Chemistry - Topic 6 Alkanes
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Note no mention of saturation, general formula, physical properties e.g. melting points and differences in fractionating column - refer to spec points and notes for this
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
How are alkanes obtained?
Fractional Distillation, Cracking and Reforming of Crude Oil
What is reforming?
The processing of straight-chained hydrocarbons into branched-chain alkanes and cyclic hydrocarbons for efficient combustion
Reforming - Conditions
Catalyst (Ni), high temperature
Reforming - reasons
cycloalkanes are added to fuel to improve its performance
Cracking - reasons
Crack longer less useful alkanes to form shorter more useful alkanes and alkenes. Shorter alkanes are more useful as they are better fuels. Alkenes can be turned into polymers via addition polymerisation which are used as feedstocks for the petrochemical industry.
Cracking - Conditions
Catalyst ( Porcelain chips / alumina), high temperature
Pollutants formed during combustion of alkanes
Carbon monoxide
oxides of nitrogen and sulfur
carbon particulates
unburned hydrocarbons
What problems arise from pollutants from combustion of fuels?
carbon monoxide is a toxic gas - binds to haemoglobin in cells and reduces efficiency of its transport of oxygen around body to respiring tissues - fatigue and even death
acidity of oxides of nitrogen and sulfur - cause acid rain (erosion of limestone, decreased pH of water in lakes and soil (kills aquatic organisms, damages plants/ trees)
carbon dioxide - enhanced Greenhouse Effect - global warming
carbon (soot) - breathing / respiratory problems, smog (global dimming)
What causes sulfur dioxides to form during combustion?
Sulfur impurities in fuel react with oxygen from air (car exhausts, petrol stations)
What causes nitrogen oxides to form during combustion?
high temperatures reached in car engines mean for nitrogen and oxygen to react from the air and form oxides of nitrogen
What does a catalytic converter do?
Converts problematic pollutants into less harmful compounds/ substances (N2, H2O, CO2)
What is catalyst converter made out of?
Platinum, Rhodium, Palladium
Why is the catalytic converter in a honeycomb structure?
larger surface area so more gas particles come into contact with the catalyst surface
more frequent successful collisions per unit time
speeds up rate of conversion
How can we produce ethanol as a carbon-neutral fuel?
Fermentation of Carbohydrates, reaction of ethene with steam
Describe the process of fermentation of carbohydrates
Equation: C6H12O6 → 2CO2 + 2C2H5OH
conditions: temp (37 degrees Celsius), pressure (atmospheric pressure), catalyst (yeast - contains zymase enzymes), low pp of O2
Raw Materials used in reaction: sugar cane/ corn (plants) - renewable
process: batch (made in batches)
reaction rate: slow (reaction takes days + must grow crops)
Purity of ethanol: impure - purified by distillation
Describe the process of the reaction of ethene with steam:
Equation: C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH
Conditions: Temp (300 degrees Celsius), pressure (60-70 atmosphere), catalyst (H2SO4 / H3PO4 acid)
Raw Materials: ethene (+ steam) - non-renewable (ethene produced from crude oil)
Process: continuous
Reaction rate: fast
purity of ethanol: purer (nearly 100%)
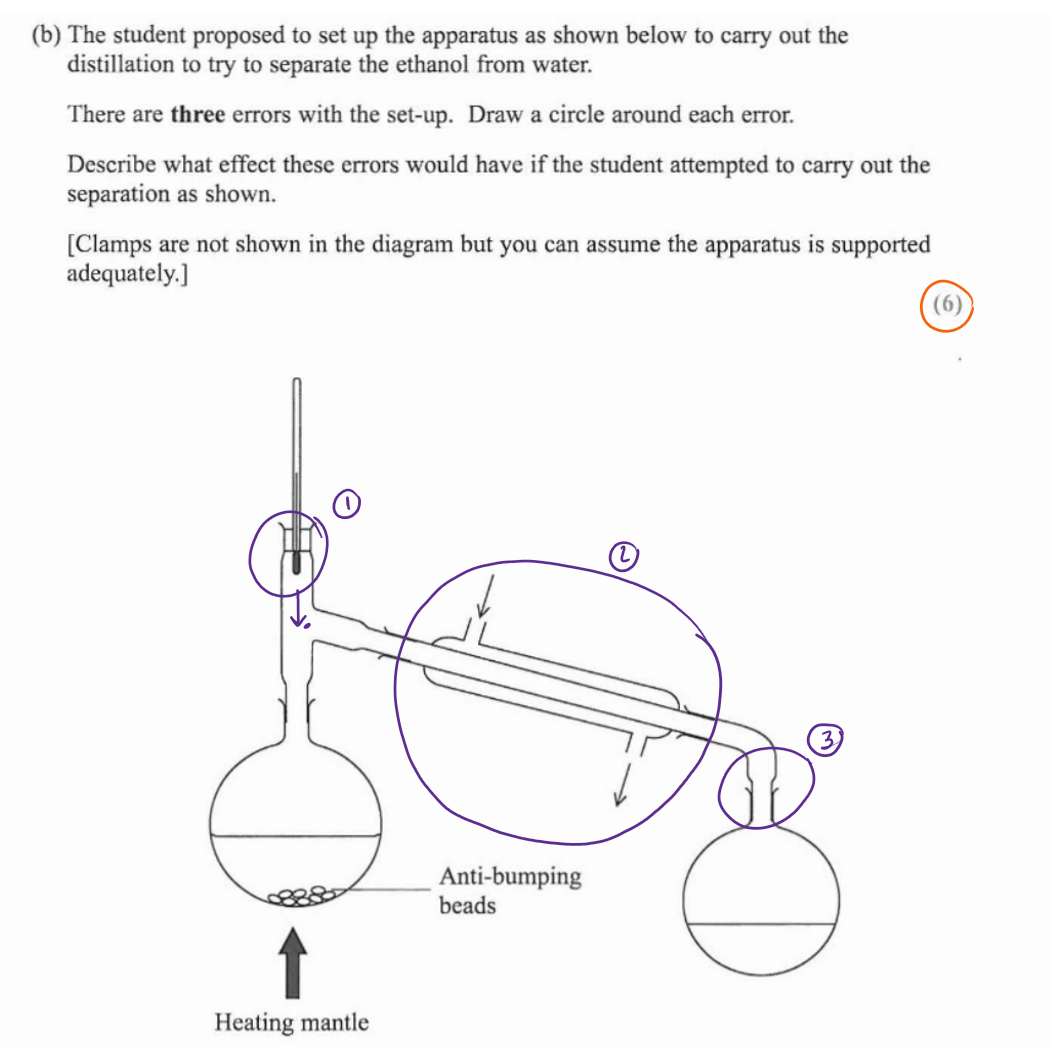
thermometer is not opposite entrance of condenser - leads to inaccurate readings of temp of vapour as it enters condenser
water is going incorrect way into the condenser - leads to formation of air bubbles so inefficient cooling
apparatus fully sealed - this would lead to build up of pressure and cause and explosion
What is a suitable drying agent to absorb water with ethanol after distillation?
Anhydrous Calcium chloride - leave for suitable amount of time before decanting off the ethanol
Explain what is meant by a carbon-neutral fuel
a fuel that takes in as much CO2 as is released during its production / combustion/ when used
OR
a fuel that produces no CO2 when burnt
Suggest two reasons why biofuels may not be carbon neutral and two effects that large scale production of biofuels may have on society. Which of the biofuels do you think is the most sustainable? Justify your choice.

What is a radical?
a species with an unpaired electron and is represented by mechanisms by a single dot
is formed from homolytic fission of a covalent bond and results in the formation of radicals
What do alkanes react with ?
oxygen in air (combustion)
halogens
What steps are there in free radical substitution?
Initiation, propagation and termination
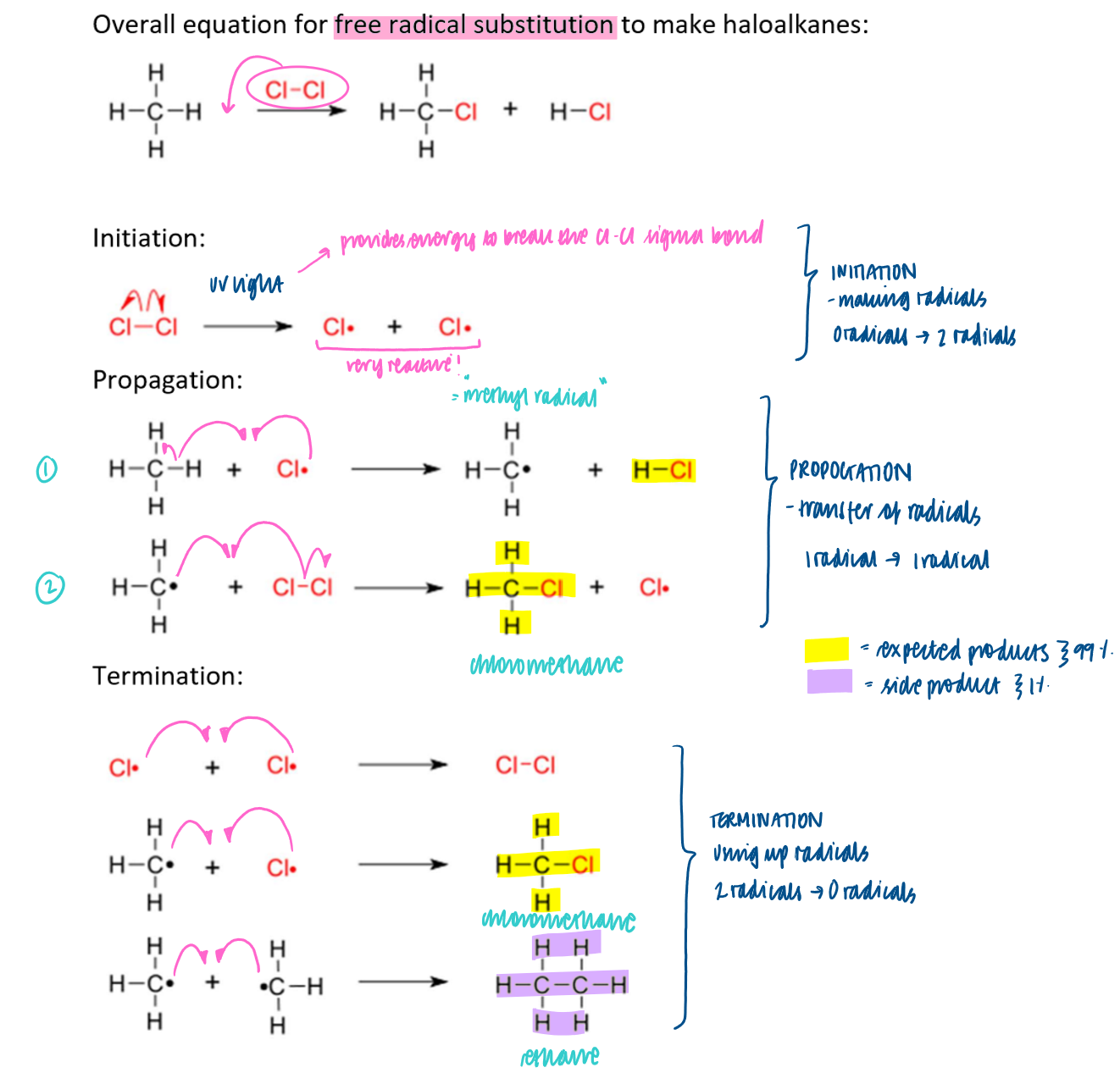
What are some limitations of free radical substitution in the synthesis of organic molecules?
mixture of reactants, expected products and side products
radicals = very reactive so many possible termination steps can occur
low % yield / atom economy
difficult to obtain pure sample of product as halogen radical can remove hydrogen from anywhere in the propane molecule