ap gov ACHS midterm
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
representative democracy
a system of government in which officials are elected to represent the people.
participatory democracy
a model of democracy in which citizens have the power to make decisions directly, rather than through elected representatives.
pluralist democracy
a form of democracy that recognizes the diversity of interests within a society and allows for multiple groups to compete for influence in decision-making.
elite democracy
a theory of democracy that emphasizes the role of a small number of elites in influencing political decision-making, often at the expense of broader public participation.
shay’s rebellion
a series of protests in 1786-1787 by American farmers against state and local enforcement of tax collections and judgments.
factions
groups of people or organizations that share common interests and seek to influence political decisions.
anti-federalists
a political group that opposed the ratification of the Constitution, fearing it would create a central government too powerful and threaten individual liberties.
great compromise
an agreement reached during the Constitutional Convention that established a bicameral legislature, balancing the needs of both small and large states.
electoral college
A body of electors established by the Constitution, responsible for formally electing the President and Vice President of the United States.
3/5 compromise
A constitutional agreement reached during the Constitutional Convention that determined how slaves would be counted for representation and taxation purposes, allowing states to count three-fifths of their slave population.
commerce clause
A provision in the US Constitution that grants Congress the power to regulate commerce with foreign nations, among the states, and with Native American tribes.
slave trade compromise
A constitutional agreement during the Constitutional Convention that addressed the importation of slaves, allowing the continuation of the slave trade for twenty years before Congress could regulate it.
articles 1-7
The sections of the US Constitution that outline the structure and powers of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, as well as the relationship between states and the federal government.
checks and balances
A system in the US government that ensures no one branch becomes too powerful by giving each branch the ability to limit the powers of the others.
federalism
A system of government in which power is divided between a central authority and constituent political units, allowing for shared governance.
delegated powers
Powers specifically granted to the federal government by the Constitution, such as the ability to regulate interstate commerce and conduct foreign affairs.
reserved powers
Powers not specifically granted to the federal government by the Constitution, which are reserved for the states.
concurrent powers
Powers shared by both the federal and state governments, such as the ability to tax, build roads, and create lower courts.
policy
A course of action adopted and pursued by a government or organization to achieve specific goals.
constituents
The individuals represented by elected officials, who have the power to vote and influence government policy.
block grants
Federal funds given to state or local governments for broad purposes with fewer restrictions.
categorical grants
Federal funds provided to state or local governments for specific purposes, with detailed requirements and restrictions on their use.
devolution
The transfer of powers and responsibilities from the federal government to state or local governments, promoting greater autonomy and local control.
10th amendment
The constitutional amendment that reserves powers not delegated to the federal government for the states and the people, reinforcing the principle of federalism.
14th amendment
The constitutional amendment that grants citizenship to all persons born or naturalized in the United States and ensures equal protection under the law. It also prohibits states from denying any person life, liberty, or property without due process.
McCulloch v. Maryland
A landmark Supreme Court case that established the principle of federal supremacy over state laws and affirmed the constitutionality of the Second Bank of the United States. This case reinforced the implied powers of Congress and the use of the Necessary and Proper Clause. It confirmed that states cannot tax federal institutions.
US v. Lopez
A landmark Supreme Court case that limited the scope of Congress's power under the Commerce Clause by ruling that possession of a gun in a school zone is not an economic activity that affects interstate commerce.
Declaration of Independence
A historic document that announced the thirteen American colonies' separation from British rule. It was primarily authored by Thomas Jefferson and articulated the principles of individual rights and government by consent.
Articles of Confederation
The first constitution of the United States, ratified in 1781, which established a weak central government and provided limited powers to Congress, leading to various challenges in governance and ultimately its replacement by the Constitution in 1789.
Constitution
The supreme law of the land that outlines the framework of government in the United States, establishing the separation of powers, checks and balances, and individual rights.
Federalist #10
An essay written by James Madison, published in 1787, arguing for the ratification of the Constitution. It addresses the dangers of factionalism and advocates for a large republic to mitigate these risks.
Brutus #1
An anti-Federalist essay arguing against the ratification of the Constitution, emphasizing the dangers of a large central government and the importance of individual liberties.
Federalist #51
An essay written by James Madison that discusses the importance of checks and balances in government, arguing that each branch should be independent to prevent any one from becoming too powerful.
Roles of the House
The roles of the House of Representatives include proposing legislation, initiating revenue bills, and representing the interests of constituents. It also has the exclusive power to impeach federal officials and elect the President in case of an Electoral College tie.
Roles of the Senate
To represent states, approve treaties, confirm appointments, and conduct impeachment trials.
enumerated powers
The specific powers granted to Congress by the Constitution, including the authority to tax, regulate commerce, and declare war.
implied powers
Powers not explicitly stated in the Constitution but are necessary to implement the enumerated powers. They allow Congress to carry out its functions effectively.
Bill to law process
The series of steps a proposed law goes through in Congress, including introduction, committee review, debate, and approval by both chambers before being sent to the President for signing or veto.
Committee system
A system in which Congress uses committees to review, amend, and recommend legislation before it is presented to the full chamber for a vote.
Rules Committee
A committee in the House of Representatives responsible for determining the rules for debate and the scheduling of bills on the floor.
Conference Committee
a temporary committee made up of members from both the House and the Senate to reconcile differences between versions of a bill passed by both chambers
Pocket veto
When the president takes no action on a bill for 10 days while Congress is not in session, effectively vetoing it
Speaker of the House
The leader of the House of Representatives and second in line to the presidency. The Speaker sets the legislative agenda and presides over House meetings
President of the Senate
The Vice President of the US, who presides over the senate and casts tie-breaking votes
Whips
Party leaders in both the House and Senate who ensure party discipline, secure votes, and maintain communication between party members
Filibuster
A tactic used in the Senate to delay or block a vote on a bill by extending debate
Cloture
A procedure to end a filibuster in the Senate, requiring a 3/5 vote (60 senators)
Discharge petition
A process in the House to bring a bill out of committee and to the floor for a vote, requiring the signature of a majority of House members
Discretionary spending
Government spending implemented through appropriations bills, which can be adjusted annually (e.g. defense, education)
Mandatory spending
Spending that is required by law and not subject to annual appropriations, such as Social Security and Medicare
Appropriations
Legislation that allocated funding to government programs and agencies
Pork barrel legislation
Government spending for localized projects secured primarily to bring money to a representative’s district
Logrolling
A practice where legislators agree to trade votes to support each other’s proposals
Divided government
A situation where different parties control the presidency and one of both chambers of Congress, often leading to legislative gridlock
Partisanship
Strong allegiance to one’s political party, often leading to unwillingness to compromise with the other party
Models of representation
Trustee: Legislators use their judgment to make decisions
Delegate: Legislators act according to their constituents’ wishes
Politico: A hybrid approach that balances both
Gerrymandering
The process of redrawing electoral districts to benefit a particular party
Baker v. Carr
a 1962 case that established the principle of “one person, one vote” requiring states to draw legislative districts with roughly equal populations. Redistricting issues are justifiable.
Shaw v. Reno
A 1993 case in which SCOTUS ruled that racial gerrymandering is unconstitutional. Districts cannot be drawn solely based on race.
Constitution Article I
Establishes the legislative branch (Congress), outlines its powers, and includes the Necessary and Proper Clause, which allows for implied powers
Policy agenda
The set of issues and priorities the president focuses on during their term, often outlined in the State of the Union address
Roles of the President
Chief Executive, Commander in Chief, Chief Diplomat, Chief Legislator, and Party Leader
Executive orders
Directives issued by the president that have the force of law but do not require congressional approval
Signing statements
Written comments issued by the president when signing a bill into law, often explaining their interpretation or intentions regarding enforcement
Senate
As the president nominates officials (judges, cabinet members, etc.), the _______ must confirm appointments
Formal powers
Powers explicitly granted to the president by the Constitution, such as vetoing bills, commanding the armed forces, and making treaties
Informal powers
Powers not explicitly stated in the Constitution but derived from the president’s role, such as issuing executing orders and using the “bully pulpit” to influence public opinion
Judicial review
The power of the judiciary to determine the constitutionality of laws and executive actions (established in Marbury v. Madison)
Stare decisis
The legal principle of determining cases based on precedent
Limits of SCOTUS power
SCOTUS relies on other branches to enforce its rulings and cannot initiate cases (must wait for cases to be brought to it)
Amicus curiae briefs
“Friend of the court” briefs submitted by non-parties to a case to provide additional perspectives or expertise to influence the court’s decision
Writ of certiorari
An order by SCOTUS to a lower court to send up a case for review
Court of appeals
Intermediate federal courts that review district court decisions and rule on appeals
Independent judiciary
A judiciary that operates free from political pressures to ensure impartiality and fairness
Rule of four
The Supreme Court practice where four justices must agree to grant a writ of certiorari for a case to be heard
Marbury v Madison
A landmark 1803 case that established judicial review, allowing SCOTUS to strike down laws it deems unconstitutional
Patronage job
A position given as a political reward rather than based on merit
Merit system
A system of hiring and promotion based on qualifications and competence rather than political connections
Iron triangle
A relationship among bureaucratic agencies, interest groups, and congressional committees that creates policy and enforces legislation
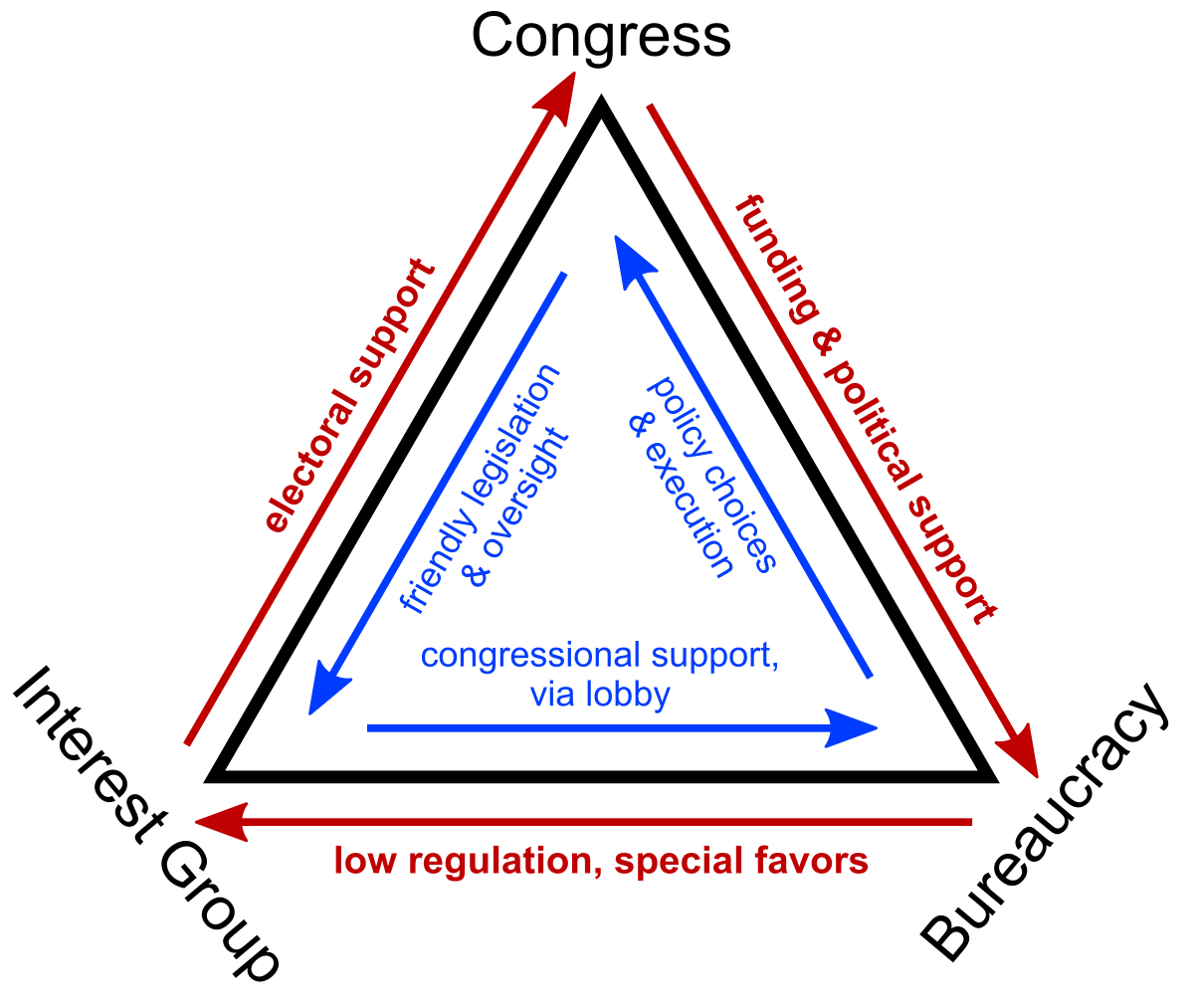
Issue network
A broader coalition of interest groups, experts, and stakeholders influencing policy on specific issues
Civil service
The professional workforce of government employees hired based on merit
Delegated discretionary authority
The power Congress grants to federal agencies to interpret and implement laws
Oversight
Agencies monitor policy implementation through inspections, reports, and audits to ensure compliance with regulations
Power of the purse
Congress’s authority to control government spending and approve budgets for federal agencies
Accountability
President and Congress hold bureaucracy through oversight hearings, funding control, and appointing officials
Federalist #70
Advocates for a single, energetic executive to ensure accountability and effective leadership
Federalist #78
Argues for an independent judiciary and emphasizes the importance of judicial review
12th Amendment
Modified the electoral process by requiring separate votes for president and vice president
20th Amendment
Changed the start dates for presidential and congressional terms, reducing the “lame duck” period
22nd Amendment
Limits the president to 2 terms or a maximum of 10 years in office
25th Amendment
Whenever there is a vacancy in the office of the Vice President, the President shall nominate a Vice President who shall take office upon confirmation by a majority vote of both Houses of Congress
Civil liberties
Fundamental rights and freedoms (e.g. Bill of Rights) protected from government interference, such as freedom of speech and religion
Civil rights
Protections against discrimination and guarantees of equal treatment under the law (e.g. 14th Amendment’s Equal Protection Clause)
Selective incorporation
The process by which the Supreme Court applies the Bill of Rights to the states through the 14th Amendment’s Due Process Clause (case by case approach)
Freedom of Association
The right to join or form groups and organizations without government interference
Establishment Clause
The 1st Amendment provision prohibiting the government from establishing an official religion
Lemon Test
A 3-part test from Lemon v Kurtzman to determine of a law violates the Establishment Clause
Exercise Clause
The 1st Amendment provision protecting individuals’ right to freely practice their religion
Sherbert Test
A standard from Sherbert v. Verner to determine if a government action substantially burdens religious exercise
Prior Restraint
Government actions that prevent materials from being published, often considered unconstitutional