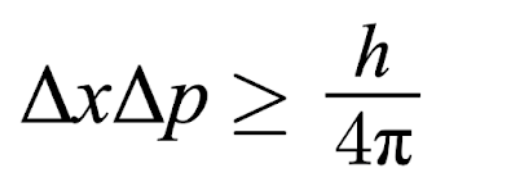Wave-Particle Duality
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
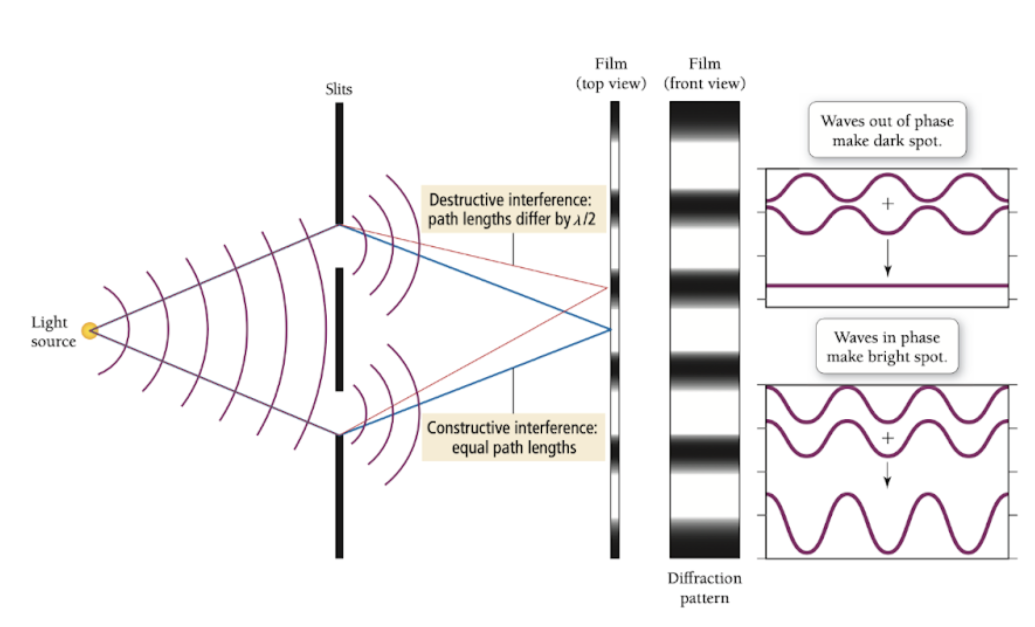
Double slit experiment
Proved light has wave-like properties
Wave interference - occurs when two waves meet
Constructive interference - waves are continuous (light bands)
Destructive interference - waves are discontinuous (dark bands)
Photoelectric effect
Proved light has particle-like properties
light of high enough frequency can eject electrons from metal
↑ intensity = ↑ electrons
↑ energy/frequency = ↑ velocity of ejected electrons
De Broglie wavelength
Proved wave-particle duality in matter
(only affects very small matter
λde Broglie is inversely proportional to momentum
greater momentum = shorter wavelength
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
The more precisely we know the momentum of an object, the less precisely we know its position
Exists because of all the innate dual nature of all things
How to find threshold frequency
Note: KE = 0 at threshold since there is no excess energy to give electrons velocity
v = frequency (Hz = s-1)
Φ = work function, threshold frequency (J)
h = 6.626 × 10-34 Js
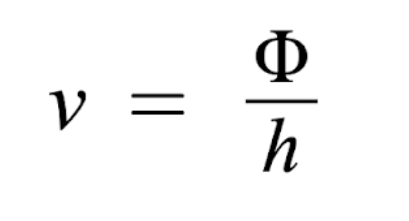
How to find maximum kinetic energy (photoelectric effect)
h = 6.626 × 10-34 Js
v = frequency (Hz = s-1)
Φ = work function, threshold energy (J)
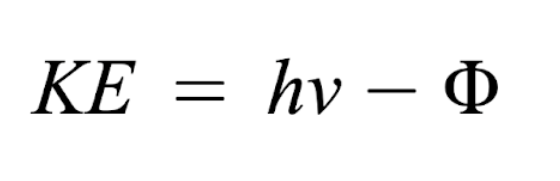
How to find work function/energy
v = frequency (Hz = s-1)
h = 6.626 x 10-34 J x s
Φ = work function, threshold energy (J)

How to find maximum number of electrons that could be ejected
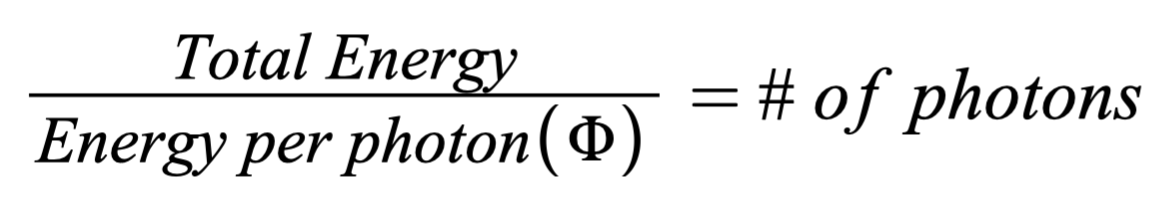
How to find De Broglie wavelength
h = 6.626 x 10-23 J×s
m = mass (kg/atoms)
v = velocity (m/s)
Note: mol → atoms (1 mol/6.022 × 1023 atoms)
Note: to find velocity, use KE formula
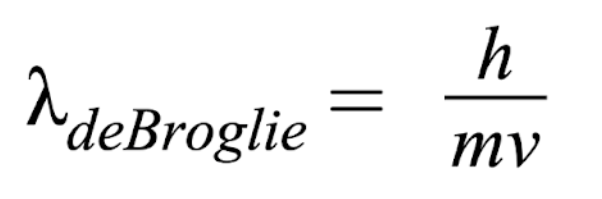
How to determine if quantum or classical
If λde Broglie > size = quantum
If λde Broglie < size = classical
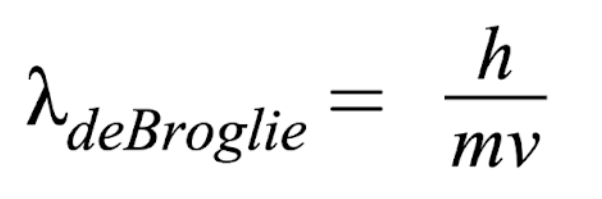
How to find uncertainty of momentum or position
X = position (m)
P = momentum (kg*m/s)
Δp = mΔv
m = mass (kg/atoms)
Δv = uncertainty in velocity (m/s)