Chemistry & Cell Biology Basics
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering atomic structure, chemical bonding, molecular polarity, intermolecular forces, and basic cell biology organelles.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Subatomic Particles
Protons, neutrons, and electrons that make up an atom.
Atomic Number
Number of protons in an atom; also equals the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
Mass Number
Sum of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
Isotope
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons and therefore different mass numbers.
Atomic Mass Unit (amu)
Standard unit of mass for subatomic particles; 1 amu ≈ 1.66 × 10⁻²⁴ g.
Electronegativity (EN)
Ability of an atom to attract shared electrons in a bond; increases up and to the right on the periodic table.
Ionic Bond
Chemical bond formed by transfer of electrons between a metal and a non-metal (ΔEN > 2.0).
Results in ions being formed
Covalent Bond
Chemical bond formed by sharing electrons between non-metal atoms (ΔEN < 2.0).
Non-Polar Covalent Bond
Bond with equal electron sharing; ΔEN < 0.5 (e.g., C–H).
Polar Covalent Bond
Bond with unequal electron sharing; 0.5 < ΔEN < 2.0 (e.g., H–Cl).
Molecular Polarity
Condition where a molecule has an uneven distribution of charge due to polar bonds and asymmetrical shape.
Symmetrical Shapes
Linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, octahedral geometries; often yield non-polar molecules if bonds are identical.
Non-Symmetrical Shapes
Bent and trigonal pyramidal geometries; often result in polar molecules.
VSEPR Theory
Model that predicts molecular shape based on repulsion between electron domains around a central atom.
Crystalline Solid
Highly ordered solid structure characteristic of ionic compounds at room temperature.
Conductivity of Ionic Compounds
Ionic substances conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water due to mobile ions.
Melting Point: Ionic vs Covalent
Ionic compounds have very high melting points (> 600 °C); covalent compounds generally melt at lower temperatures.
Like Dissolves Like
Polar solvents dissolve polar or ionic solutes; non-polar solvents dissolve non-polar solutes.
Diatomic Molecule
Molecule composed of two identical atoms (H₂, N₂, O₂, F₂, Cl₂, Br₂, I₂).
Intramolecular Forces
Forces (ionic or covalent bonds) holding atoms together within a molecule or compound.
Intermolecular Forces
Attractive forces between separate molecules: hydrogen bonding > dipole-dipole > London dispersion.
Hydrogen Bonding
Strong attraction between H bonded to N, O, or F and a lone pair on another N, O, or F atom.
Dipole-Dipole Forces
Attractions between permanent partial charges of polar molecules.
London Dispersion Forces
Temporary dipoles (positive and negative ends) arising from constant random electron movement; present in all molecules but are strongest in non-polar ones.
Animal Cell
Eukaryotic cells containing membrane-bound organelles and lacking a cell wall.
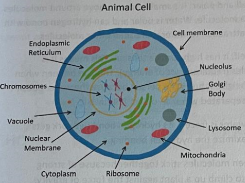
Nucleus
Houses chromosomes and controls cellular activities. Also contain nucleolus
Nucleolus
Produces ribosomal subunits used in forming proteins
Cytoplasm
a gel-like fluid containing nutrients, minerals, and water; bathes the cell and holds all organelles in place
Centriole
Involved in cellular division; pulls apart chromosomes during anaphase
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Transports materials within the cell.
Golgi Apparatus
Packages proteins so they survive out the cell
Lysosome
break down chemicals and transport unwanted materials out of the cell
Mitochondria
Generates energy for the cell (ATP); the powerhouse of the cell.
Ribosome
Site of protein synthesis
Vacuole
Membrane-bound sac for storage of water and minerals; very large in plant cells.
Plasma Membrane
Regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell.
Flagella
Long whip-like structures that propel certain animal cells (e.g., sperm).
Structure that enables motility
Cilia
Short hair-like projections that aid movement or fluid flow (e.g., in tracheal cells).
Structure that enables motility
Plant Cell
Eukaryotic cell type that contains chloroplasts and a cell wall.
Chloroplast
Organelle containing green chlorophyll where photosynthesis occurs. (Only in plant cells)
Cell Wall
Rigid layer outside the plasma membrane in plant cells providing strength and structure.