Head and Neck Lab Practical
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
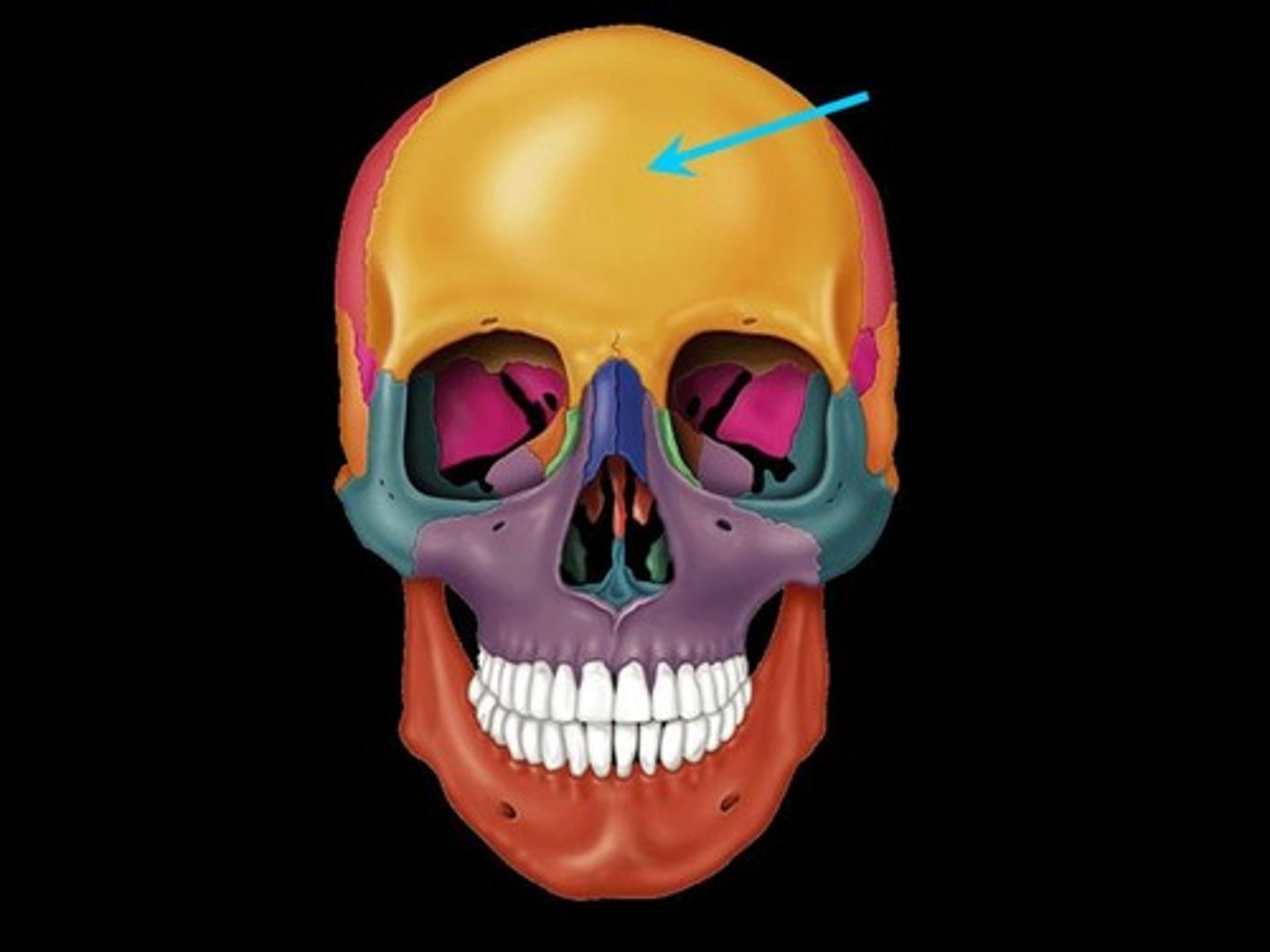
Frontal Bone
Bone that forms the forehead
Frontal Sinus
Mucosa-lined air spaces located above the eye brows
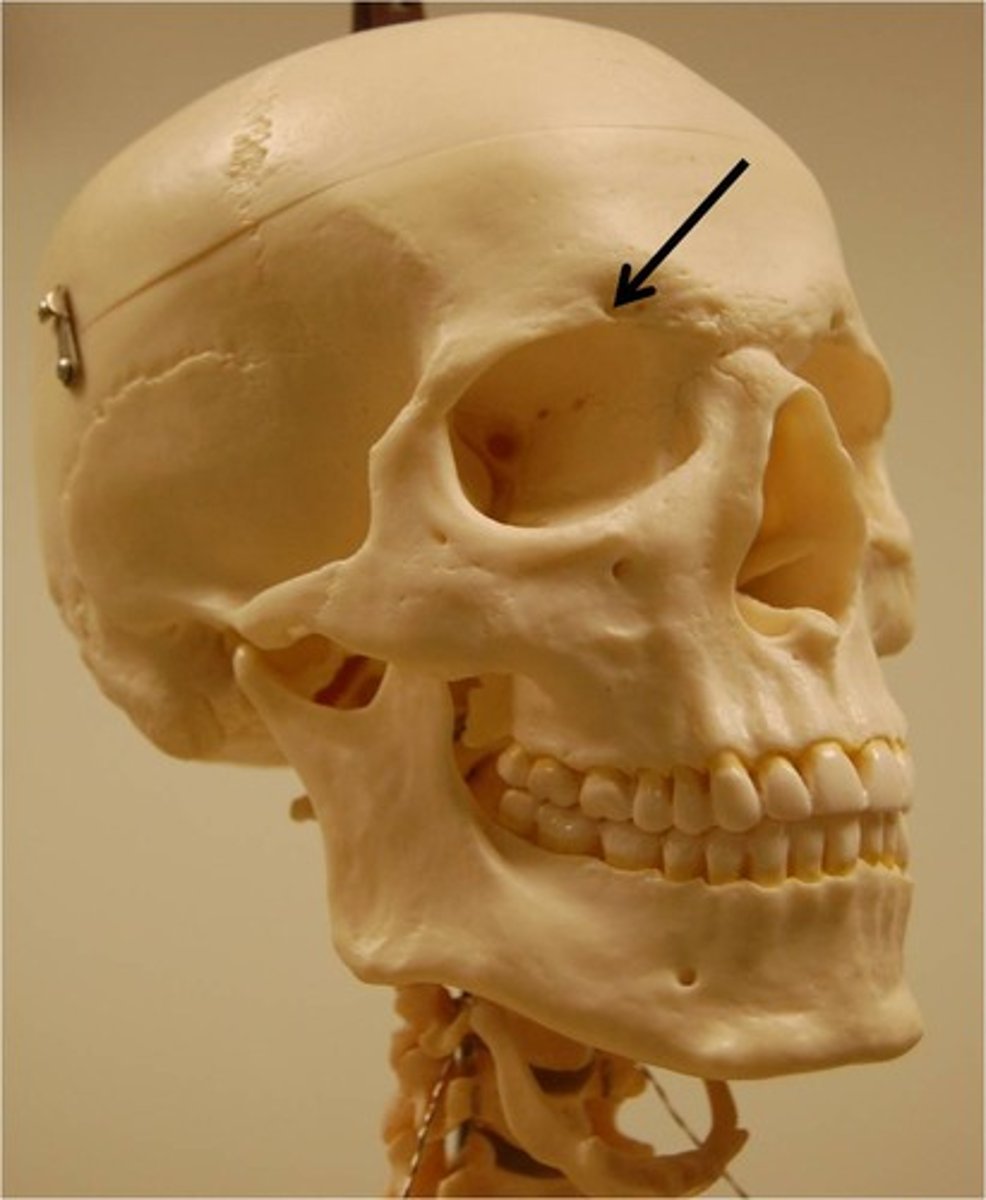
Supraorbital Foramen
A bony elongated opening located above the orbit (eye socket) and under the forehead
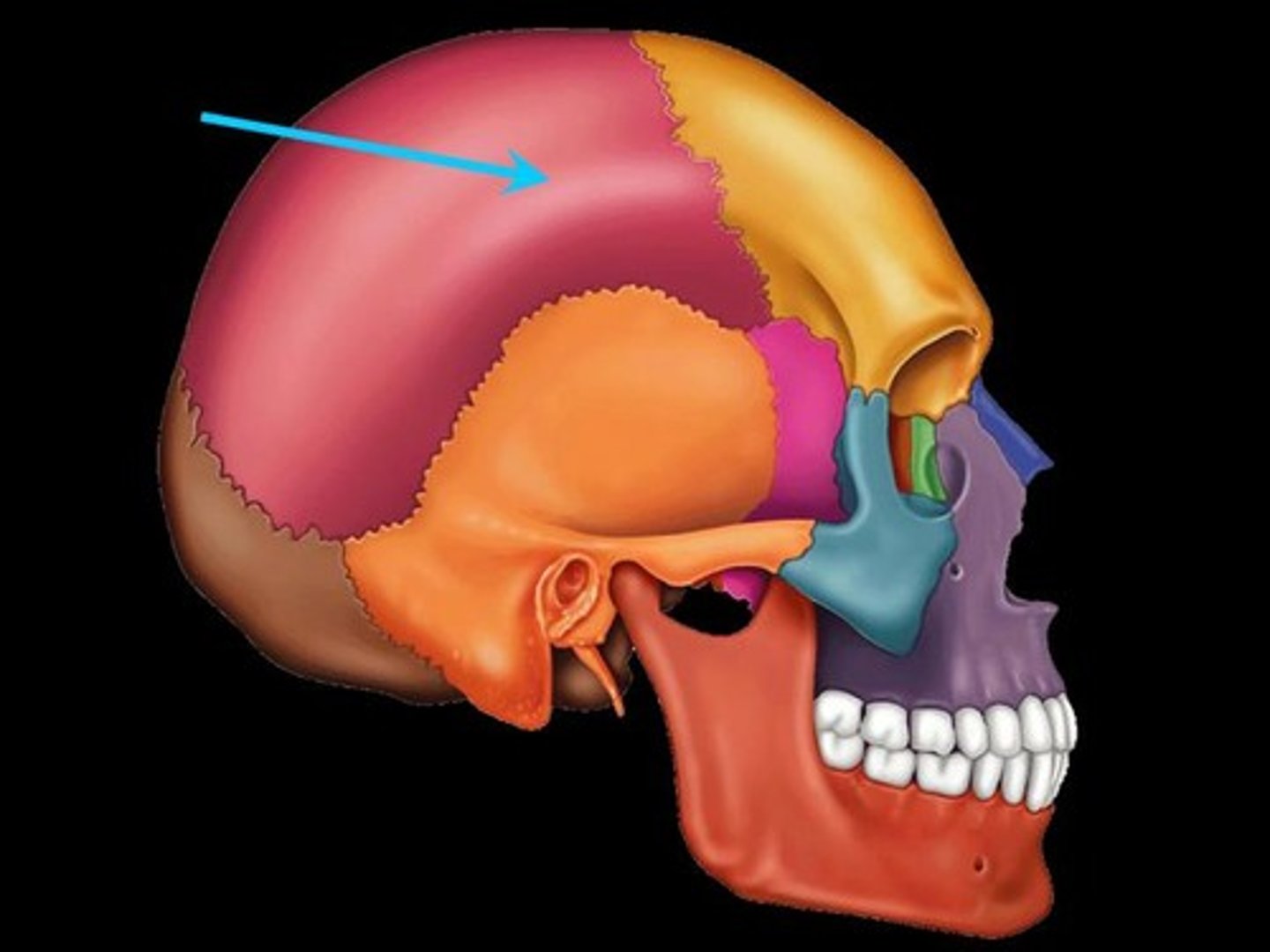
Parietal Bones
Bones that form the sides and top of the cranium.
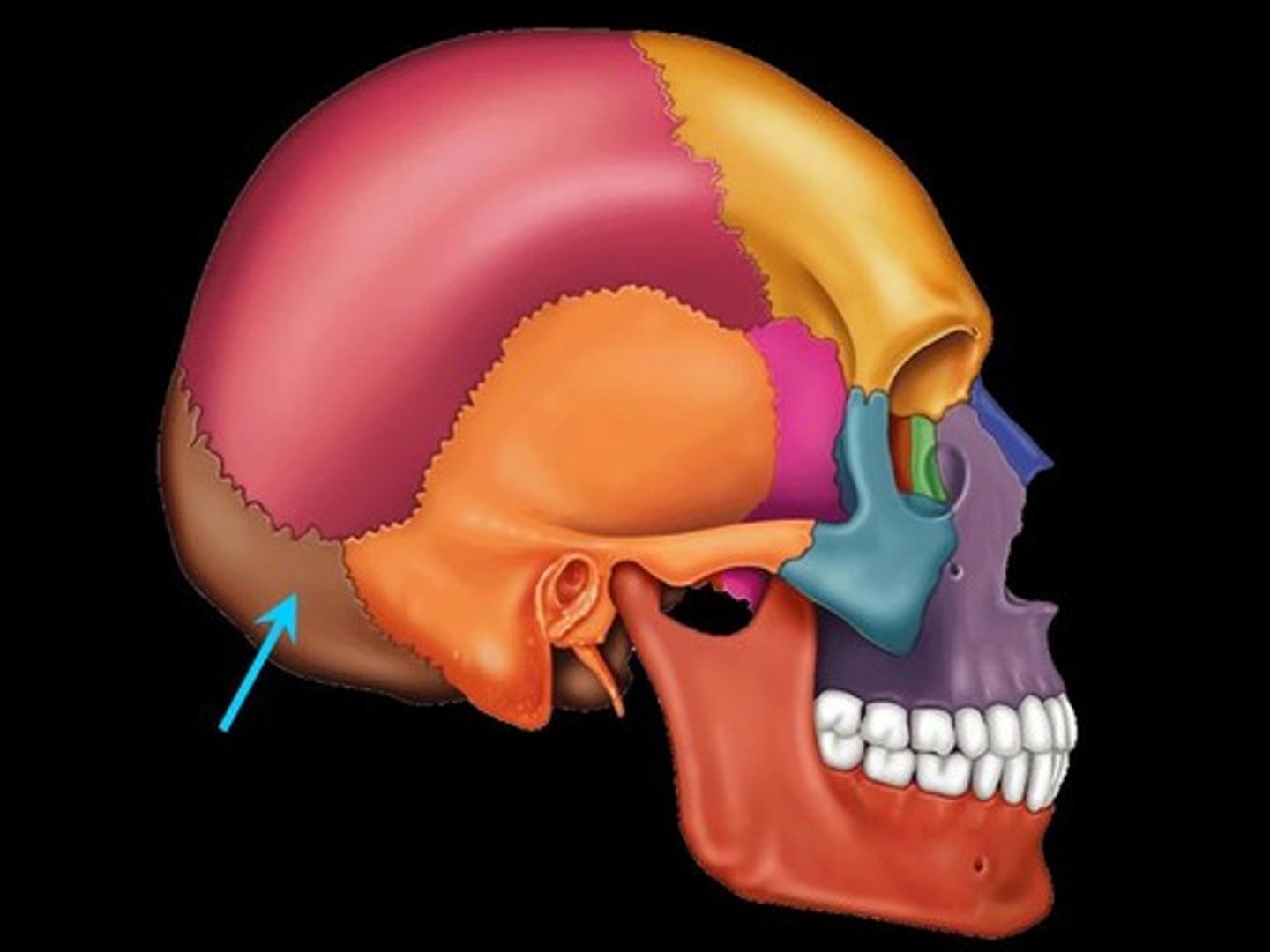
Occipital Bone
Bone that protrudes at the base of the skull
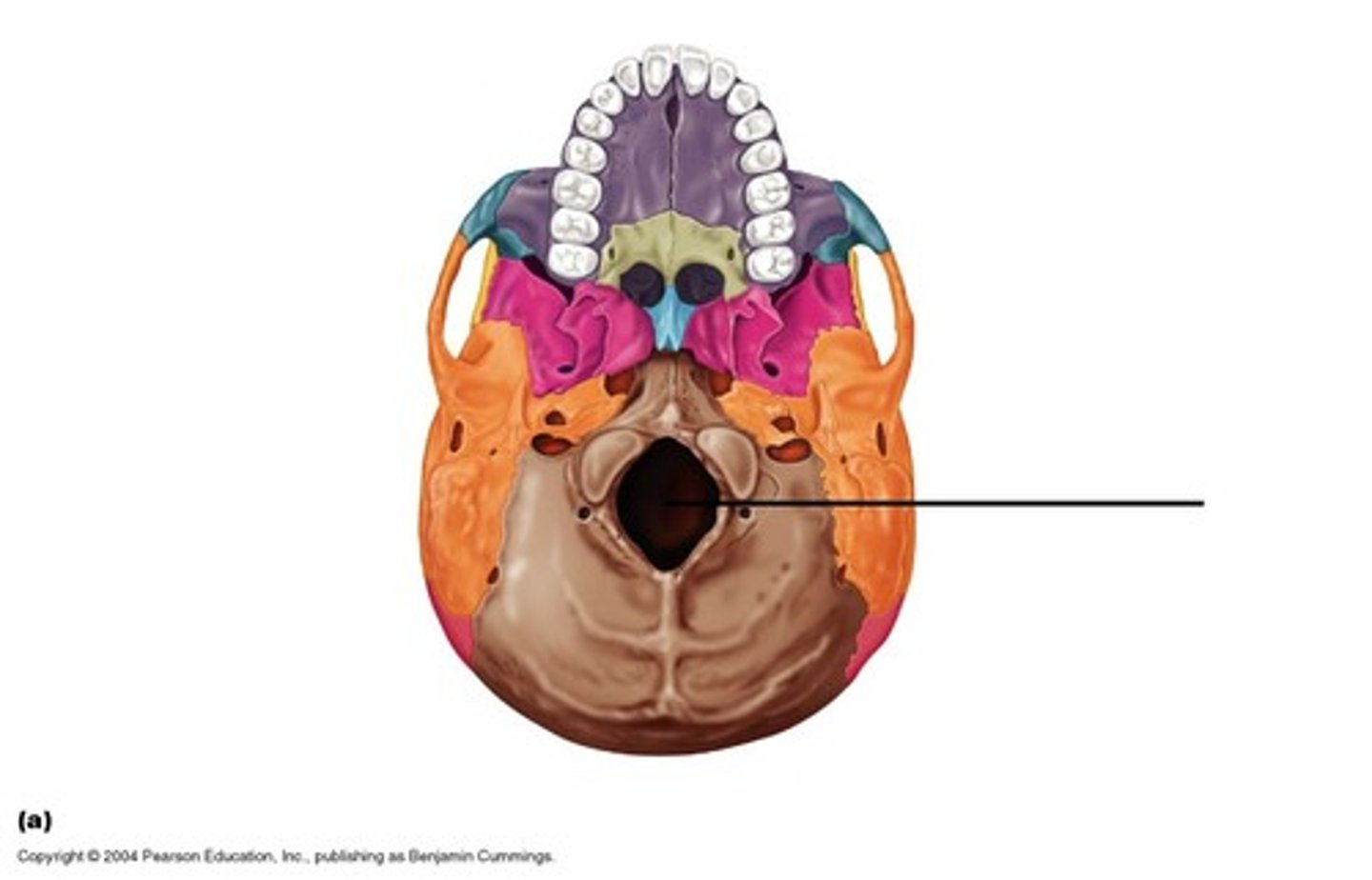
Foramen Magnum
The hole in the base of the skull through which the spinal cord passes
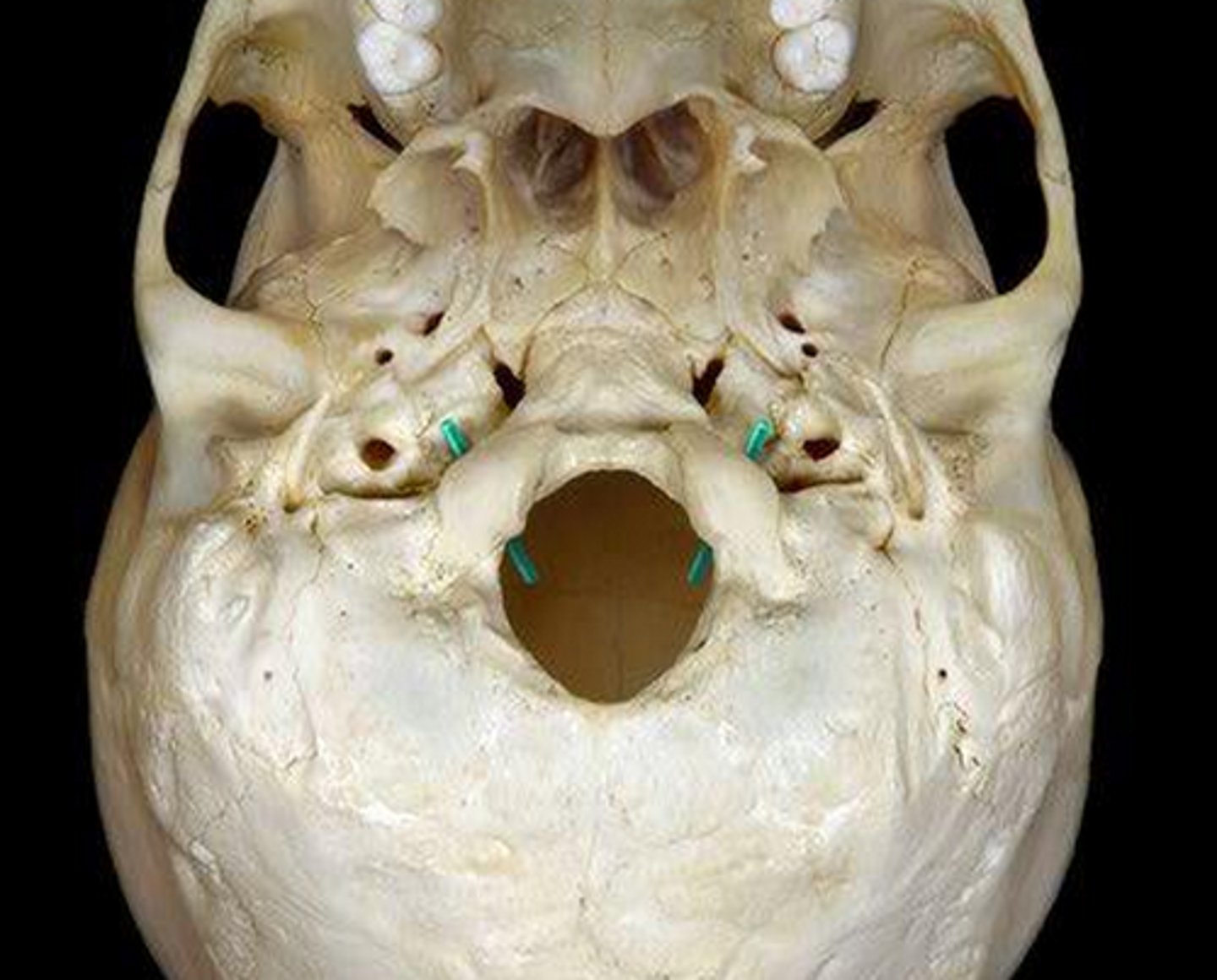
Hypoglossal Canal
Foramen in the occipital bone of the skull through which the hypoglossal nerve traverses
Foramen Lacerum
A triangular hole in the base of the skull located between the sphenoid, apex of petrous temporal and basilar part of occipital
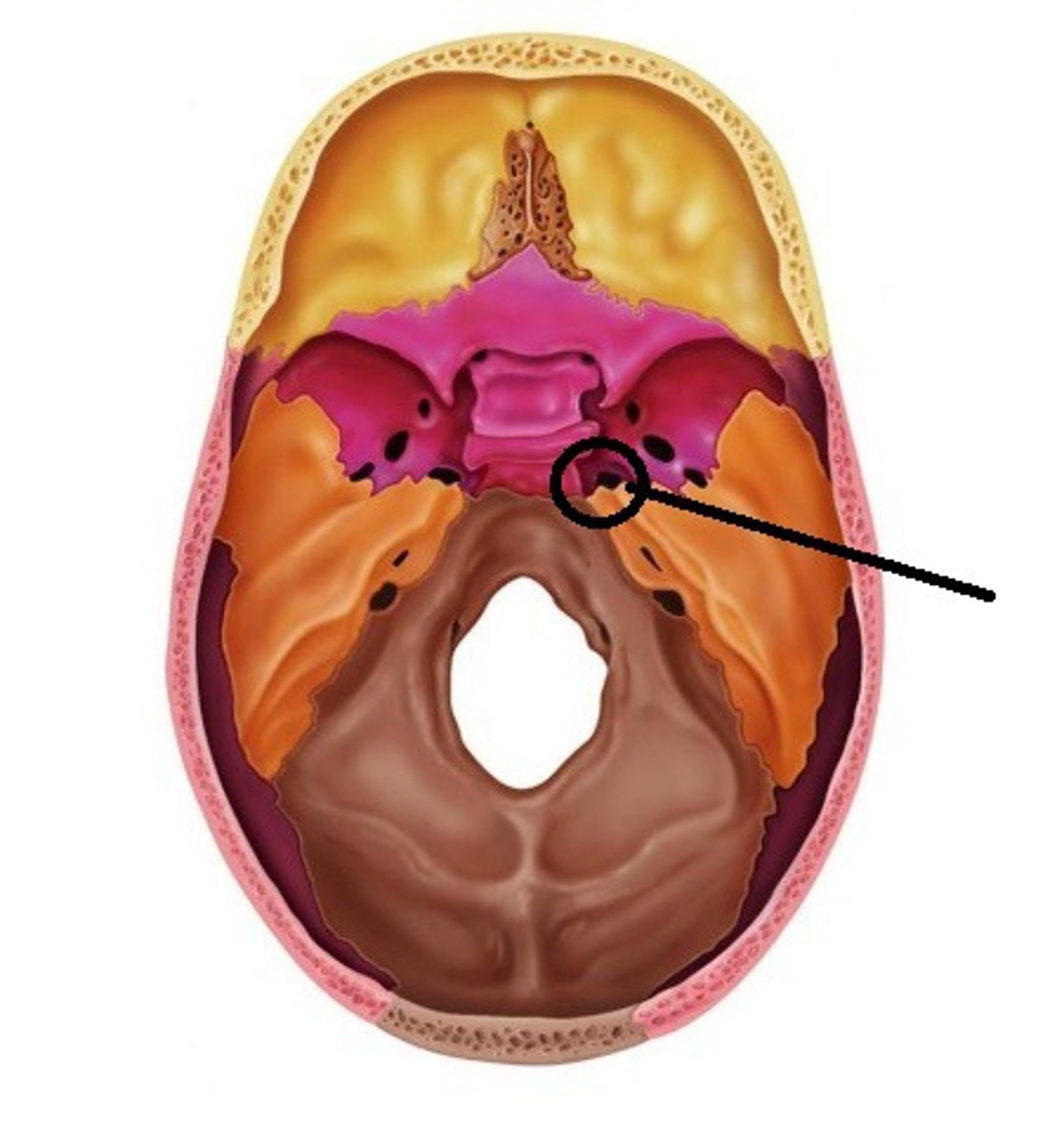
Jugular Foramen
CN IX, X, XI, superior bulb of internal jugular, inferior petrosal and sigmoid sunuses, meningeal branches of ascending pharyngeal and occipital arteries pass through
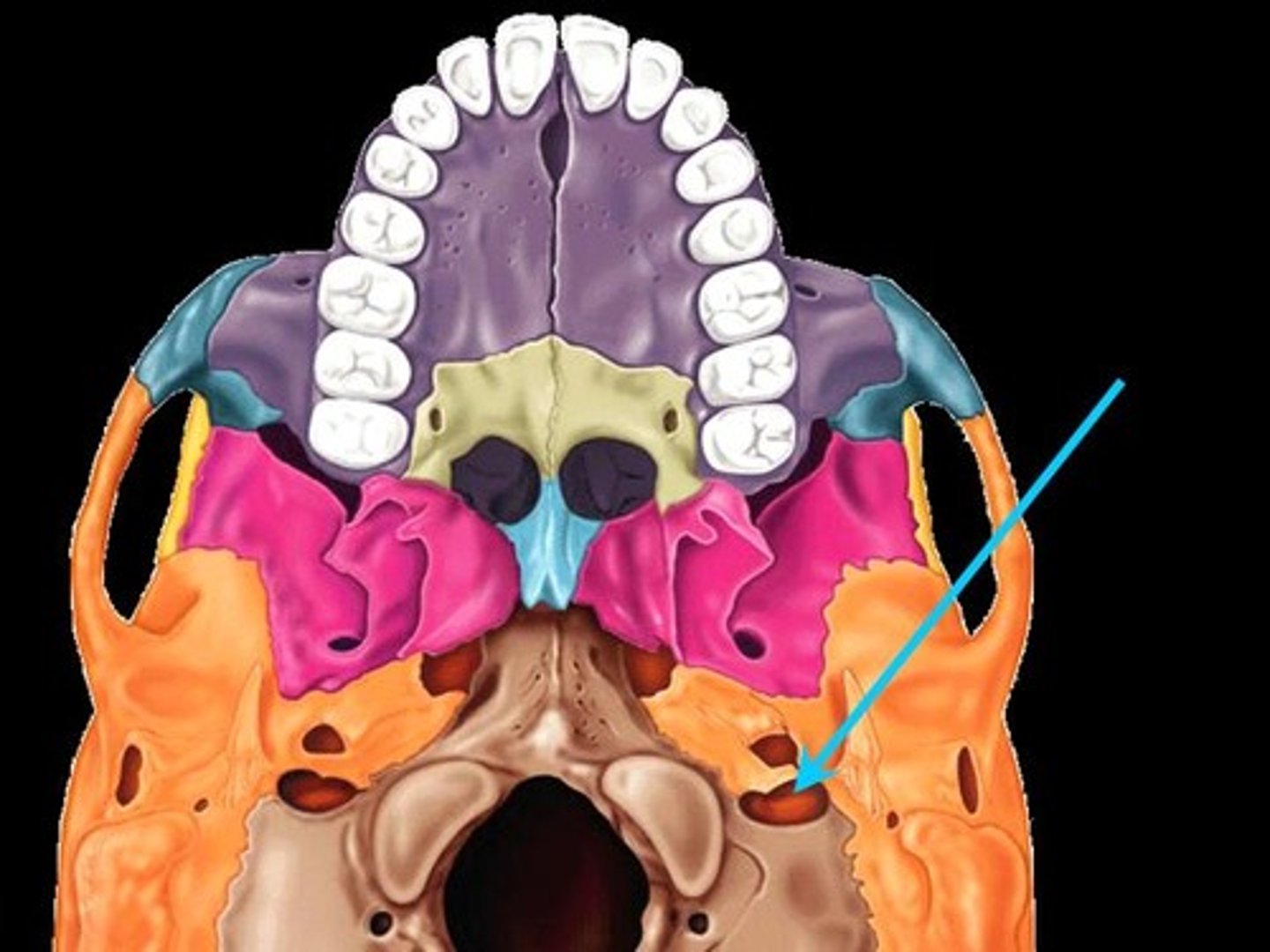
Occipital Condyles
Rounded projections lateral to the foramen magnum that articulate with the first cervical vertebra (atlas)
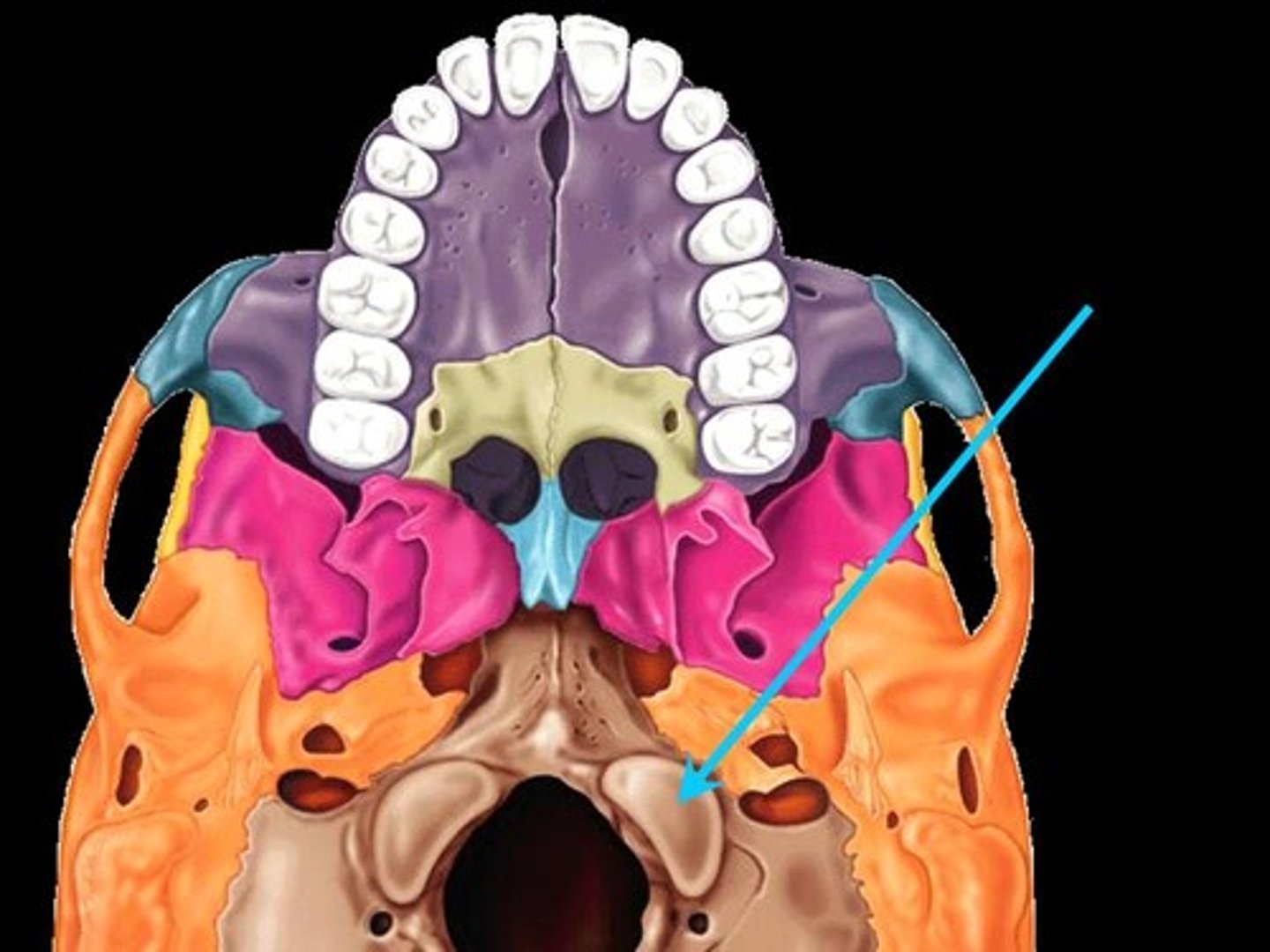
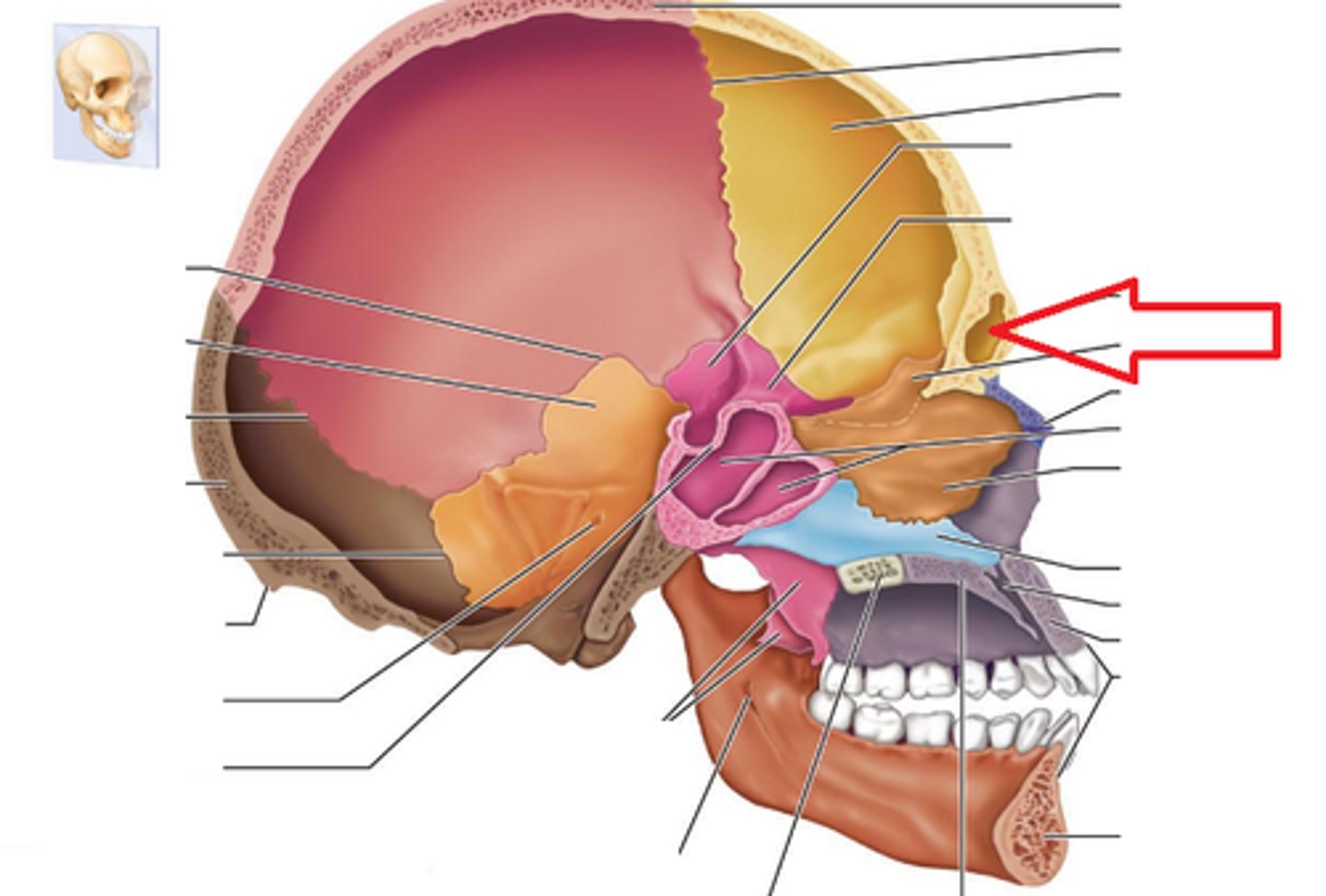
Sphenoid Bone
Forms part of the base of the skull and parts of the floor and sides of the orbit
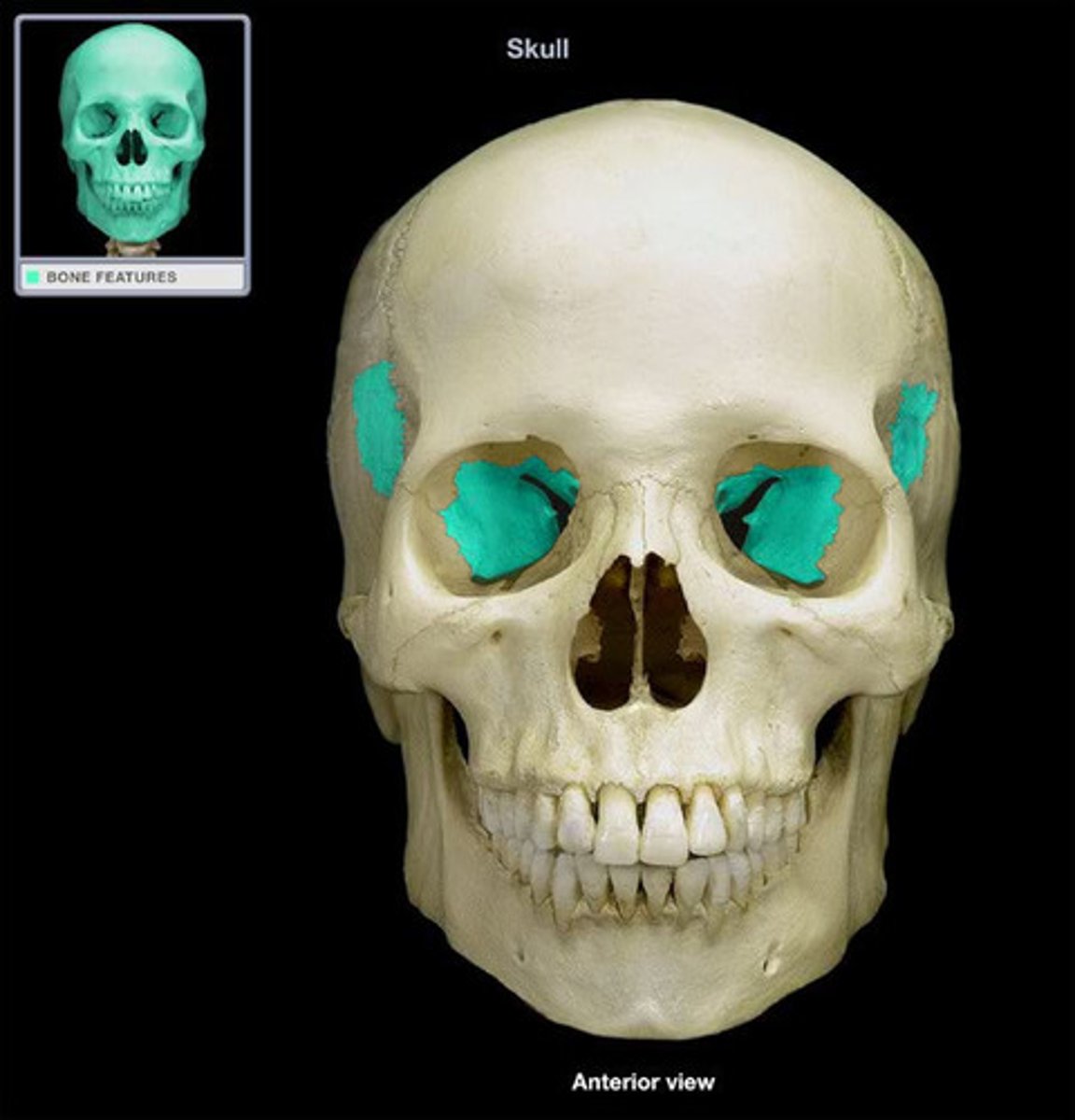
Sphenoid Sinus
Found deep within the skull behind the Ethmoid sinuses. They are small cavities approximately the size of a large grape. The left and right sit next to each other and are separated by a thin plate of bone (septum).
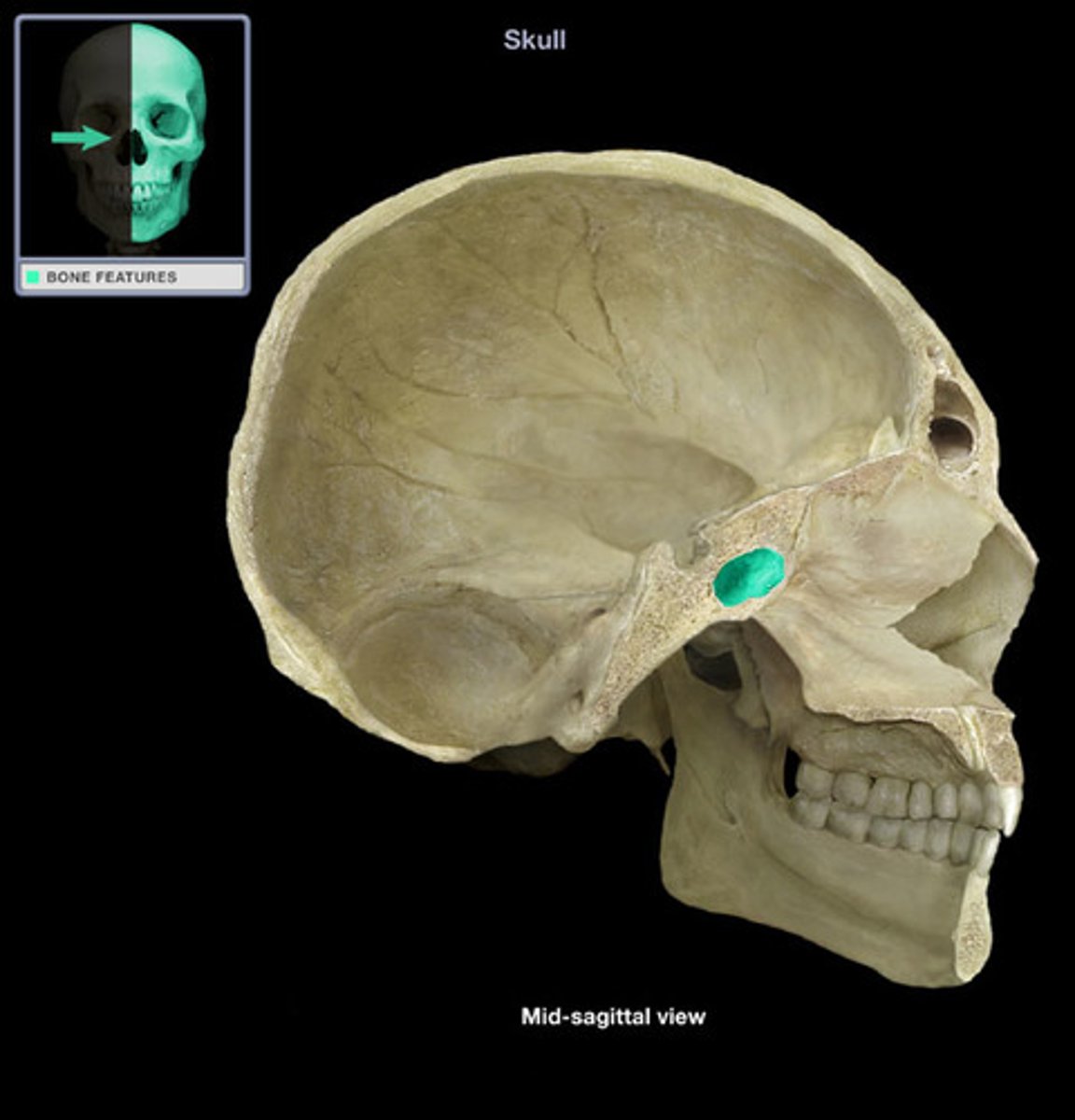
Superior Orbital Fissure
A foramen in the skull lying between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone
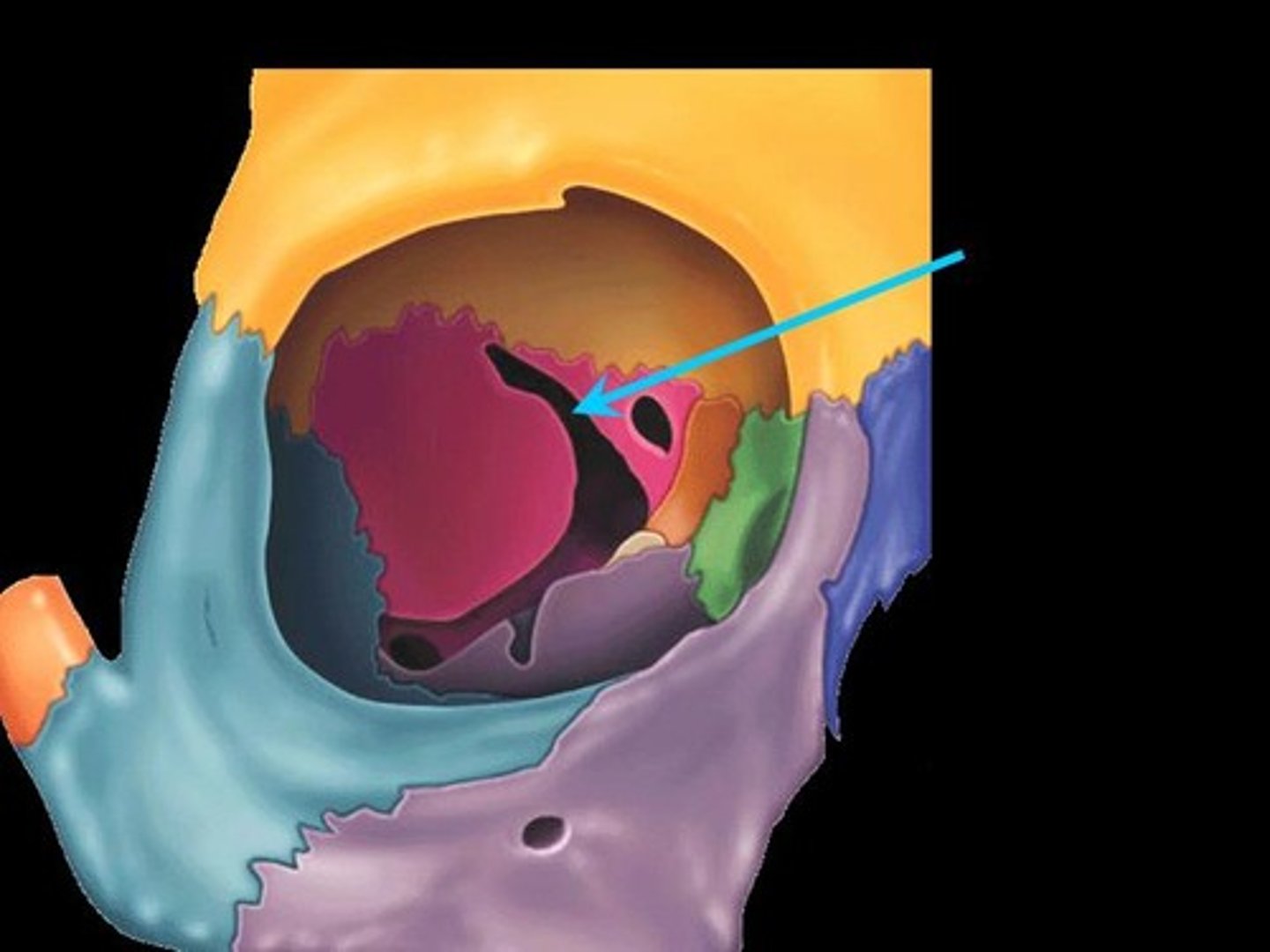
Inferior Orbital Fissure
An opening in the maxillary bone of the skull located below the infraorbital margin of the orbit. It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve.
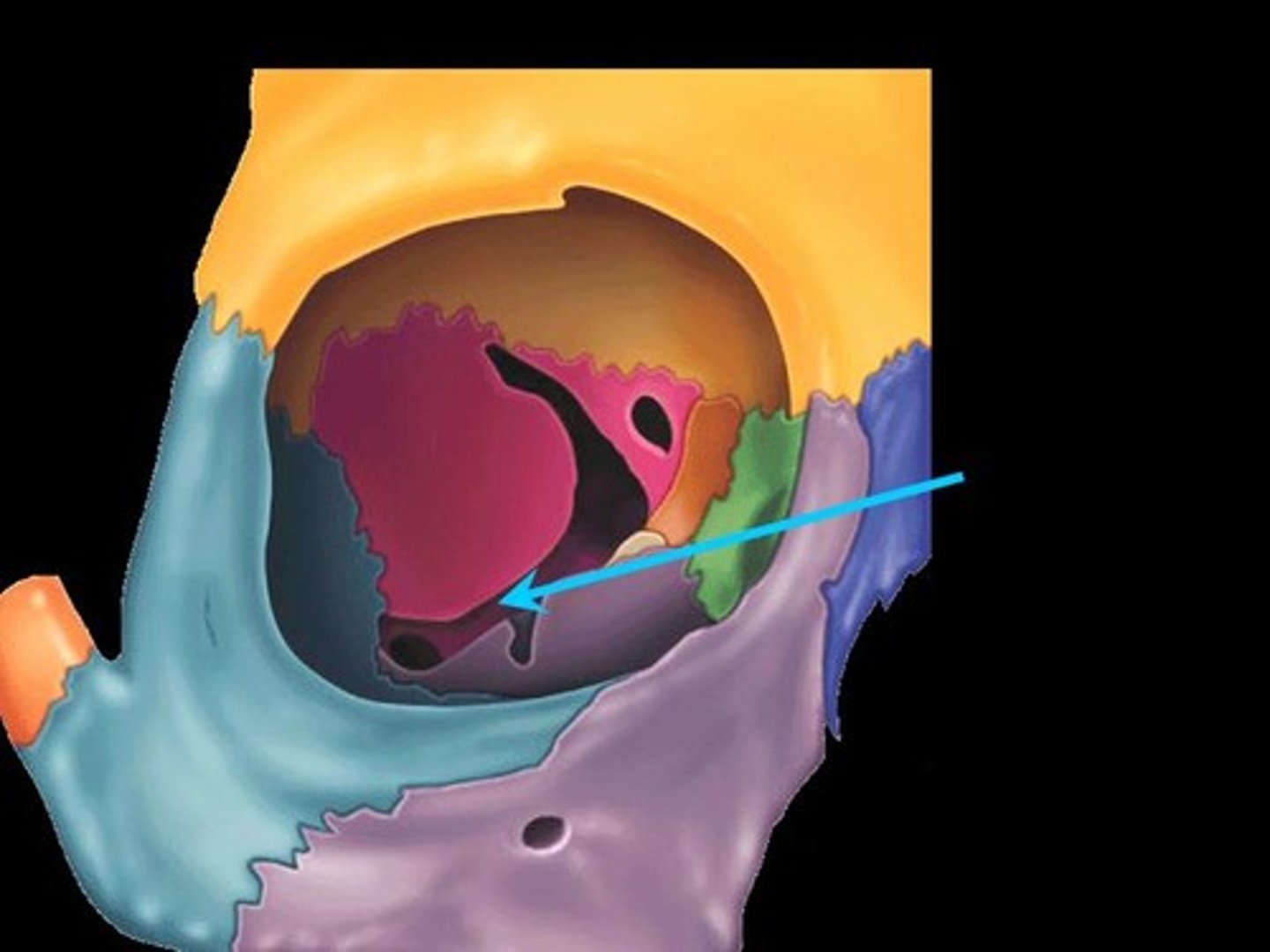
Optic Canal
A cylindrical canal running obliquely through the lesser wing of sphenoid bone near the base where it joins the body of sphenoid. It transmits the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery.
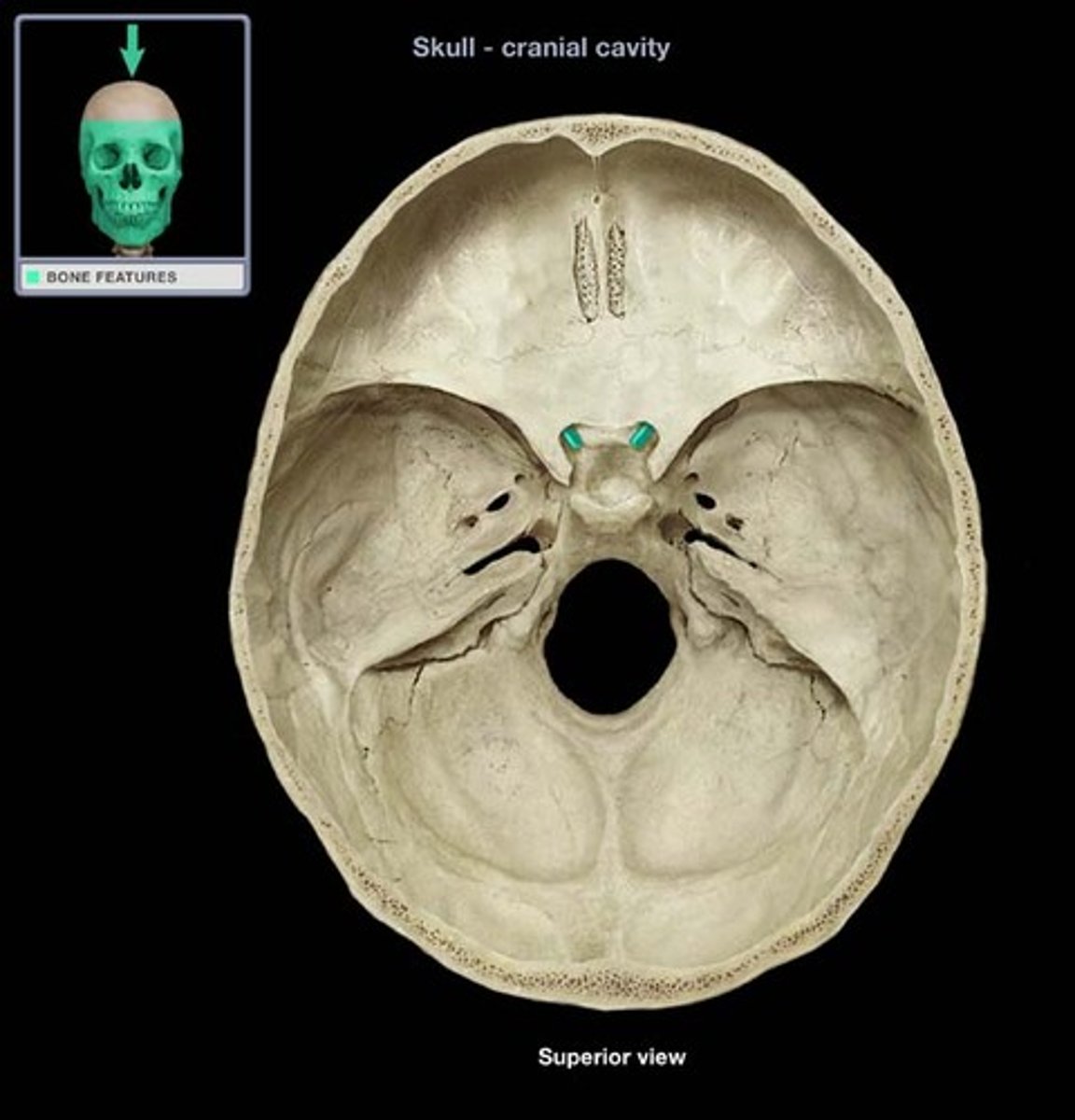
Foramen Rotundum
Located at the base of the greater wing of the sphenoid, inferior to the superior orbital fissure. It provides a connection between the middle cranial fossa and the pterygopalatine fossa. The maxillary nerve (branch of the trigeminal nerve, CN V) passes through this foramen.
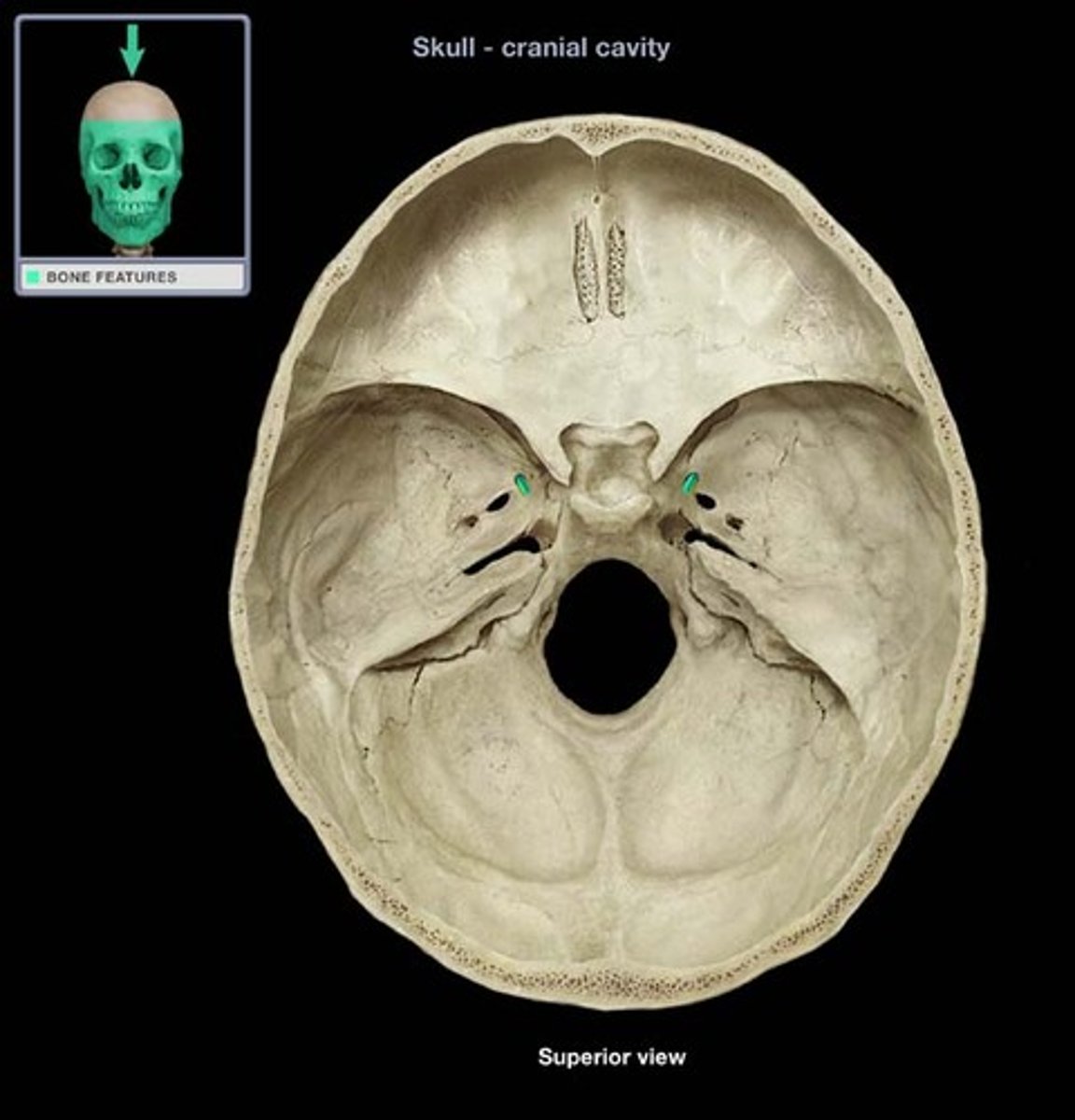
Foramen Spinosum
The middle meningeal artery, middle meningeal vein, and the meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve pass through the foramen.
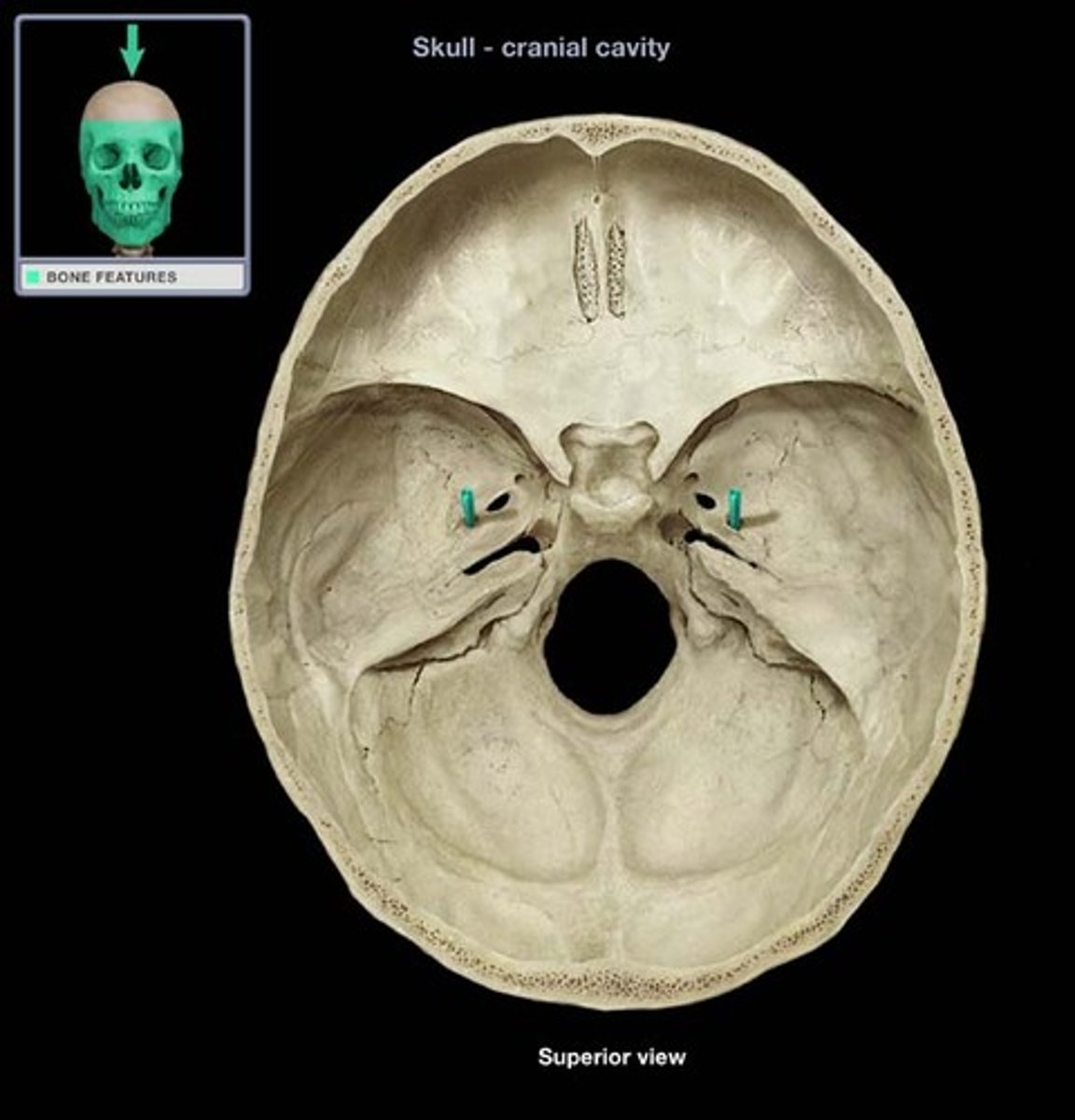
Foramen Ovale
An oval shaped opening in the middle cranial fossa located at the posterior base of the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. It transmits the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3) and the accessory meningeal artery.
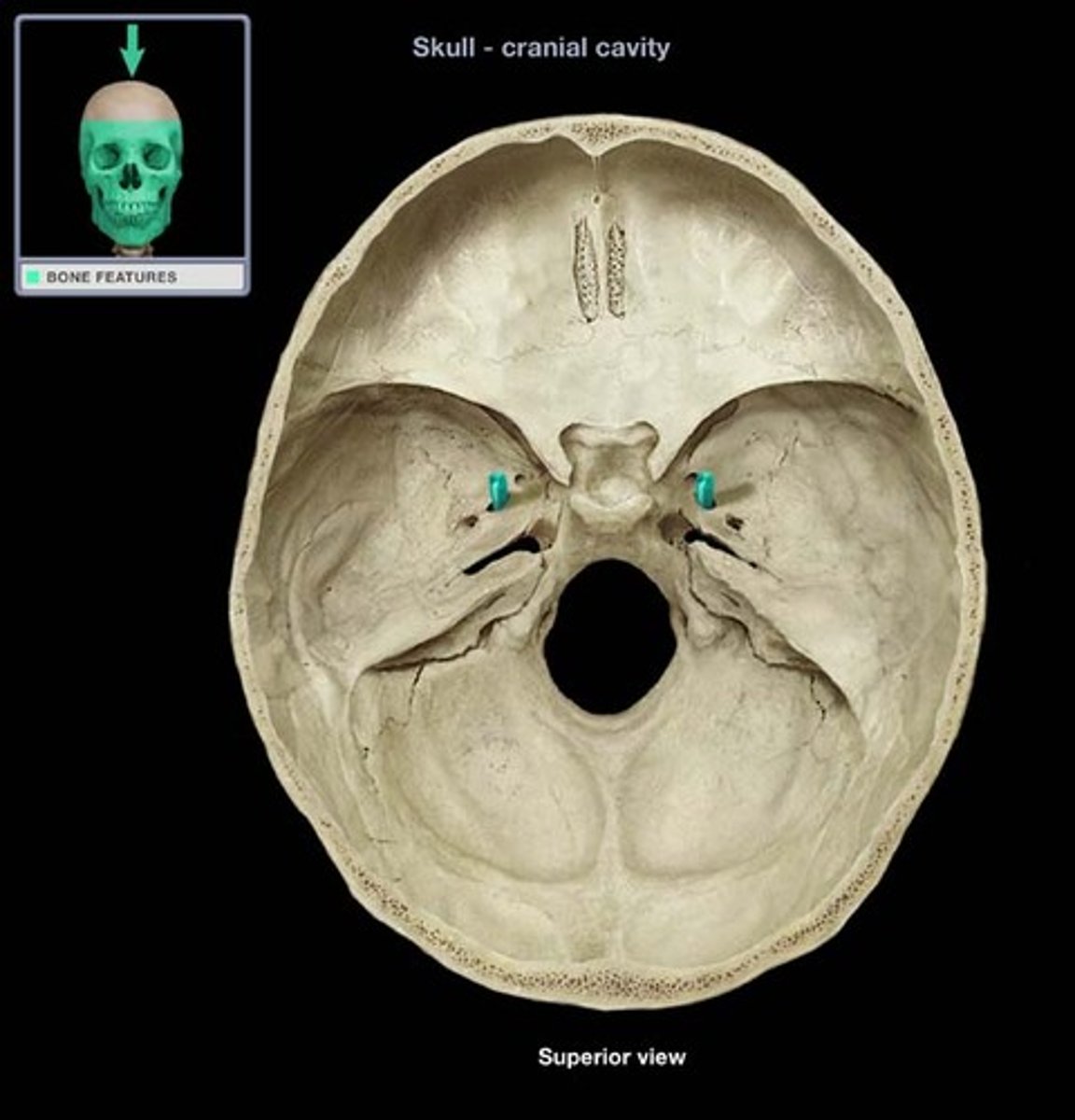
Sella Turcica
Depression in the sphenoid bone where the pituitary gland is located
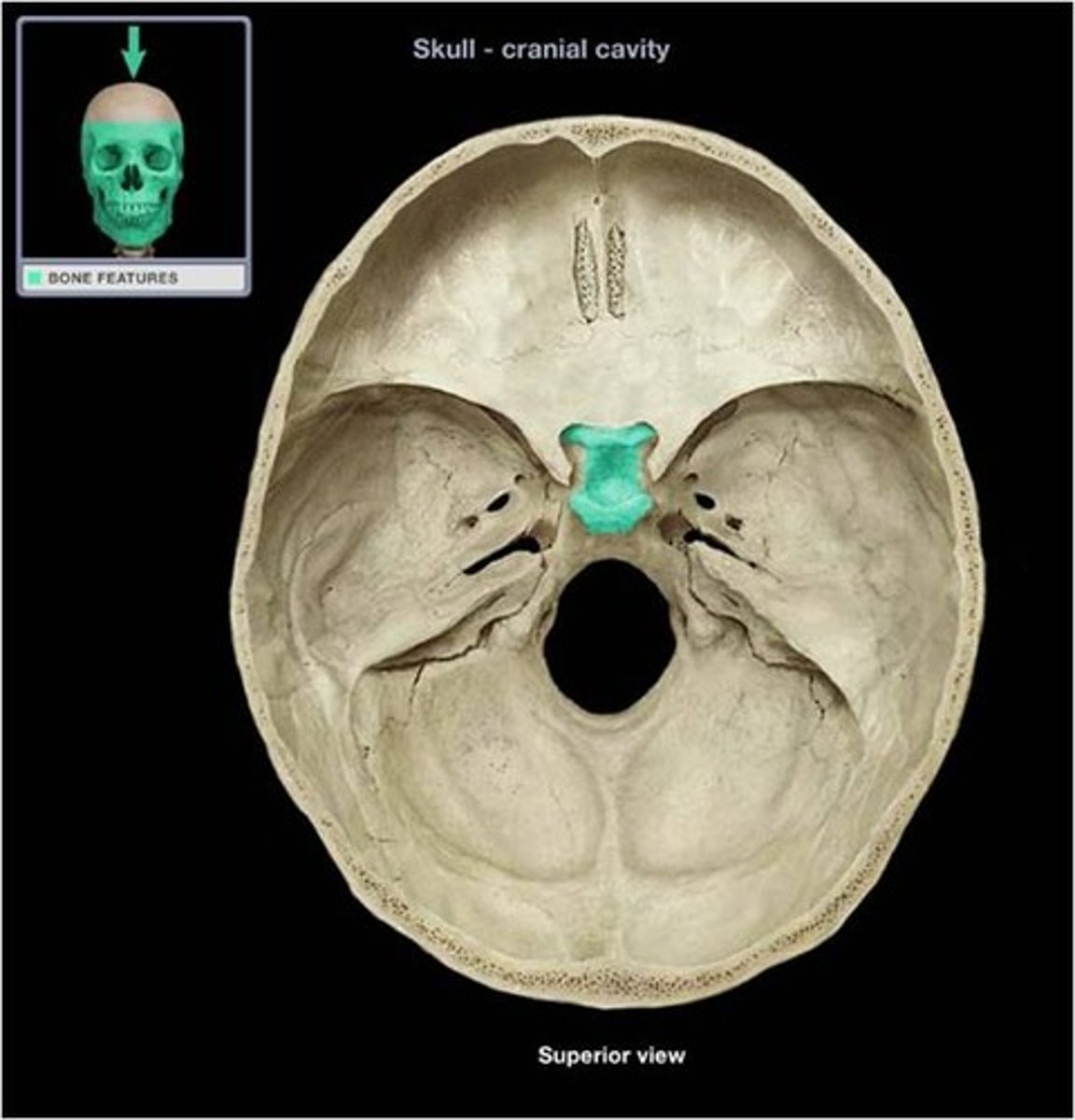
Pterygoid Process
Process of the sphenoid bone, consisting of two plates
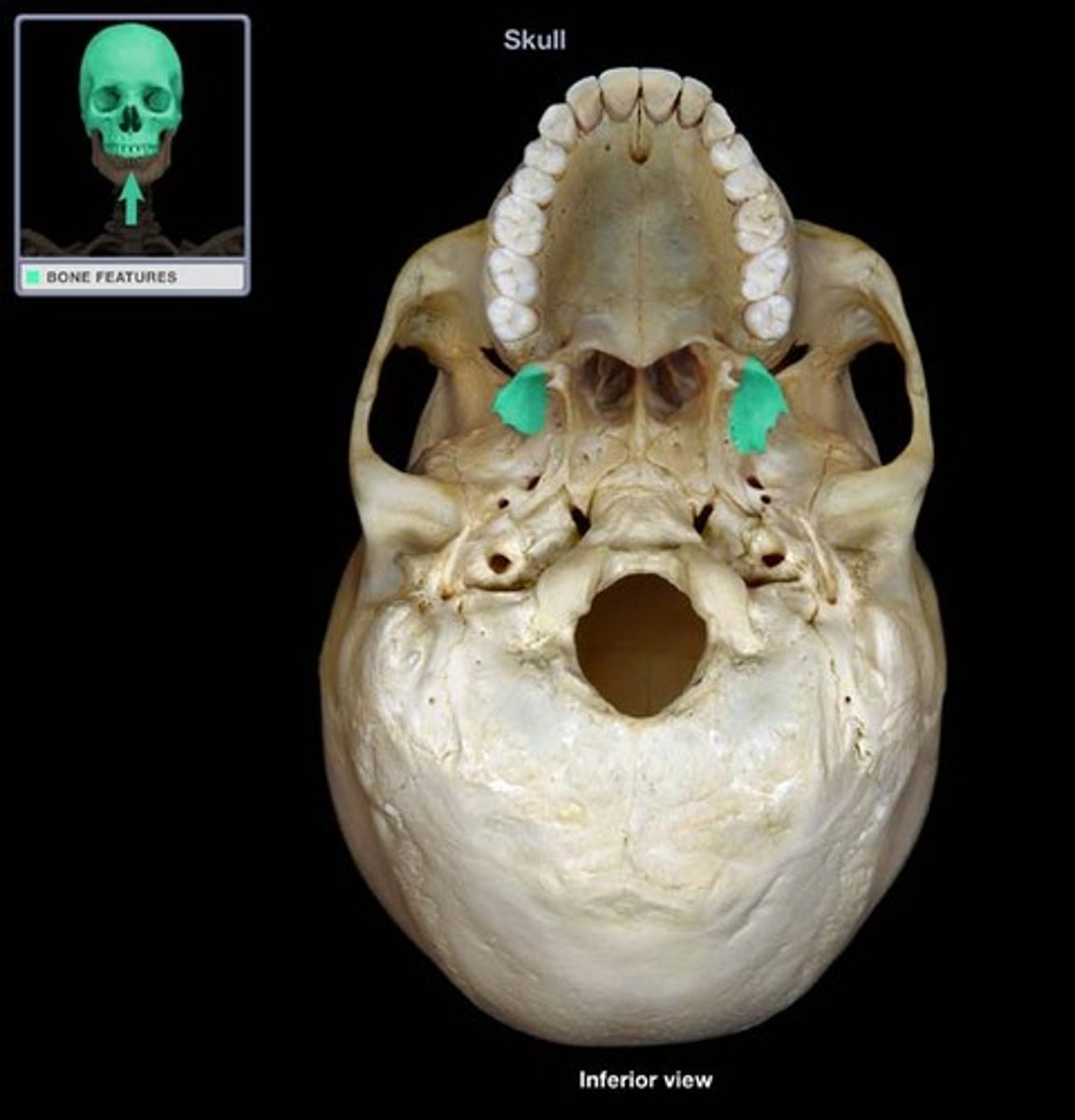
Temporal Bones
The lateral bones on each side of the cranium; the temples
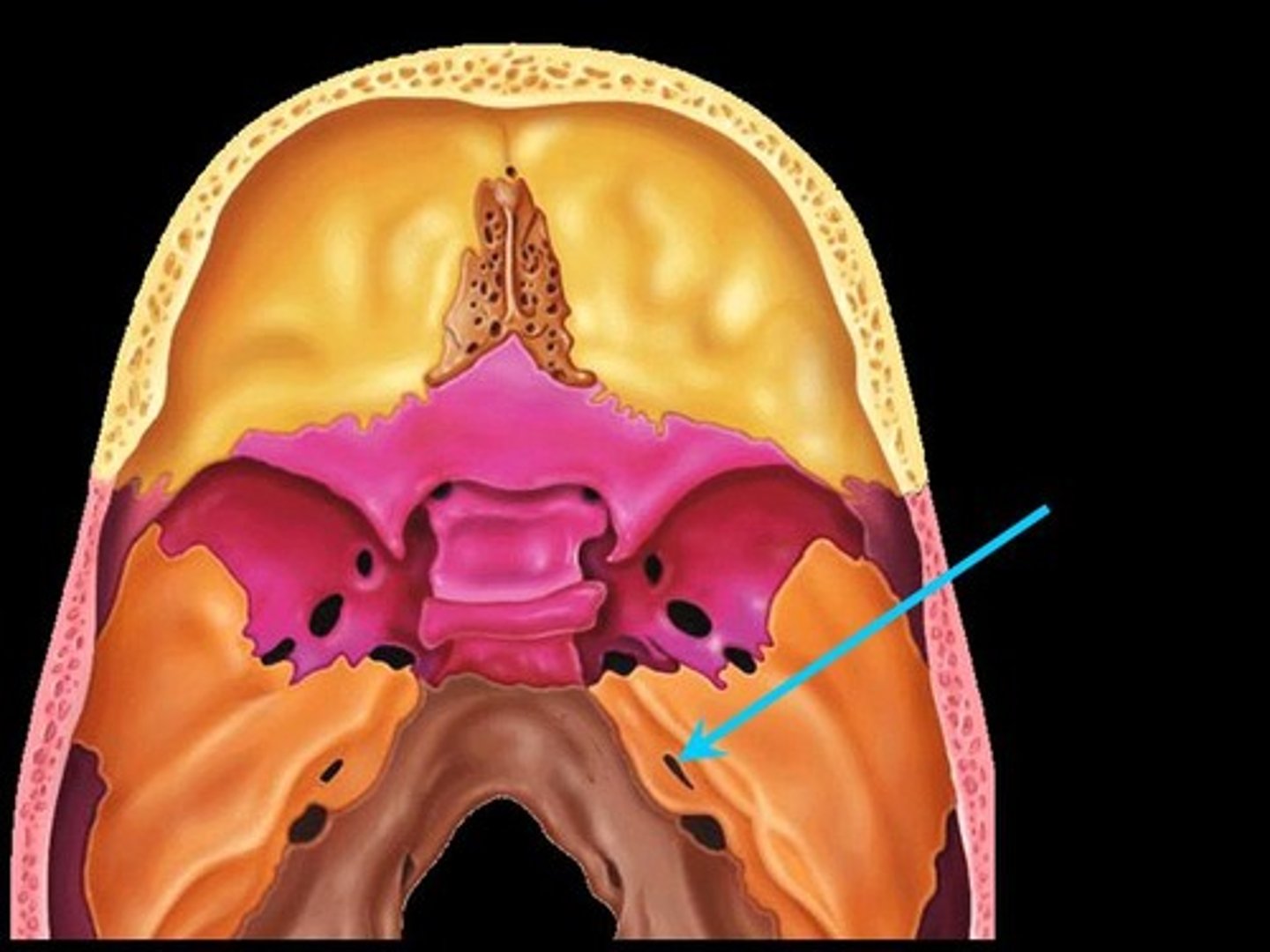
Internal Acoustic Meatus
A passage for CN VIII from the inner ear to the brain
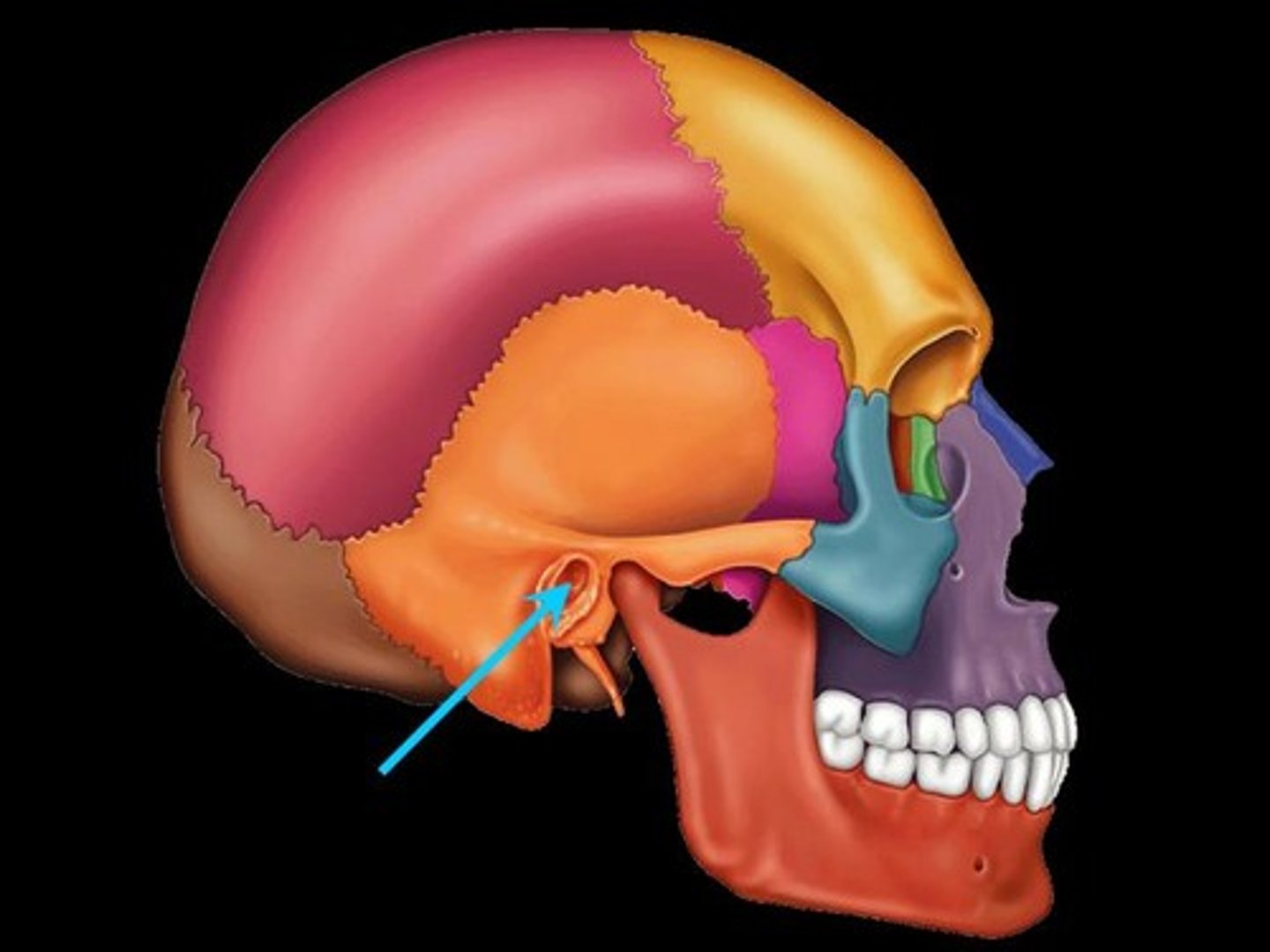
External Acoustic Meatus
Canal leading to eardrum and middle ear
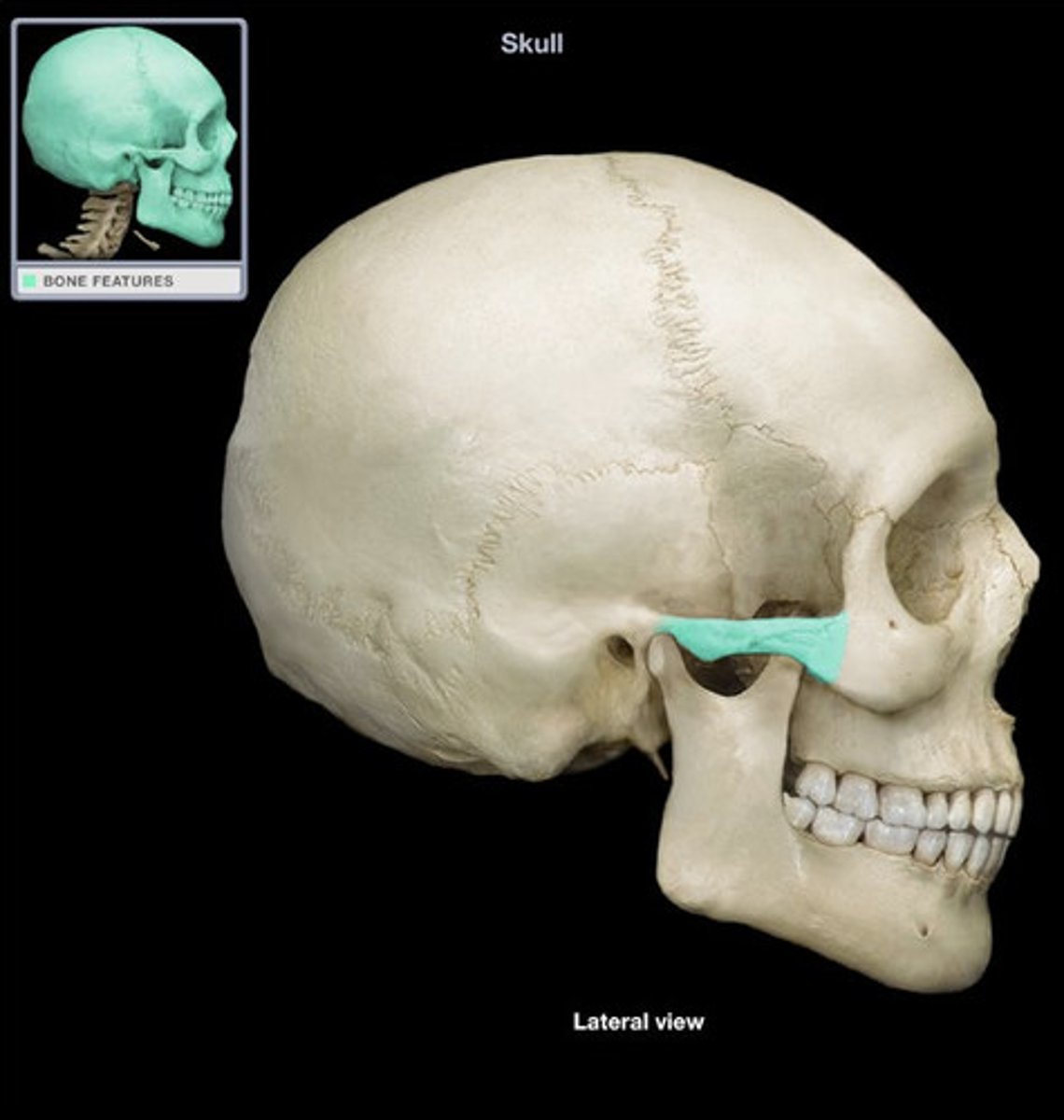
Zygomatic Process/Arch
Extends out, touches cheek (bridge-like)
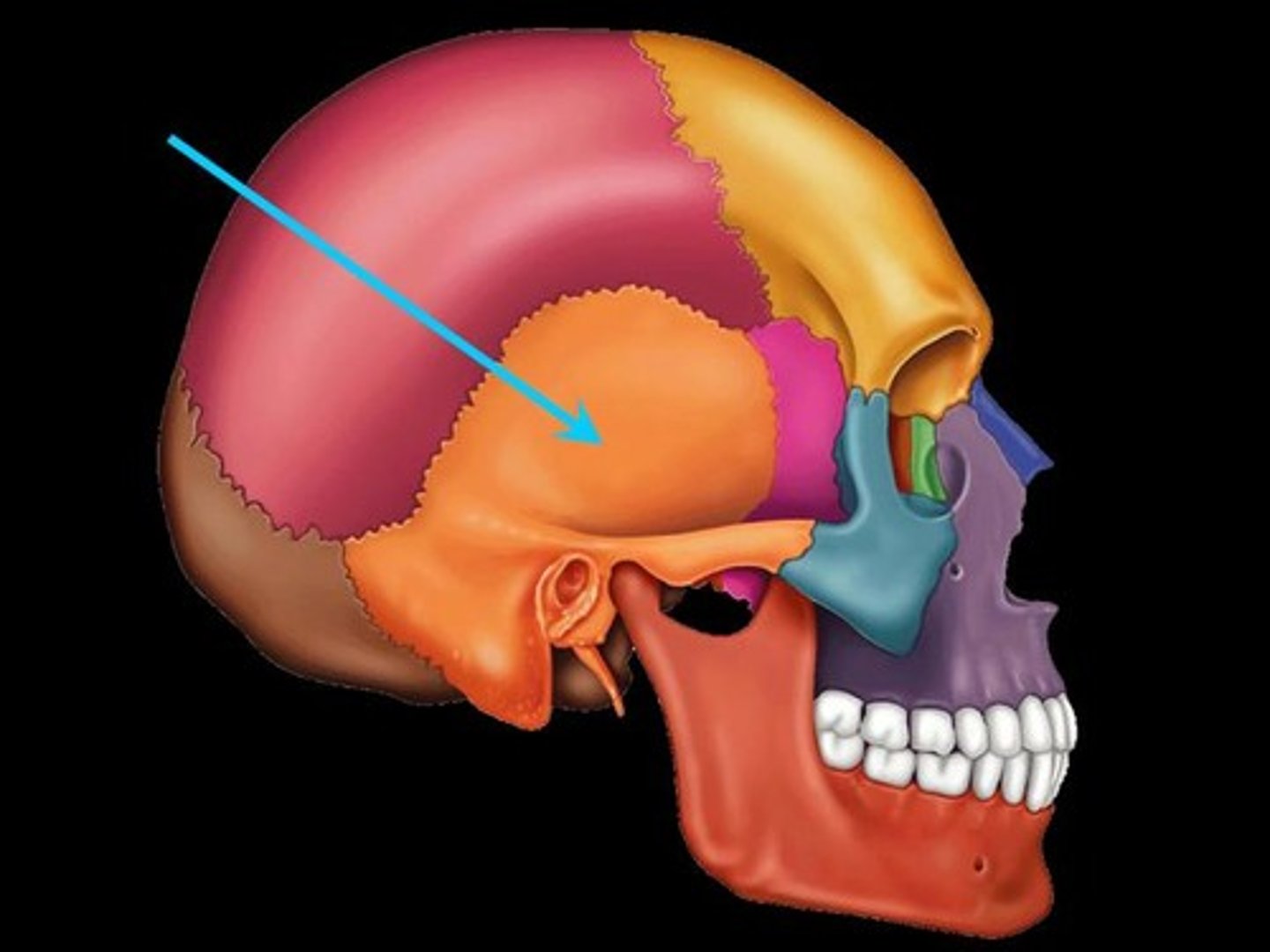
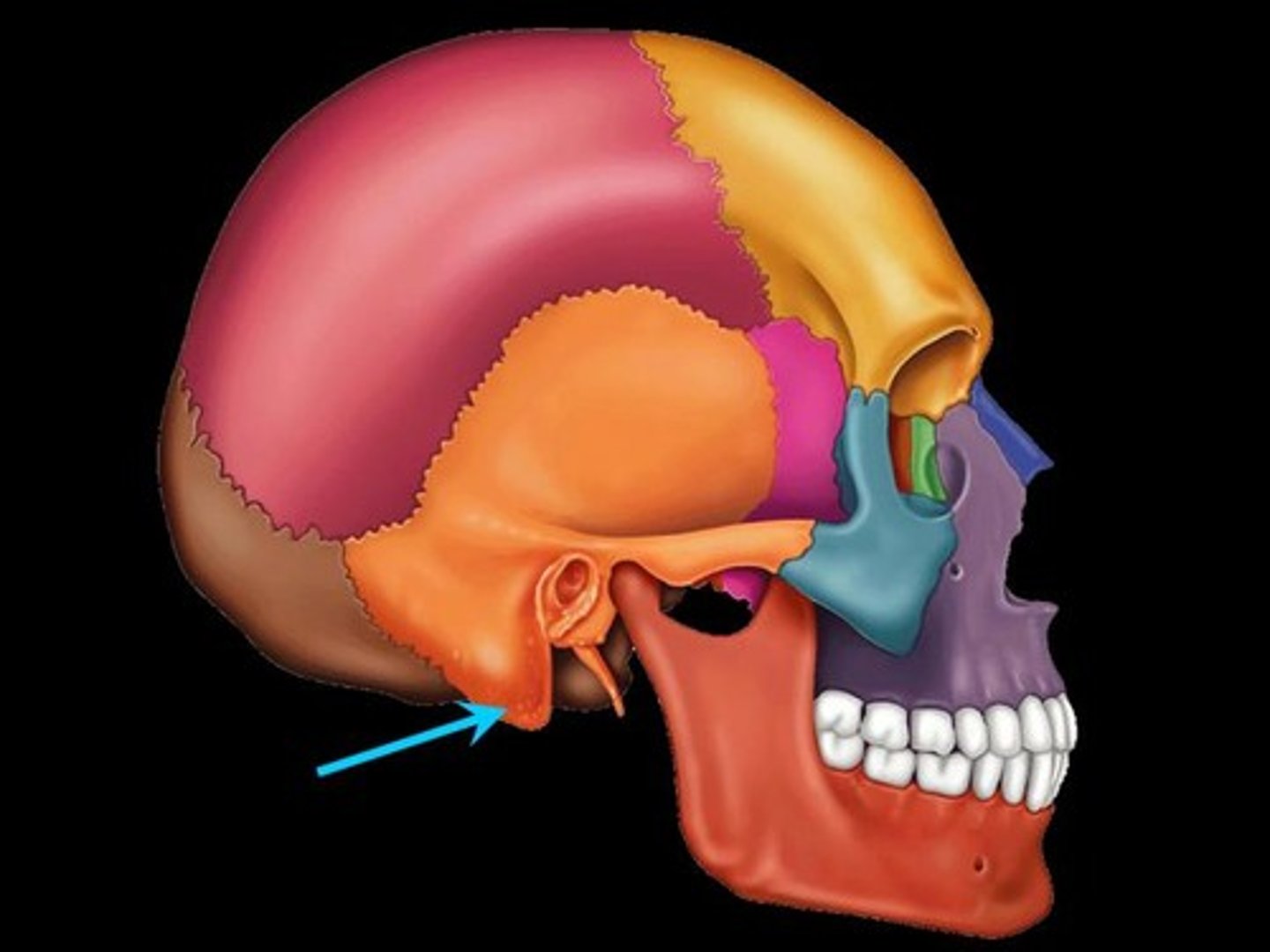
Mastoid Process
Round projection on the temporal bone behind the ear
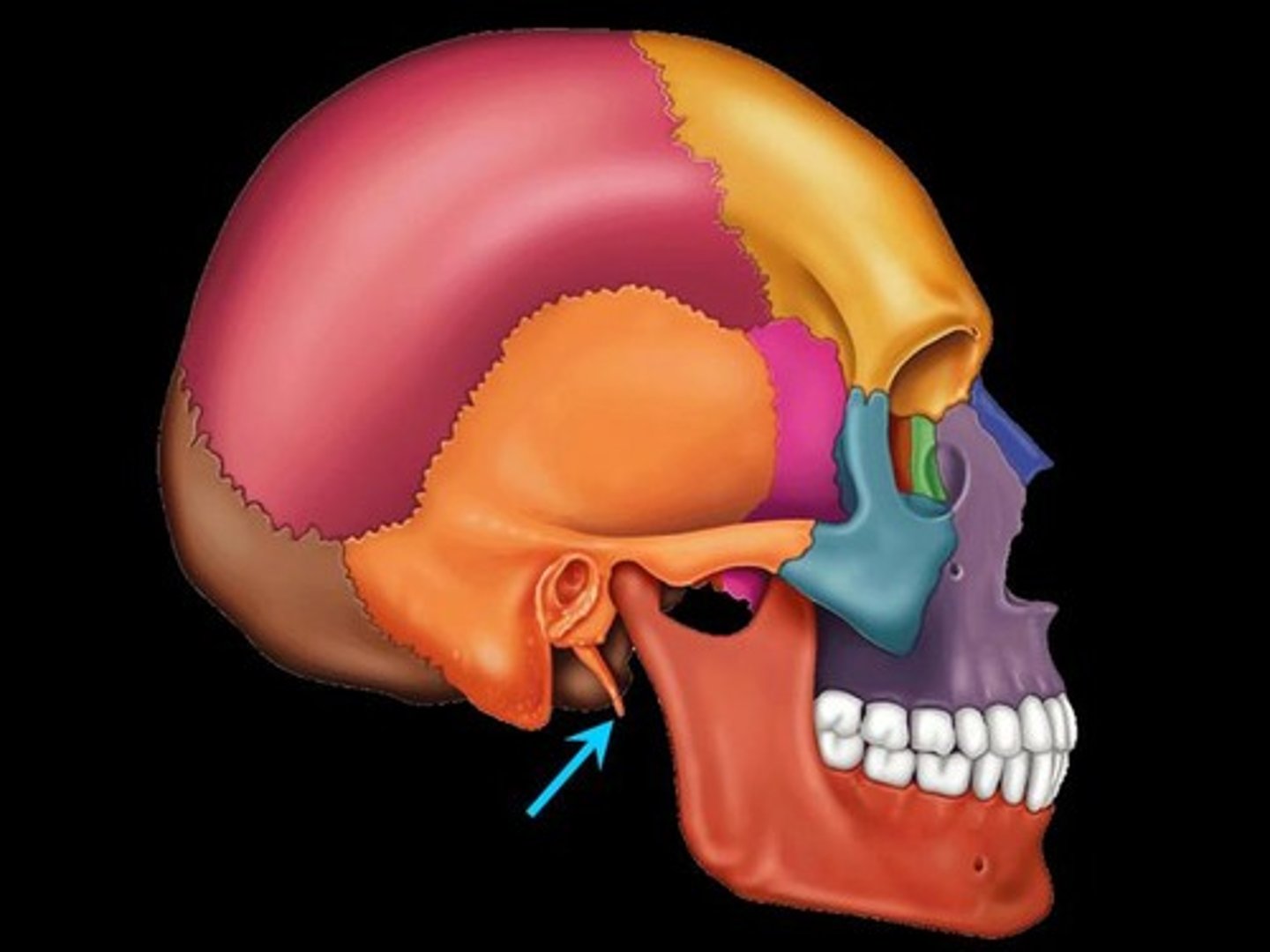
Styloid Process
Pole-like process extending downward from the temporal bone on each side of the skull
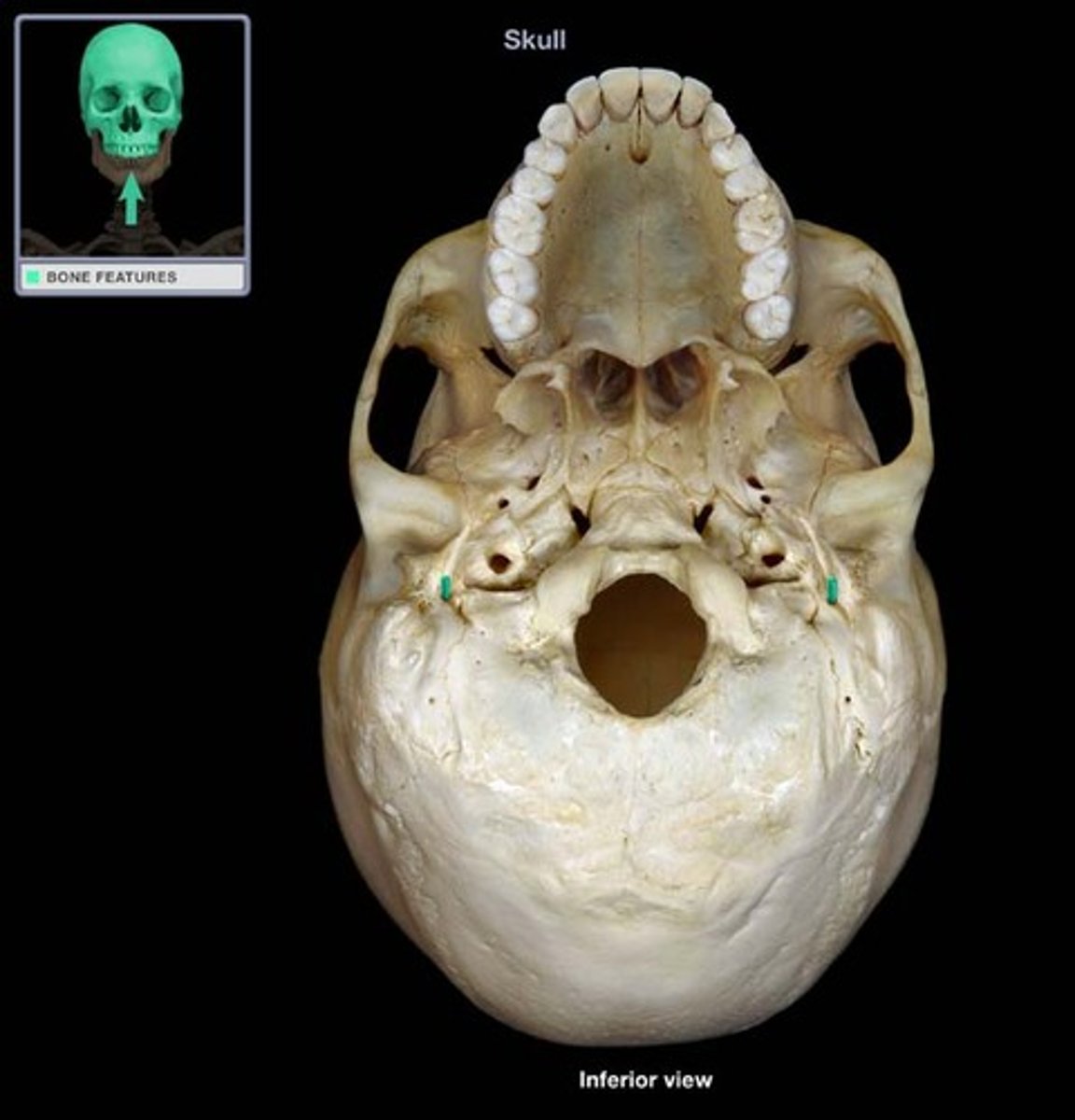
Stylomastoid Process
A rounded opening on the inferior surface of the petrous temporal bone, between the base of styloid and the mastoid process of the temporal bone. It transmits the facial nerve.
Carotid Canal
The passageway in the temporal bone through which the internal carotid artery enters the middle cranial fossa from the neck
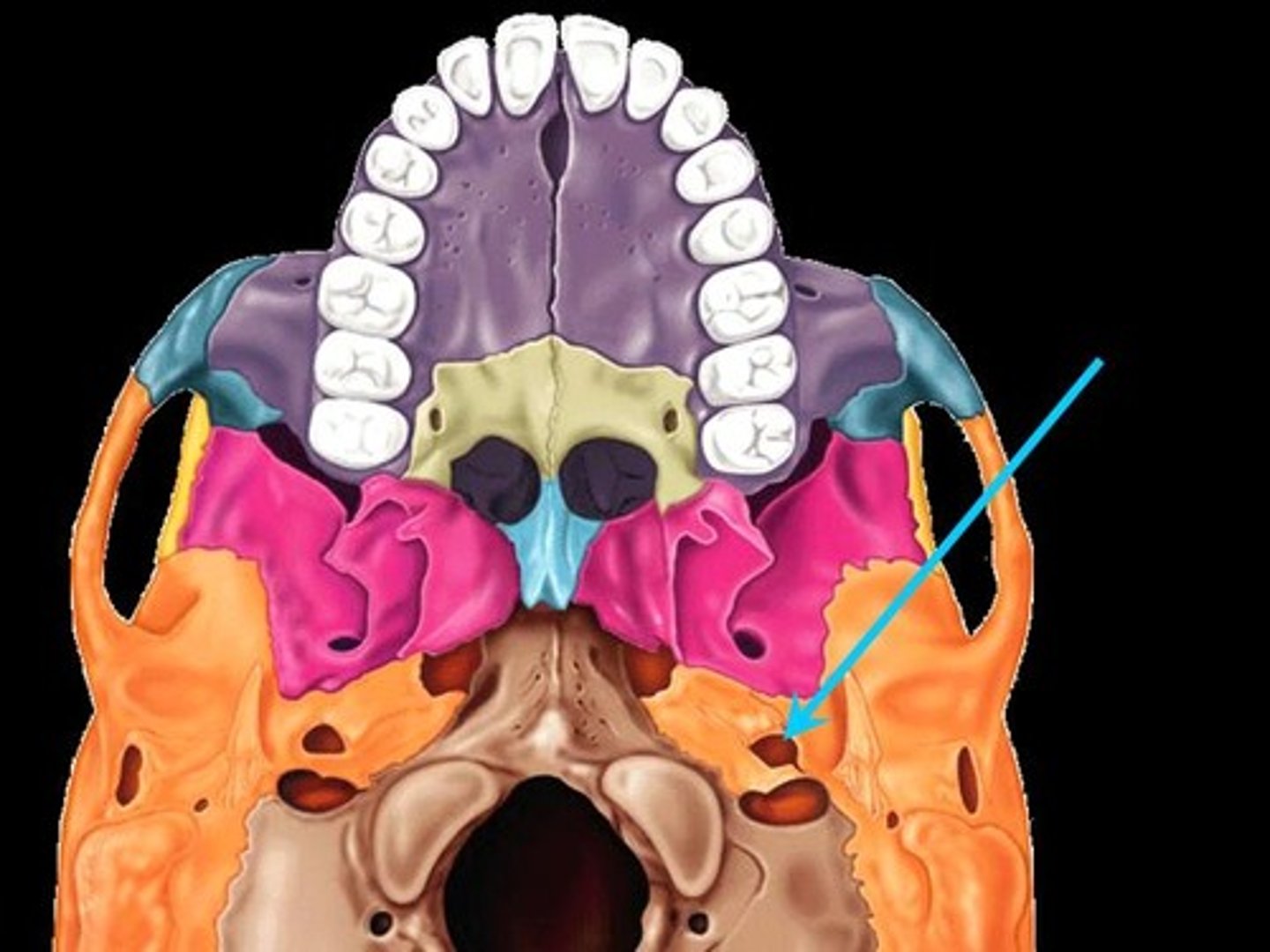
Mandibular Fossa
The depression in the temporal bone into which the condyle of the mandible fits
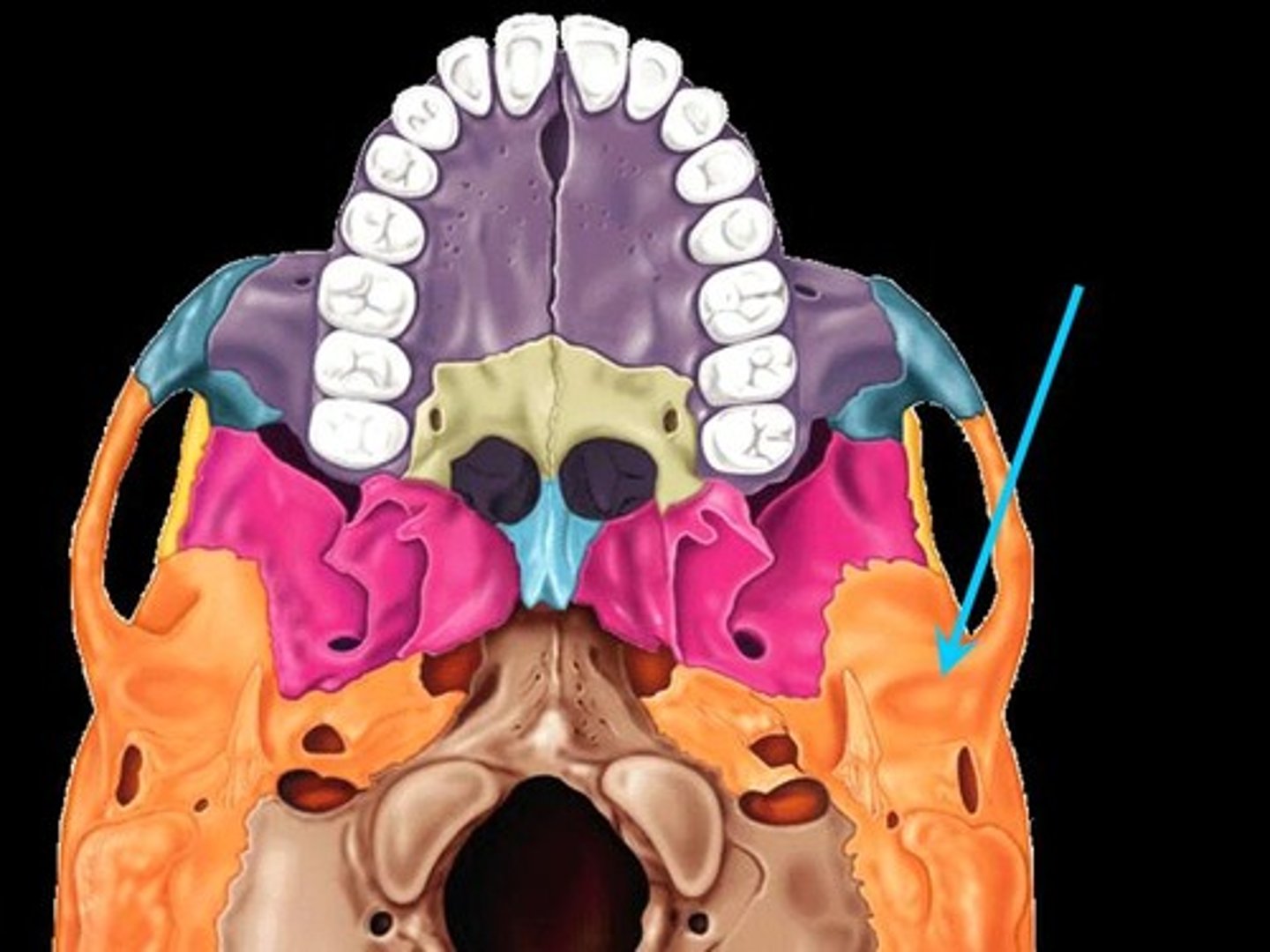
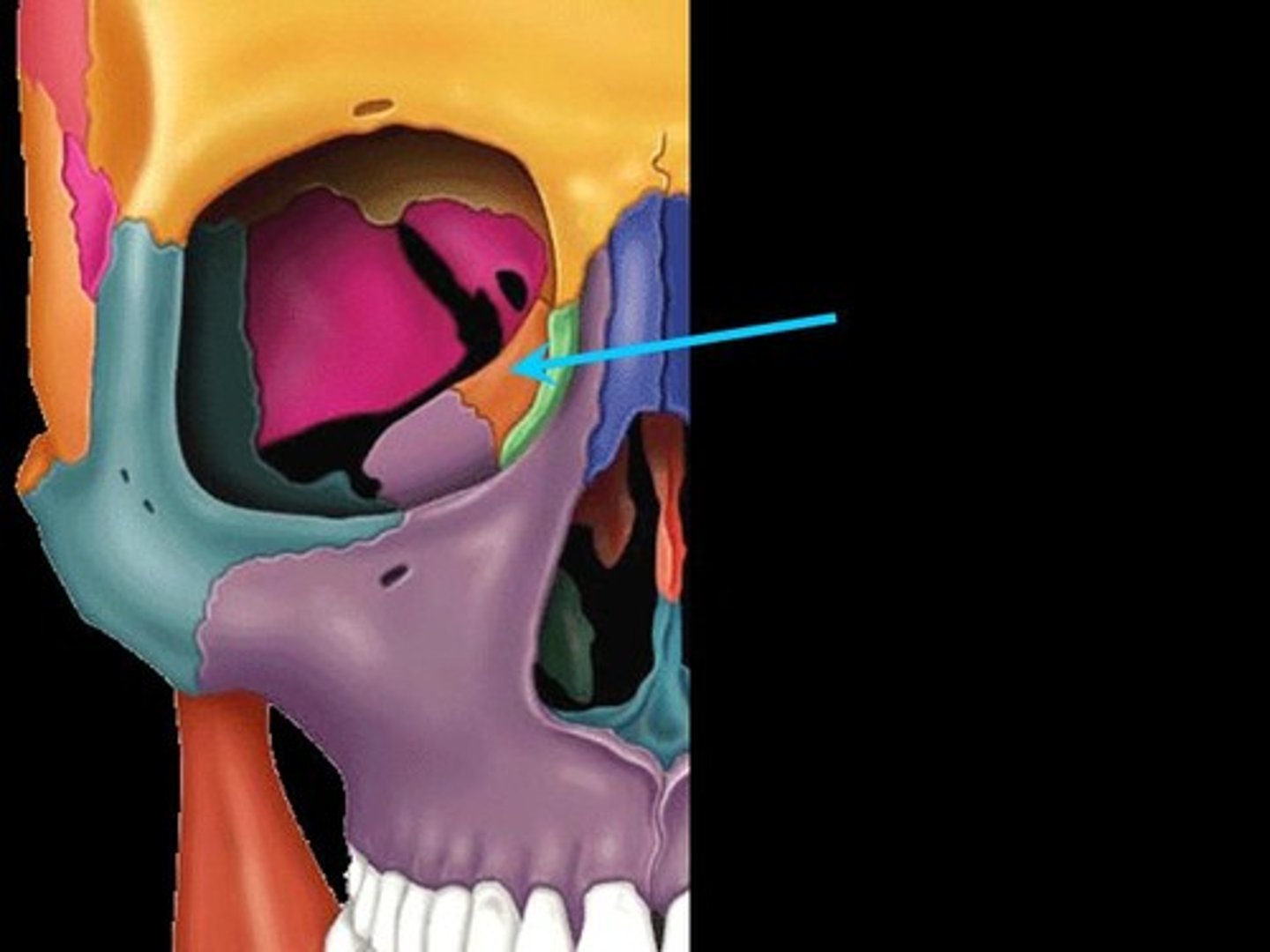
Ethmoid Bone
Forms part of the posterior portion of the nose, the orbit, and the floor of the cranium
Cribriform Plate
Superior surface of the ethmoid; perforated by a foramina which allows passage of the olfactory nerves, which provide sense of smell
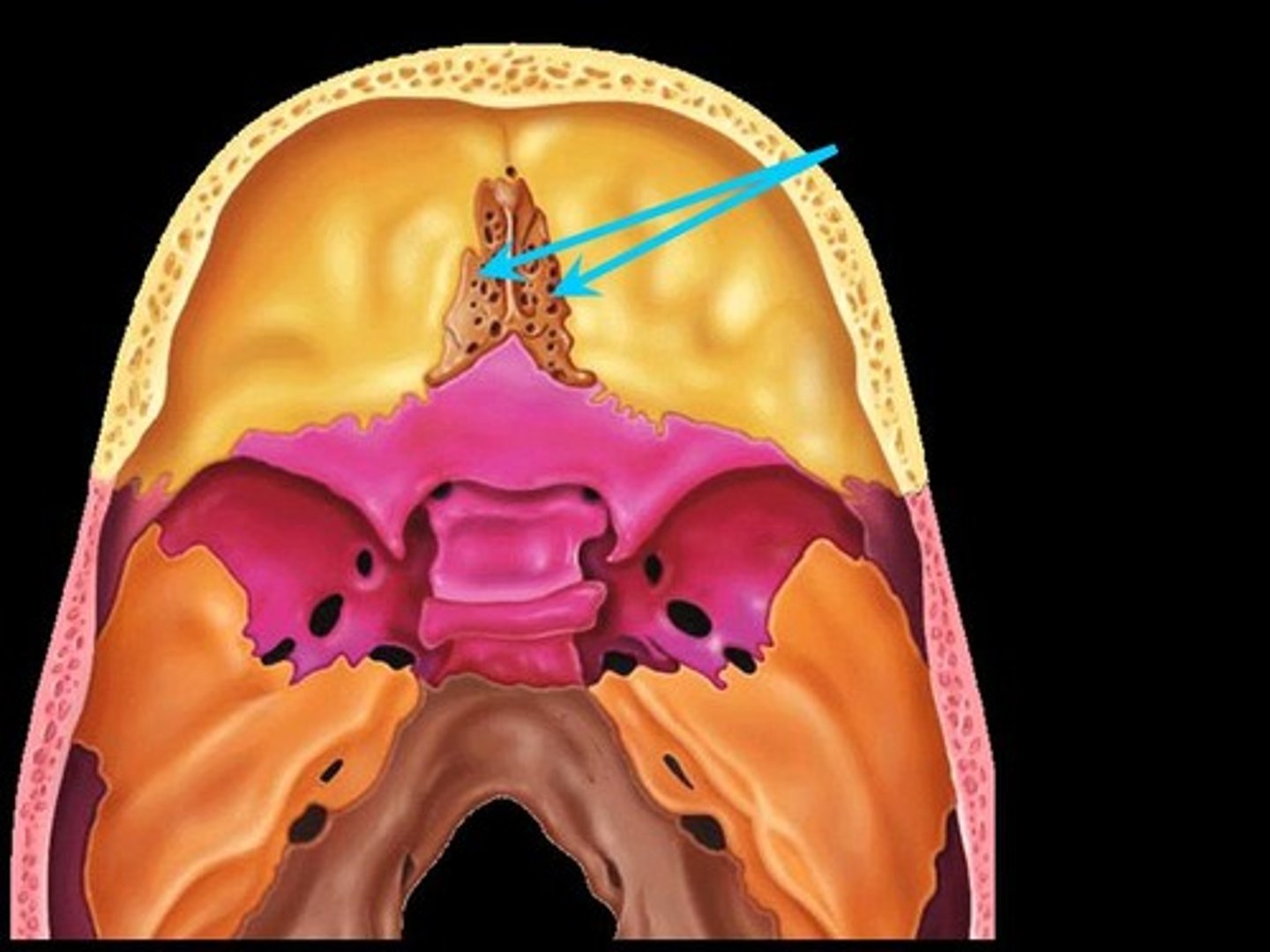
Crista Galli
A thick, midline, smooth triangular process arising from the superior surface of the ethmoid bone, projecting into the anterior cranial fossa. Attaches to fall cerebri.
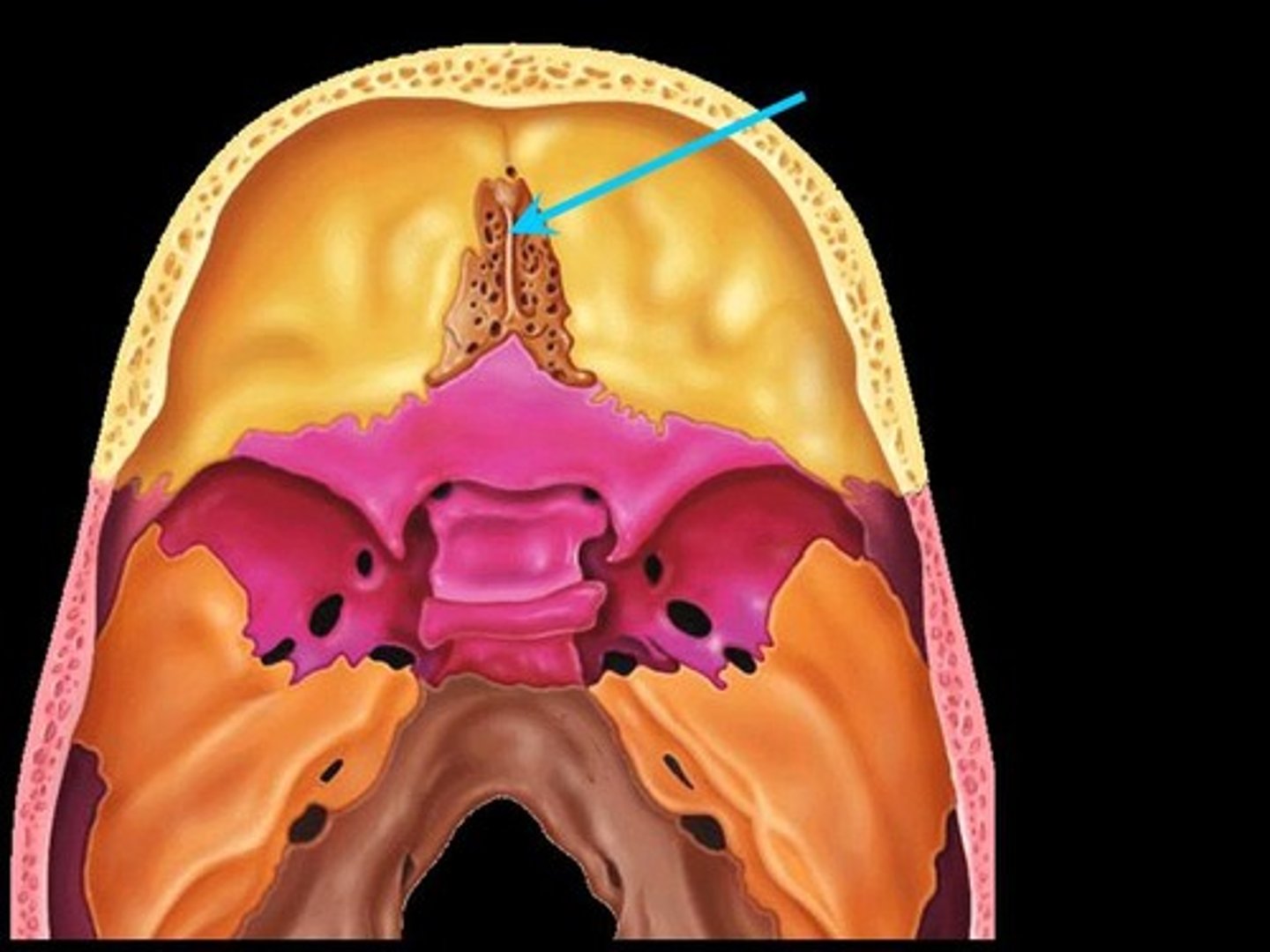
Vomer Bone
Flat, thin bone that forms part of the nasal septum
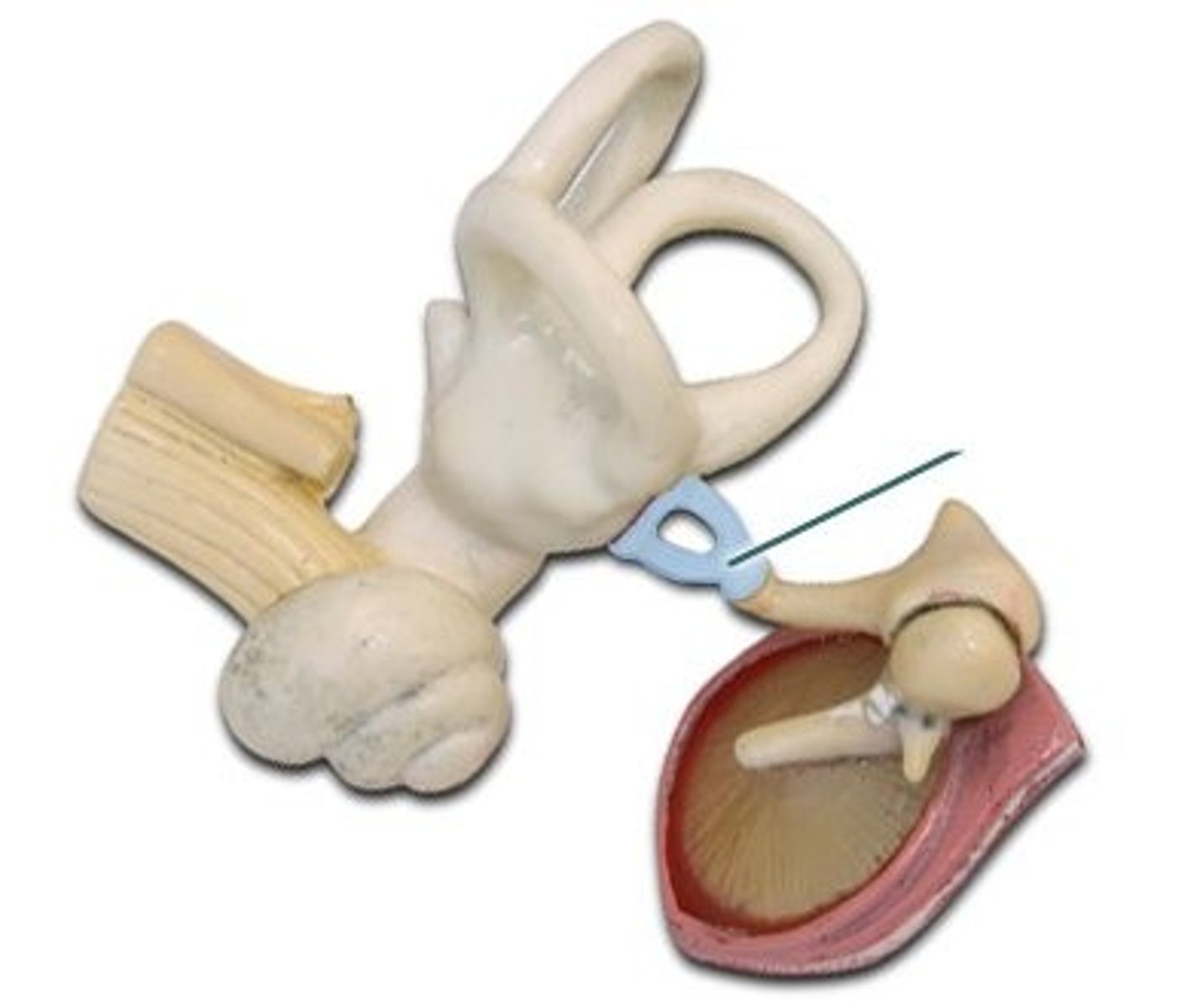
Ear Ossciles
Malleus, incus, stapes: The three tiniest bones in the body form the coupling between the vibration of the eardrum and the forces exerted on the oval window of the inner ear
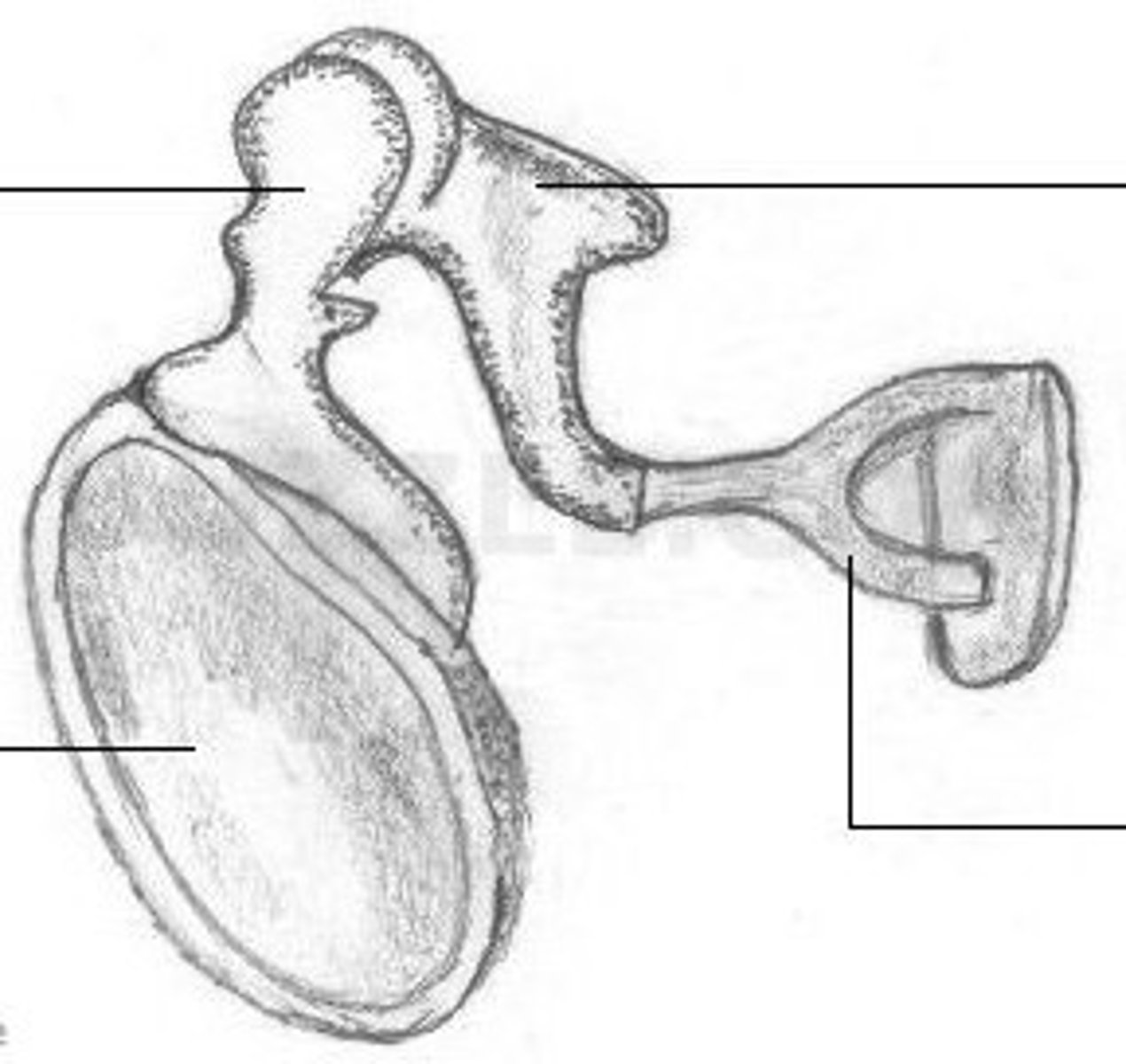
Malleus
Hammer; first of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
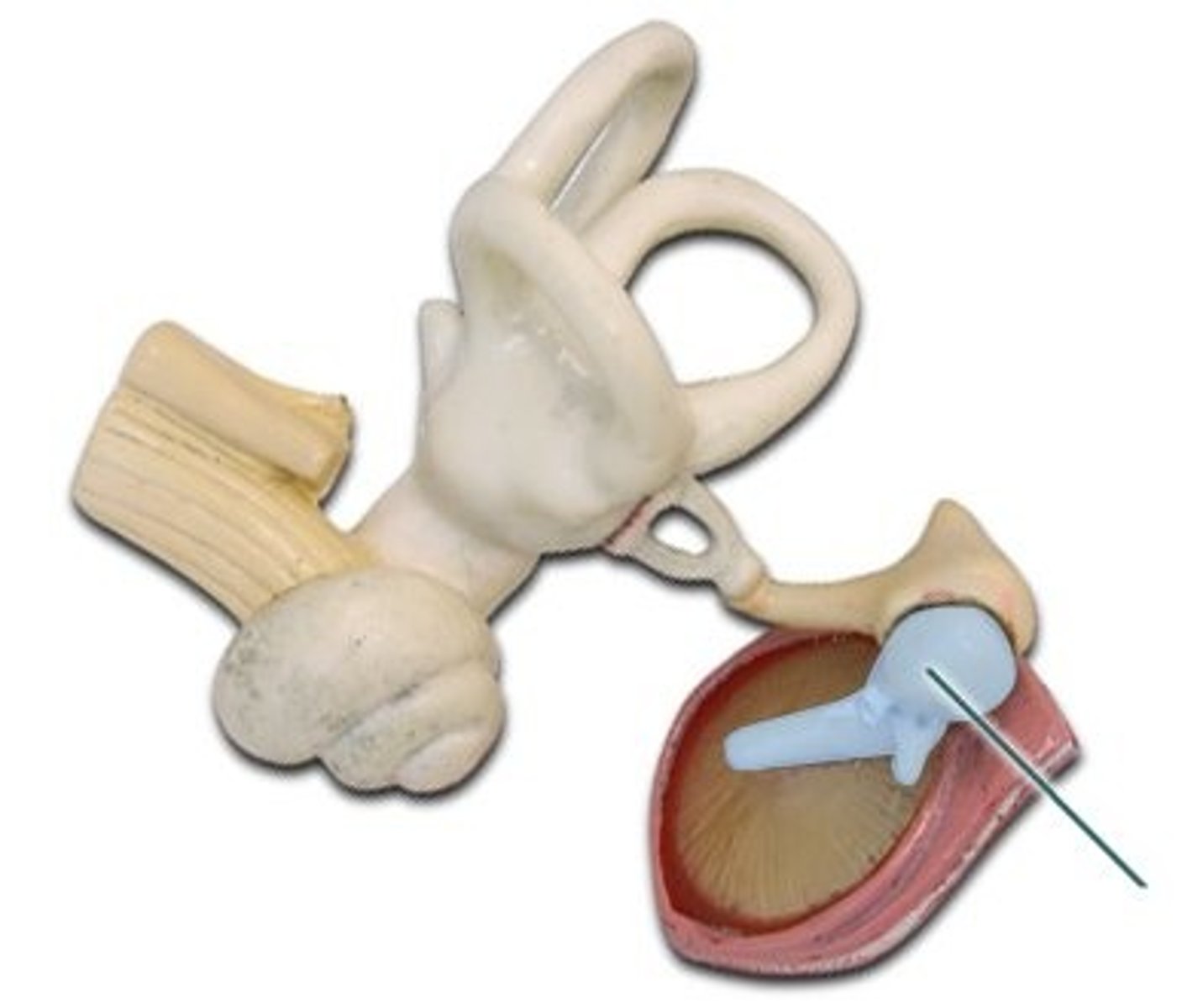
Incus
Anvil; middle of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
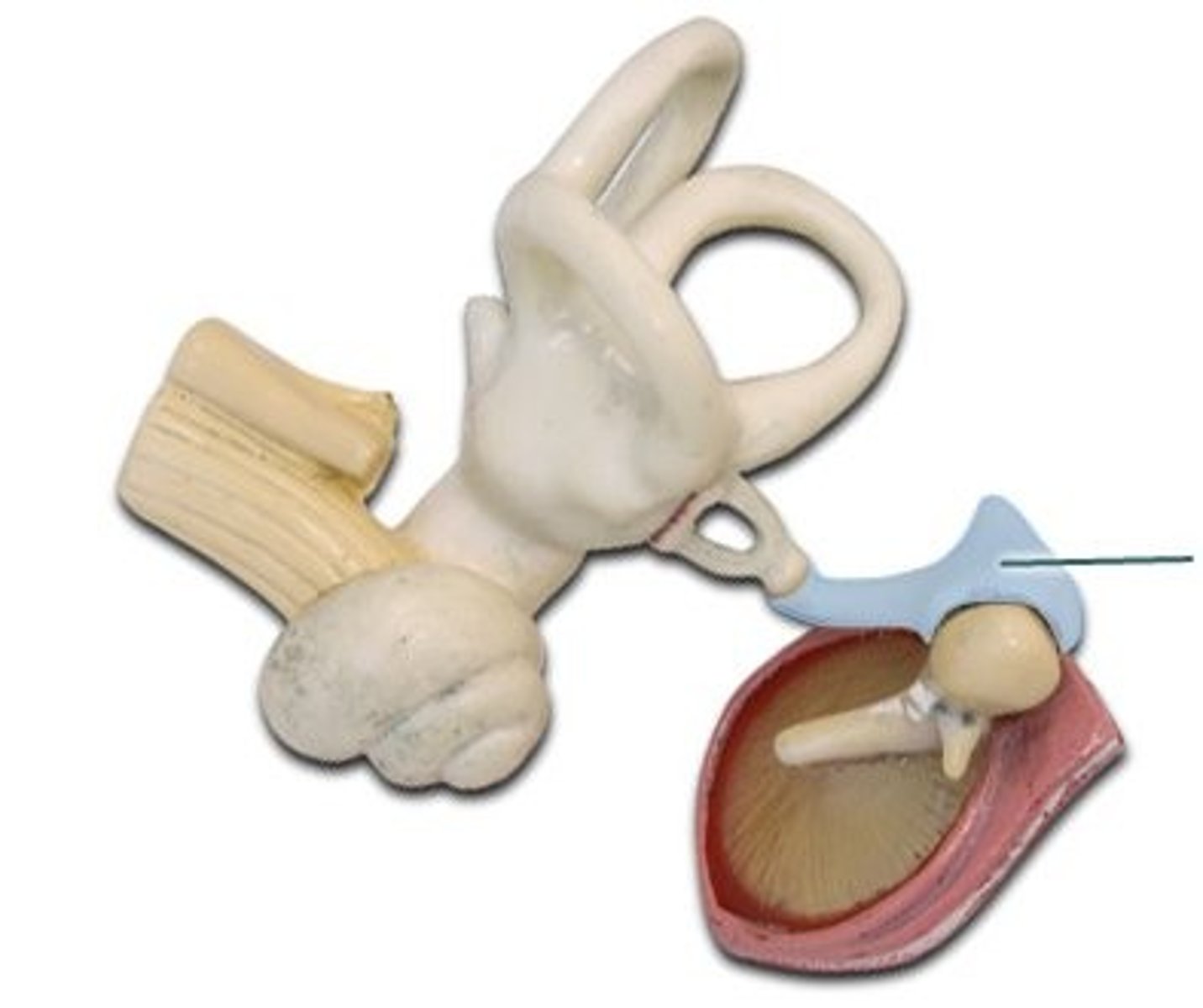
Stapes
Stirrup; last of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
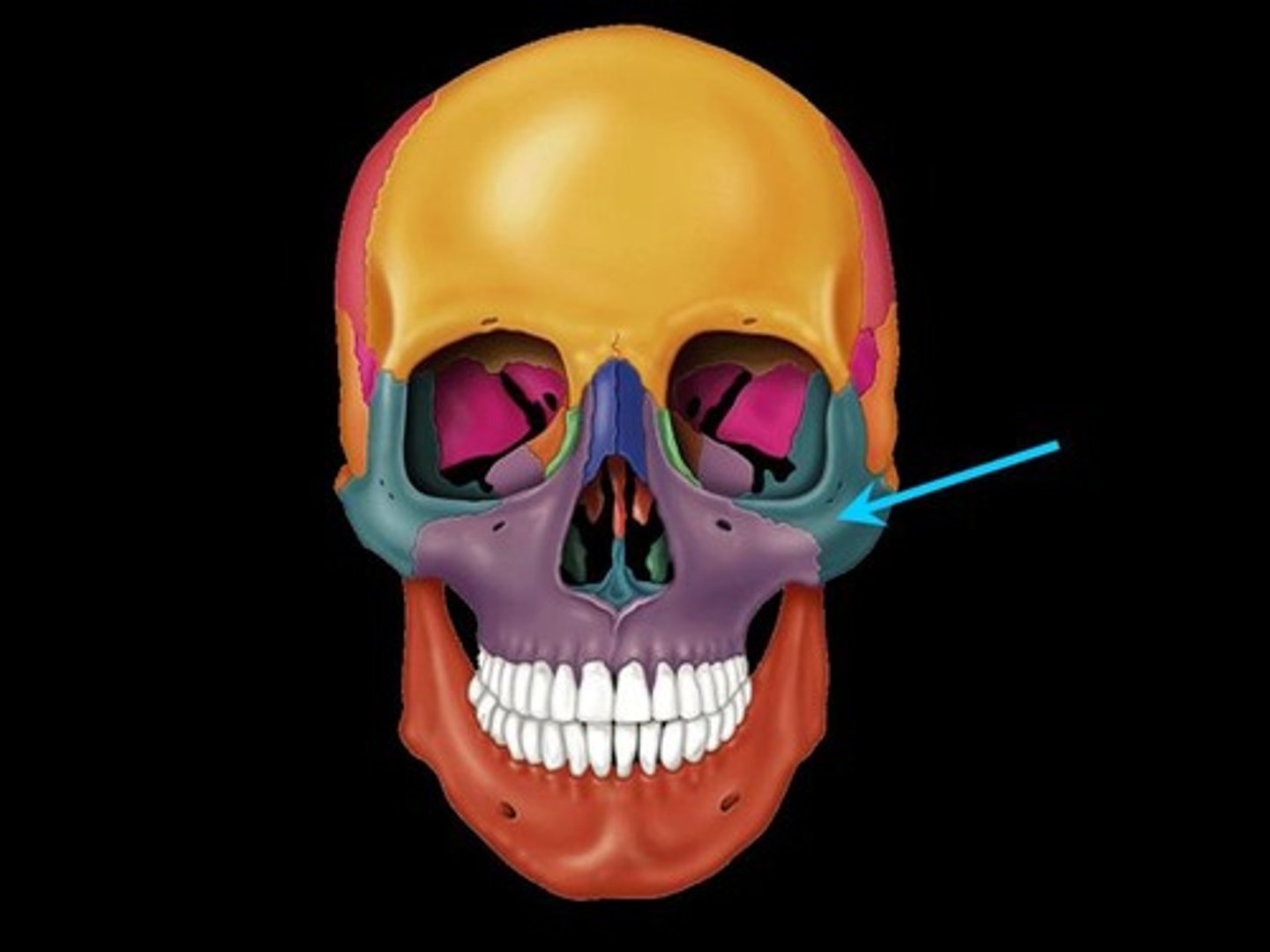
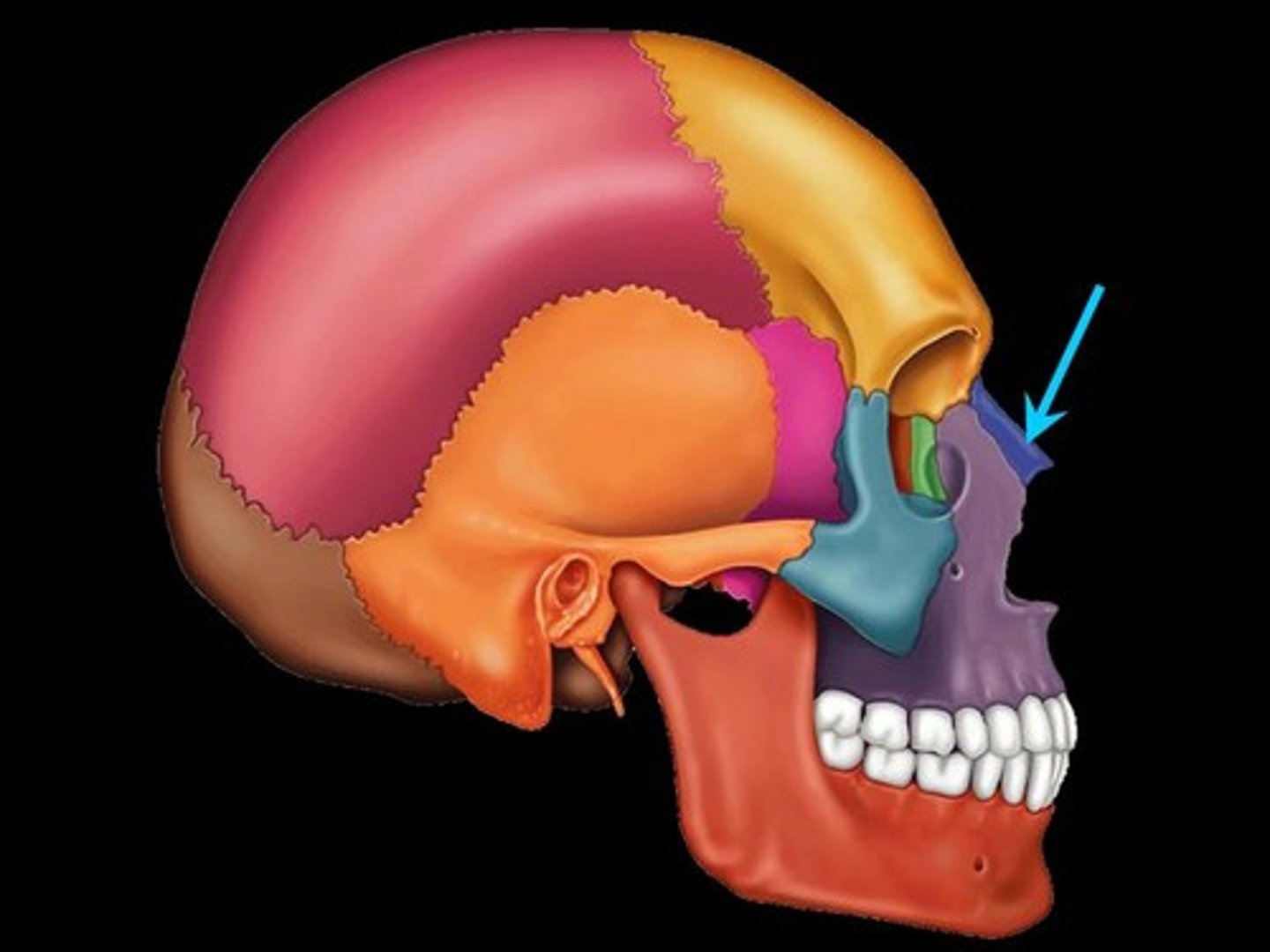
Zygomatic Bones
The two bones, one on each side of the face, that form the high portion of the cheek
Nasal Bones
Bones that form the bridge of the nose
Lacrimal Bones
Small, thin bones located at the front inner wall of the orbits (eye sockets)
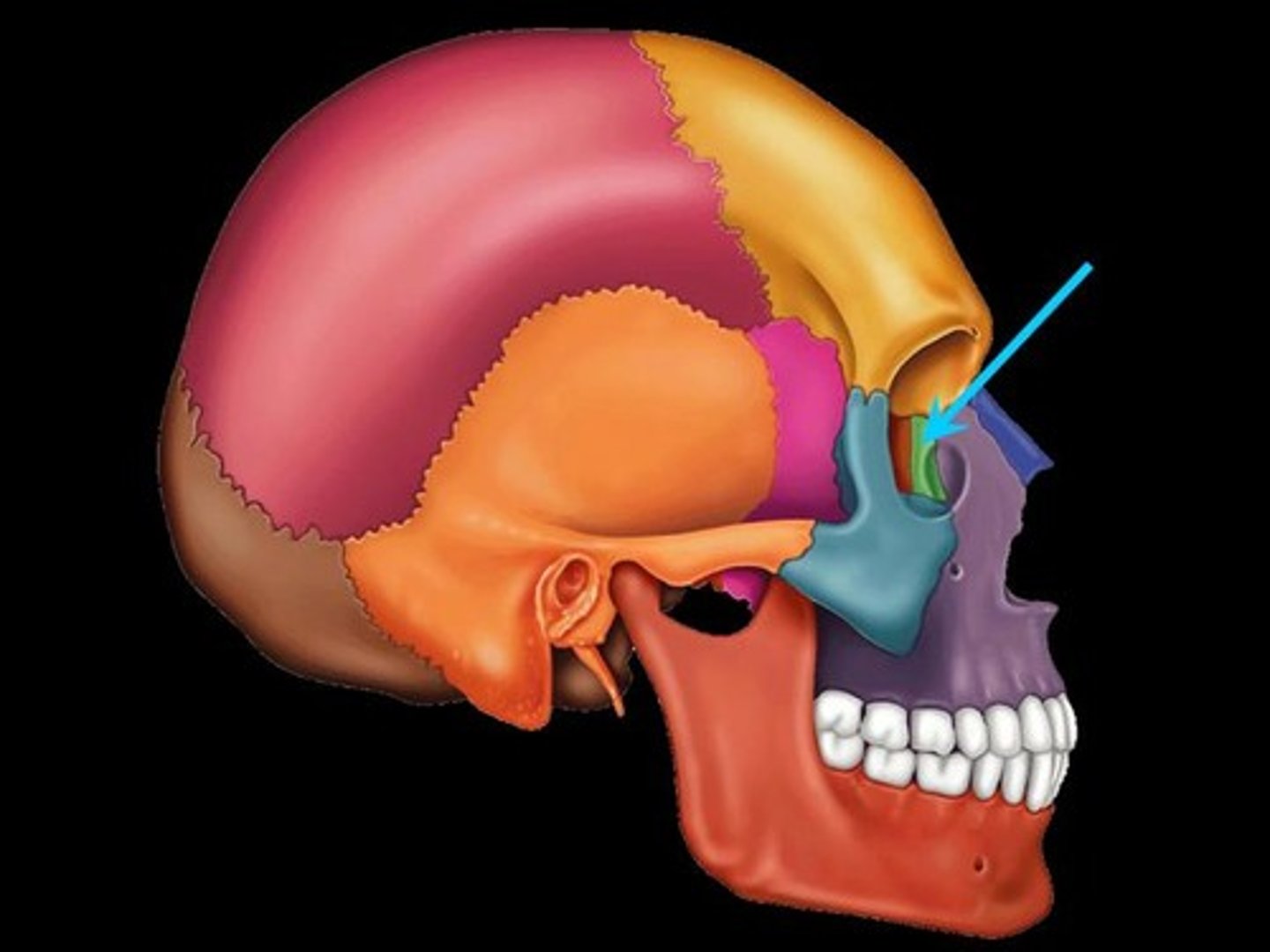
Maxilla Bones
The maxilla bones are paired bones joined in the midline. They are located in the upper lip region and together are commonly referred to as the "upper jaw." They also form a portion of the wall of the orbit, the wall of the nasal cavity, the hard palate, and they contain the upper row of teeth.
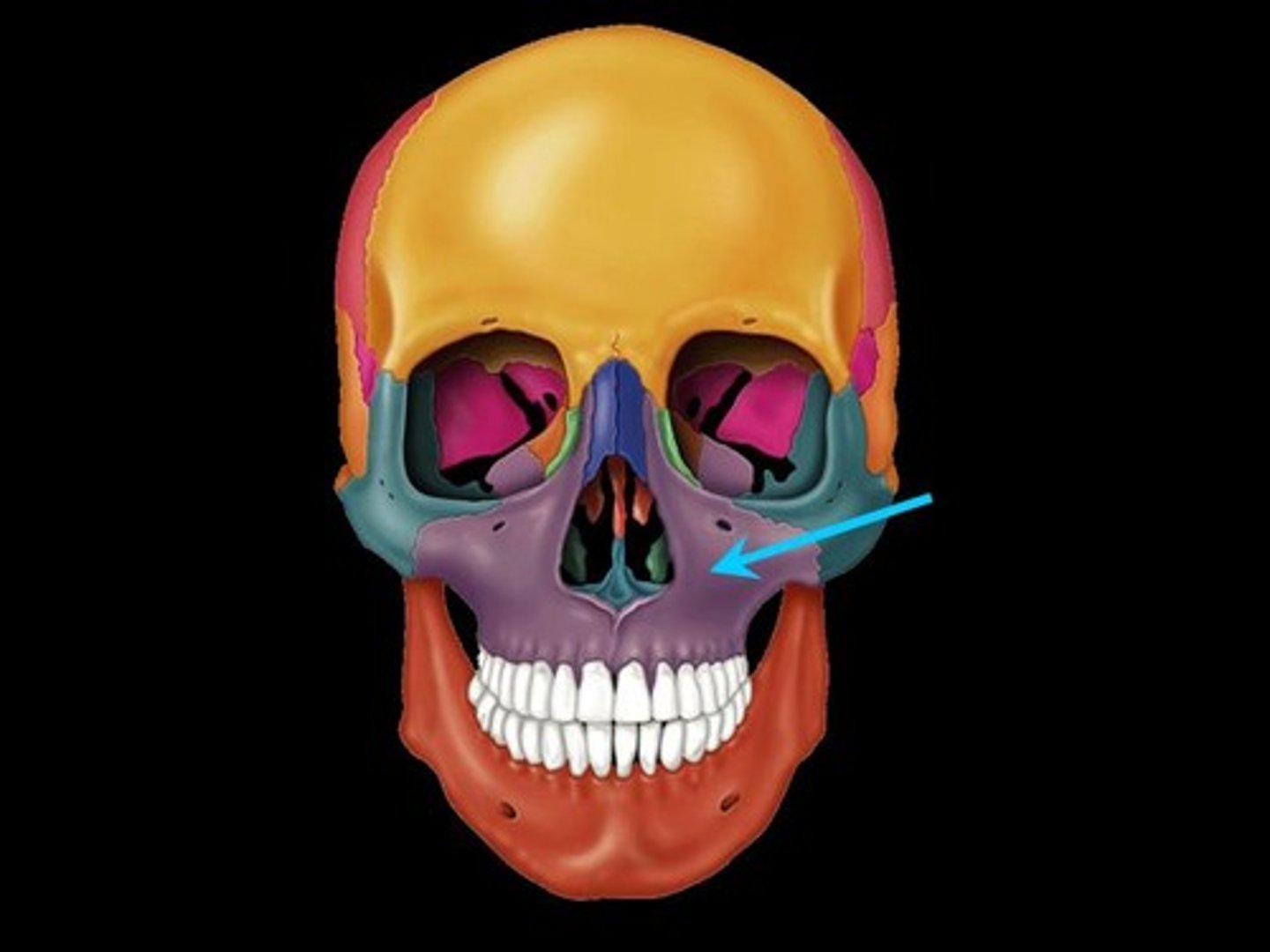
Infraorbital Foramen
Opening under the orbit carrying the infraorbital nerves and blood vessels the the nasal region
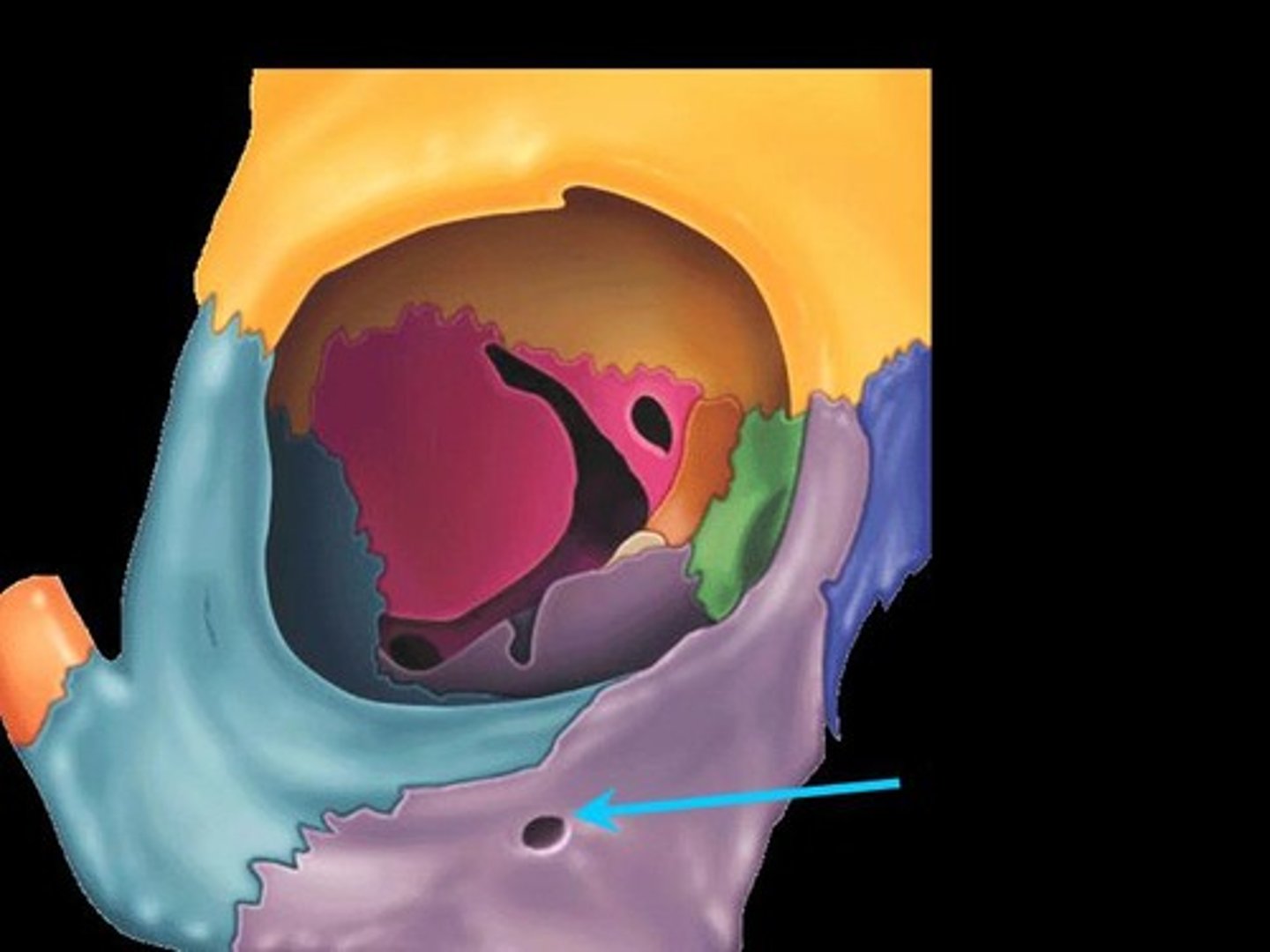
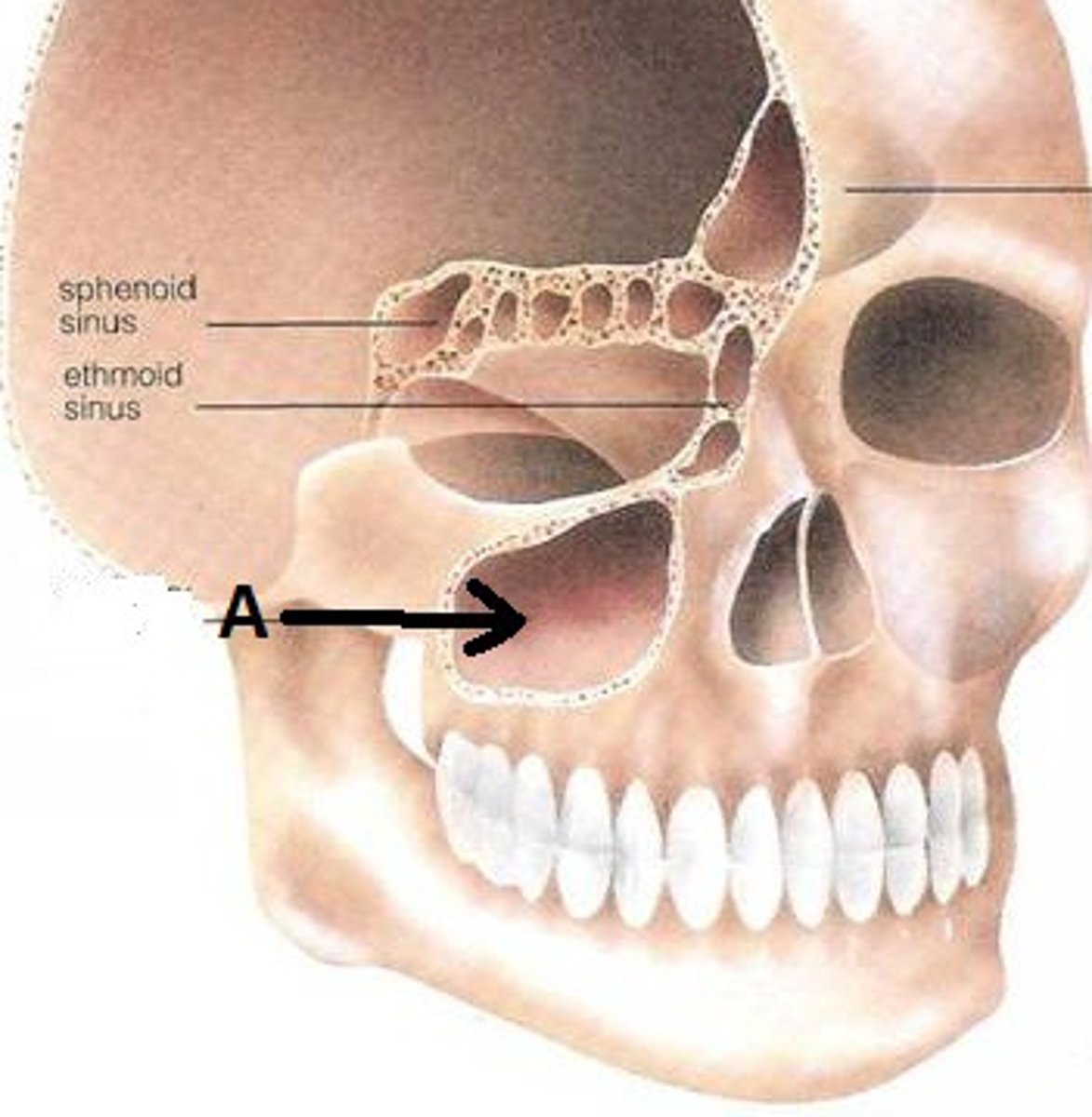
Maxillary Sinus
Largest paranasl sinus; pyramidal; on cheek bone lateral to nasal bone
Nasal Conchae
Two bones that help to complete the nasal cavity by forming the side and lower wall
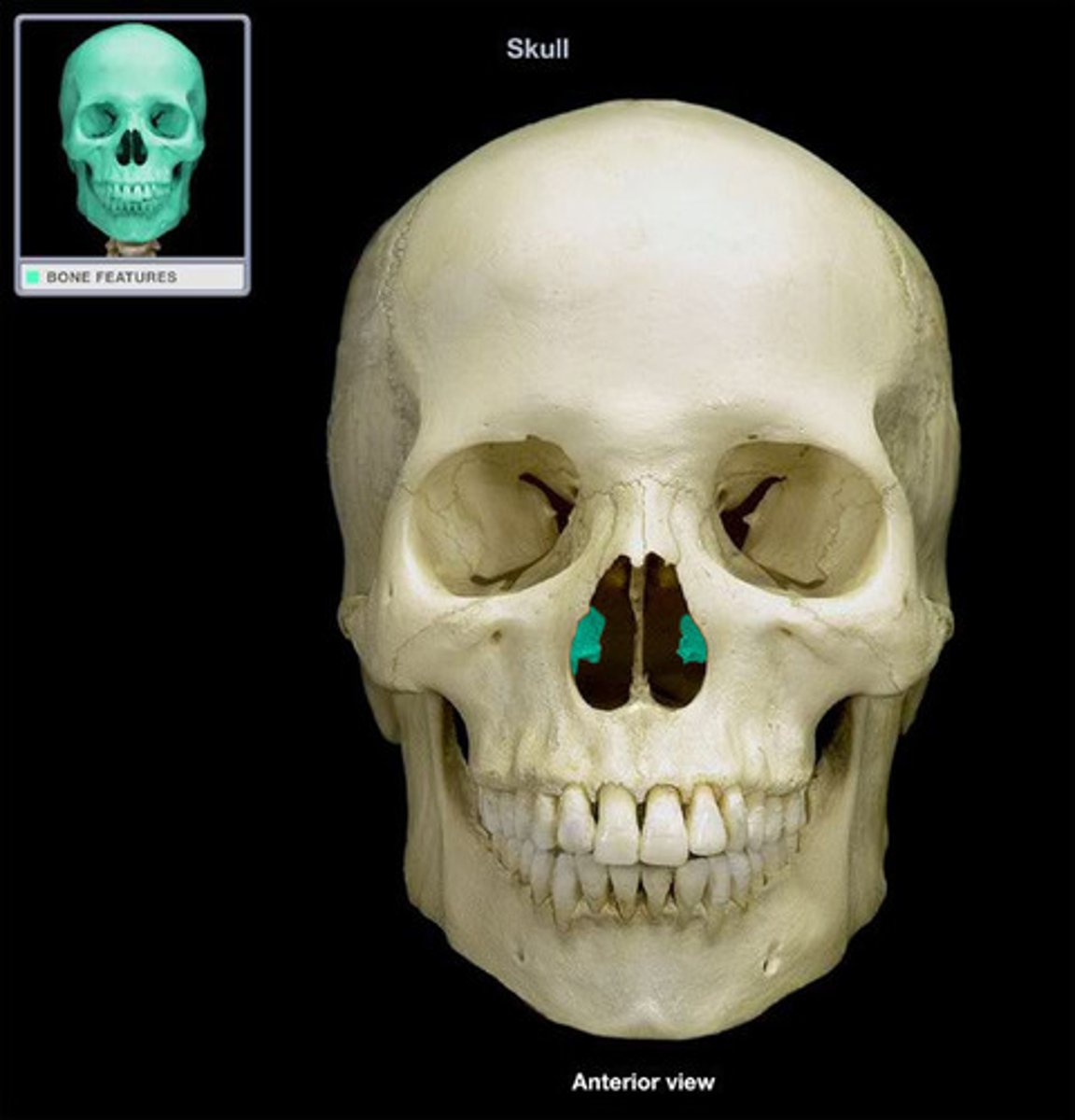
Palatine Bones
Form the anterior part of the hard palate of the mouth and the floor of the nose
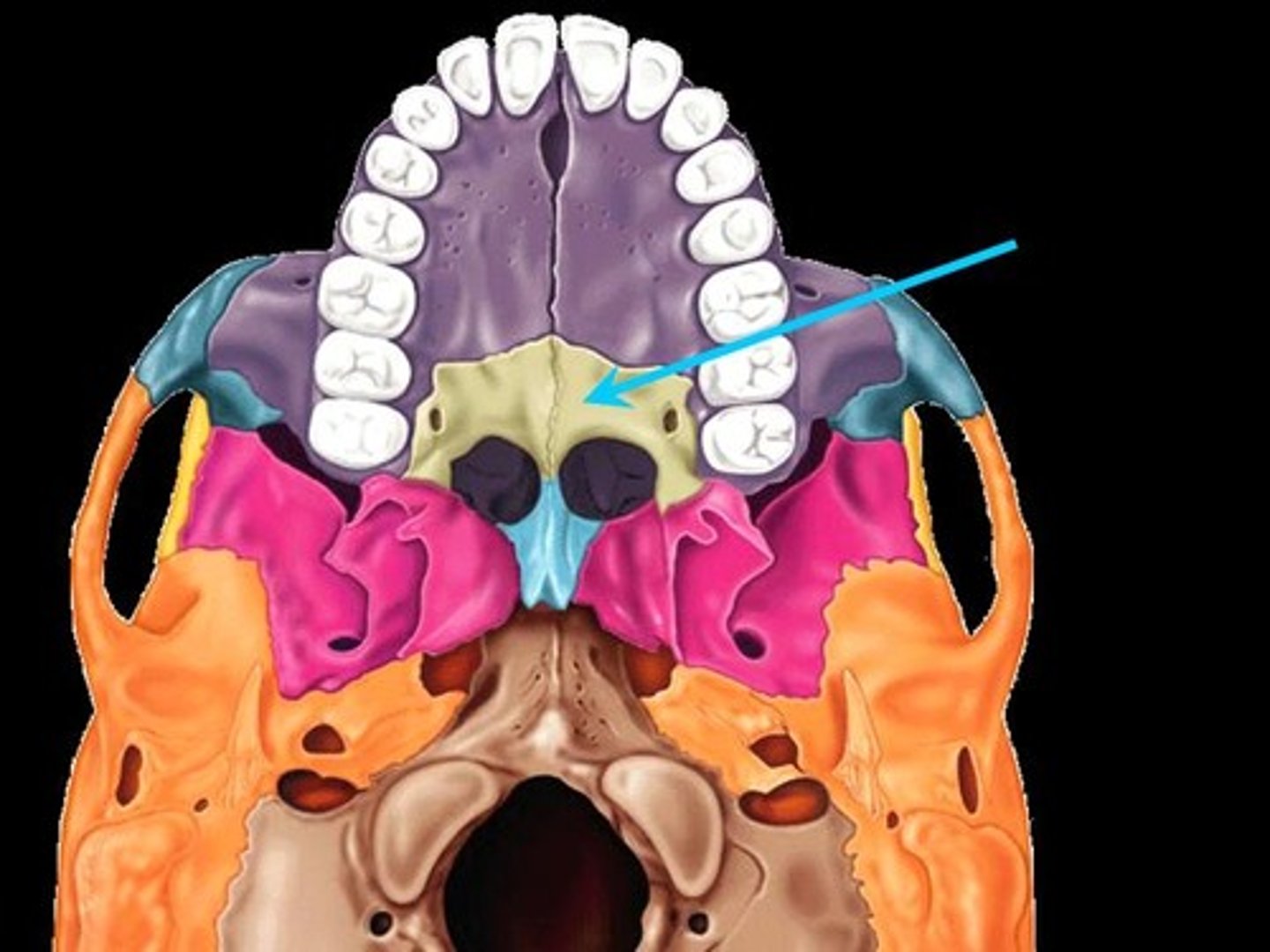
Mandible
Lower jaw bone
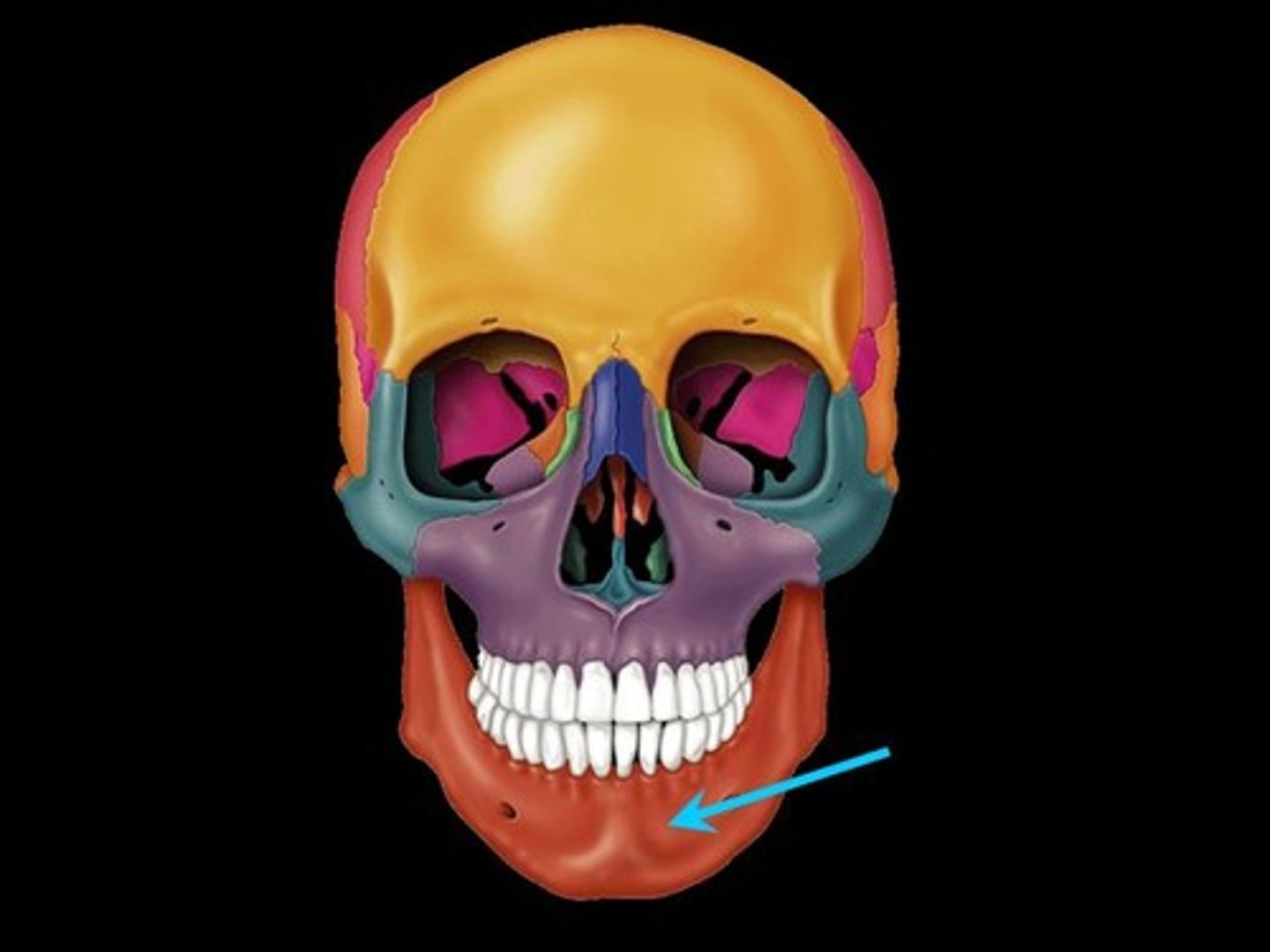
Coronoid Process
A thin, triangular eminence on the mandible
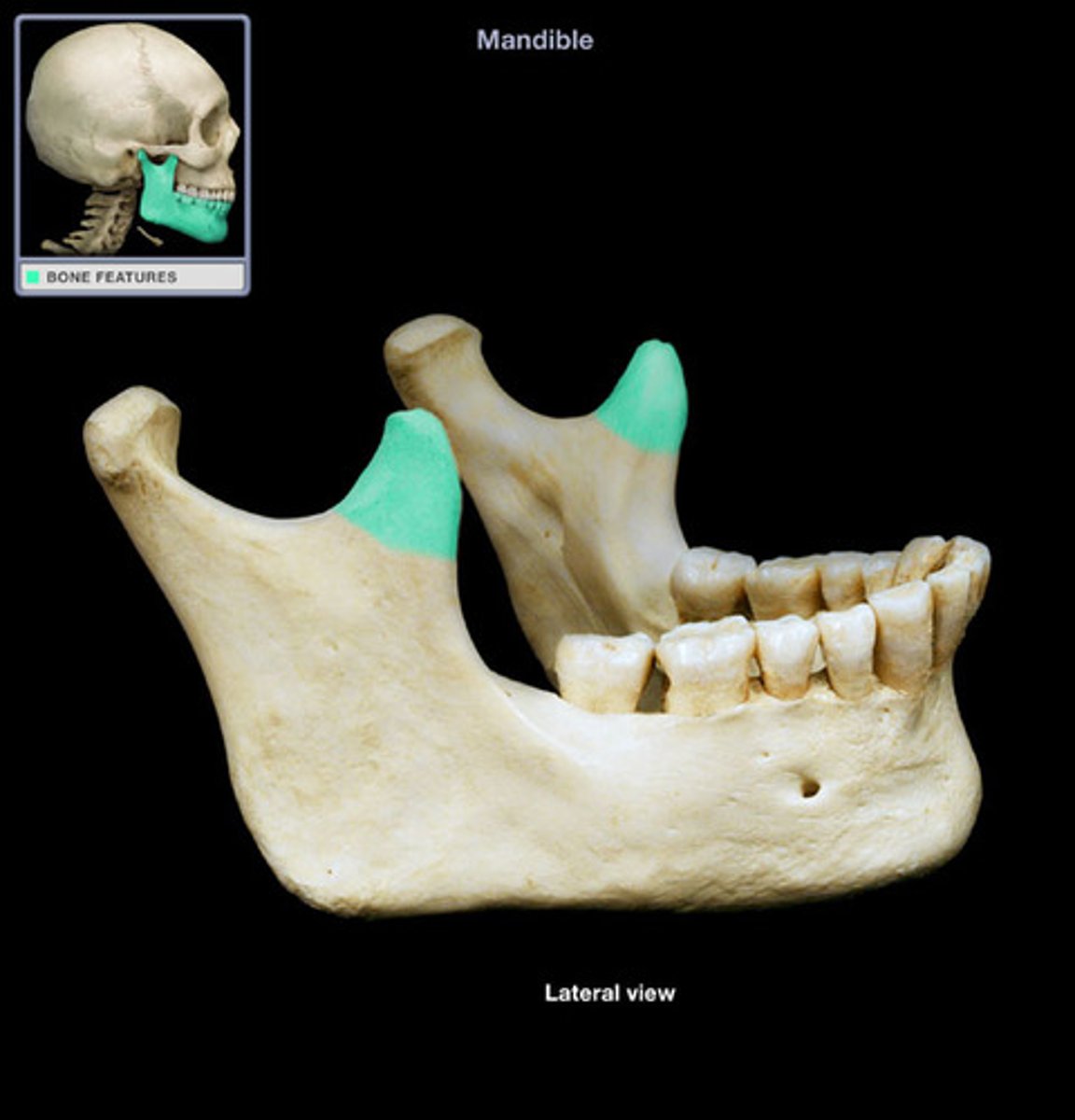
Mandibular Condyle
Articulation point of the mandible with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone
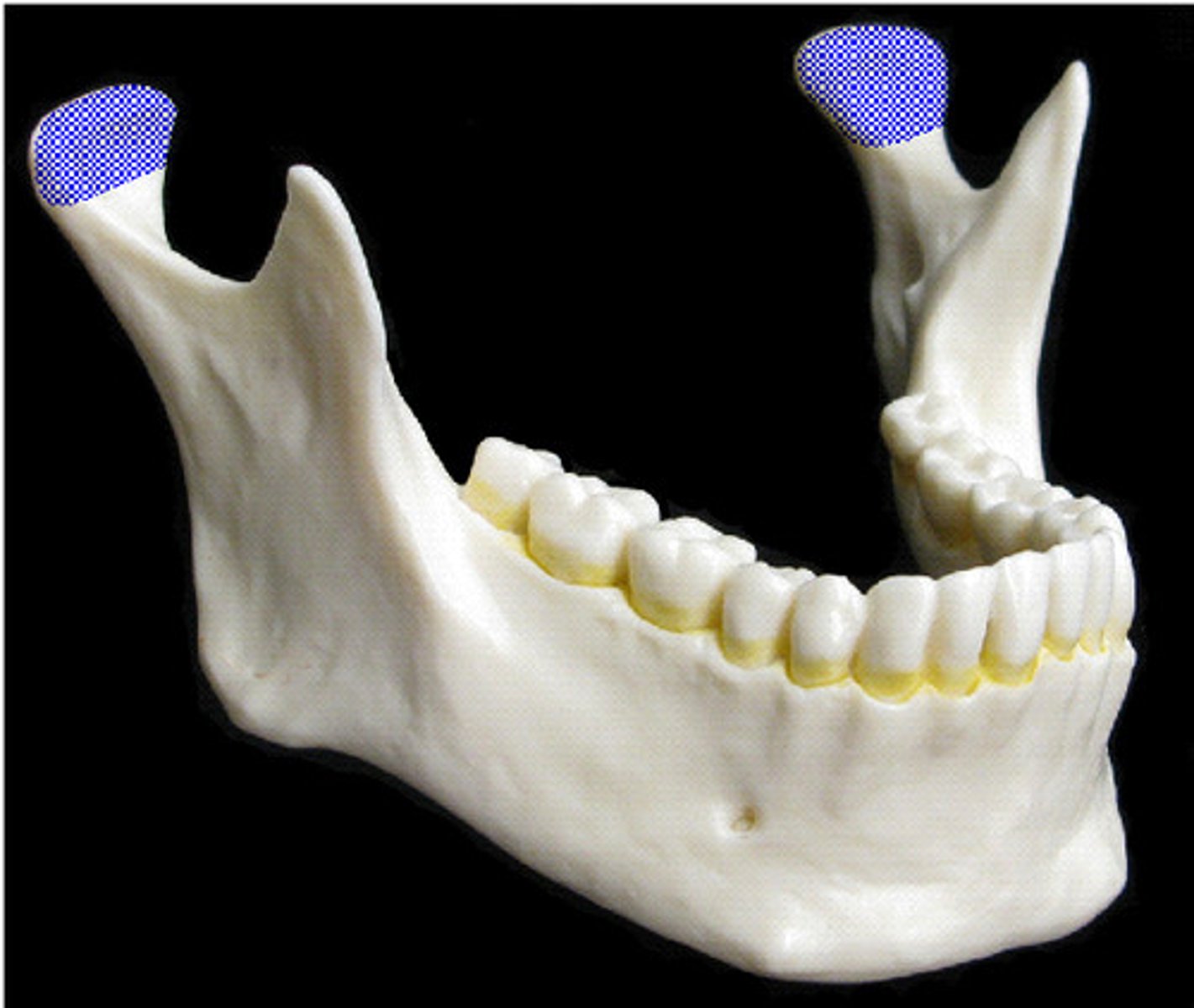
Mandibular Foramen
An opening on the internal surface of the ramus of the mandible for divisions of the mandibular nerve and blood vessels to pass through
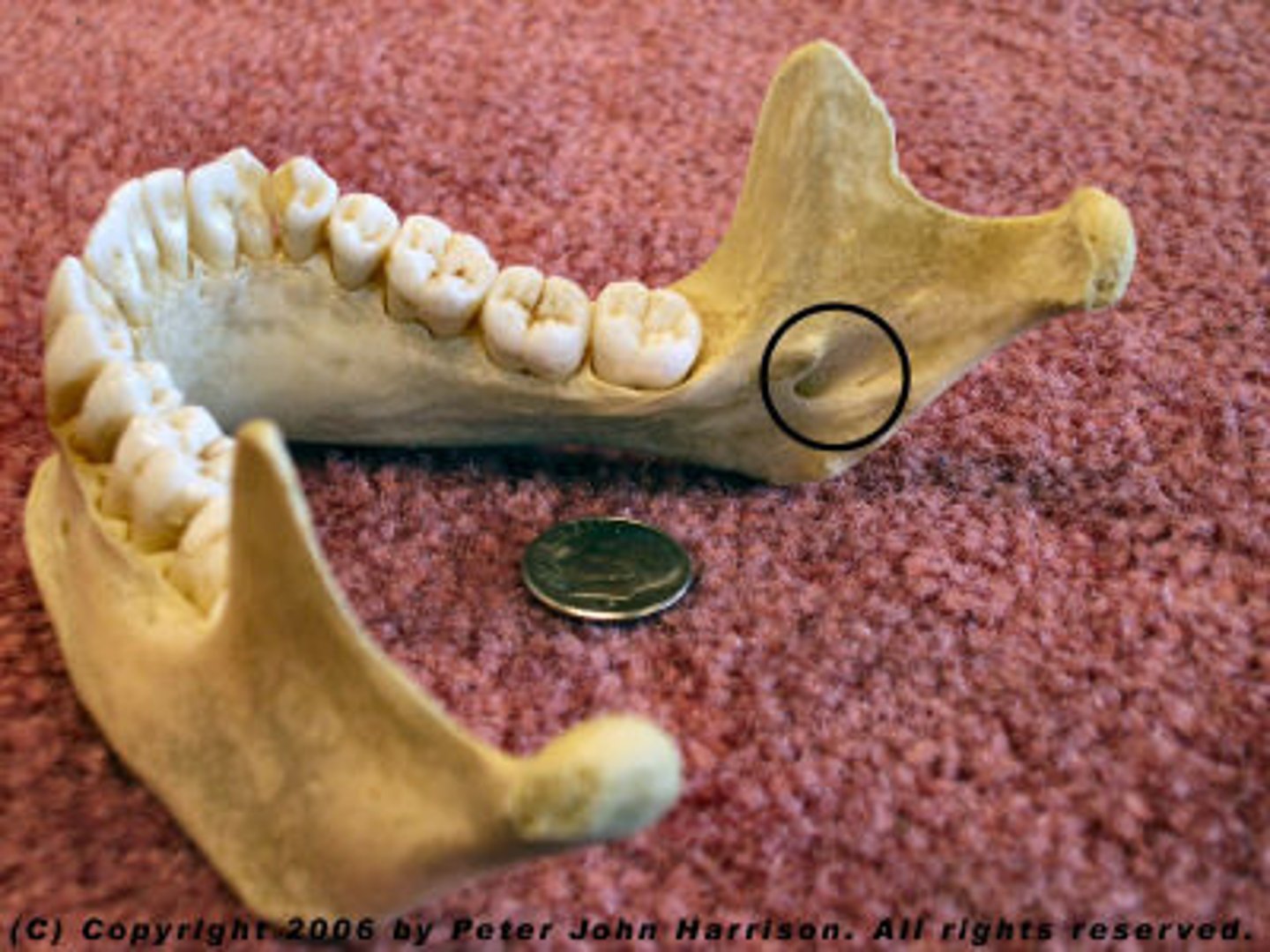
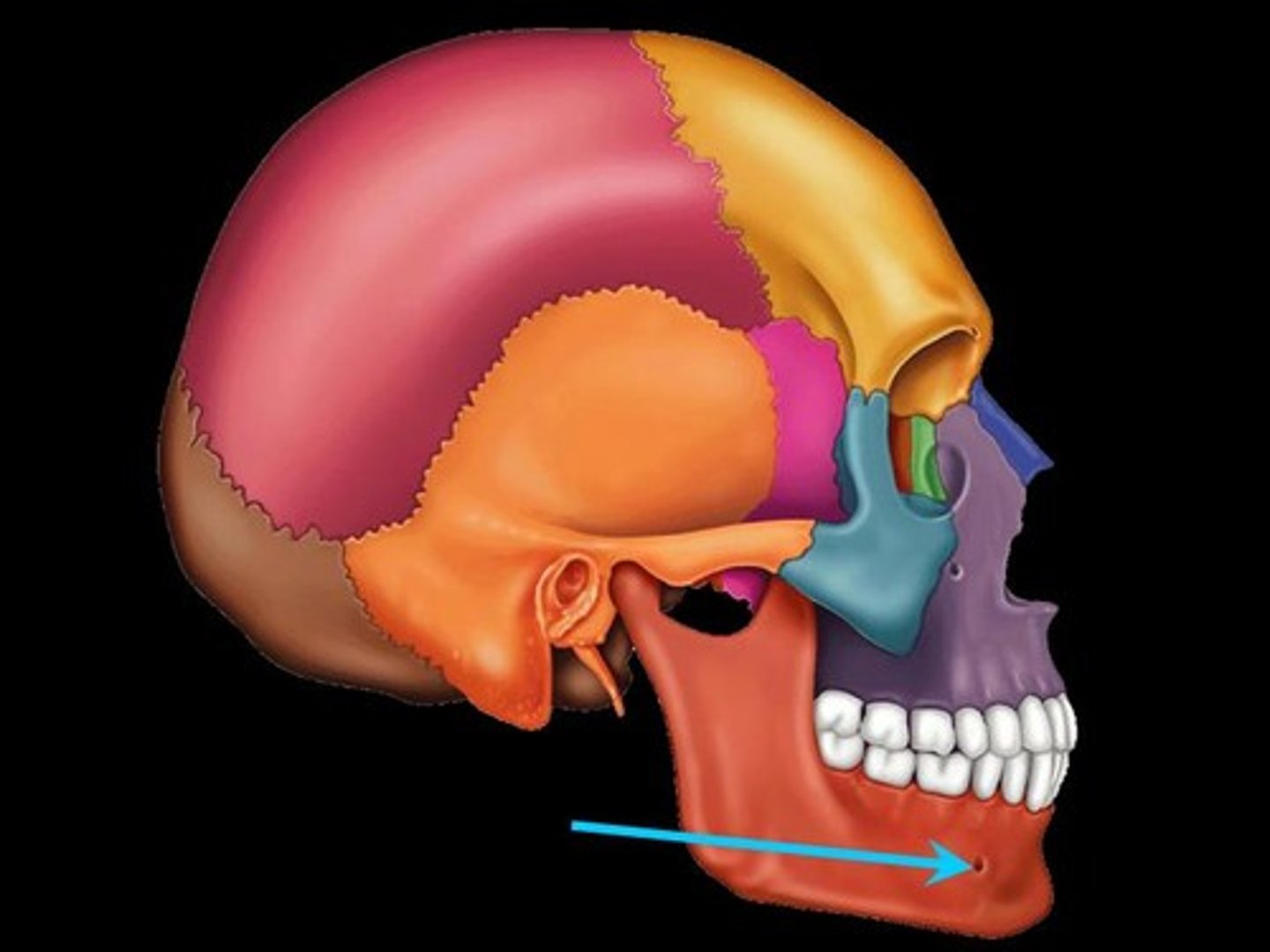
Mental Foramen
One of two foramina located on the anterior surface of the mandible. It transmits the terminal branches of the inferior alveolar nerve and vessels (the mental artery).
Hyoid Bone
U-shaped bone at the base of the tongue that supports the tongue and its muscles
Cervical Vertebra
C1-C7
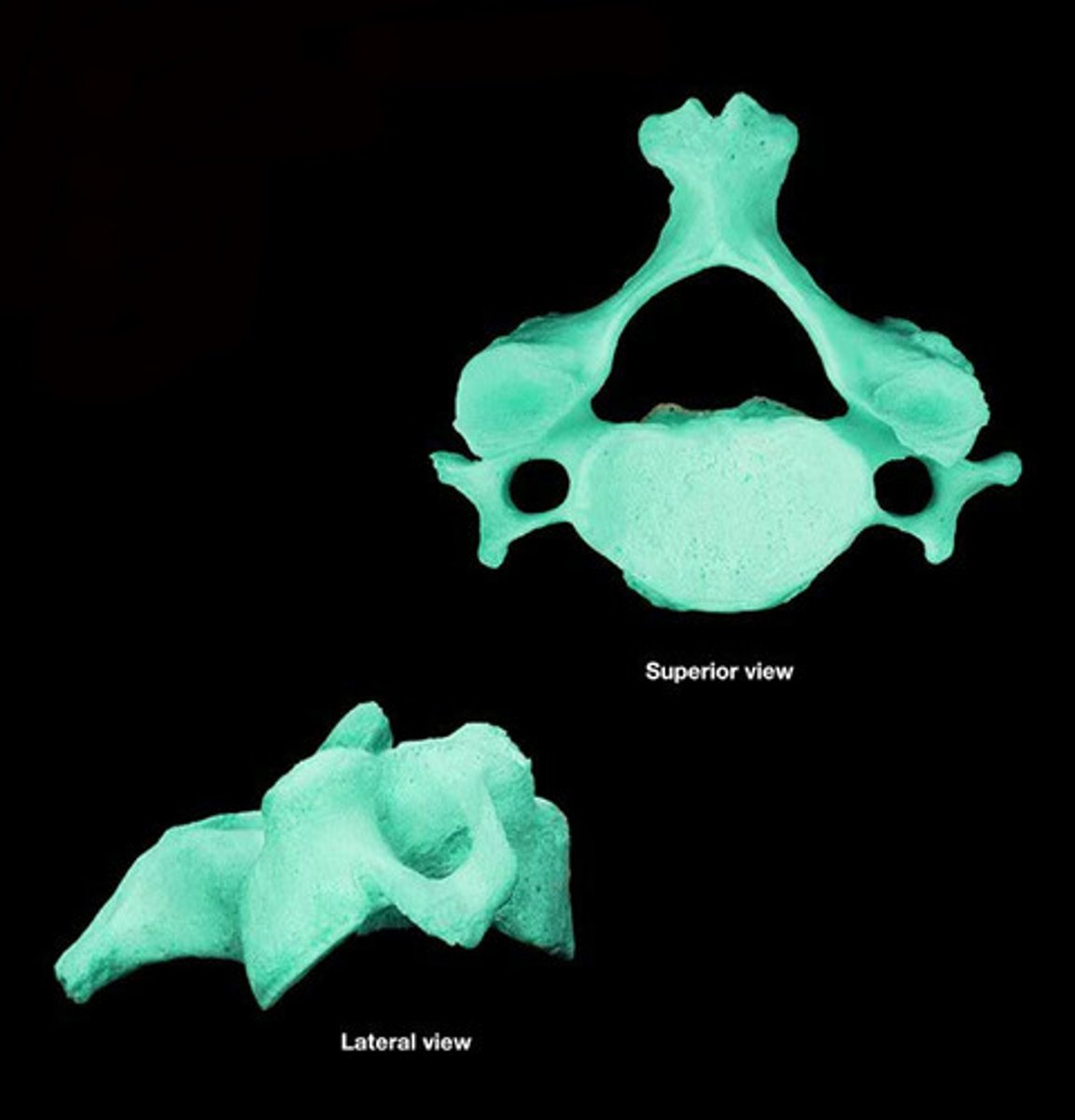
Body (Centrum)
Disc-like, weight-bearing part of the vertebra facing anteriorly in the vertebral column
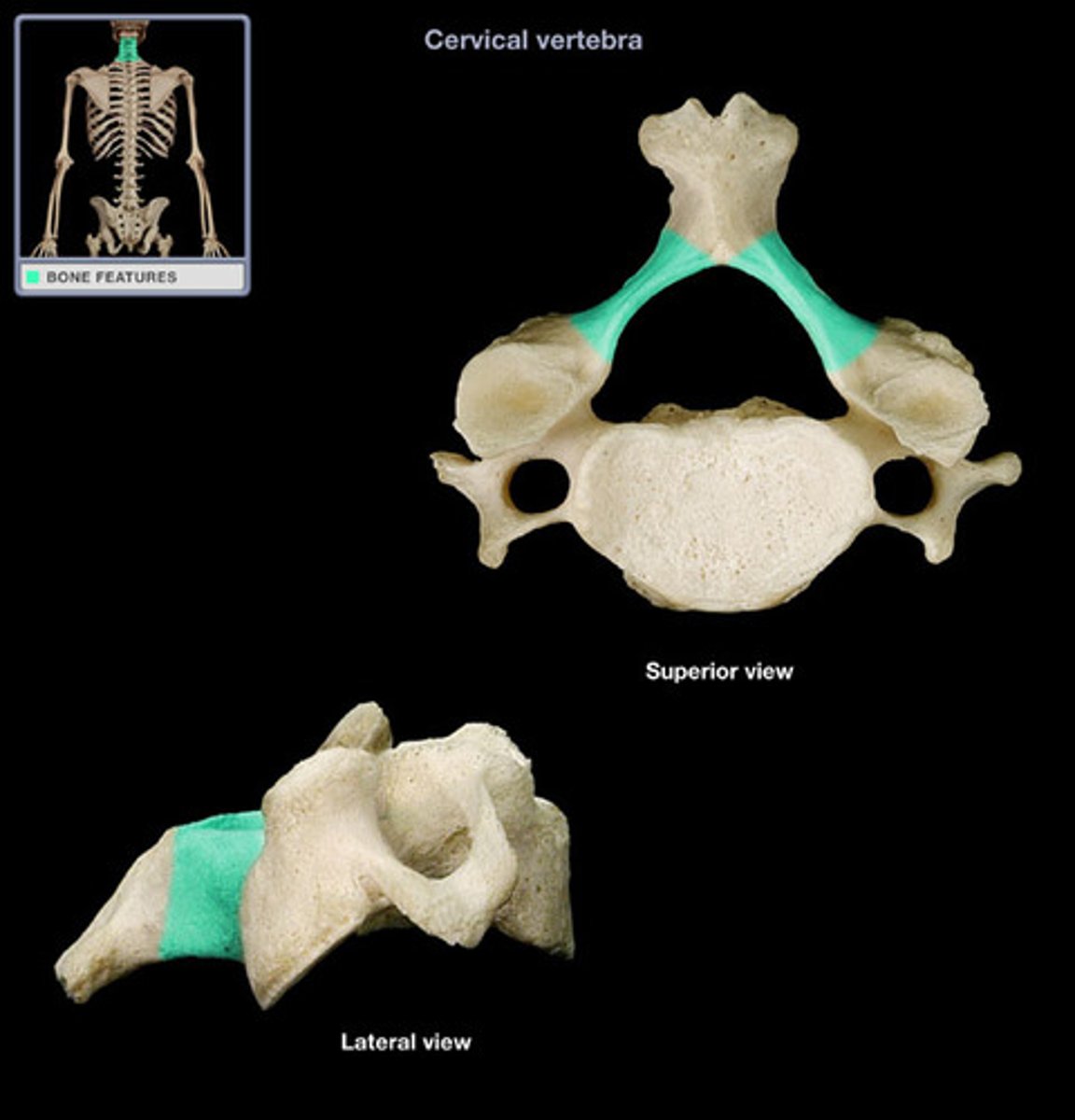
Lamina
Plates of bone that form the posterior walls of each vertebra, enclosing the spinal cord
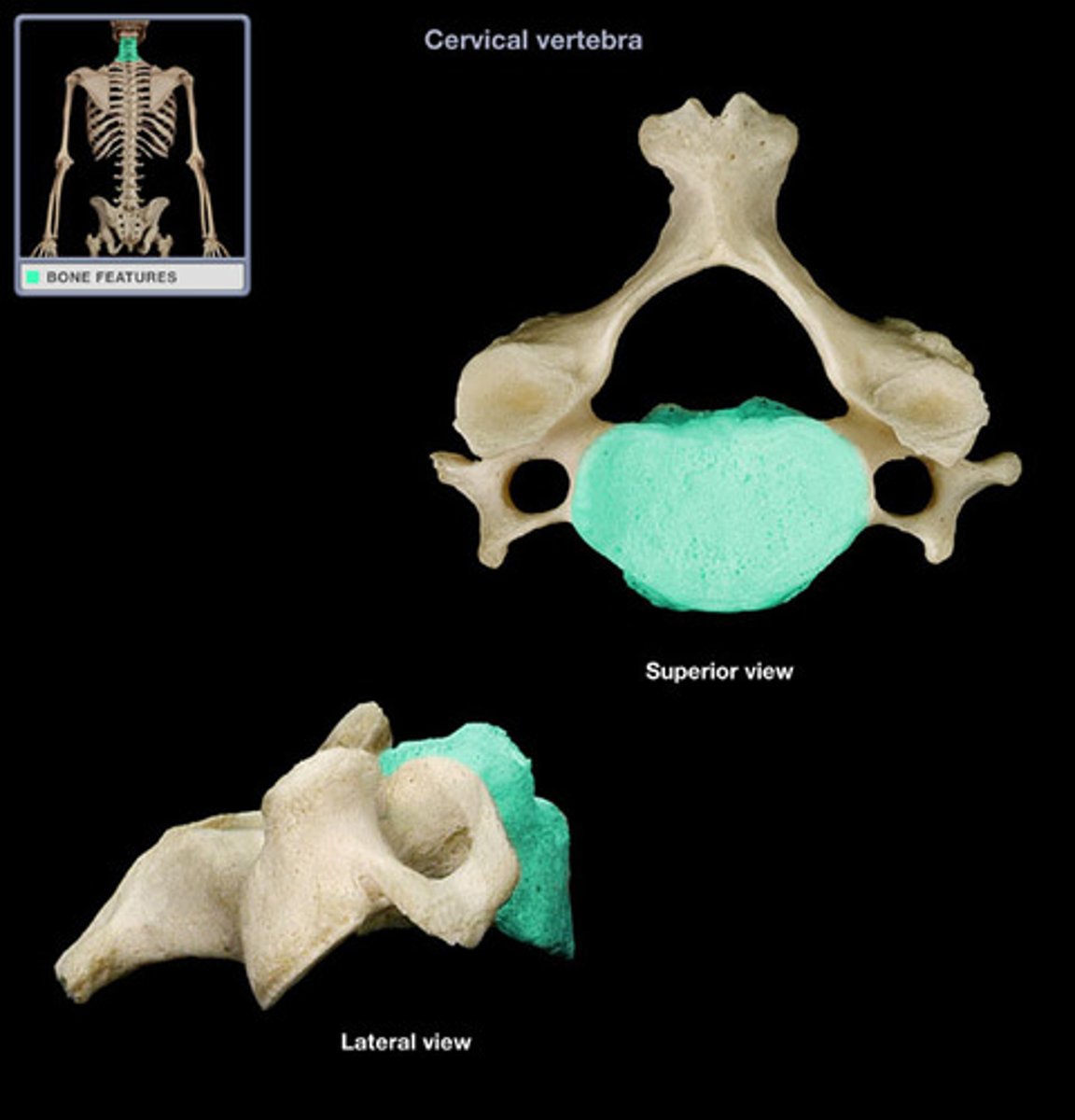
Vertebral Foramen
Canal through which spinal cord passes
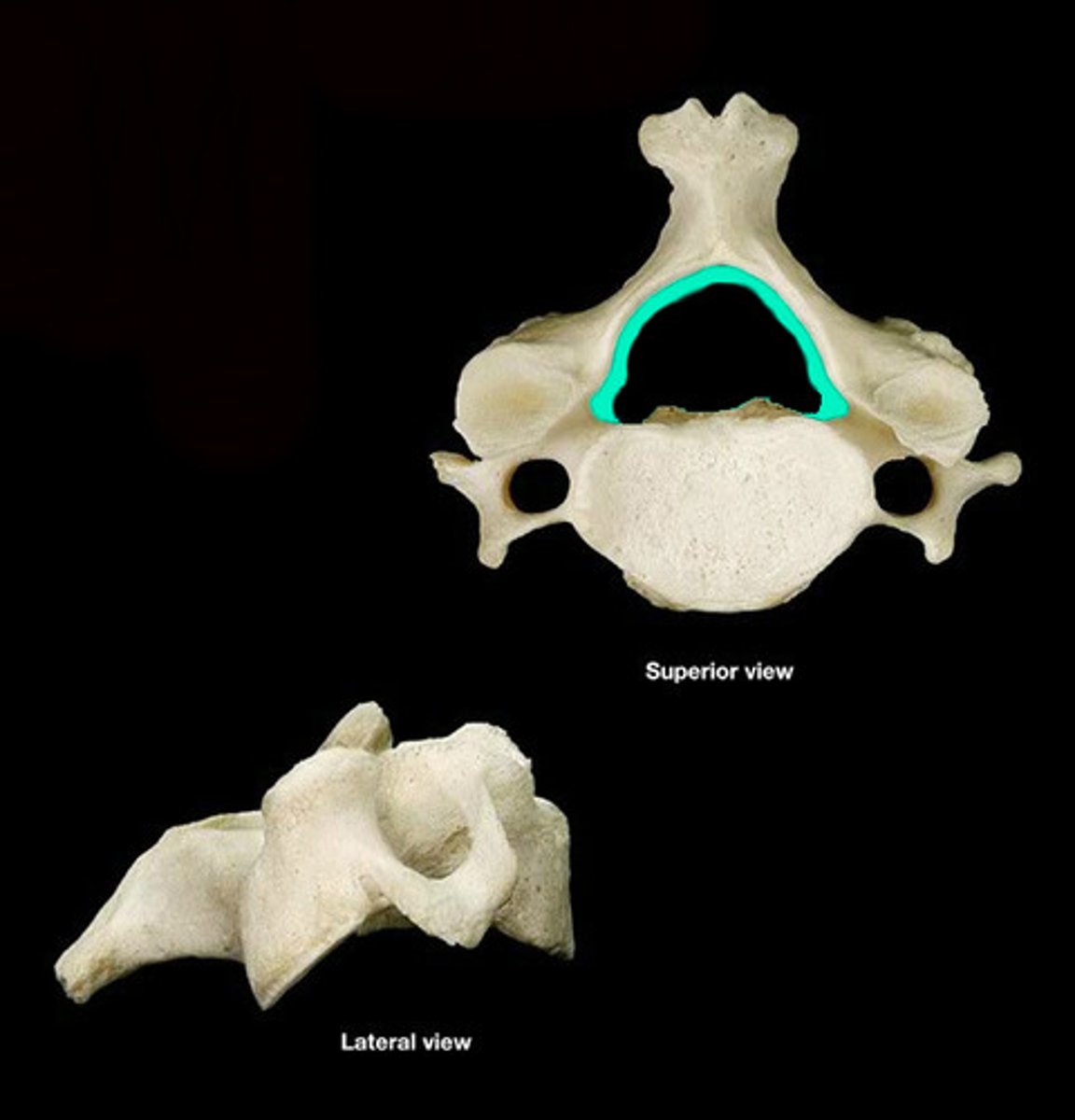
Spinous Process
Sharp, slender projection on the posterior side of cerebral vertebrae
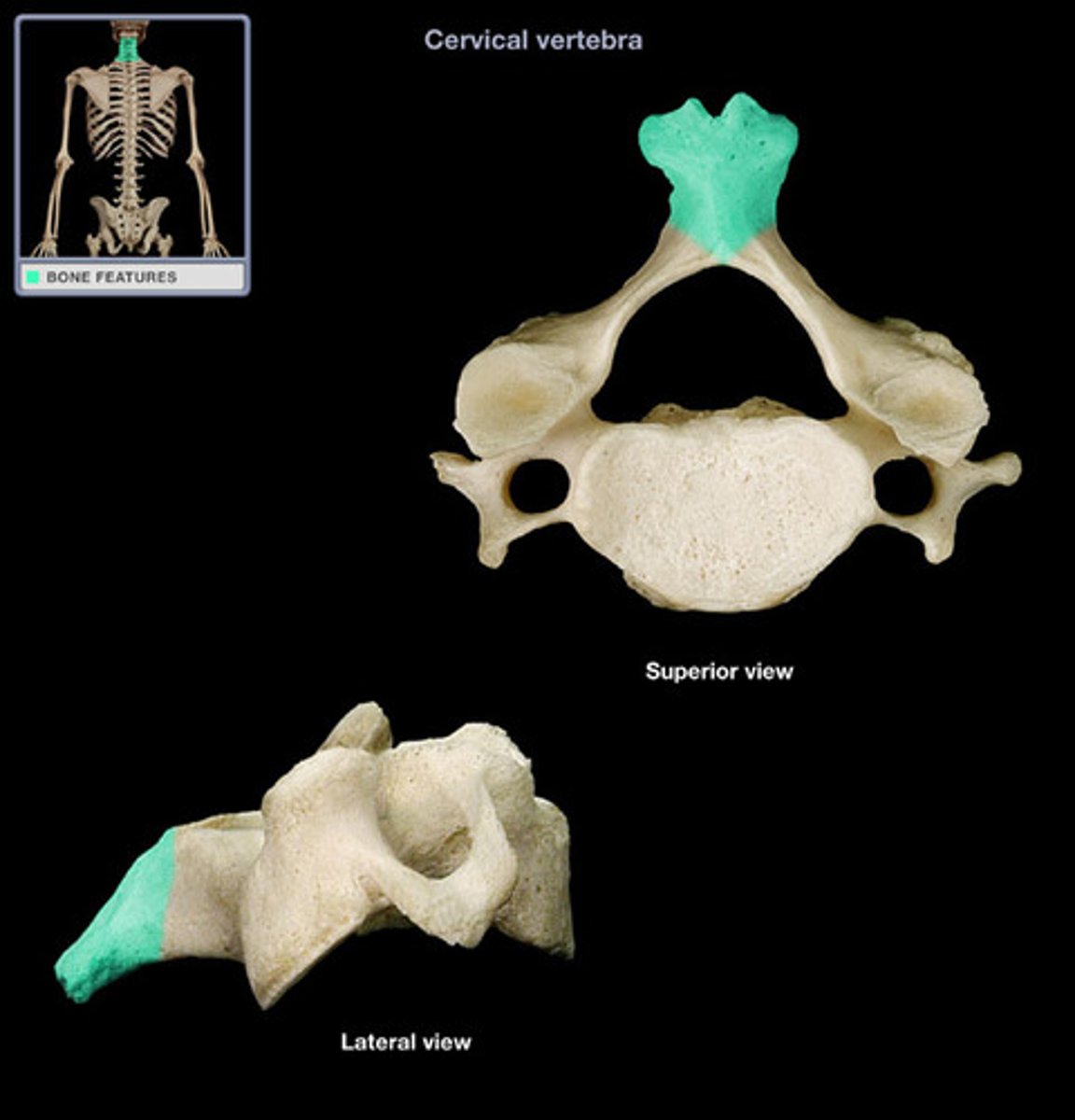
Transverse Process
Lateral projections on both sides of the vertebral arch
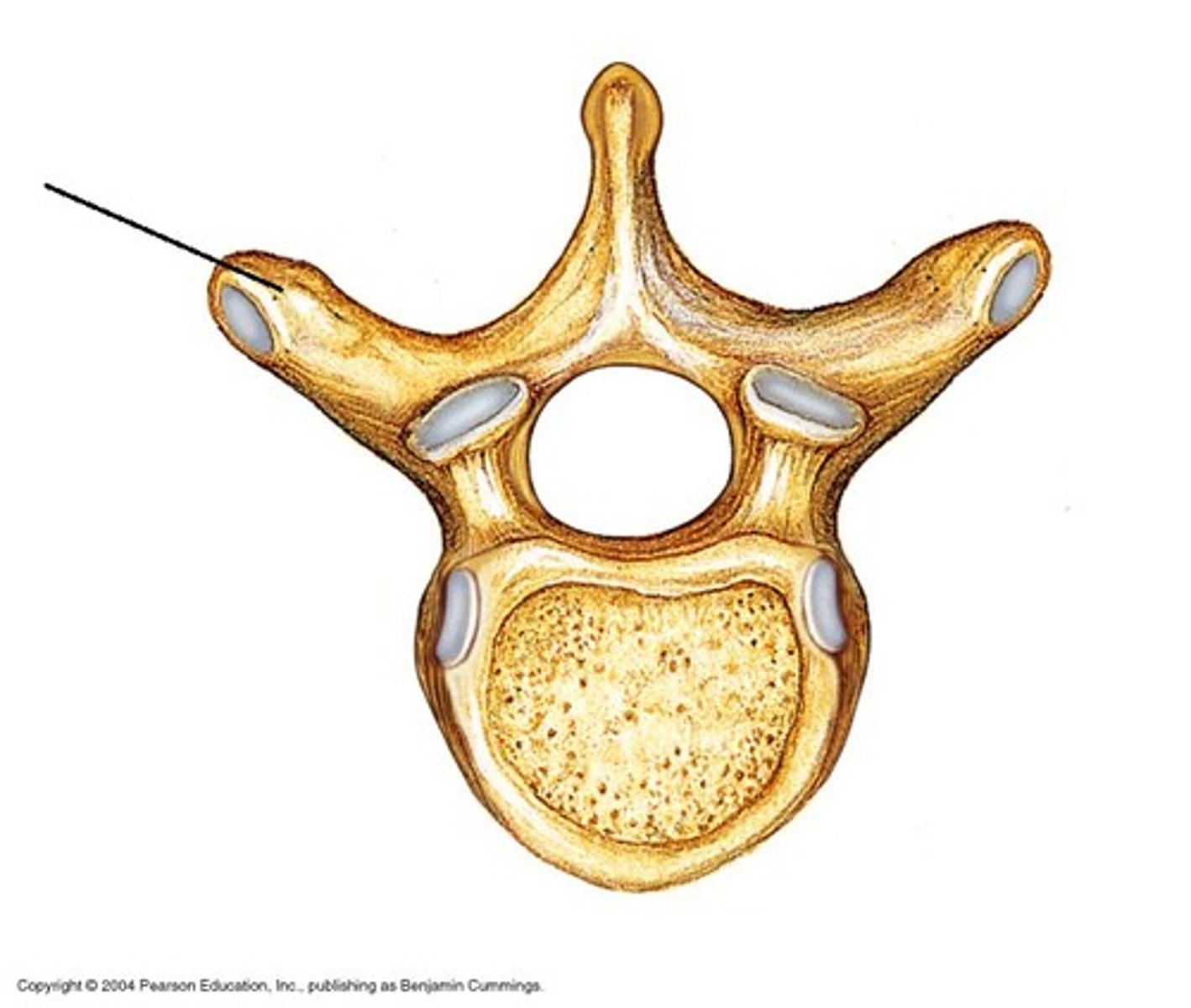
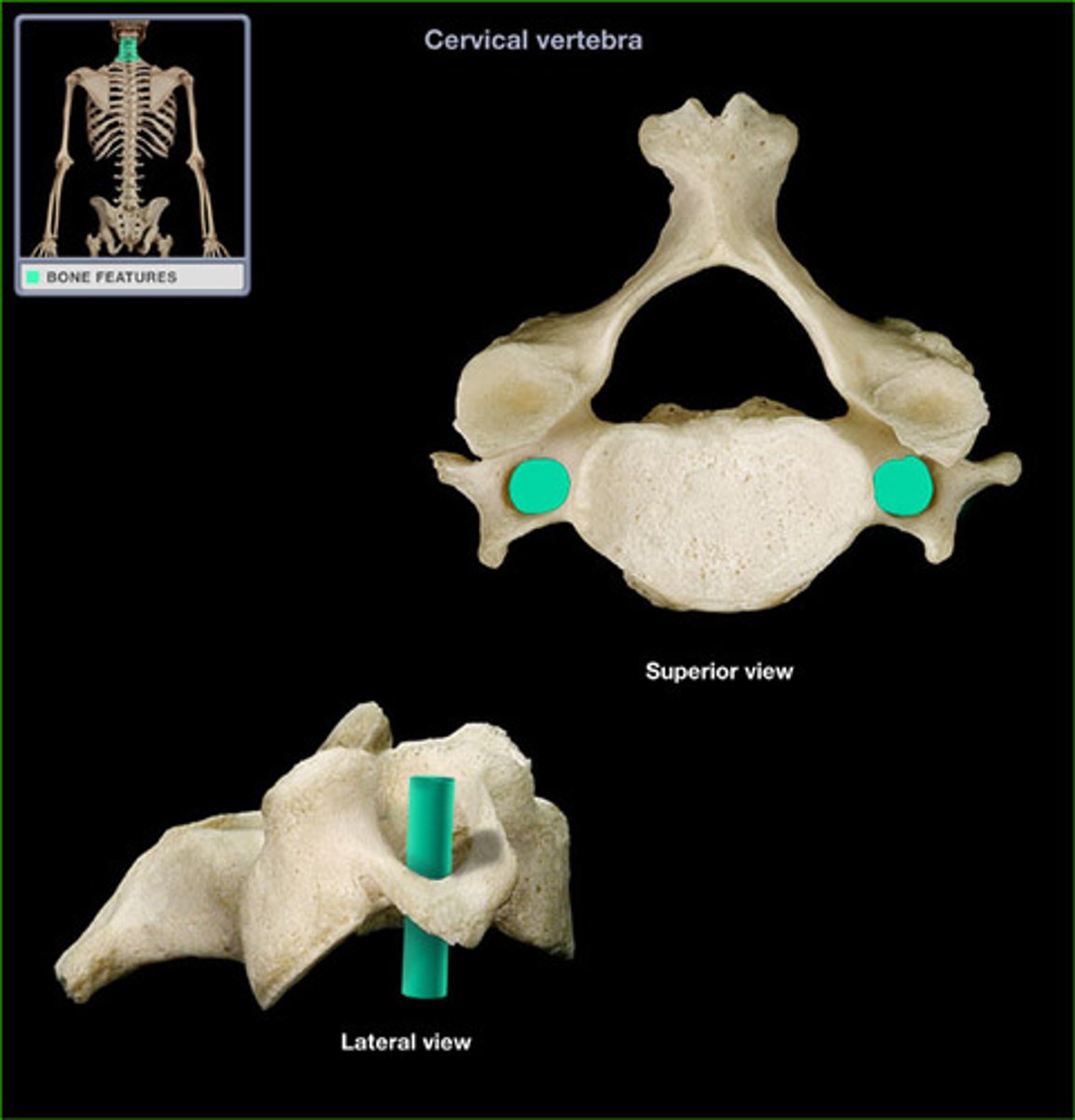
Transverse Foramen
Only found in the cervical vertebrae and allow passage of the vertabral artery, vein, and nerve
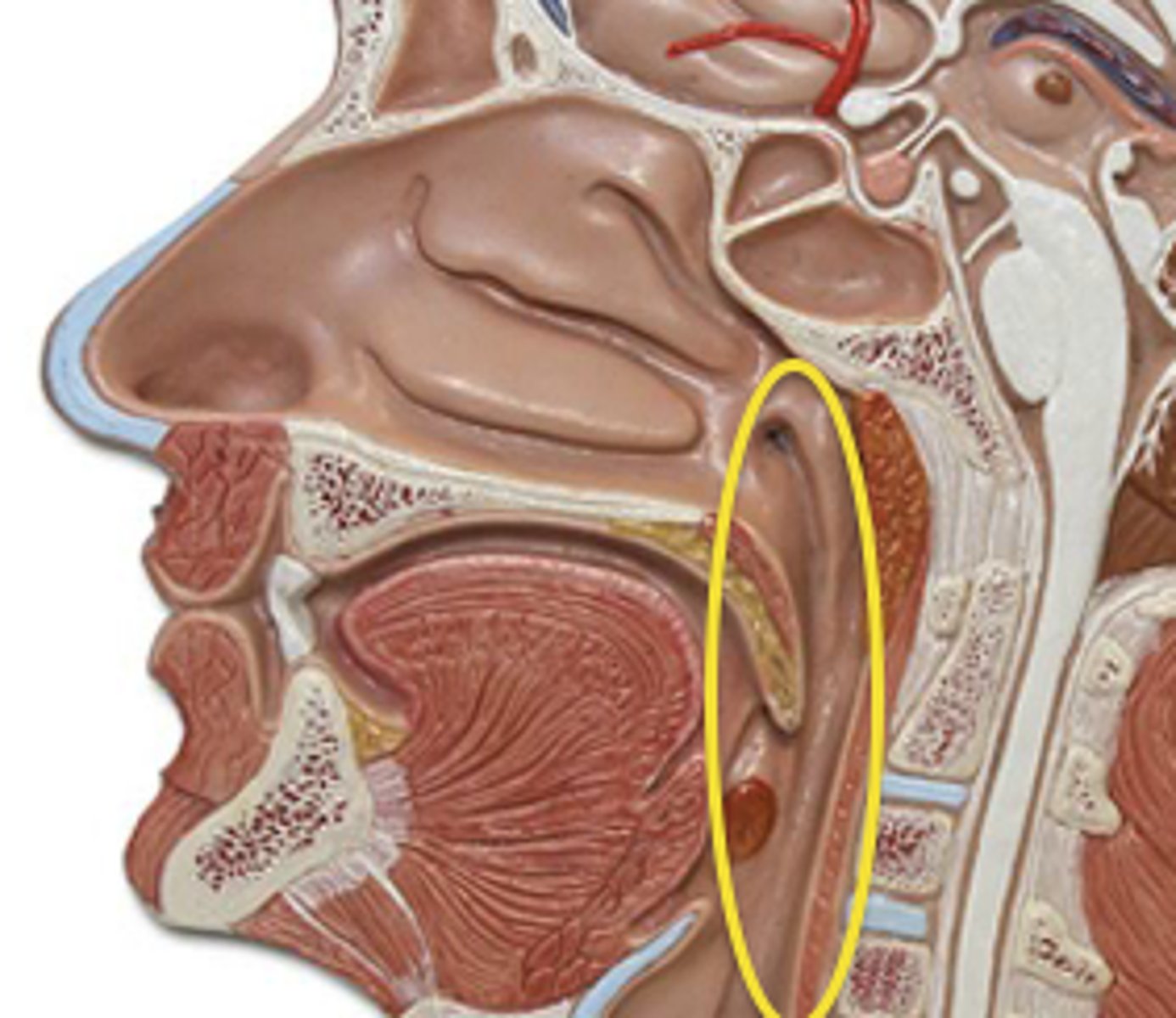
Pharynx
The membrane-lined cavity behind the nose and mouth, connecting them to the esophagus.
Nasopharynx
Region of the pharynx at the back of the nose and above the soft palate
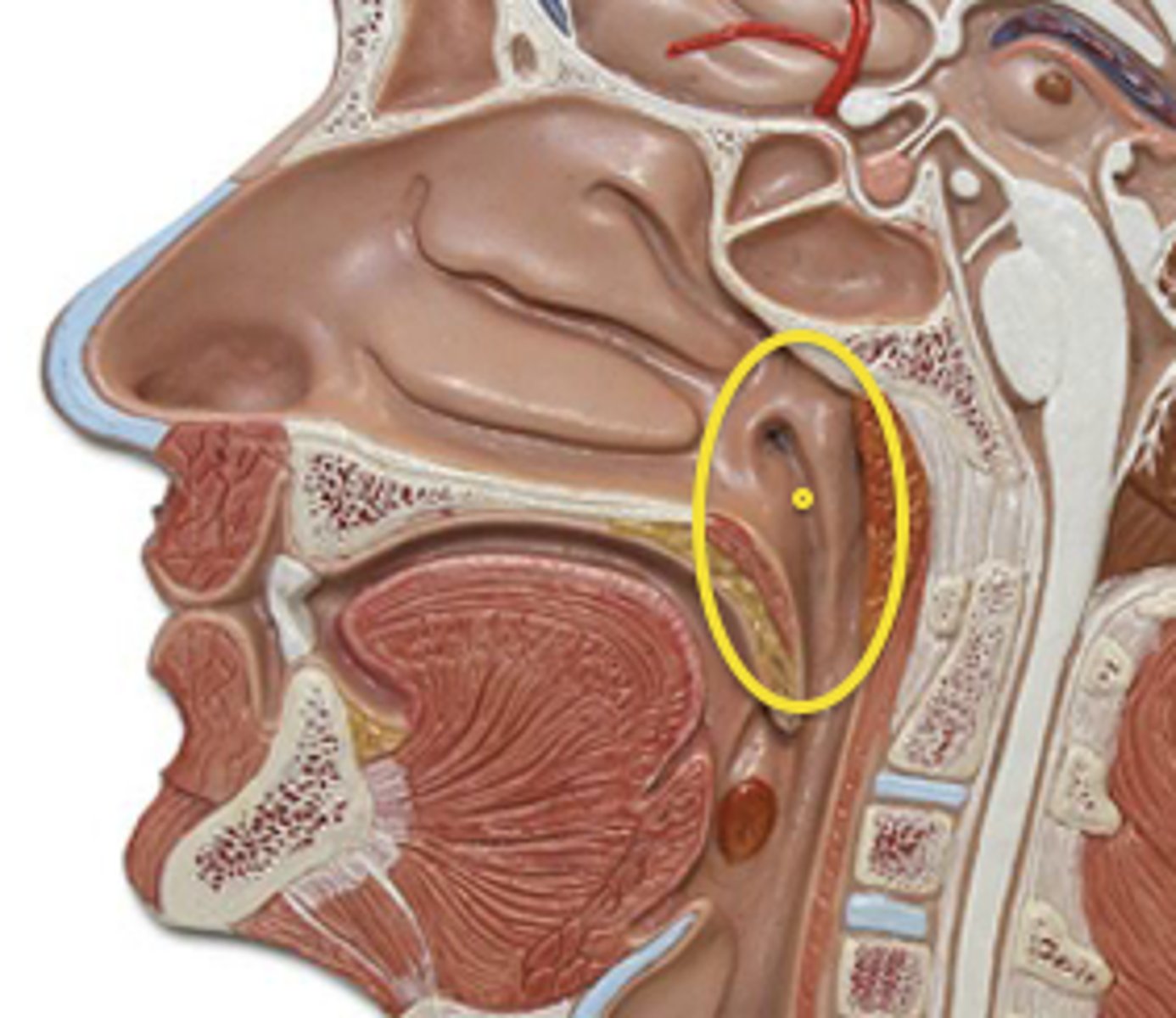
Pharyngeal Orifice of Pharyngotympanic Tube
The base of the cartilaginous portion of the auditory tube
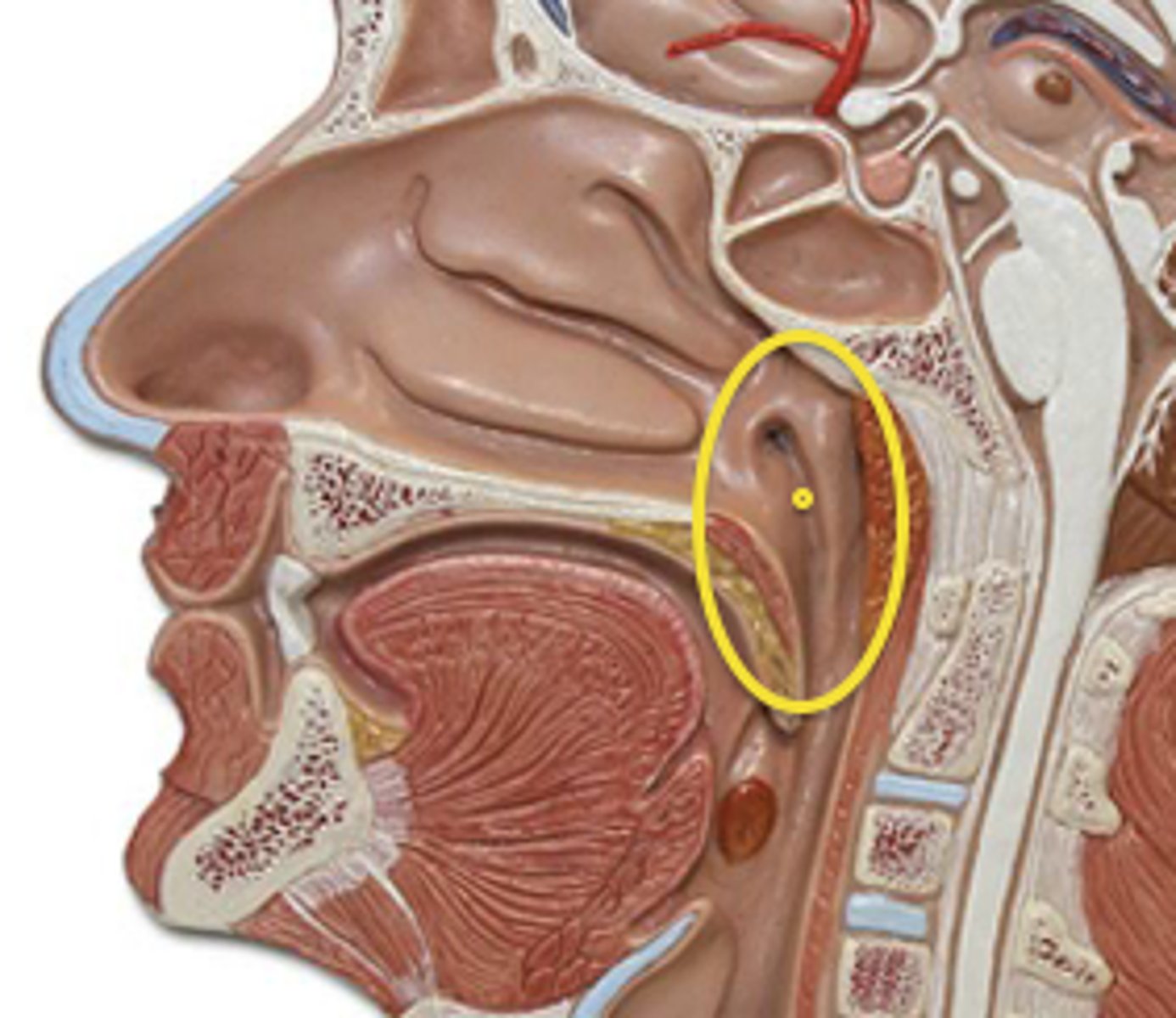
Oropharynx
Central portion of the pharynx between the roof of the mouth and the upper edge of the epiglottis
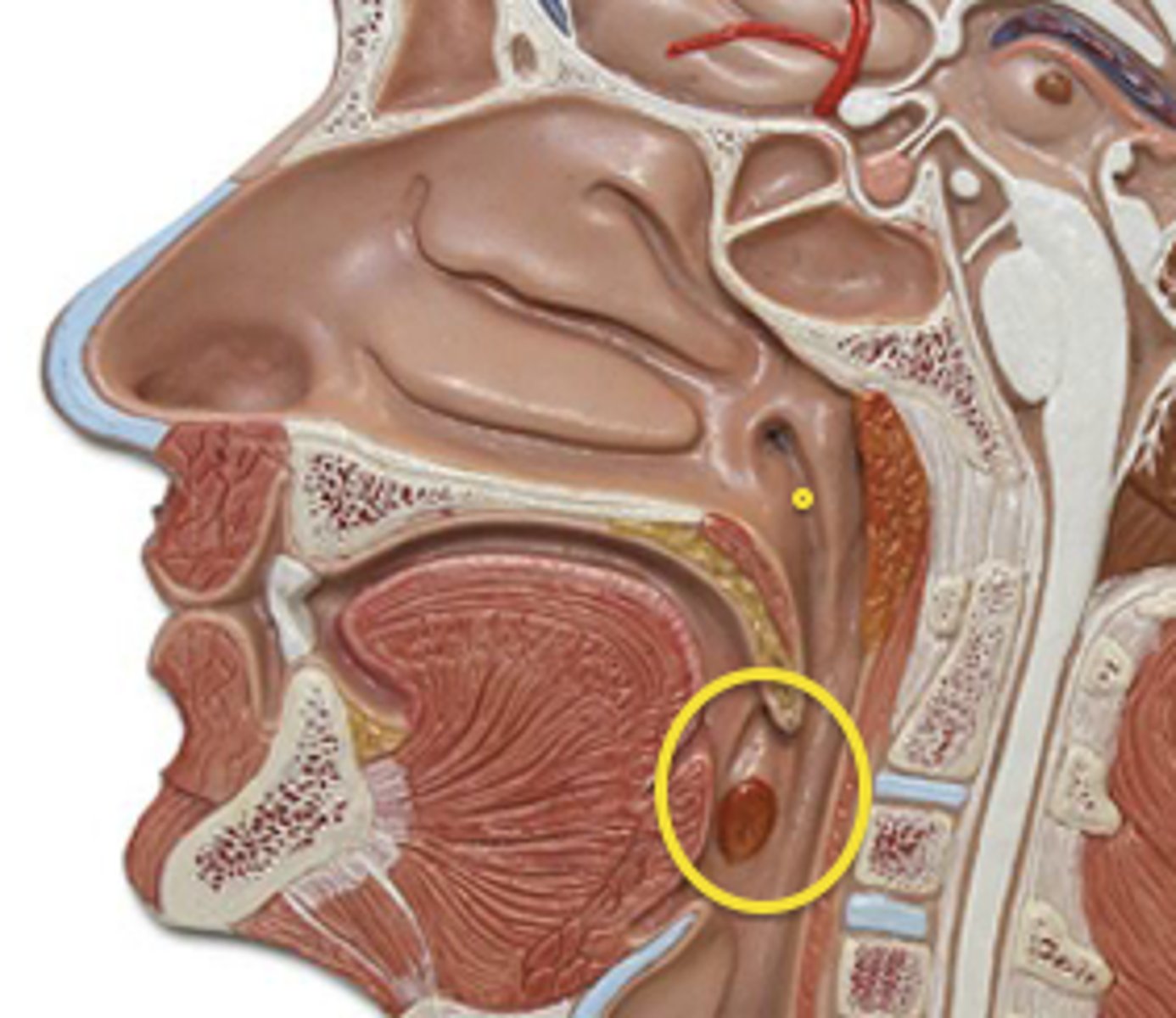
Laryngopharynx
Lower part of the pharynx, just below the oropharyngeal opening into the larynx and esophagus
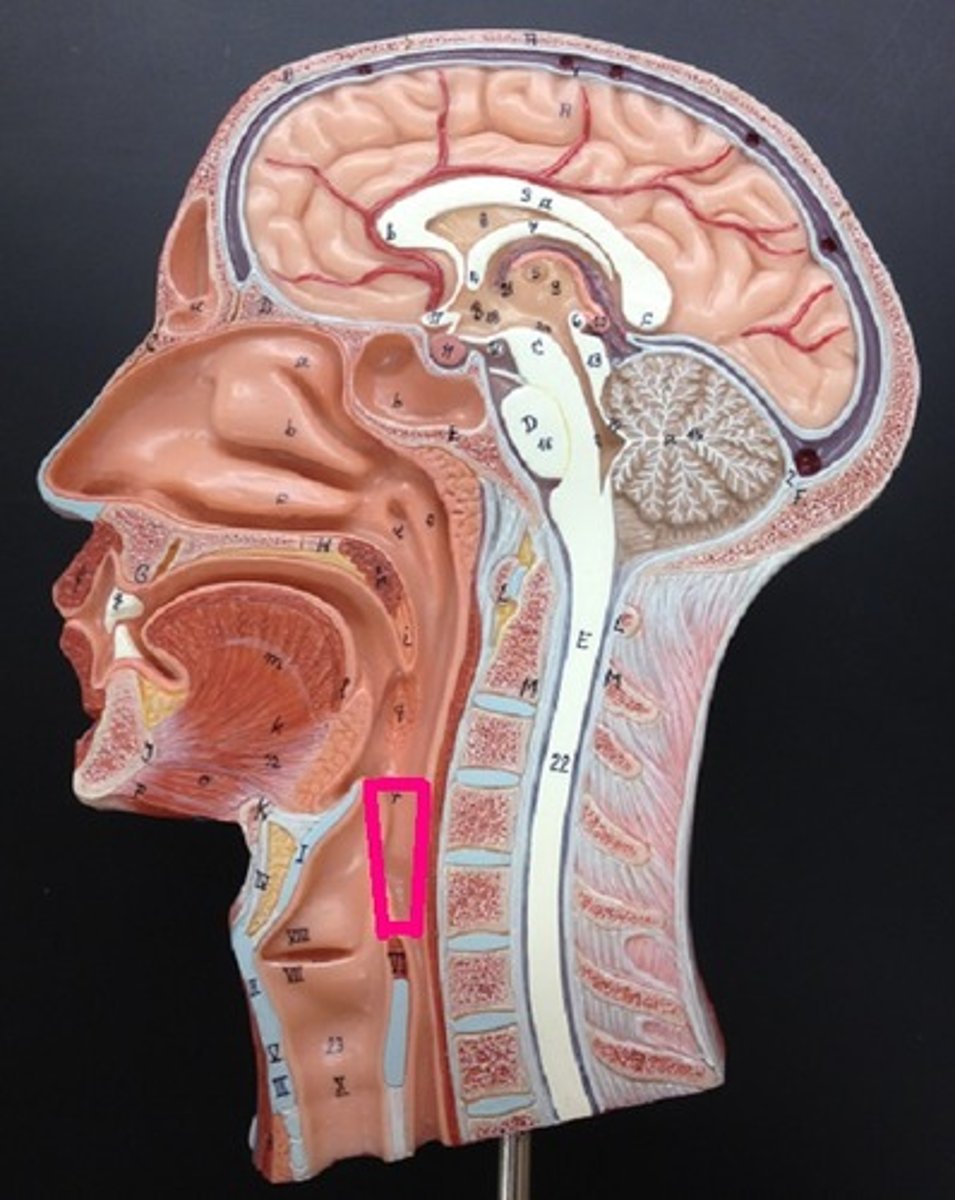
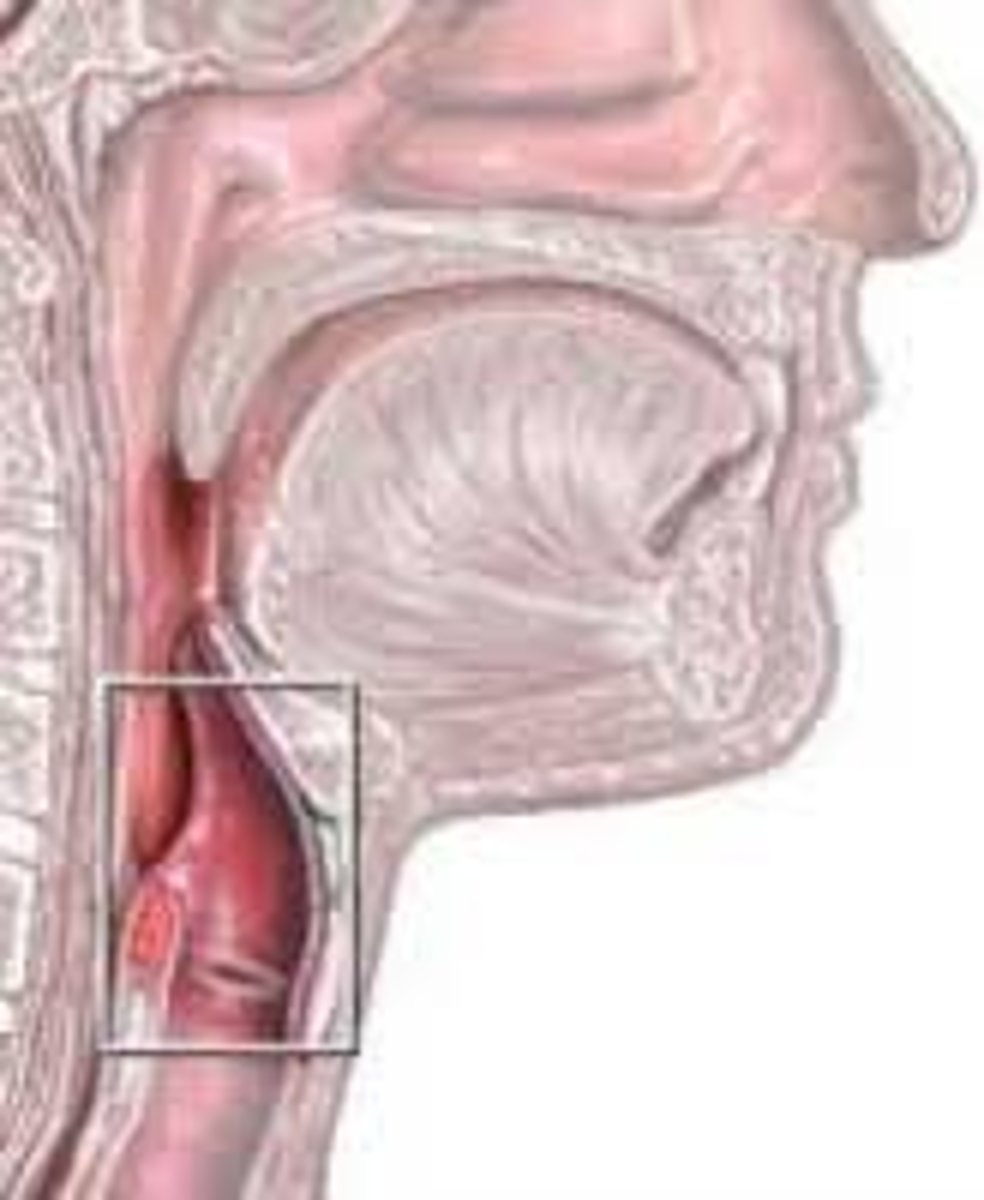
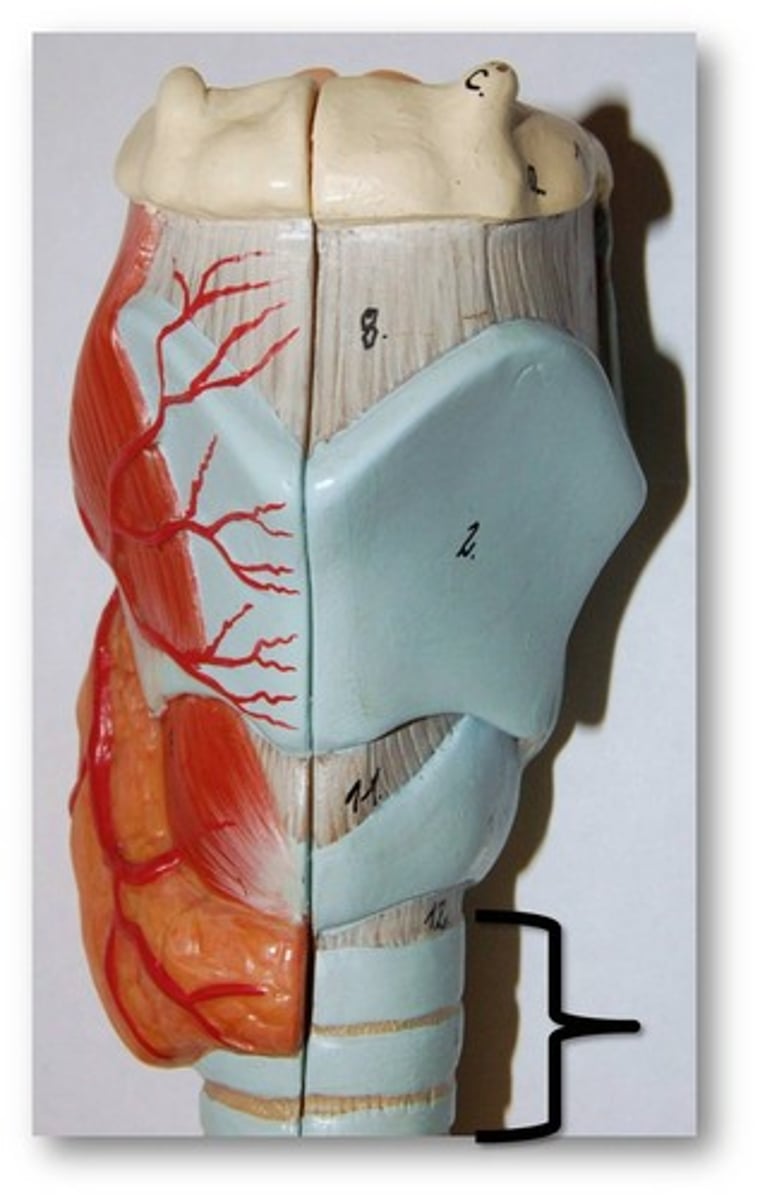
Larynx
Voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
Laryngeal Cartilages
Largely construct the larynx (voice box)
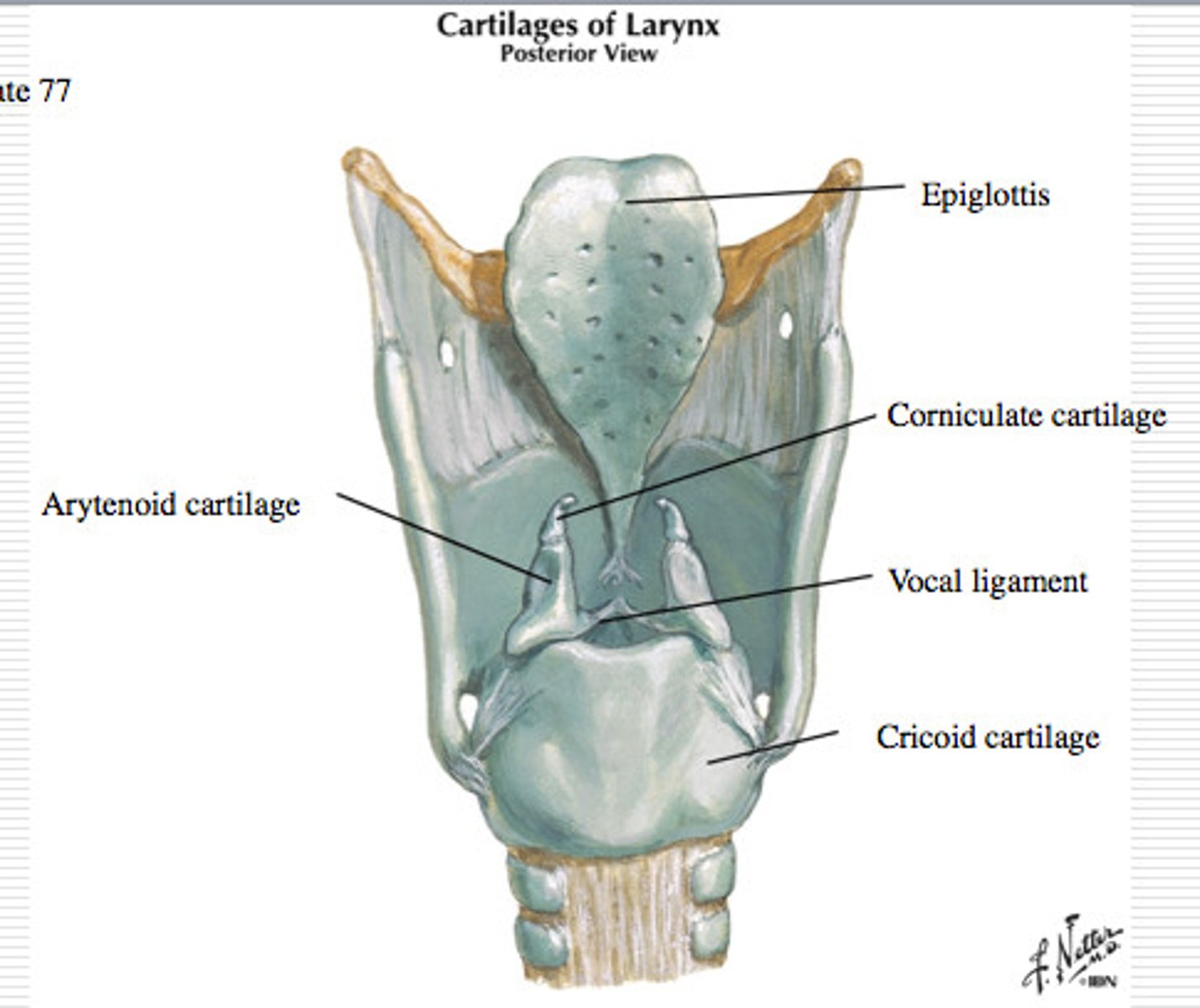
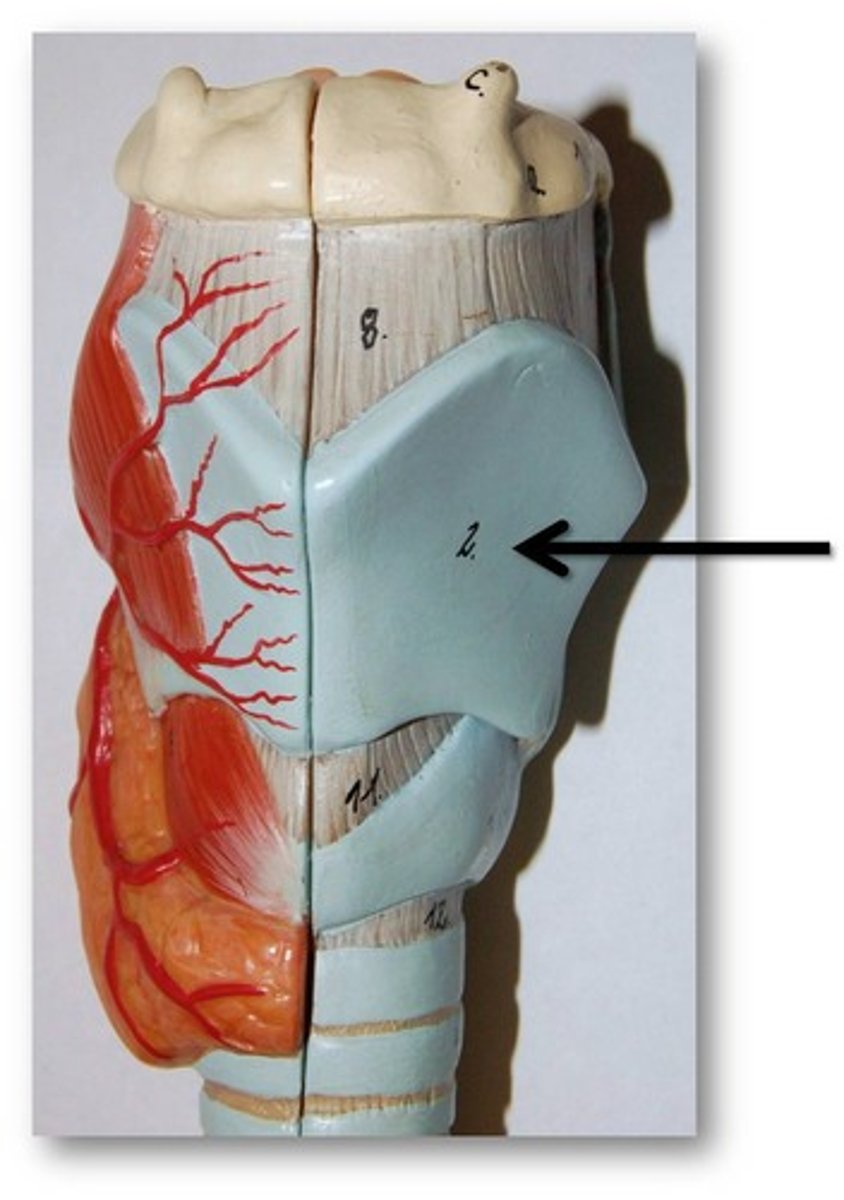
Thyroid Cartilage
A firm prominence of cartilage that forms the upper part of the larynx; the Adam's apple
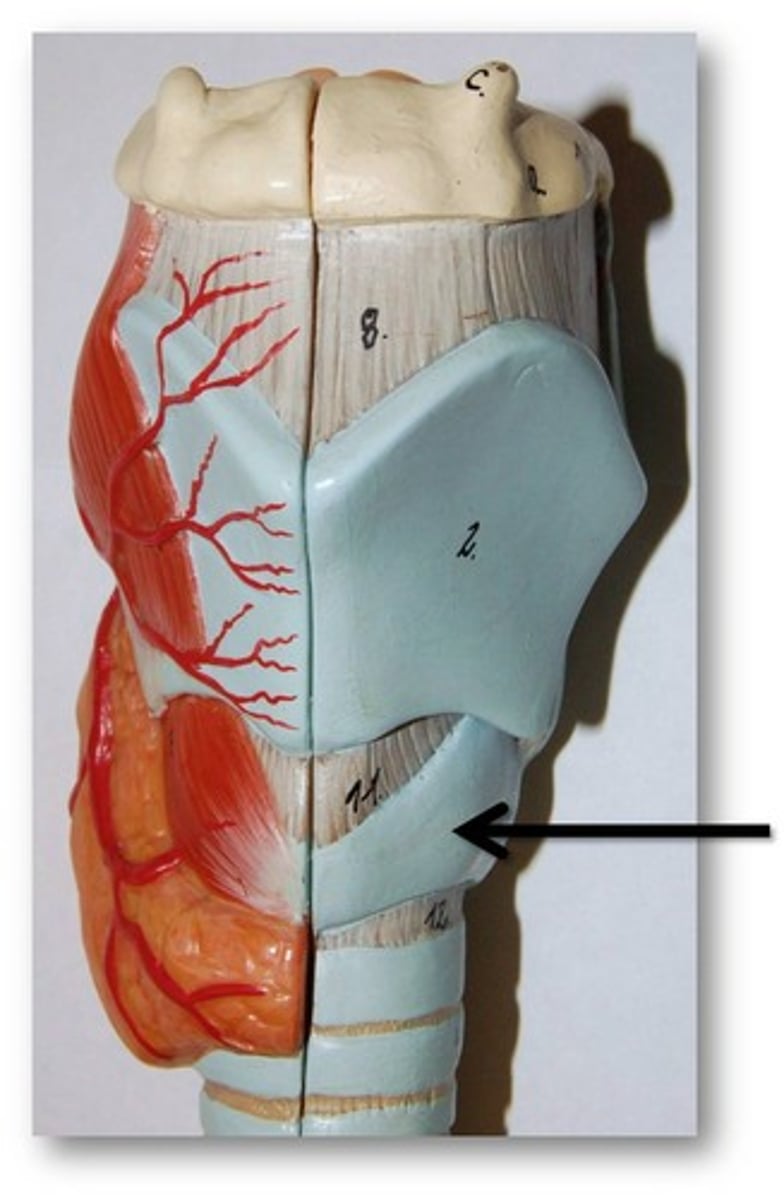
Cricoid Cartilage
The ring-shaped structure that forms the lower portion of the larynx
Vocal Folds
Mucosal folds that function in voice production (speech); also called the true vocal cords.
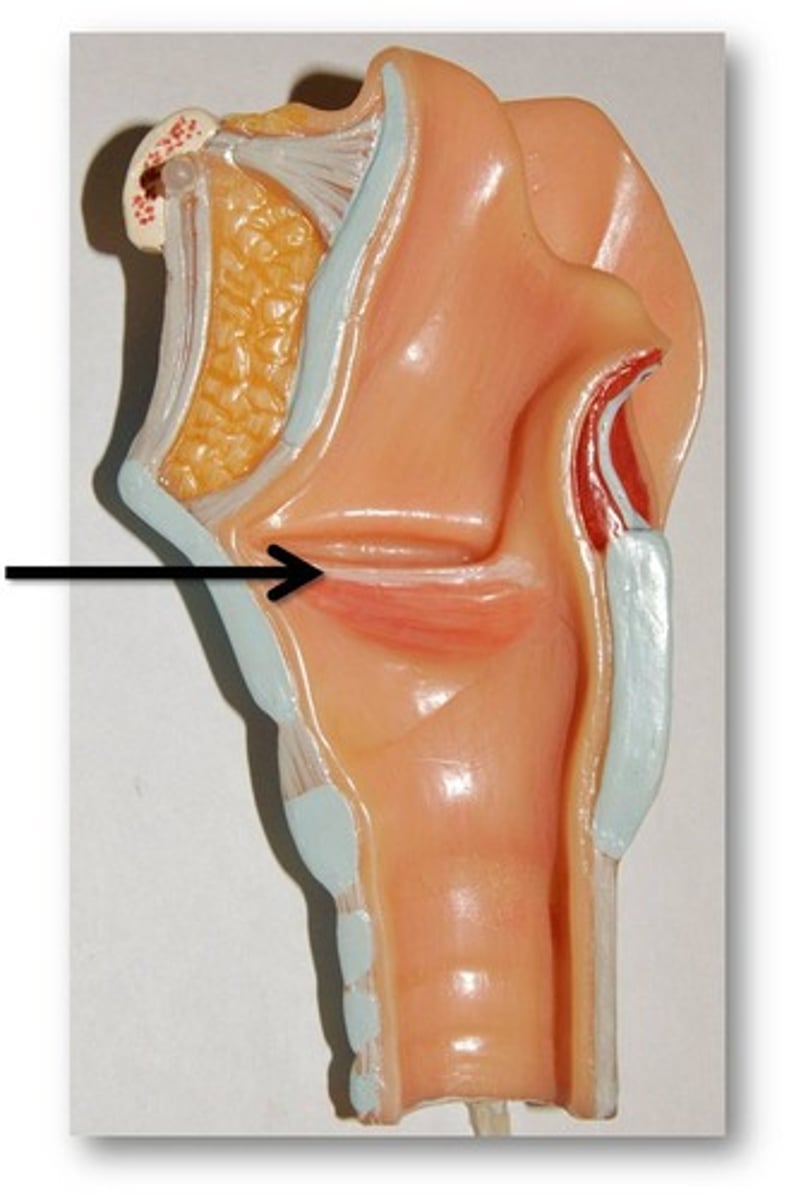
Epiglottis
A flap of cartilage at the root of the tongue, which is depressed during swallowing to cover the opening of the windpipe
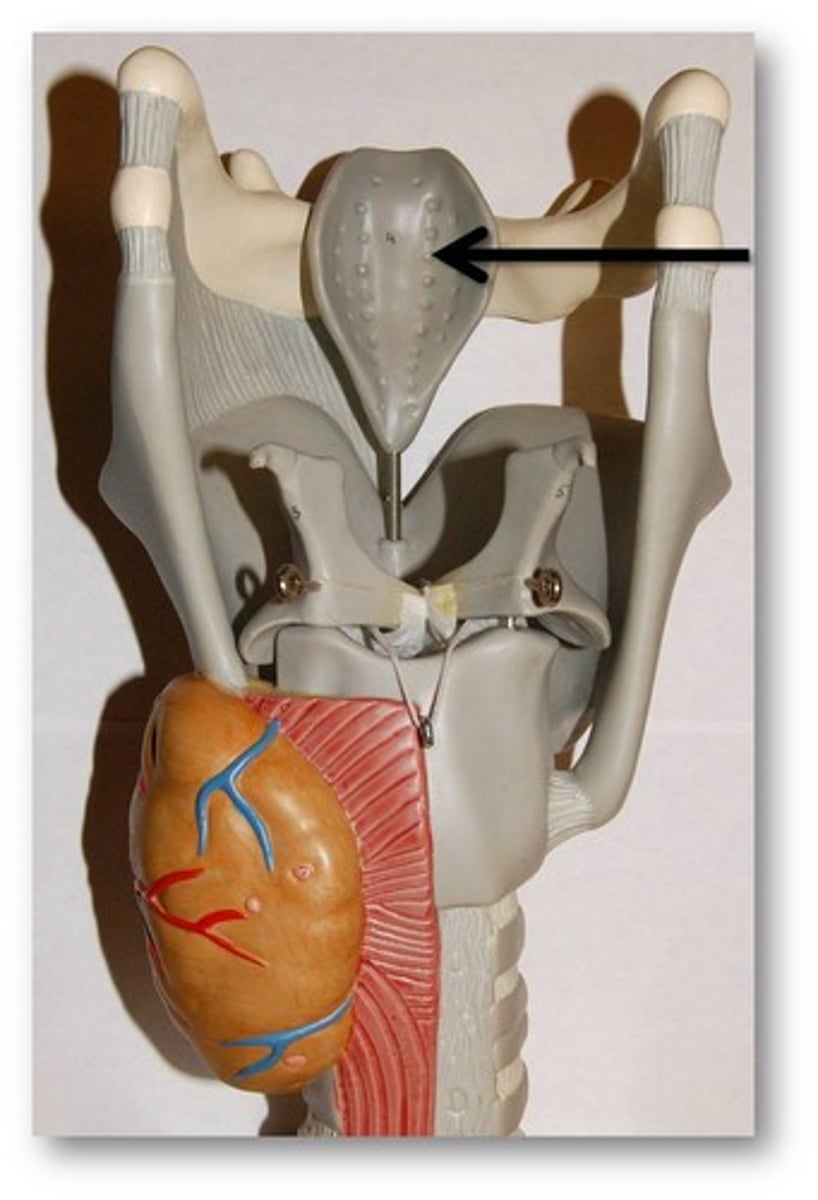
Trachea
A large membranous tube reinforced by rings of cartilage, extending from the larynx to the bronchial tubes and conveying air to and from the lungs; the windpipe.
Occipitofrontalis
A muscle which covers parts of the skull. It consists of two parts or bellies: The occipital belly, near the occipital bone, and the frontal belly, near the frontal bone.
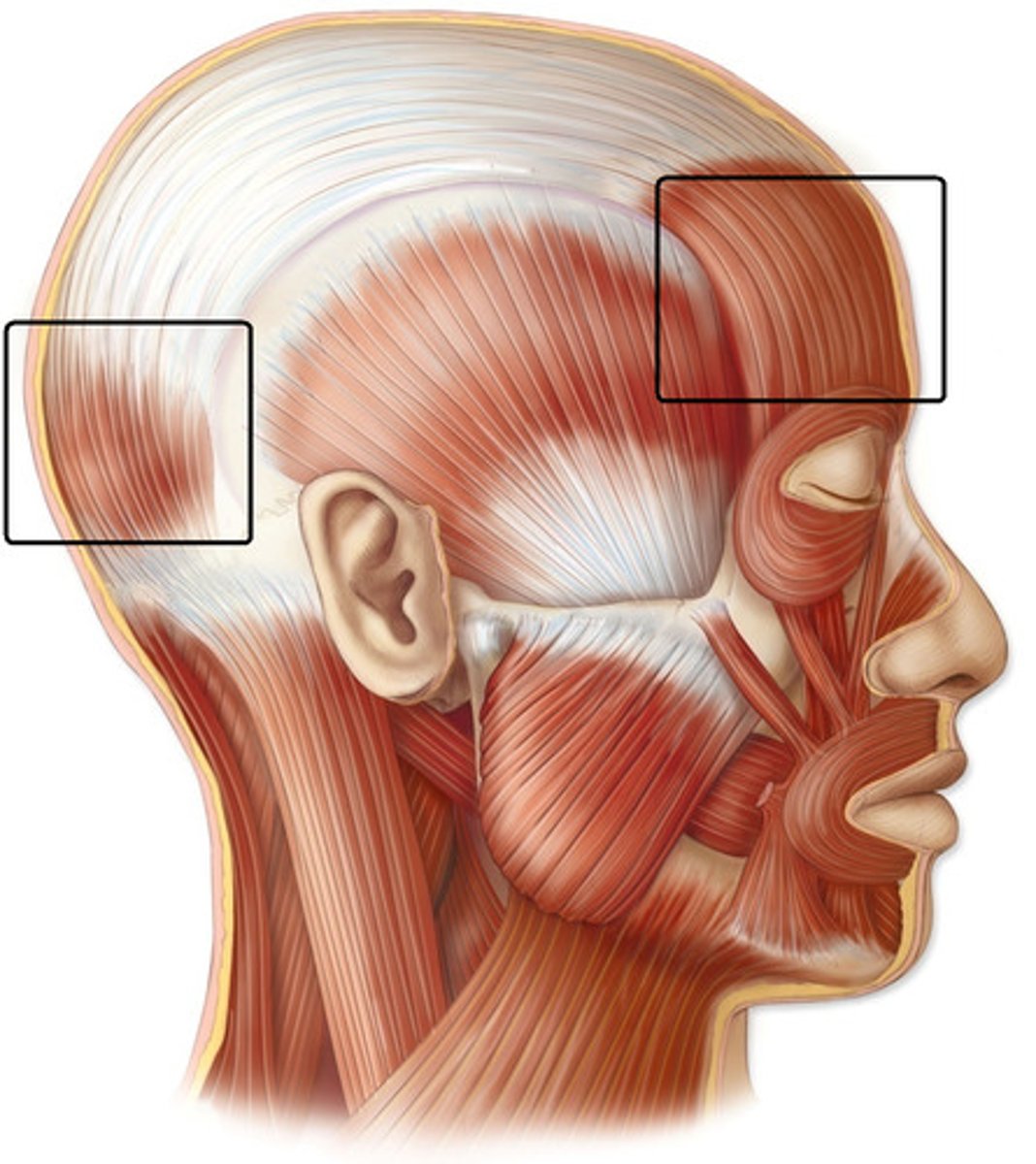
Orbicularis Oculi
A muscle in the face that closes the eyelids. It arises from the nasal part of the frontal bone.
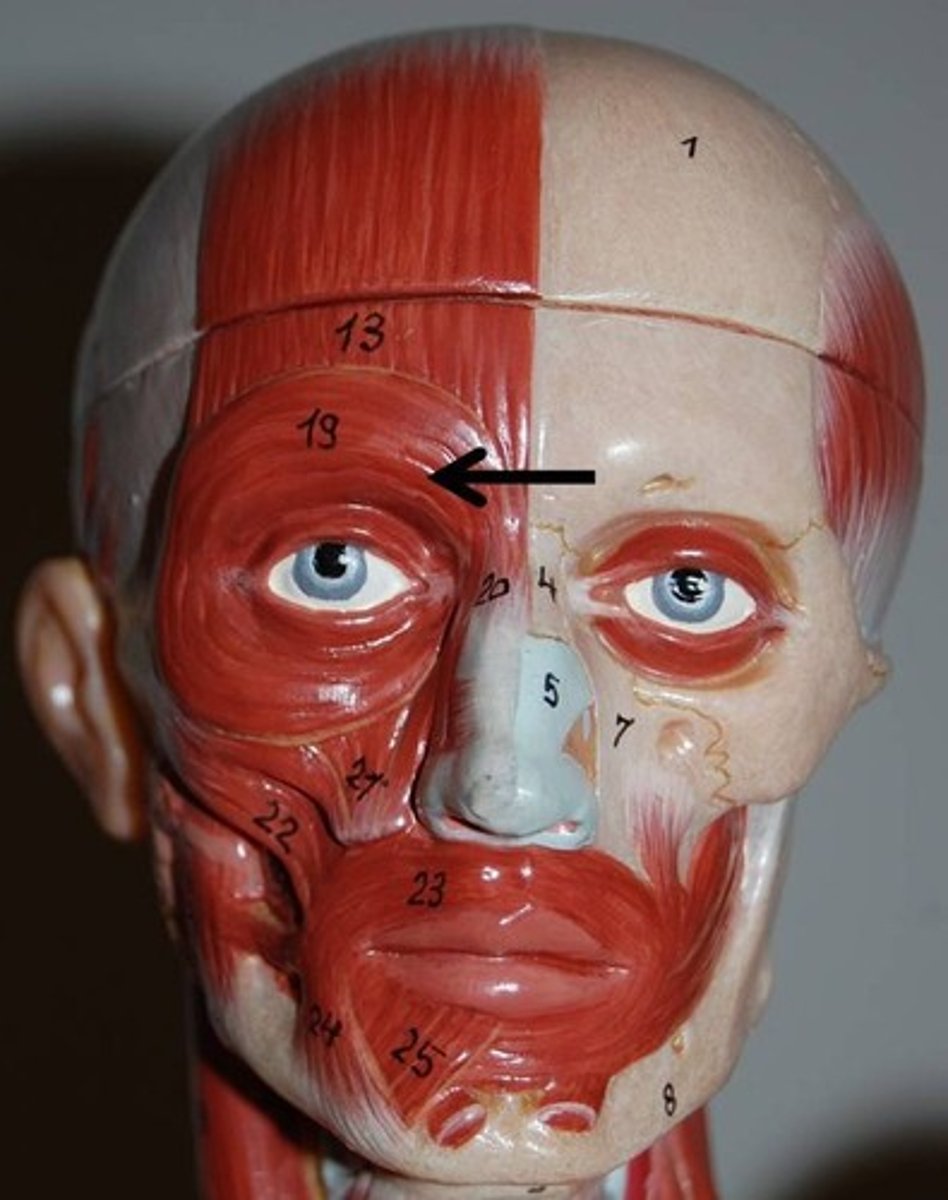
Levator Labii Superioris
A muscle of the human body used in facial expression. It is a broad sheet, the origin of which extends from the side of the nose to the zygomatic bone.
Zygomaticus Major
A muscle of facial expression which draws the angle of the mouth superiorly and posteriorly to allow one to smile. Extends from each zygomatic arch to the corners of the mouth.
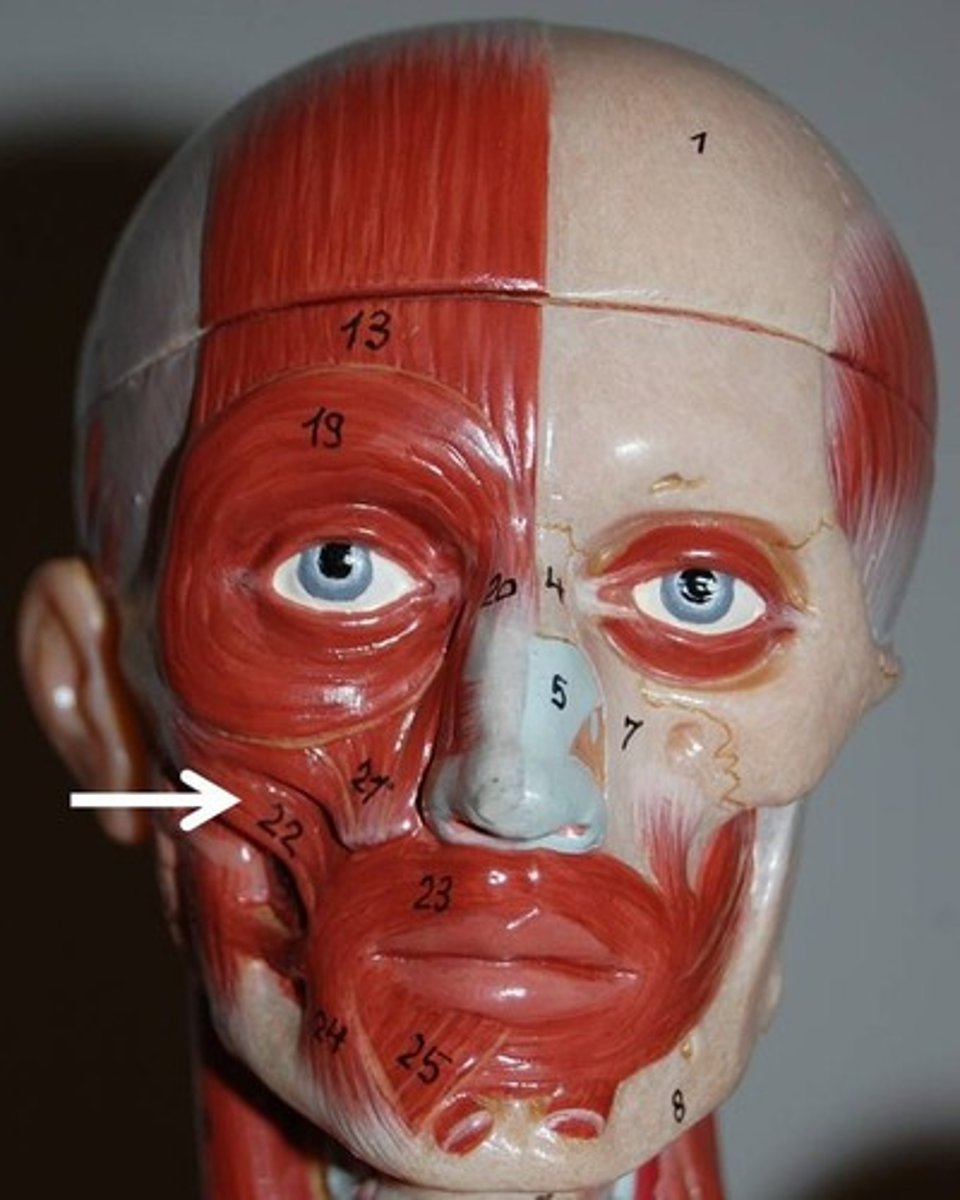
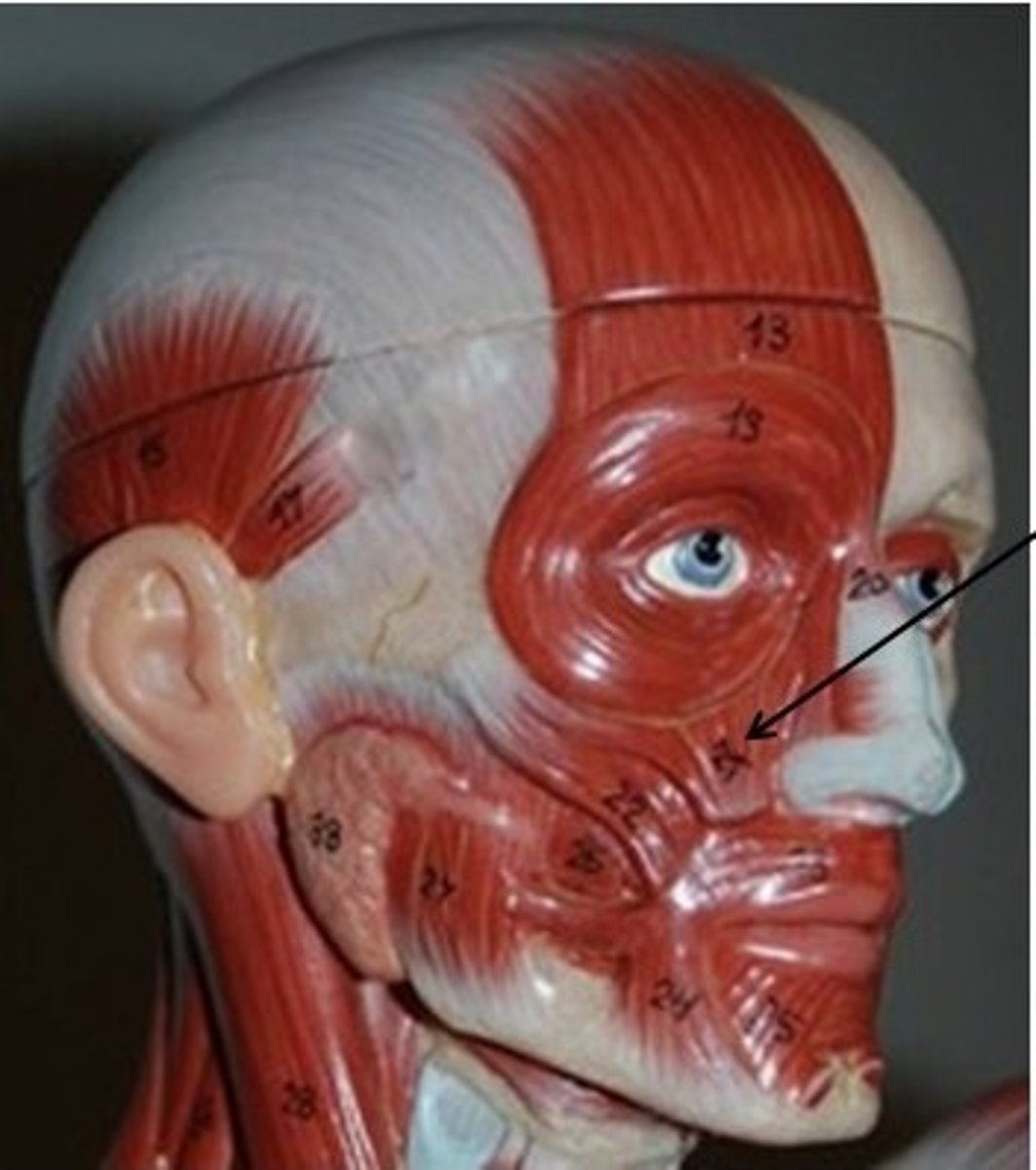
Buccinator
A flat, thin muscle in the wall of the cheek
Orbicularis Oris
Consists of numerous strata of muscular fibers surrounding the orifice of the mouth, but having different direction
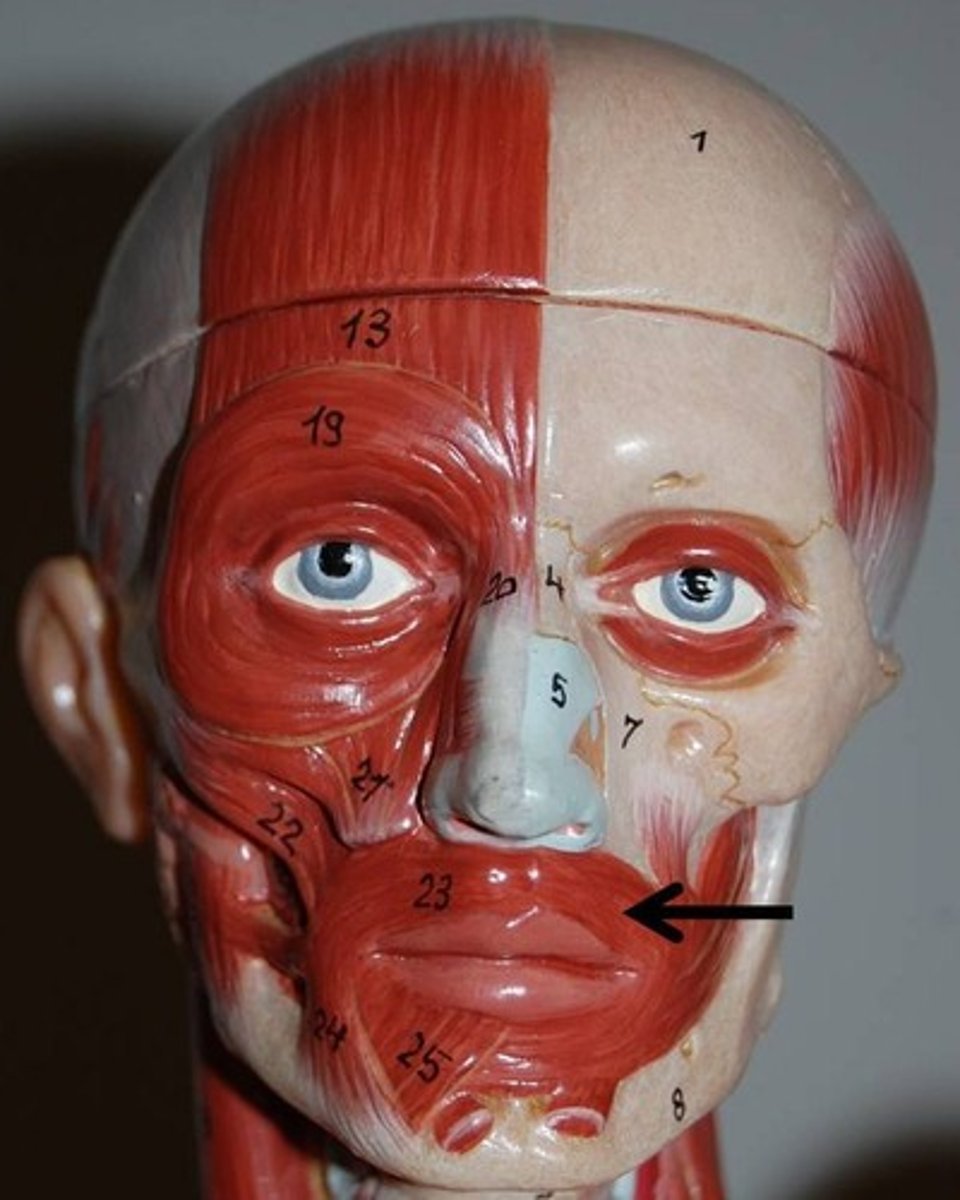
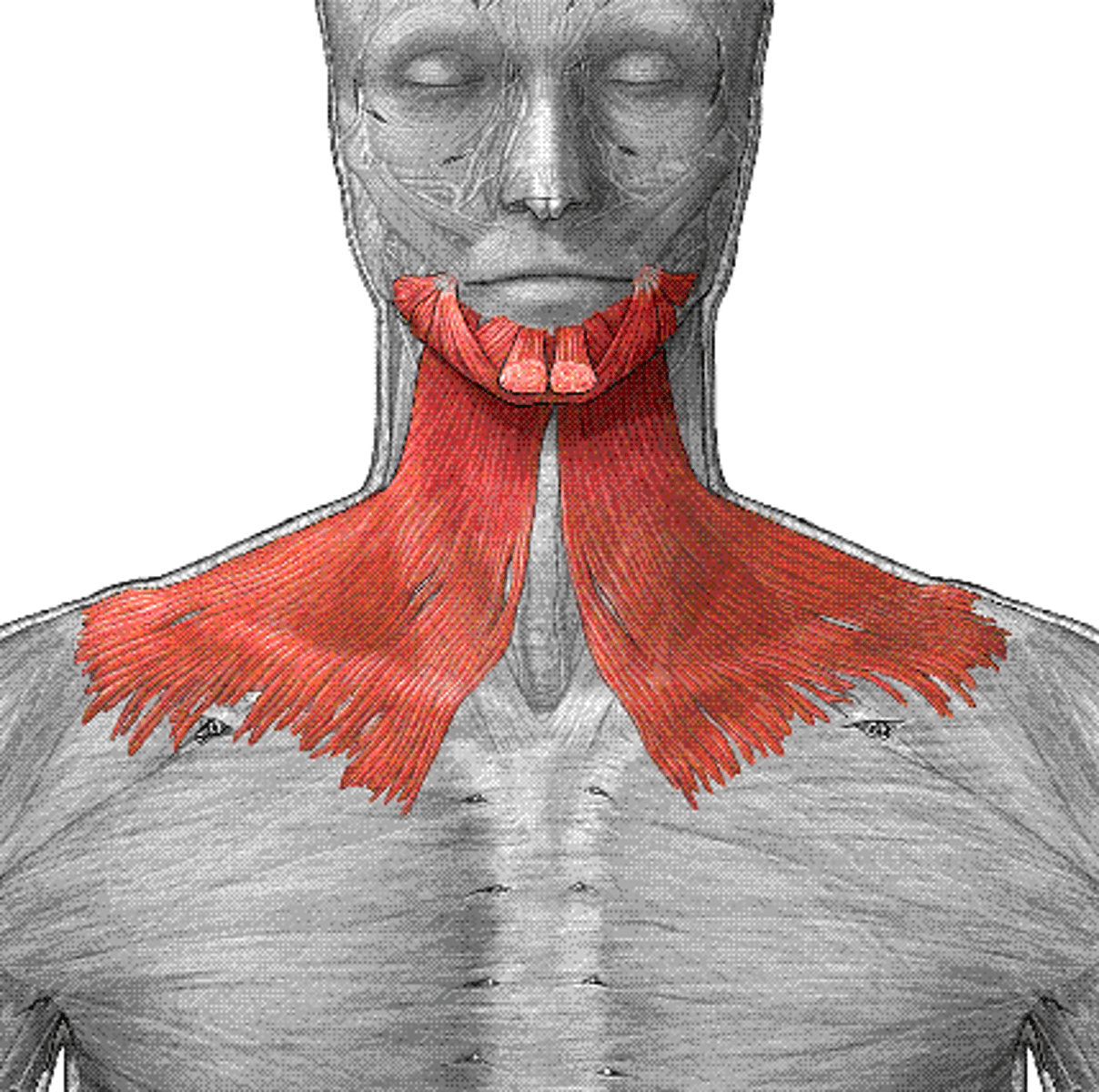
Platysma
A broad sheet of muscle fibers extending from the collarbone to the angle of the jaw
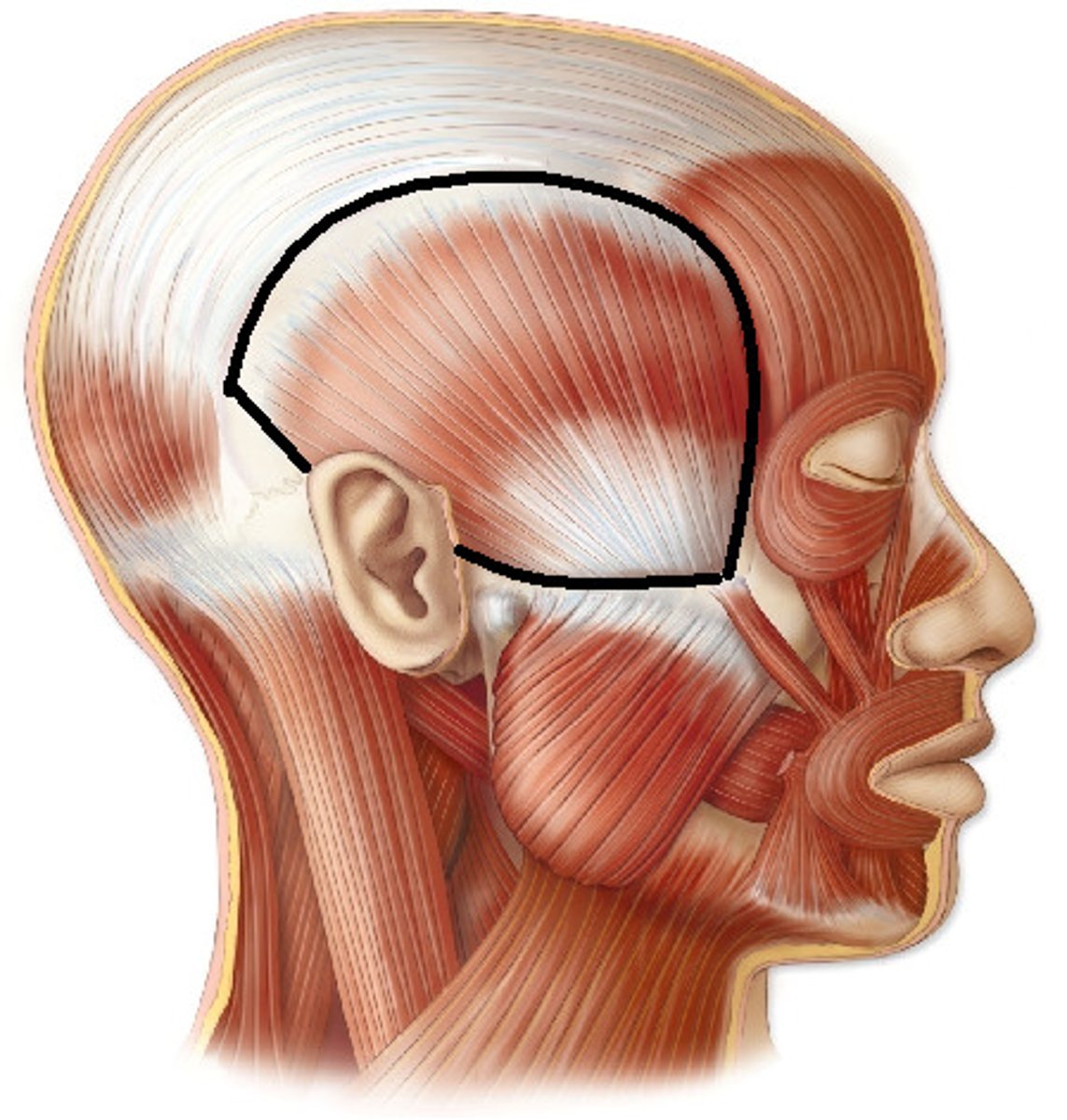
Temporalis
A broad, fan-shaped muscle on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomatic arch so it covers much of the temporal bone
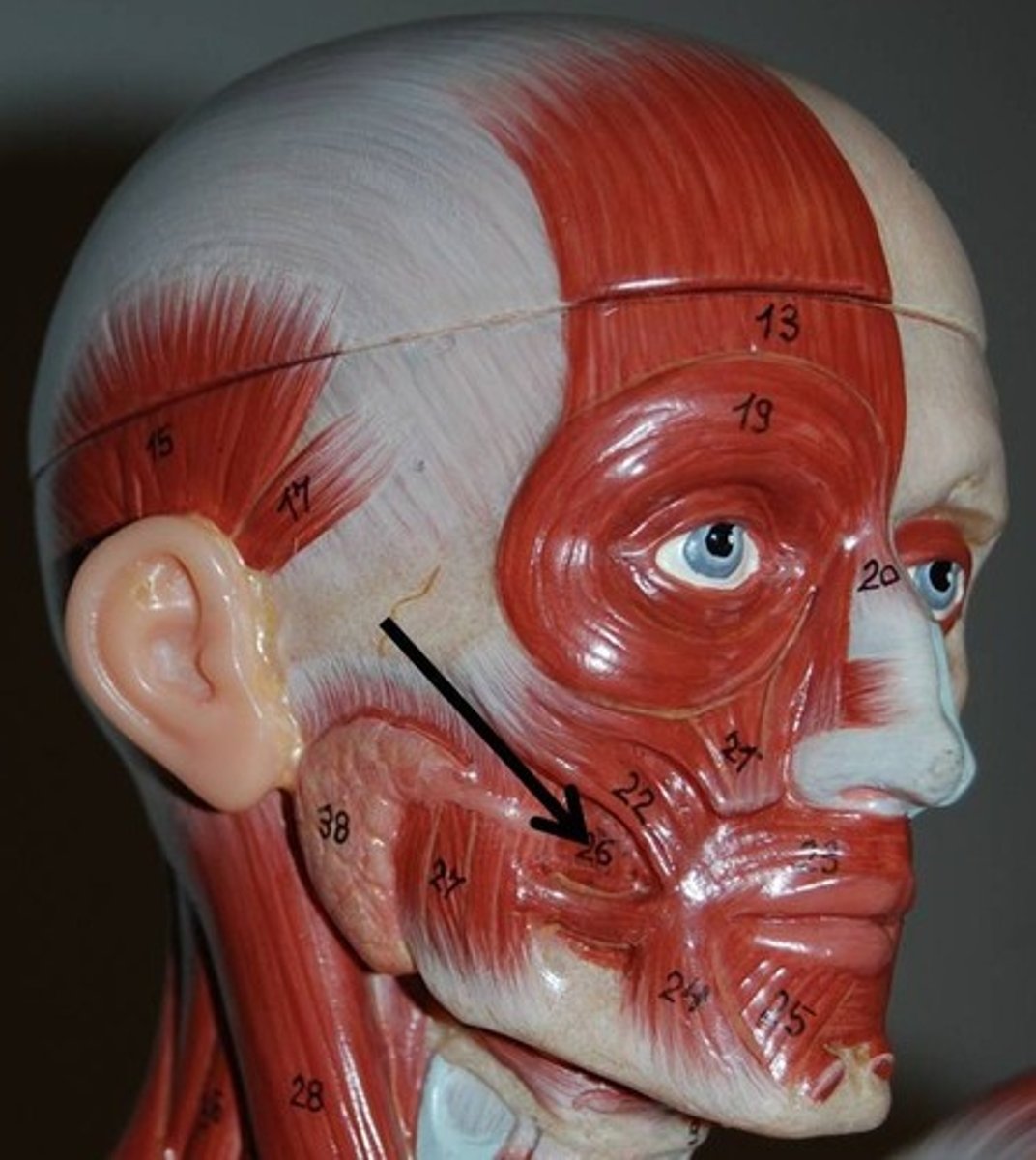
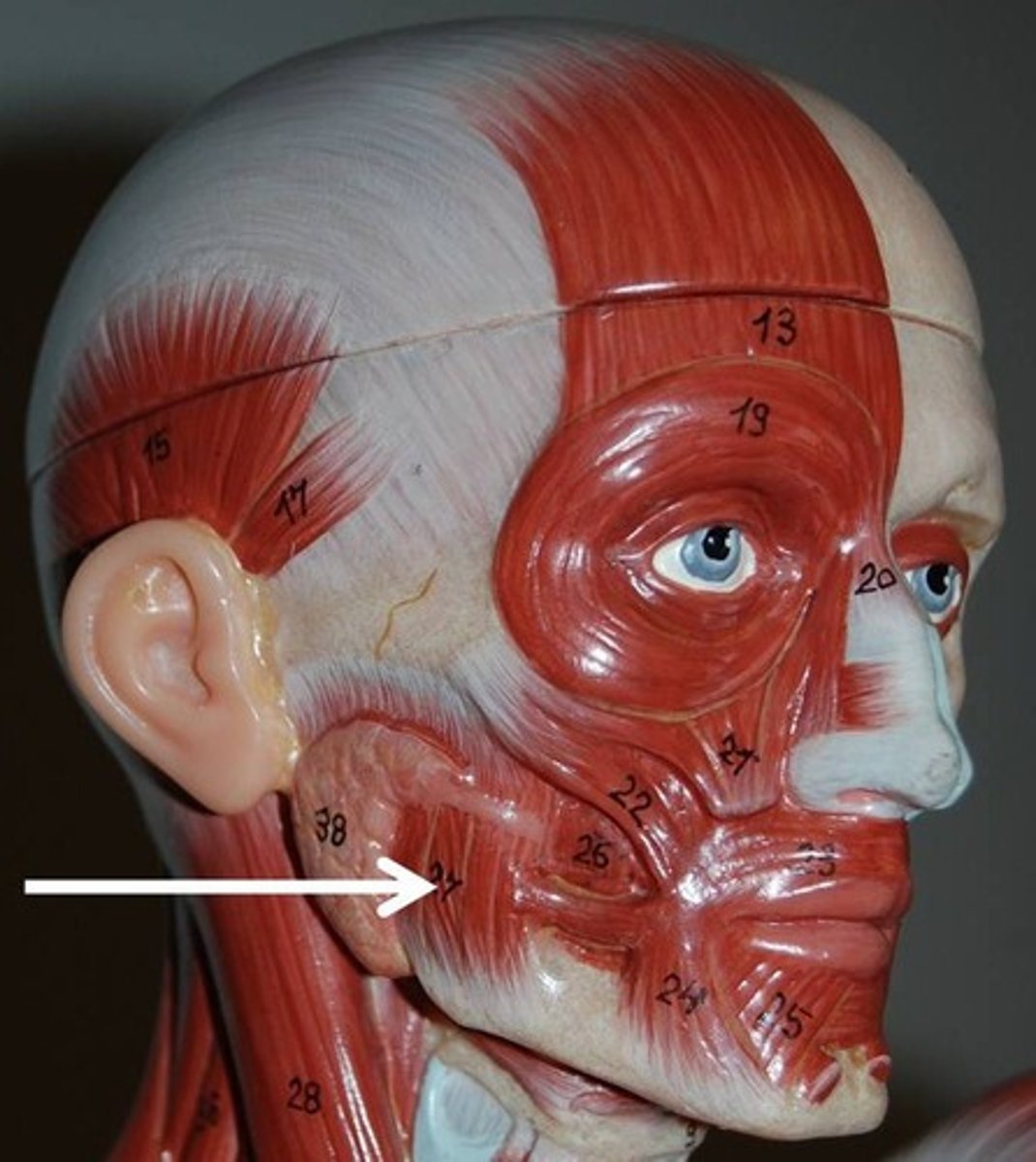
Masseter
A paired, strong, thick and rectangular muscle that is originating from the zygomatic arch down to the mandibular angle
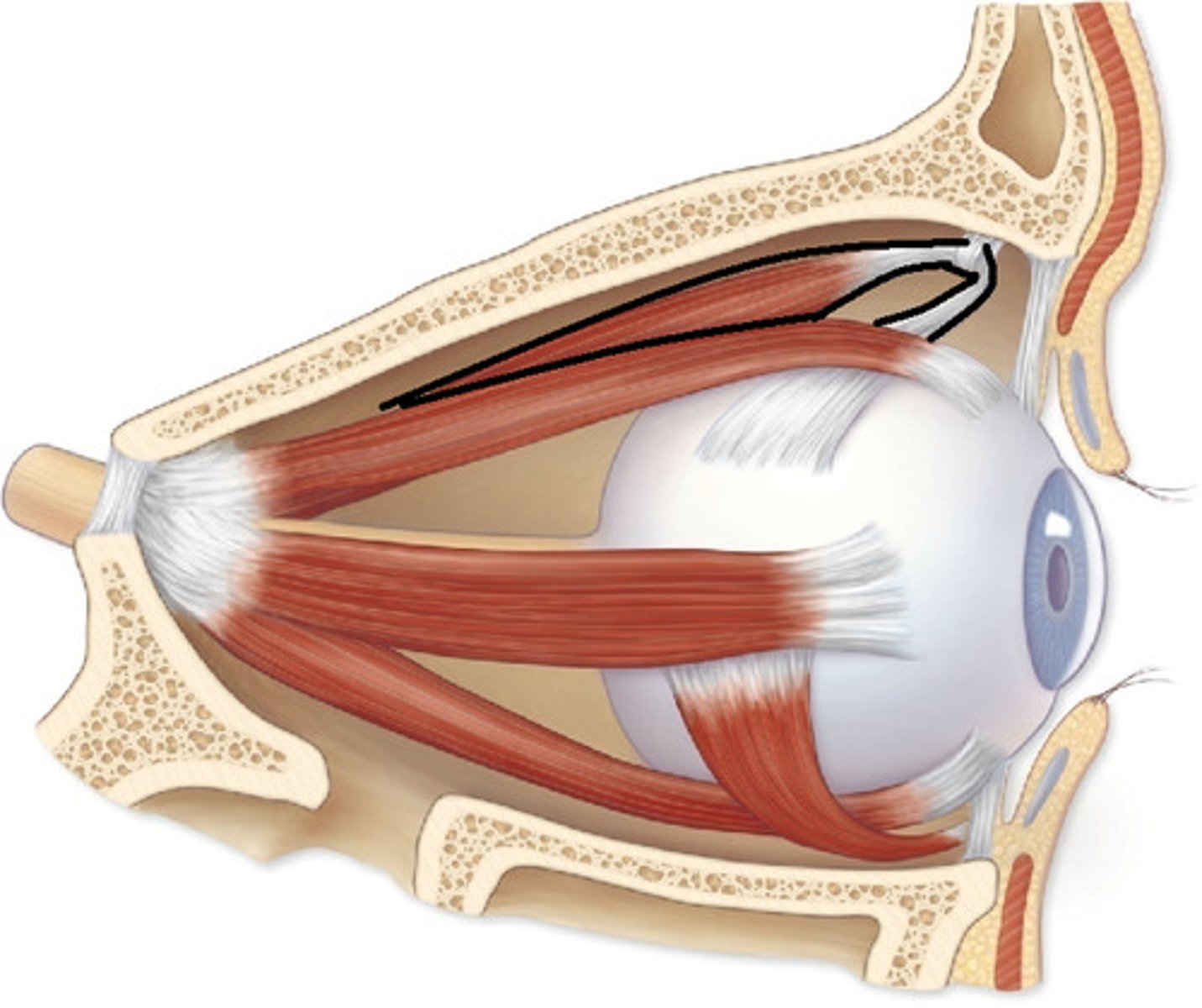
Superior Oblique
A muscle originating in the upper, medial side of the orbit which abducts, depresses and internally rotates the eye
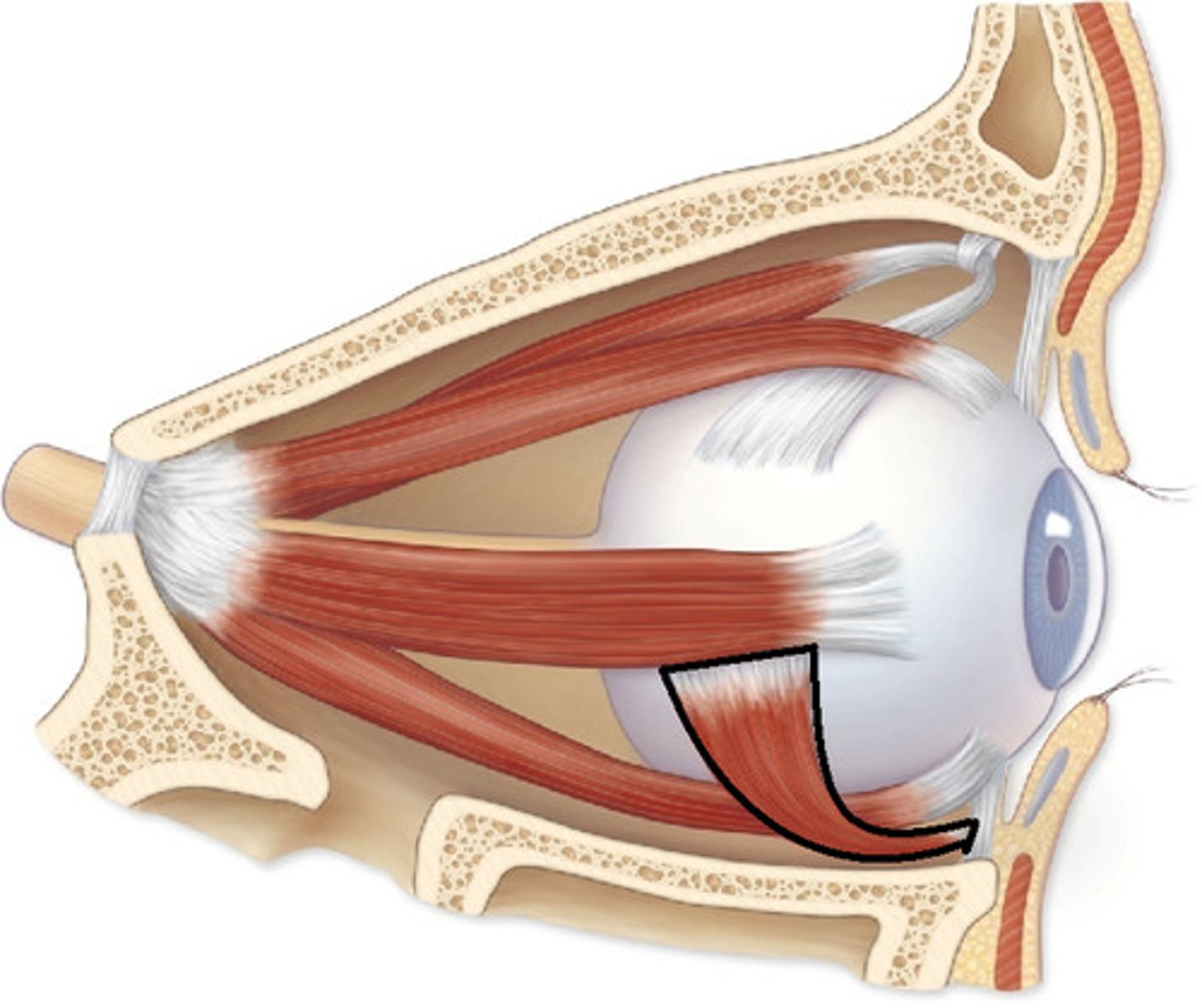
Inferior Oblique
An extraocular muscle, and is attached to the maxillary bone (origin) and the posterior, inferior, lateral surface of the eye
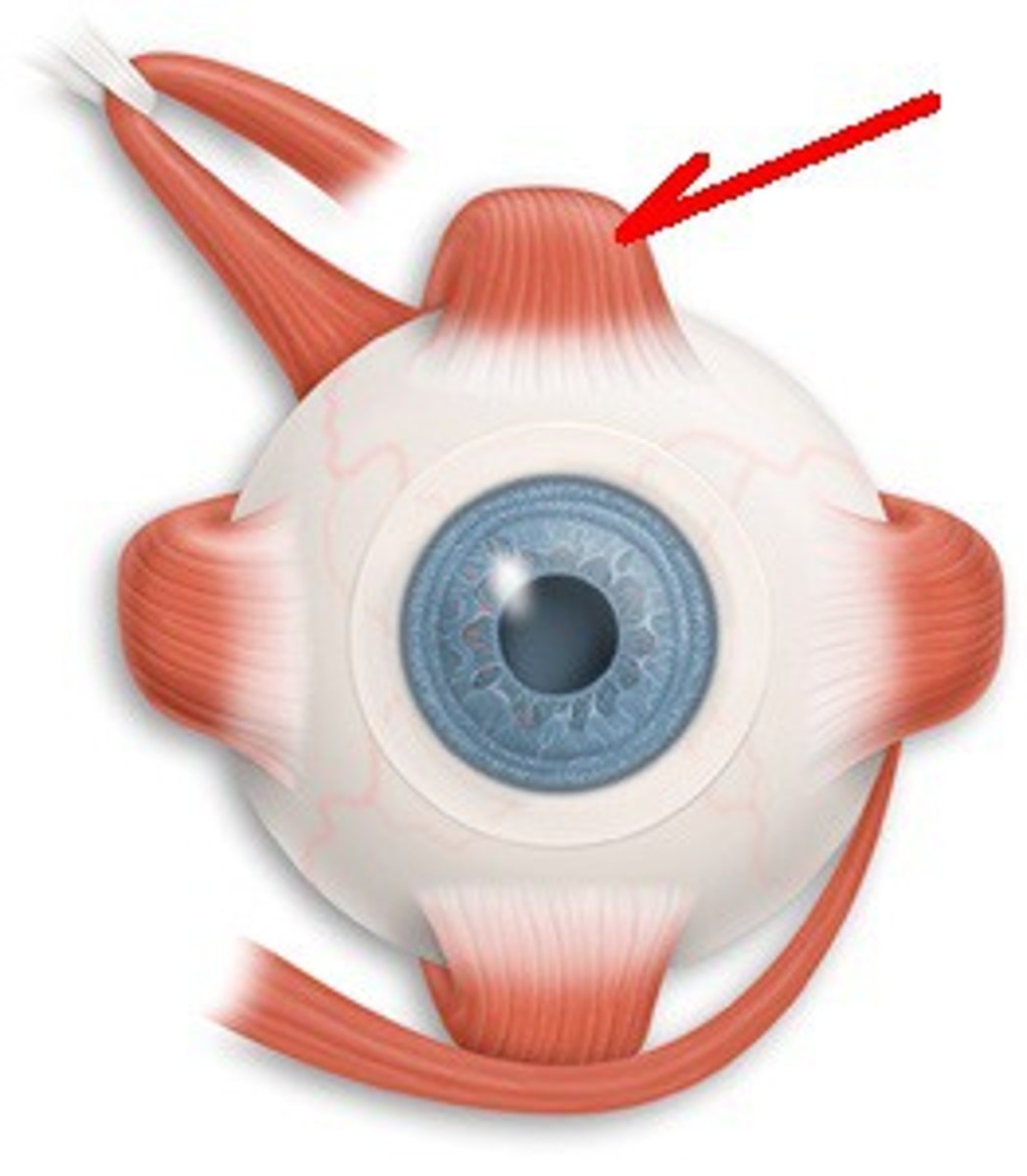
Superior Rectus
One of the extraocular muscles. It elevates, adducts, and helps intort (rotate medially) the eye.
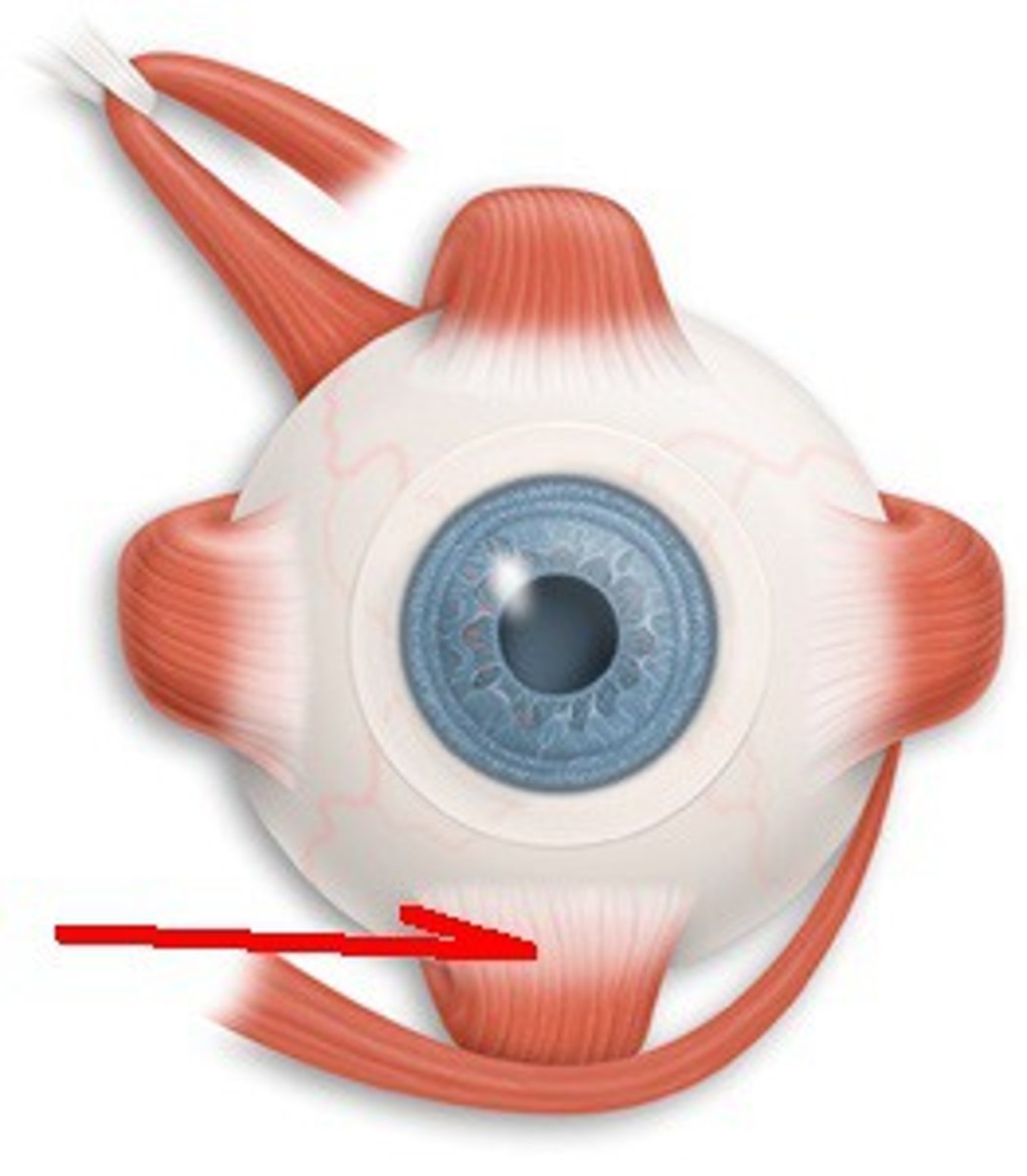
Inferior Rectus
An extraocular muscle. Depresses eye and turns it medially.
Lateral Rectus
A muscle on the lateral side of the eyeball in the orbit
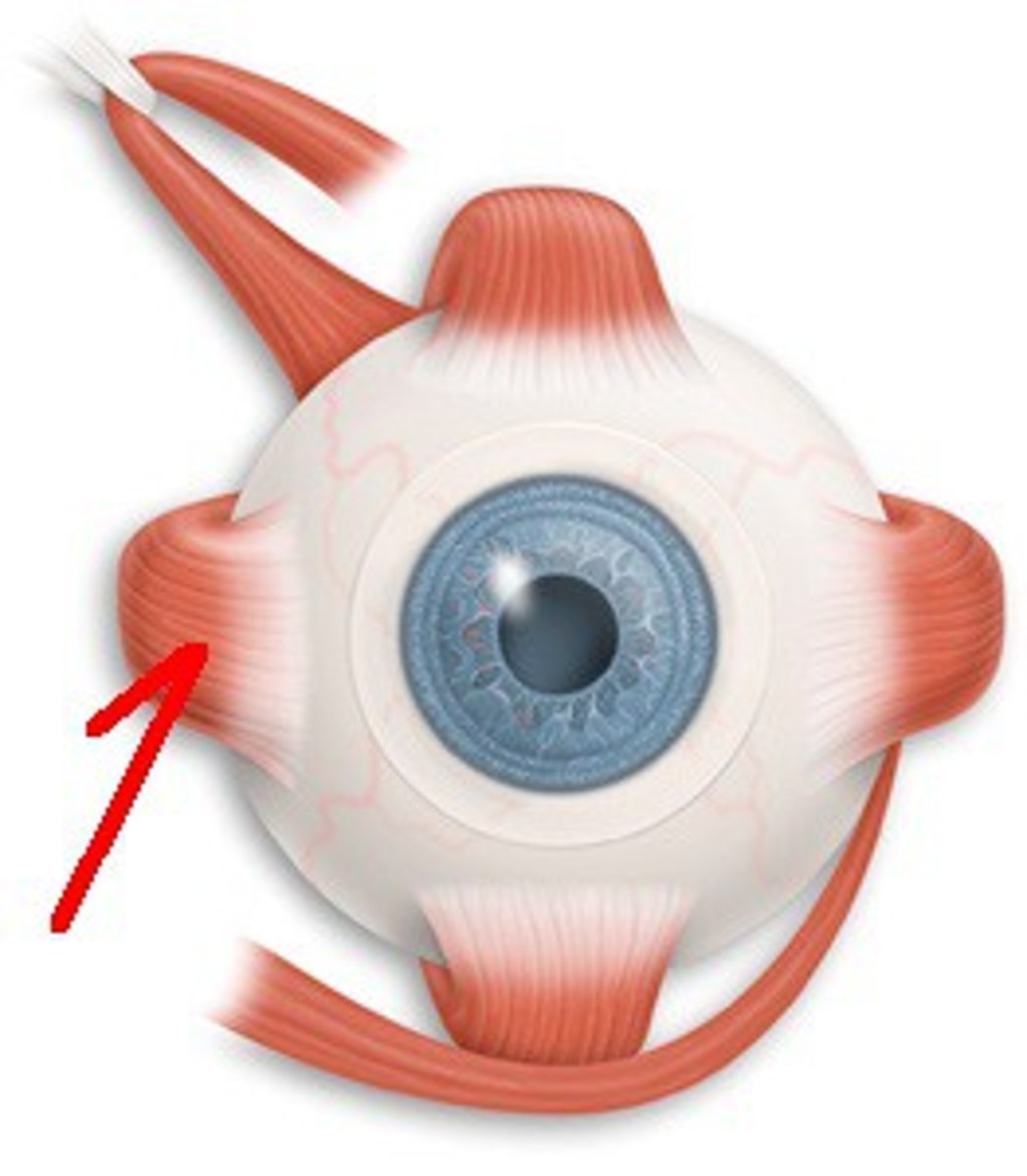
Medial Rectus
The largest of the eye's extraocular movement muscles; adducts the eyeball
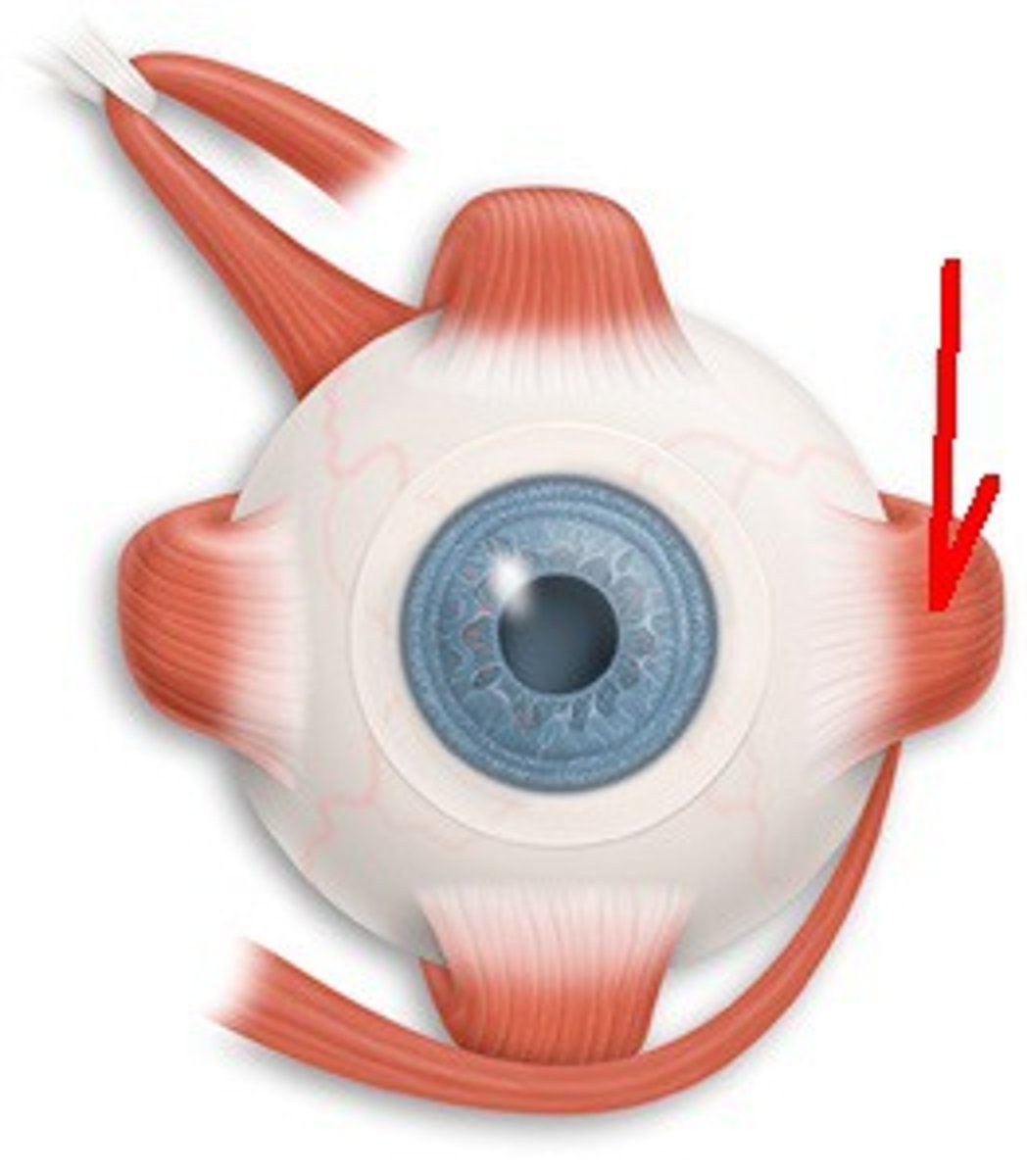
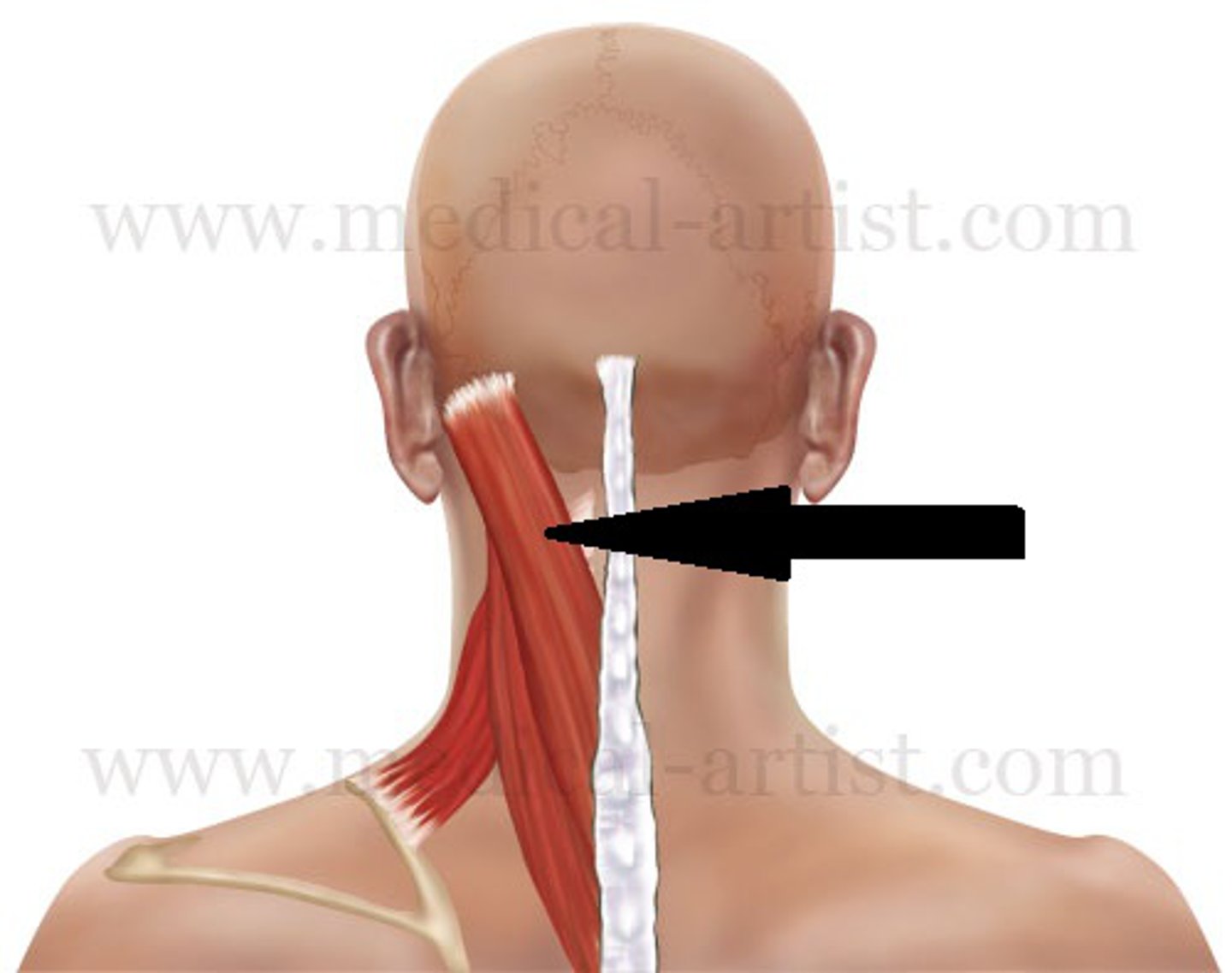
Sternocleidomastoid
Located at the base of your skull on either side of your neck, behind your ears. On both sides of your neck, each muscle runs down the front of your neck and splits to attach to the top of your sternum and collarbone.
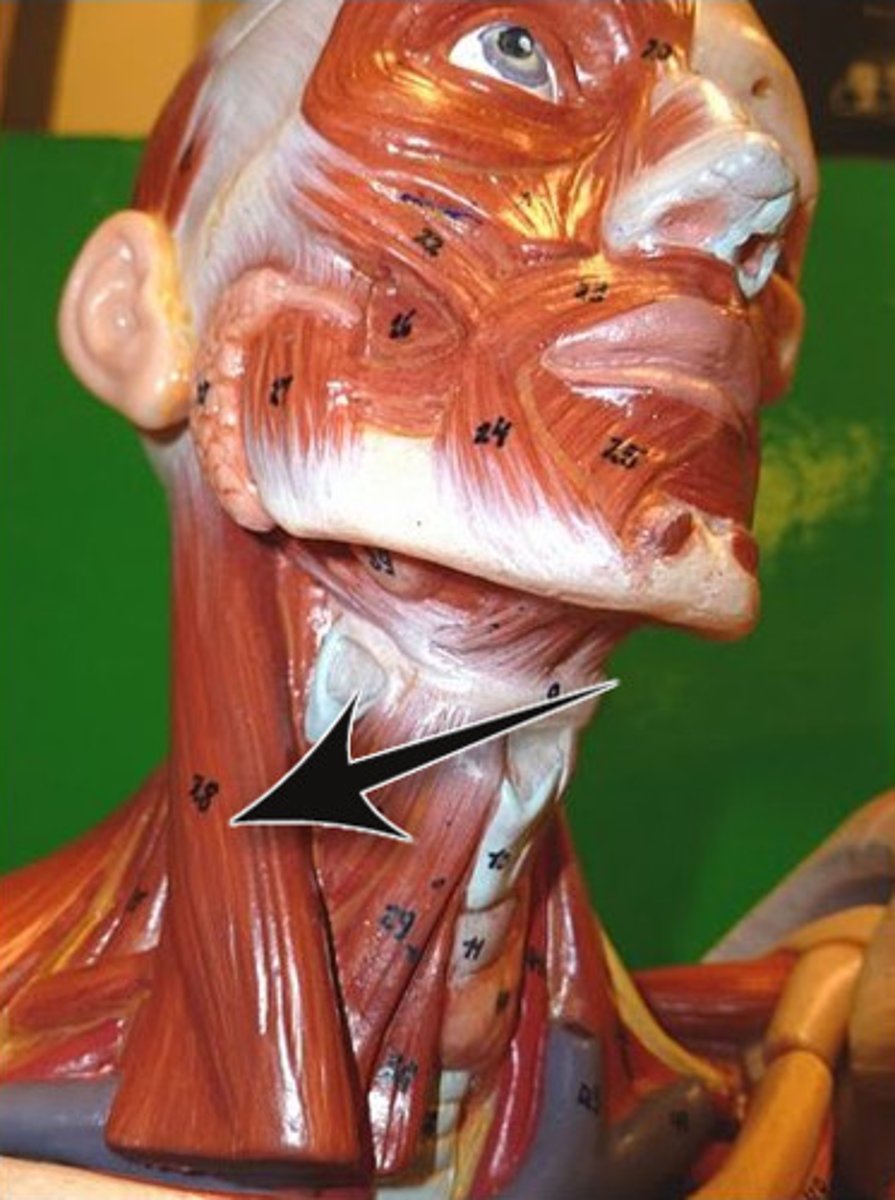
Trapezius
A large paired surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula
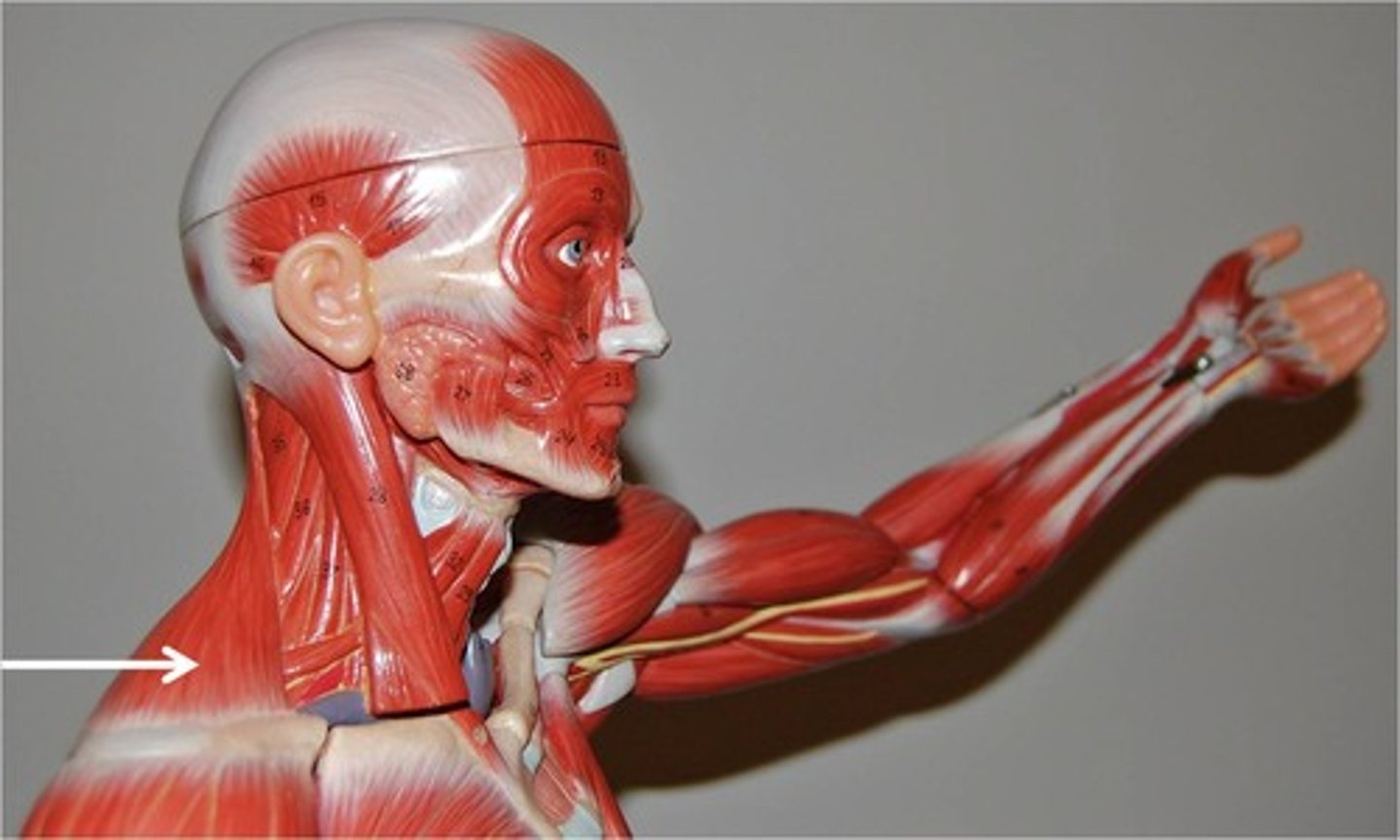
Splenius Capitus
Deep to sternocleidomastoideus at the mastoid process, and to the trapezius for its lower portion. It is one of the muscles that forms the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck
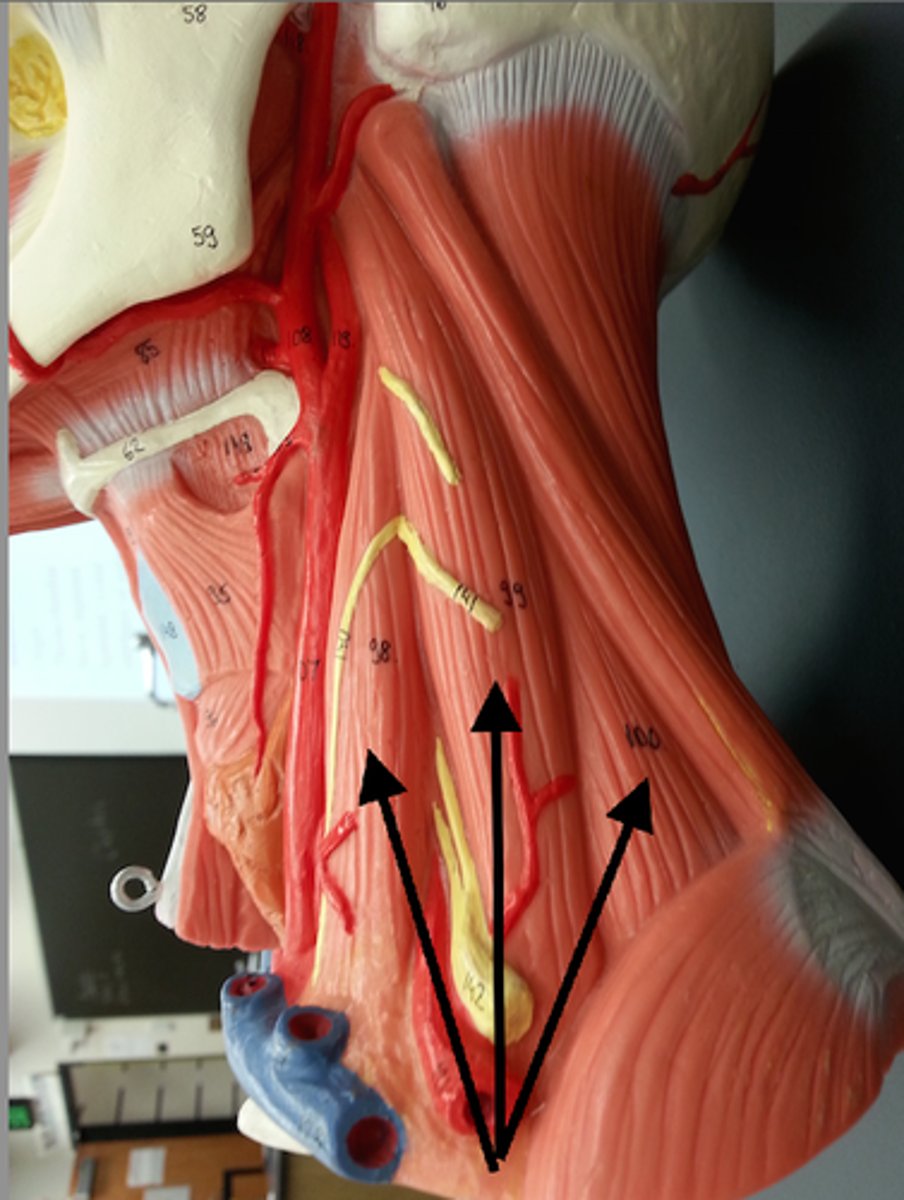
Scalene Muscles
Extend to the first 2 ribs & stabilize the thoracic cage during forced breathing. They also laterally flex the neck. Lateral muscles of the neck.
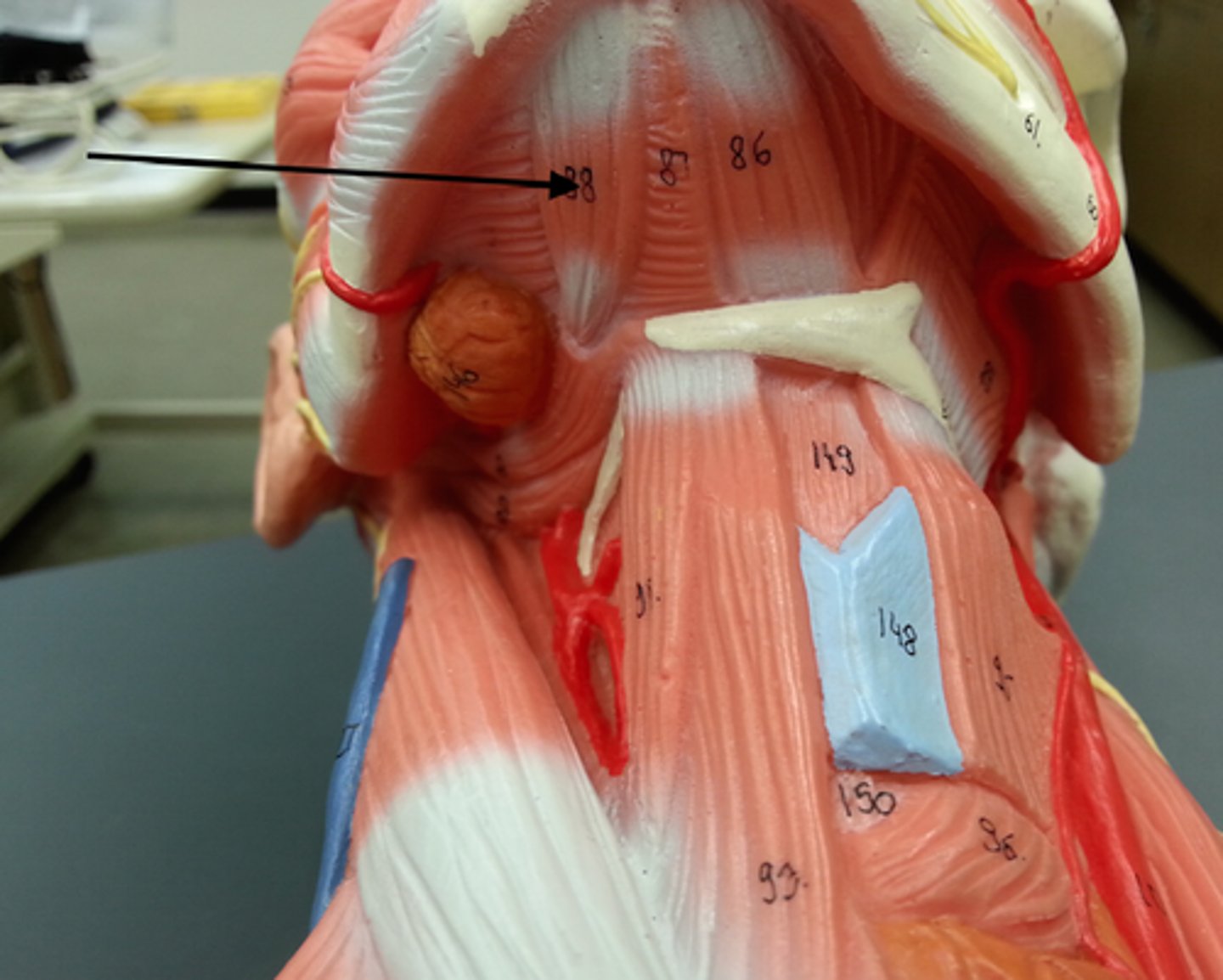
Digastric
Stretches between the mastoid process of the cranium to the mandible at the chin, and part-way between, it becomes a tendon which passes through a tendinous pulley attached to the hyoid bone
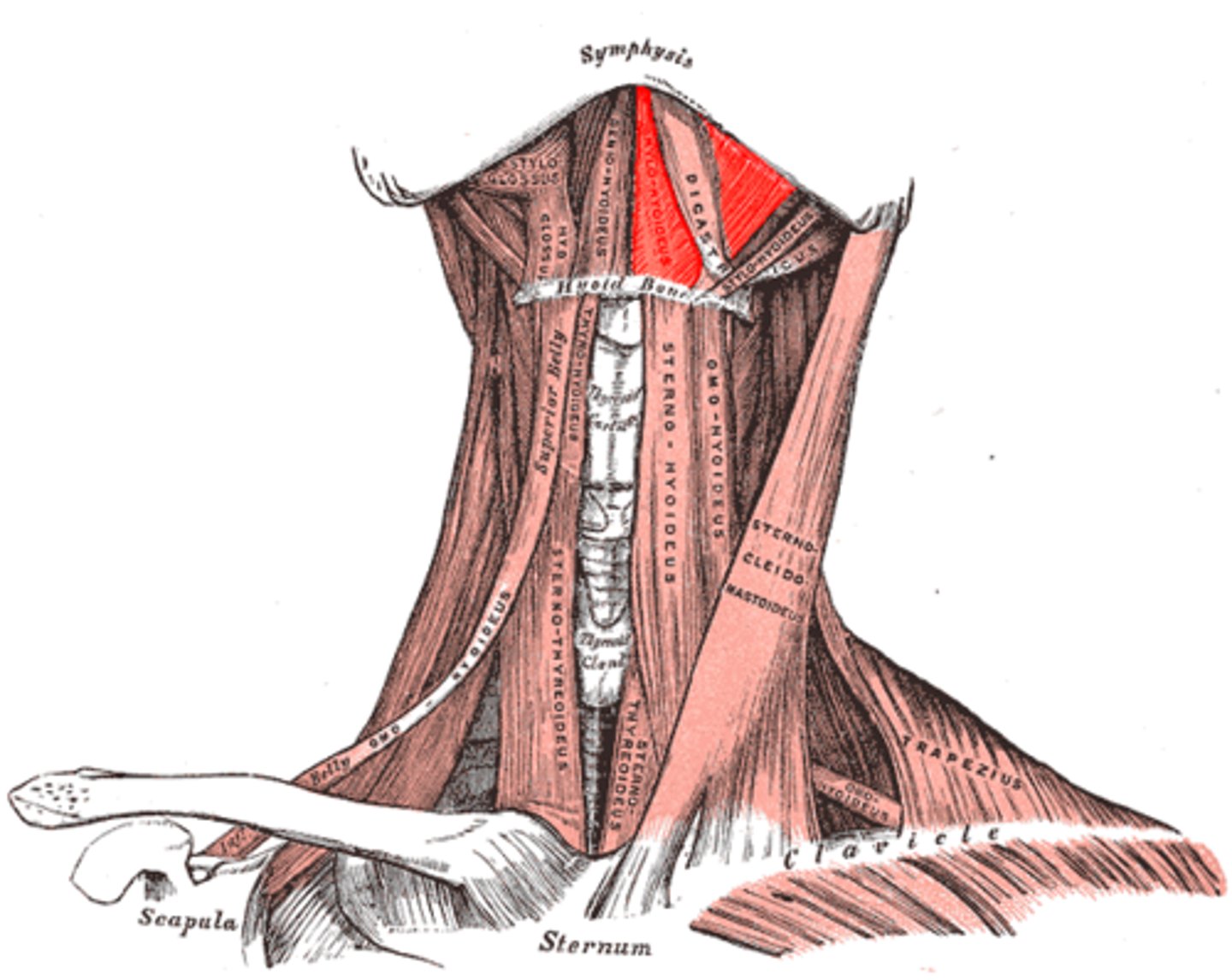
Mylohyoid
A paired muscle running from the mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the floor of the oral cavity of the mouth
Stylohyoid
A slender muscle, lying anterior and superior of the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. It shares this muscle's innervation by the facial nerve, and functions to draw the hyoid bone backwards and elevate the tongue. Its origin is the styloid process of the temporal bone.
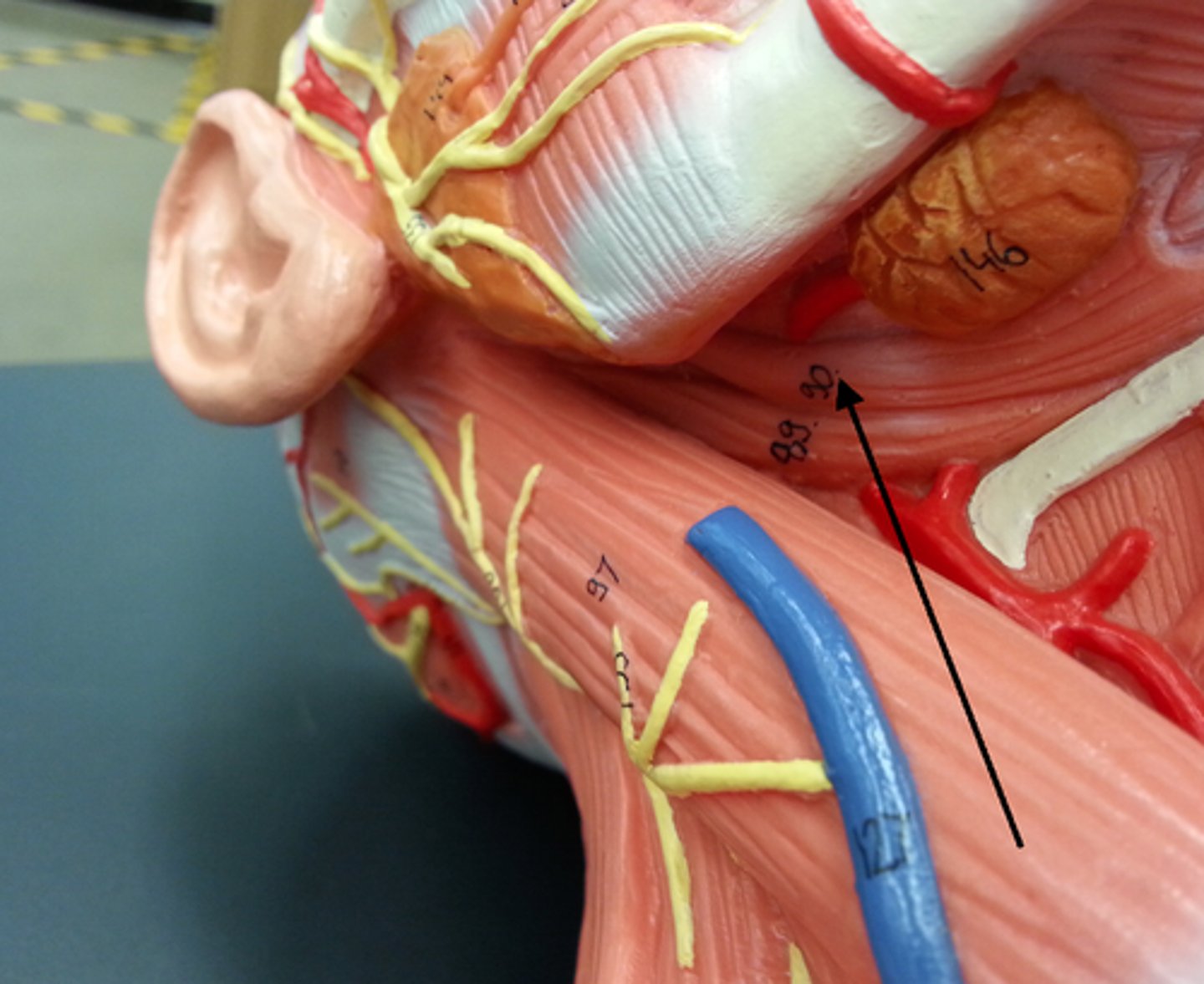
Sternohyoid
A thin, narrow muscle attaching the hyoid bone to the sternum, one of the paired strap muscles of the infrahyoid muscles serving to depress the hyoid bone
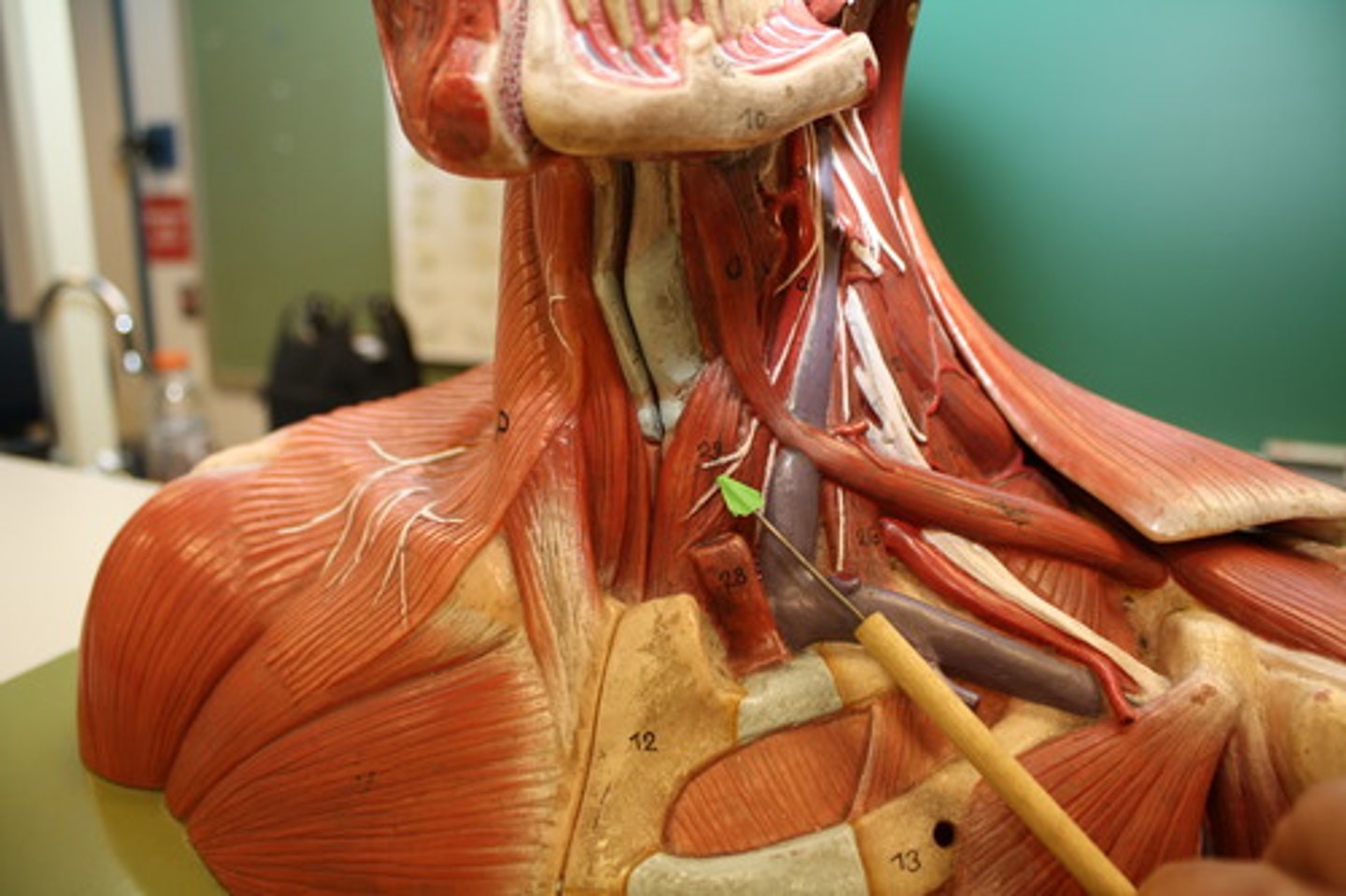
Thyrohyoid
A small skeletal muscle on the neck which depresses the hyoid and elevates the larynx
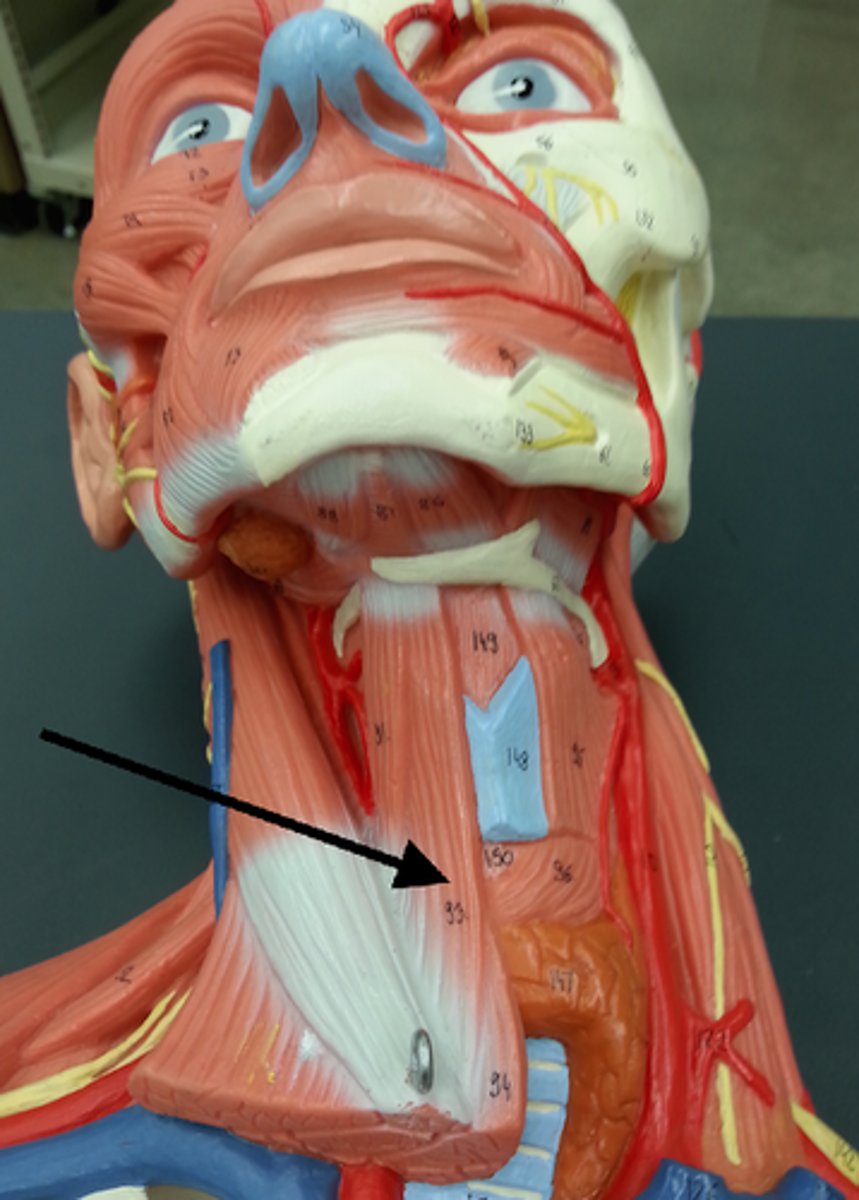
Sternothyroid
Lies underneath the sternohyoid muscle
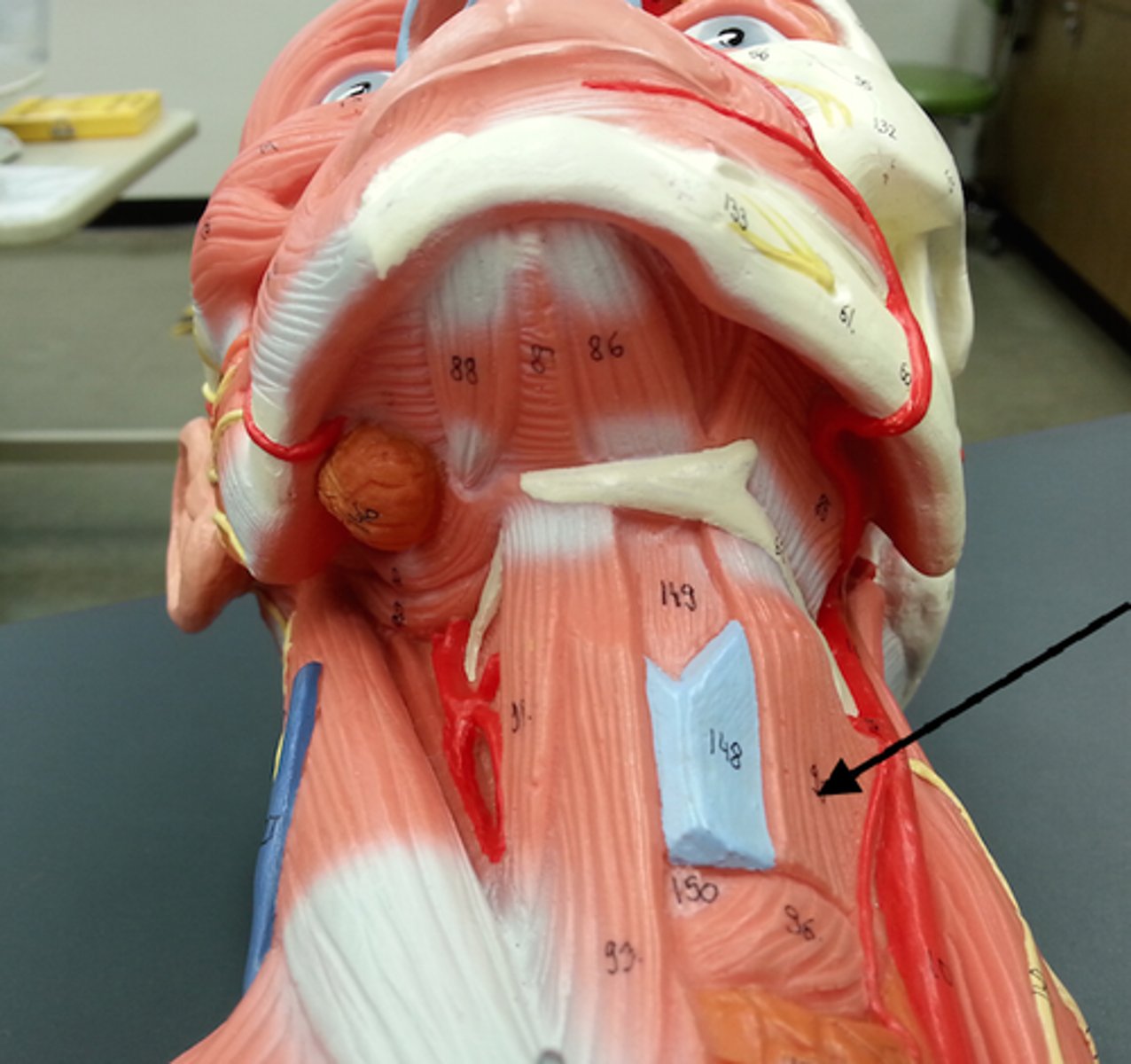
Omohyoid
A muscle that depresses the hyoid. It is located in the front of the neck and consists of two bellies separated by an intermediate tendon.
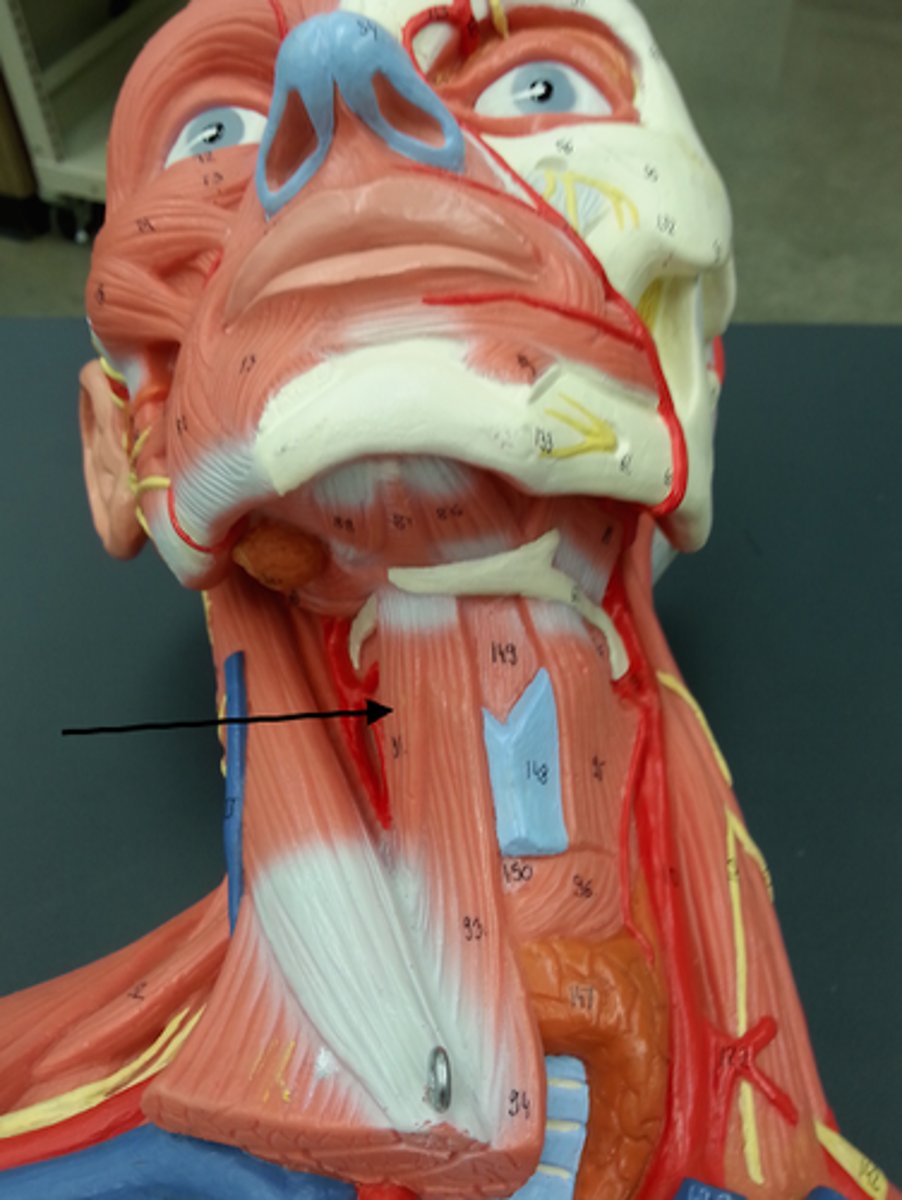
Palatoglossus
Extrinsic muscle of the tongue
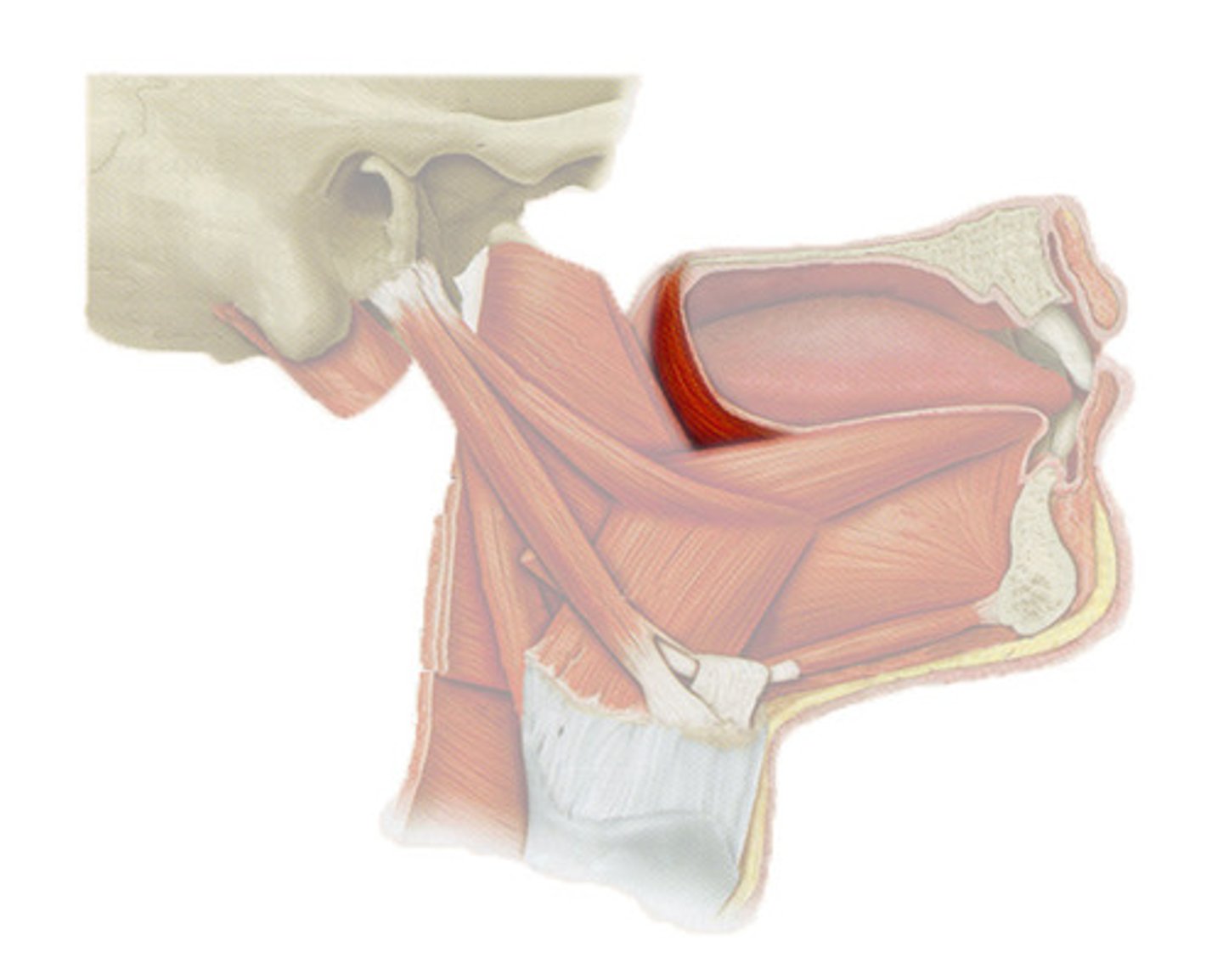
Genioglossus
The fan-shaped extrinsic tongue muscle that forms the majority of the body of the tongue
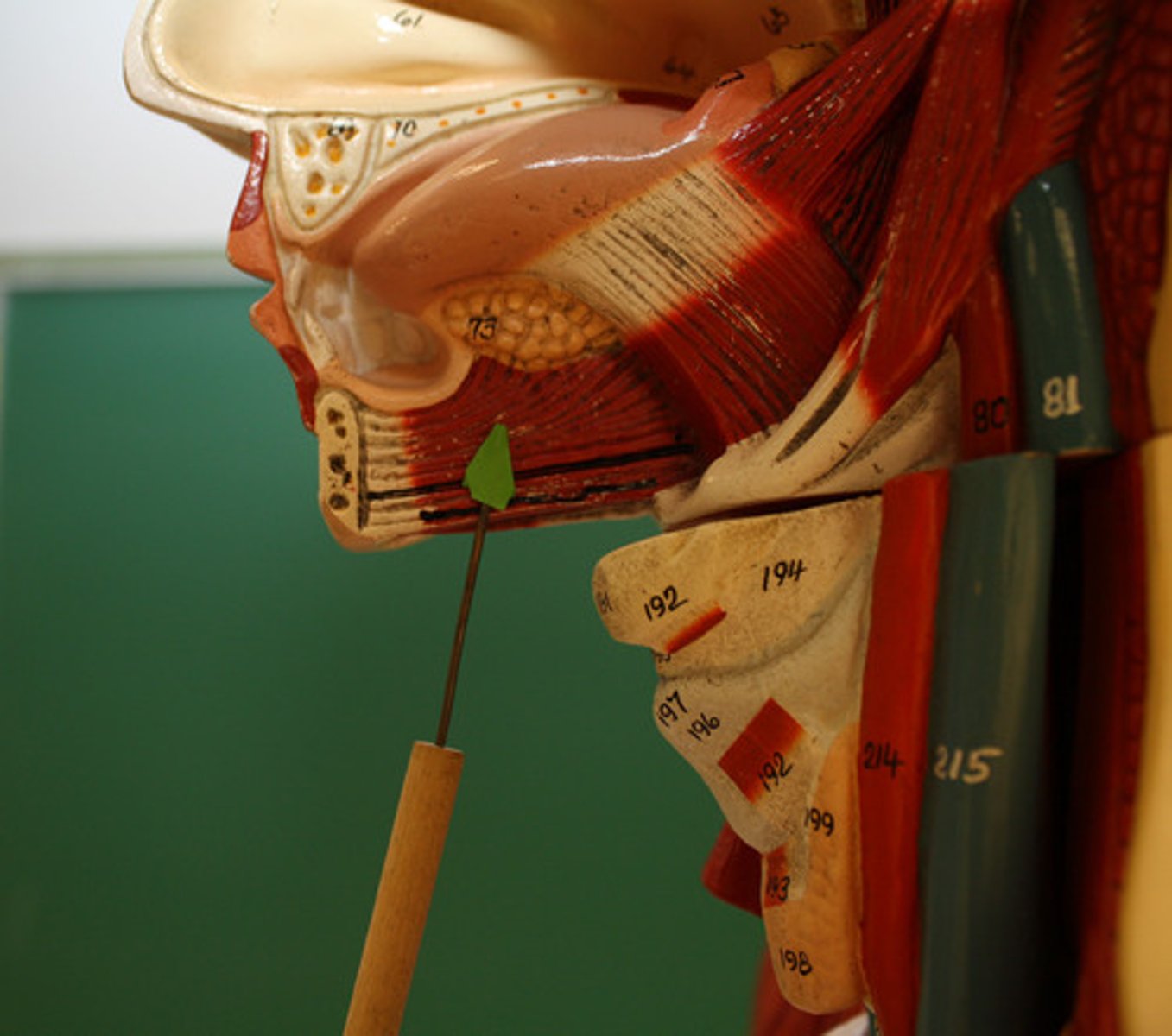

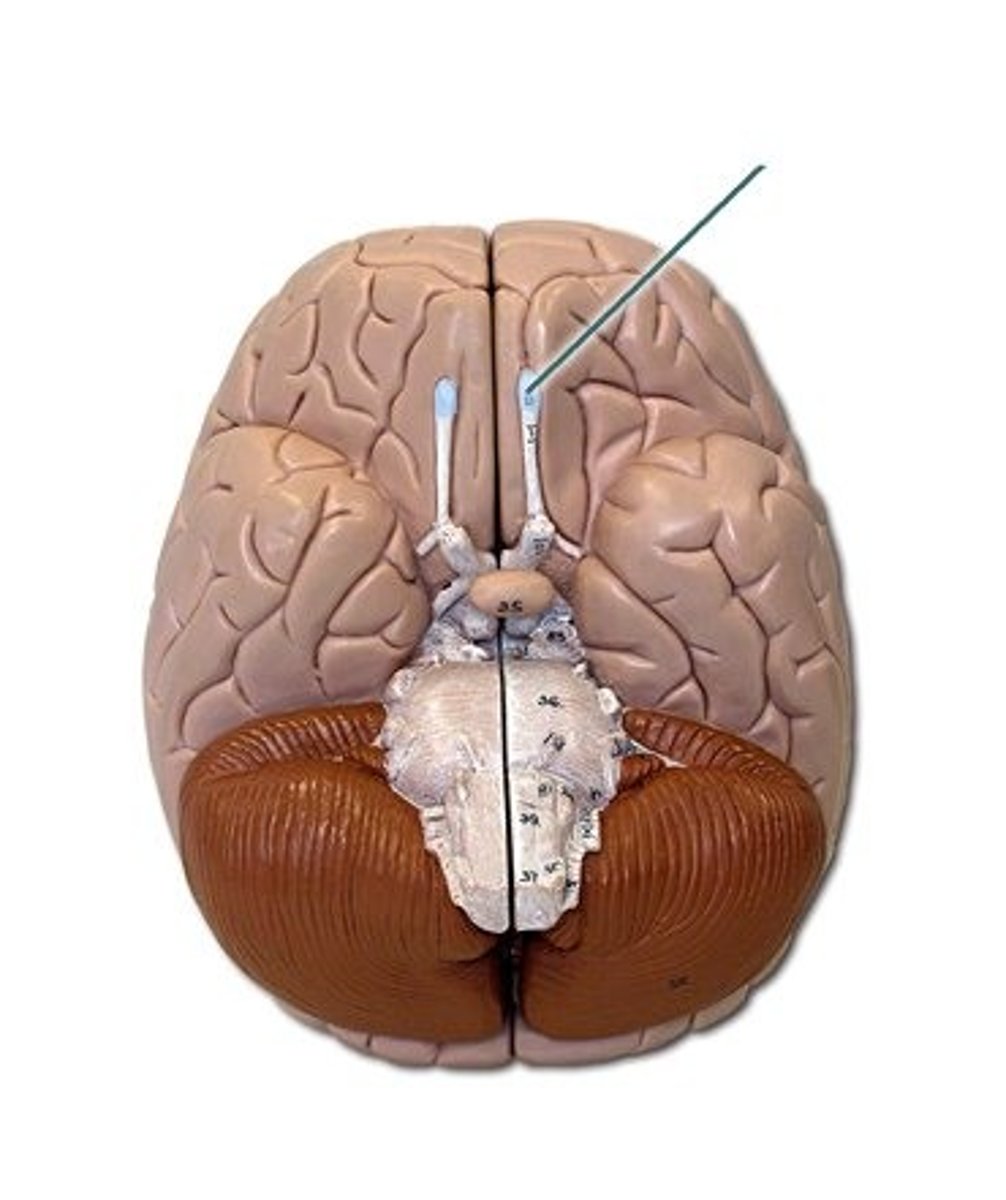
CN I: Olfactory Nerve
The first and shortest cranial nerve. It is a special visceral afferent nerve, which transmits information relating to smell.
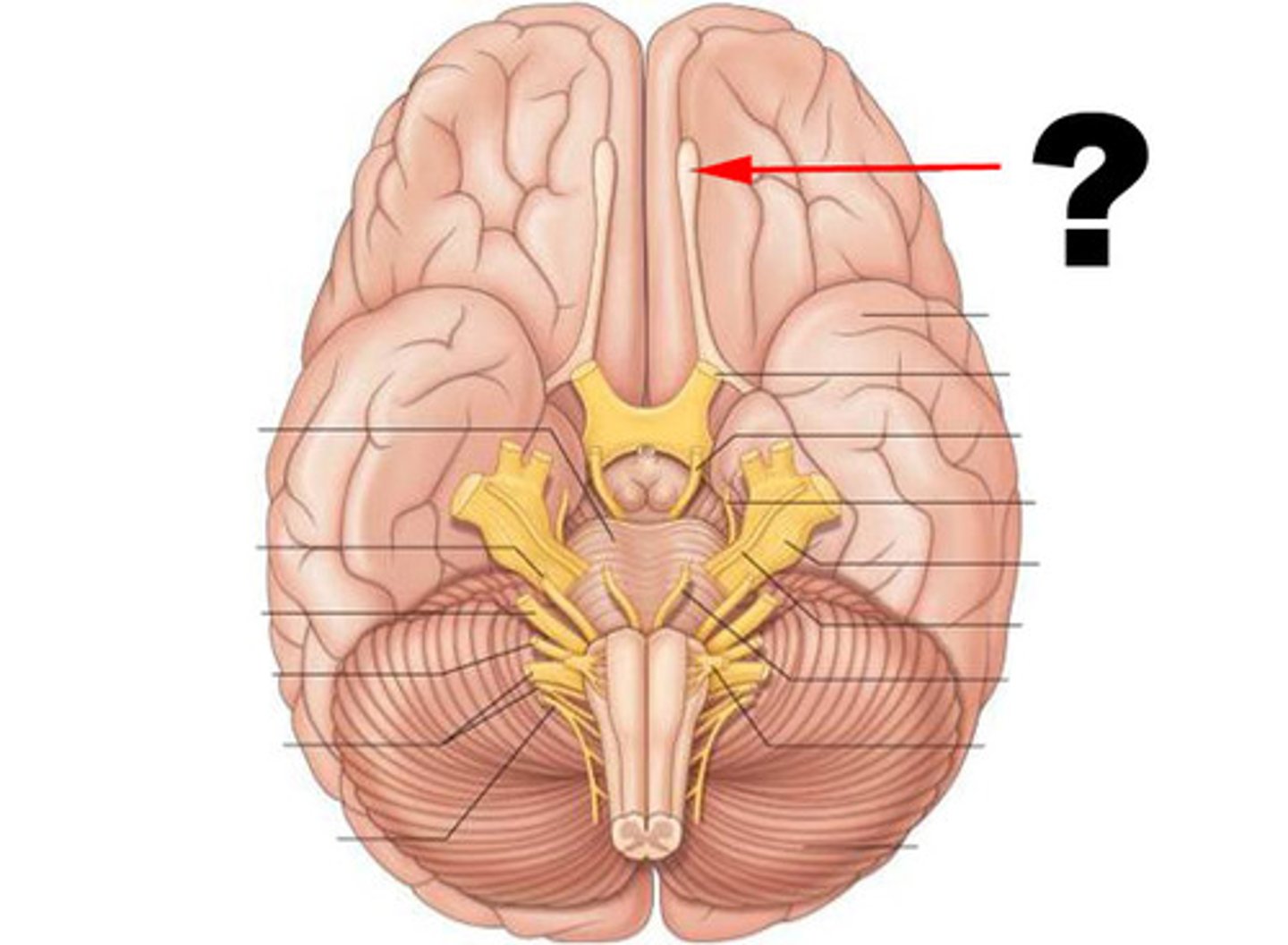
Olfactory Bulbs
Lies in the olfactory groove within the anterior cranial fossa