rainforest, river floods land which creates breeding ground when water level drops at end of rainy season

Humidity
... under very dry conditions, mosquitos will desiccate
=> warm, humid, moist environments are best for them to fly/transmit parasites in
Malaria + Poverty
Malaria is considered a disease of poverty
Only 0.2% of malaria deaths are found in the world's richest populations
- Malaria was once prevalent in many of the HICs, but was eliminated in the last decades
- Still prevalent in the LDC's and poorest countries in the world
=> poor finances make it harder to fight the disease
=> disease lowers the productivity of the economy
- Malaria keeps household in poverty, discourages domestic and foreign investment and tourism, and affects land use pattens
Malaria and Socio-economics
1. Poverty
2. Education
3. Household Income
4. Agricultural Development
5. Population Movements
Malaria - Azemar and Desbordes (2009)
found that in the median Sub-Saharan African country, FDI could have been 1/3 higher in the absence of malaria and HIV
... more than ½ of this is attributed to malaria
Malaria + education
- Low levels of awareness about malaria, prevention, and treatment strategies
- Orissa state of India, tribal people do not take treatment for malaria or protect themselves from it as they consider malaria as a mild disease
=> different perceptions + culture
Malaria + household income
- Poorly constructed household allow easy entrance to vectors and increases chances of infection among family members
- The use of mud for wall construction, absence of ceilings in a child's room, and poor cleanliness of the house were associated with the occurrence of malaria
- Low-income households cannot afford chemical sprays, insecticide treated bed nets, and drugs or other related medical costs
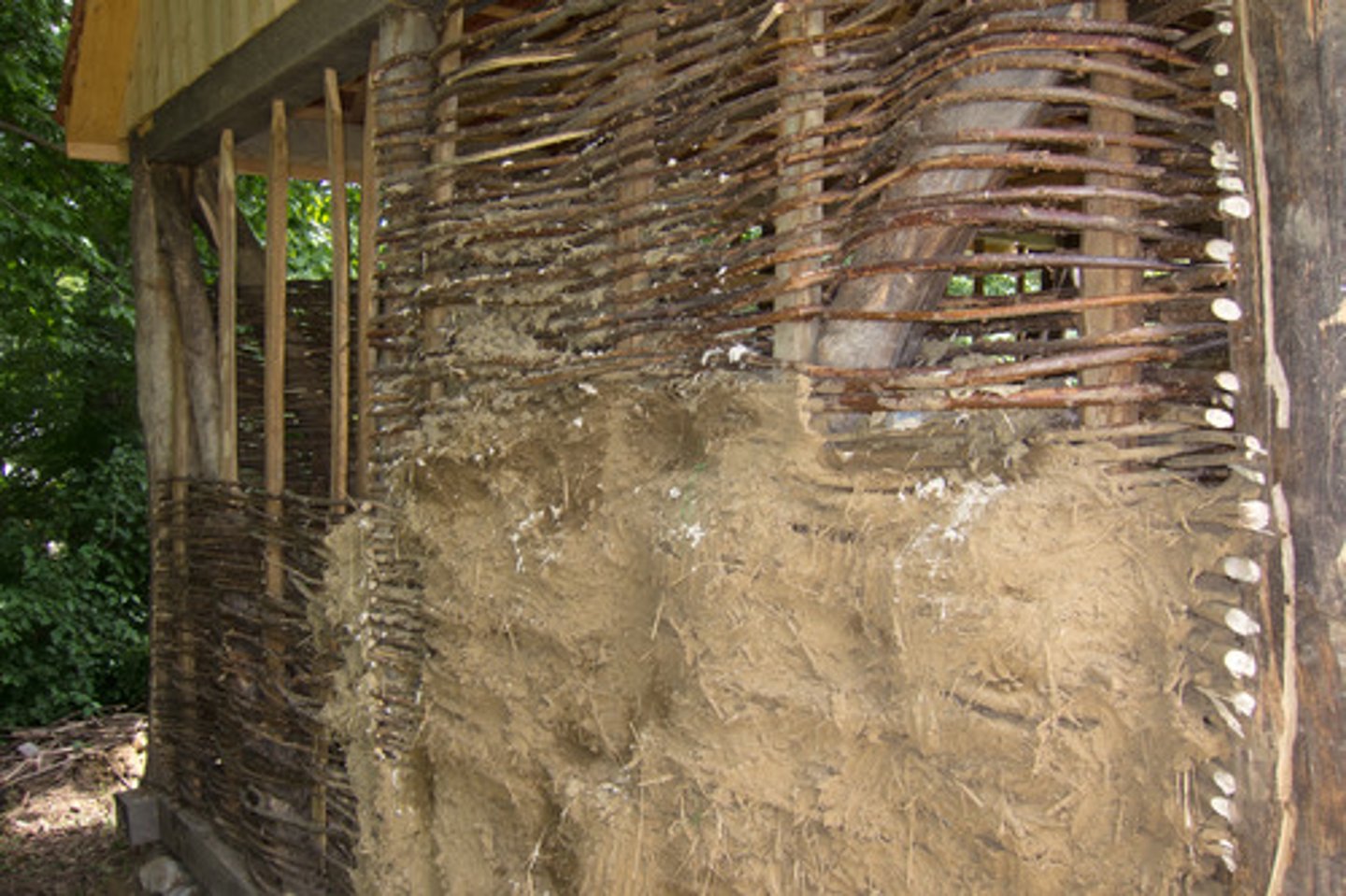

Malaria + household income CAR
Central African Republic
GDP per capita (2017) = $862
Share of population with malaria = 24%
Agricultural Development
...Common in rural agricultural communities
- More prevalent in countries where agriculture is the main employment industry
- Spend more time outside, more contact with vectors
- One type of livestock may attract particular vectors
- Use of water and irrigation creates wet, hot environments
- Clearing tropical rainforests leads to more exposed sunlight, making better breeding habitats
- Forest clearing causes soil erosion, which can form swamps and stagnant water near rivers
- Stagnant water from dug holes that have flooded (same with construction)
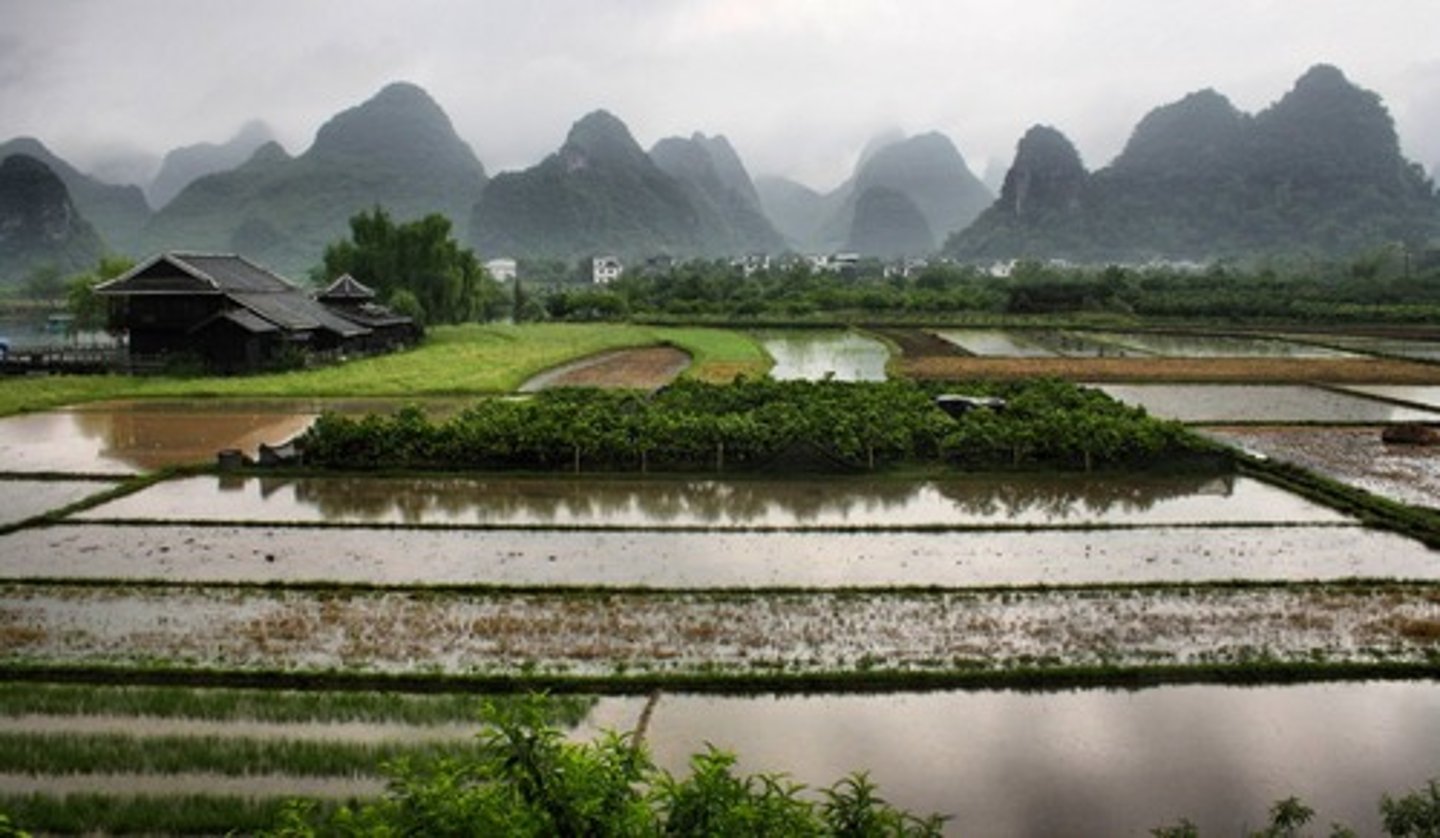
e.g., rice fields are ideal breeding sites for malaria-mosquitos in African rice farming villages
=> "The Paddies Paradox" - rice cultivation leads to more mosquitos but not more malaria - irrigated systems brought economic benefit and people could afford repellents and health care. however the adjacent communities saw a rise in the transmission of malaria
The Paddies Paradox
rice fields are ideal breeding sites for malaria-mosquitos in African rice farming villages
due to stagnant water and high humidity

Population Movements
- Religious pilgrimages, need for employment, drought, famine, war, resettlement, and tourism
- Introduces non-immune people into endemic areas or infected people into malaria free regions
- Higher incidence of malaria among Afghan refugees living in Pakistan than among indigenous populations
- Employment of migrants is often performed at night when mosquitos are likely to be biting
- Difficulty testing health of migrants and migrants are rarely served by government programmes
Environmental impacts on transmission vectors - climate
Climate
- precipitation
- humidity
- topography
- temperature
Environmental impacts on transmission vectors - climate change
- warmer world means mosquitos can travel further and live longer
- increase in rain (especially in usually dry regions) = more humid environments, more breeding grounds for mosquitos
- droughts = more stagnant water
Impact of malaria on health and well-being - Society
1. cripples' economies
2. impacts communities (social burden)
3. keeps children out of schools
4. Adults cannot work => cycle of poverty
5. Puts unnecessary pressure on fragile health systems
6. Substantial cost to governments and individuals
7. Leads to loss of work
8. 60% foetal loss of pregnant women, over 10% maternal deaths
Impact of malaria on health and well-being - Health
... Parasite matures and exits in the liver, into the bloodstream to effect red blood cells
1. Cerebral malaria
=> if parasite filled blood cells block blood vessels to brain, swelling of brain or brain damage may occur, causing seizures and comas
2. Breathing problems
=> accumulated fluid in lungs (pulmonary edema)
3. Organ failure
=> can damage kidney or liver, or cause the spleen to rupture
4. Anaemia
=> may result in not having enough red blood cells for an adequate supply of oxygen to body tissues
5. Low blood sugar
=> severe forms of malaria can cause low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia) which an result in comas/death
6. Can compromise immune system and make body vulnerable to other diseases e.g., herpes virus (EPV)
Management of Malaria
=> treated with antimalarial medicines + prescription drugs
- oral medicines, slow acting
- Artemisinin drugs
- treat the symptoms of the parasite
- kill the malarial parasites when they're in the liver of red blood cells before they cause further damage
... over last decade, partial resistance to the artemisinin drug has emerged as a global threat to malaria control efforts
(WHO concerns in Africa i.e., Eritrea, Rwanda, Uganda, and Tanzania)
Surveillance of malaria
- laboratory confirmation of presumptive diagnosis
- finding out the source of infection and identification of all cases and susceptible contacts
- identifying others who are at risk in order to prevent further spread of the disease
Mitigation of malaria - Prevention
... avoiding mosquito bites and taking medication
- use mosquito nets when sleeping in high-risk areas
- use mosquito repellents at night/in humid areas
- use coils/vaporizers to repel mosquitos
- wear protective clothing (cover ankles, arms, neck, etc.)
- use window screens
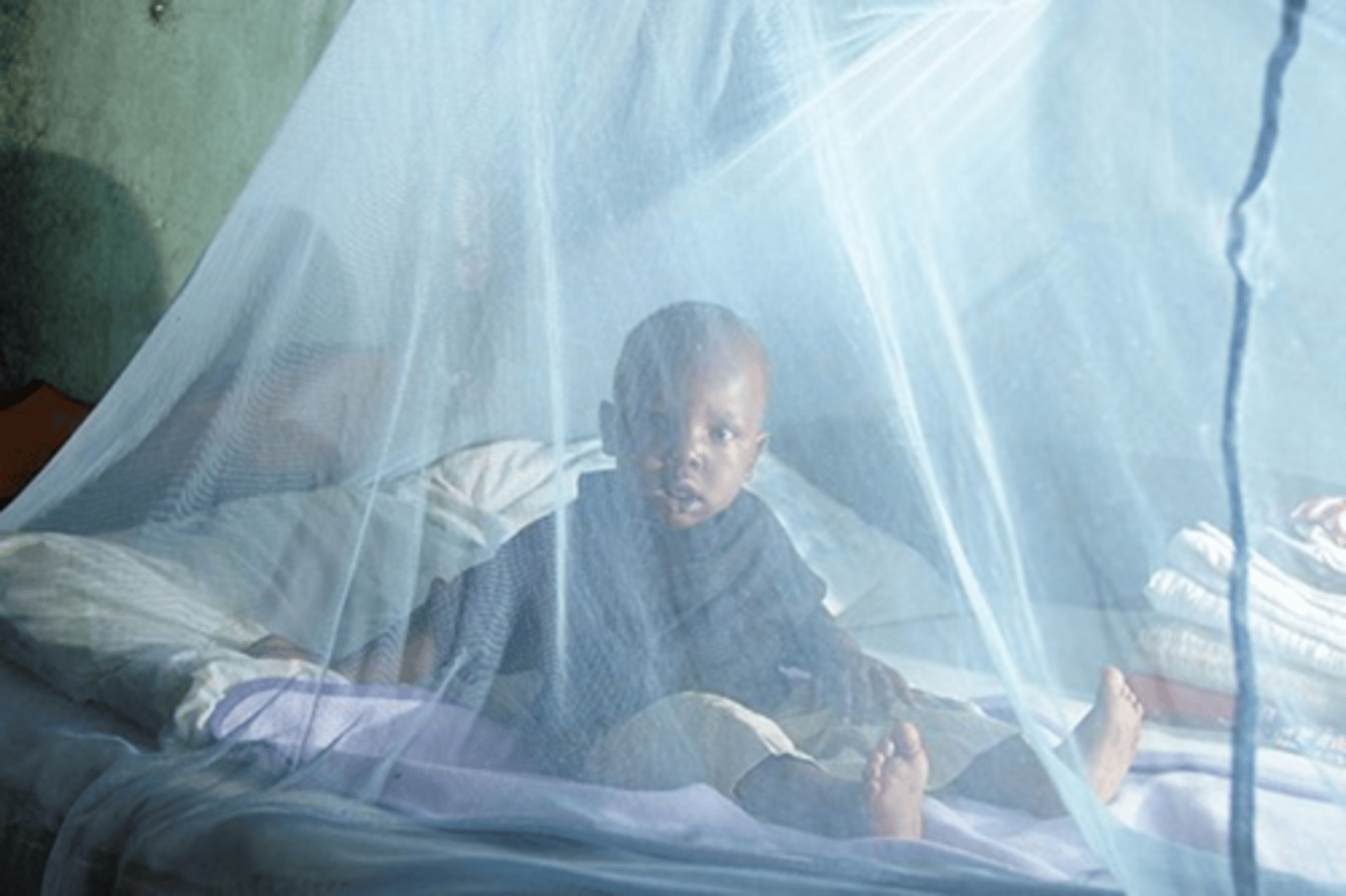

Mitigation of malaria - Vector Control
1. insecticide treated nets (ITNs)
2. Indoor residual sprays (IRS)
Mitigation of malaria - Preventive Chemotherapy
= drug therapies to prevent malaria infections and their consequences
... requires giving a full treatment course of an antimalarial medicine to vulnerable populations at designated time points during the greatest malarial risk
Mitigation of malaria - Vaccines
RTS,S/AS01 malaria vaccine for children living in high-risk P.falciparum malaria transmission areas
R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine to be used in Africa
Mitigation of malaria - Elimination
...the interruption of local transmission of a specified malaria parasite species in a defined geographical area as a result of deliberate activities
=> Continued measures to prevent re-establishment of transmission are required
Elimination of malaria
In 2022, 34 countries reported fewer than 1000 indigenous cases of the disease, up from just 13 countries in 2000
2024 - 44 countries declared malaria free by WHO
Maldives (2015), Sri Lanka (2016), Kyrgyzstan (2016), Paraguay (2018), Uzbekistan (2018), Argentina (2019), Algeria (2019), China (2021), El Salvador (2021), Azerbaijan (2023), Tajikistan (2023) and Belize (2023)
To be malaria elimination WHO certified...
... have to have achieved at least 3 consecutive years of 0 indigenous cases of malaria to be eligible for WHO certificate of elimination
WHO responses
(updated 2021)
- reducing malaria case incidence by at least 90% by 2030
- reducing malaria mortality rates by at least 90% by 2030
- eliminating malaria in at least 35 countries by 2030
- preventing a resurgence of malaria in all countries that are malaria-free
WHO plans for future without malaria
1. Playing leadership role in malaria, supporting member states and rallying partners to reach universal health coverage goals
2. Shape research agenda
3. Develop ethical and evidence-based guidance with effective support and implementation by national malaria programmes
4. Monitoring and responding to global malaria trends and threats
sucesses
Problems with managing malaria
=> Progress in global malaria control is threatened by emerging resistance to insecticides among Anopheles mosquitoes
=> other threats to ITNs include insufficient access, loss of nets due to the stresses of day-to-day life outpacing replacement, and changing behaviour of mosquitoes, as appear to be biting early before people go to bed and resting outdoor (evading exposure to insecticides)
=> vaccines = expensive and need training to be administered + drug resistance particularly south east asia
=> accessibility, cost, and training
=> lack of awareness, education towards prevention, cultural practices + perceptions
=> pandemic disruption - delays in treatment distribution + WHO warned malaria deaths could increase by the service disruptions
link to global goals
SDG 3 good health and well being - successes in malaria control have contributed to imrpoved health outcomes and increased life expectancy
SGG 1 no poverty - disease hinders economic develolpment and disproportionately affects poorest nations, reducing malaria contributes to poverty reduction. eg nigeria, uganda, mozambique
SDG 10 reduced inequalities, control inititiatives reduce health inequalities