neuropharmacology (1)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
what is psychopharmacology?
effects of drugs on psychologic parameters (such as emotion/ cognition)
what is neuropsychopharmacology?
effects of drugs on nervous system
whats the difference between in vitro and in vivo neuropharmacology?
in vitro- effects drugs on tissues or neurons & determining concentration (M) response relationships, in vivo- effects drugs on organisms and animals & determining dose (mg/kg) response relationships
what does picrotoxin do
noncompetitive GABAA receptor antagonist, can block chloride conductance, antidote to barbiturate toxicity
how did fishermen use picrotoxin
from fishberry shrub seeds
what does TTX (tetrodotoxin) do
blocks voltage gated sodium channels, in pufferfish (can be used in pain management)(inhibits production and propagation of action potentials)(competitive)
how is TTX poisoning treated?
neostigmine (reversibly binds acetylcholinesterase, increasing acetylcholine availability)
curare vine was used by indigenous people in the Amazon for what?
for arrow and dart poisons
how does the curare vine poison?
rich with alkaloids- including d-tubocurarine (acetylcholine receptor antagonist competitive)(diaphragm is resistant- cuz it has more nAchR sites?)
how is d-turbocurarine poisoning treated?
also neostigmine (d-tubocurarine could also be used in treat neuromuscular disorders)
how does novichok poison?
inhibits acetylcholinesterase (stops relaxation of muscles)(causes death by asphyxiation or cardiac arrest)
what did Hodgkin and Huxley experiment/ discover?
model of how APs initiated & propagated
what did Henry dale and otto loewi?
got nobel prize for proof Ach is a neurotransmitter
what did john Eccles do?
he realised synaptic transmission was not electrical (sparks) but chemical (soup) which
describe the leach test and assay of Ach
leah muscles put in a bath constraining eserine (potent inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase) to stop activity of acetylcholinesterase and allow accurate measurement of Ach effects (increased levels of Ach)
what are the criteria for a neurotransmitter?
-synthesised by and released by the neuron
-must be released from nerve terminal in pharmacological identifiable form
-should reproduce at the postsynaptic cell the effects seen in the presynaptic neuron
-effects are blocked by competitive antagonists in a dose-dependent manner
-there are actions to terminate the action of it (enzymatic inactivation)
name 3 differences between neuromuscular junction and central synapses?
NM- multi-vesicle release vs CS- singular release zone, NM- Ach vs CS- Glu, NM- Ach breakdown SC- Glu reuptake
what do EPSP and IPSP stand for? how do they look different?
EPSP- excitatory post-synaptic potential (depolarisation), IPSP- inhibitory post-synaptic potential (hyperpolarisation)(Cl- enters due to gradient and K+ leaves)
define affinity
strength of binding of a ligand to a receptor
define efficacy
measure of the Max bio effect that a drug can produce
define potency
amount of ligand required to achieve or prevent effect
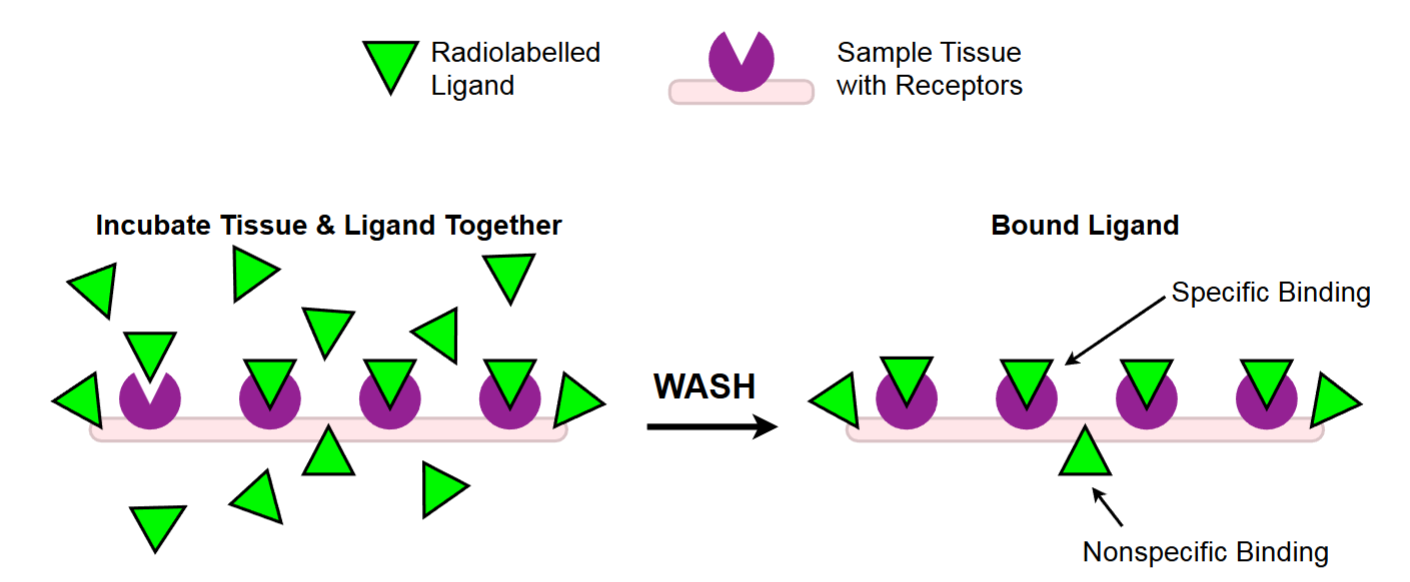
how to tell the difference between specific and non-specific ligand?
specific is saturable (has a Max so will flatten on a graph), non-specific is non-saturable (has no Max so will constantly increase ina graph)

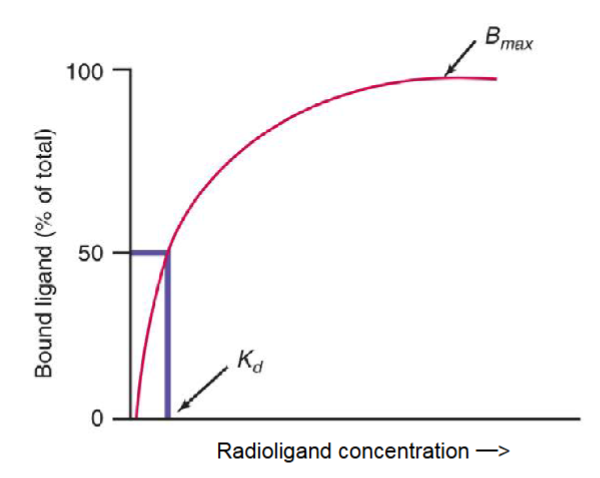
how is the affinity of binding expressed?
a dissociation constant (Kd)
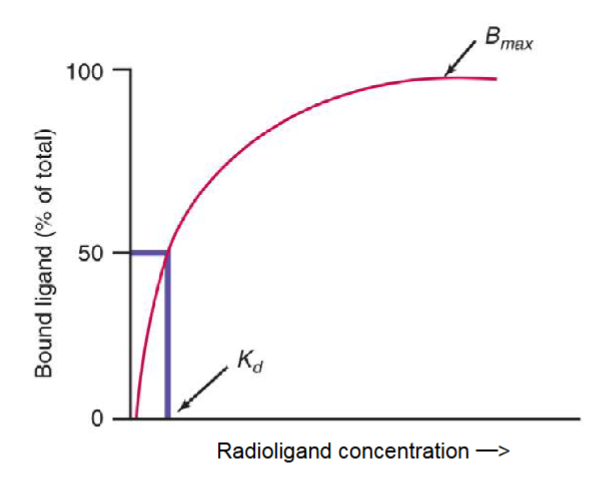
how is the total amount of binding expressed?
Bmax (maximal binding sites)
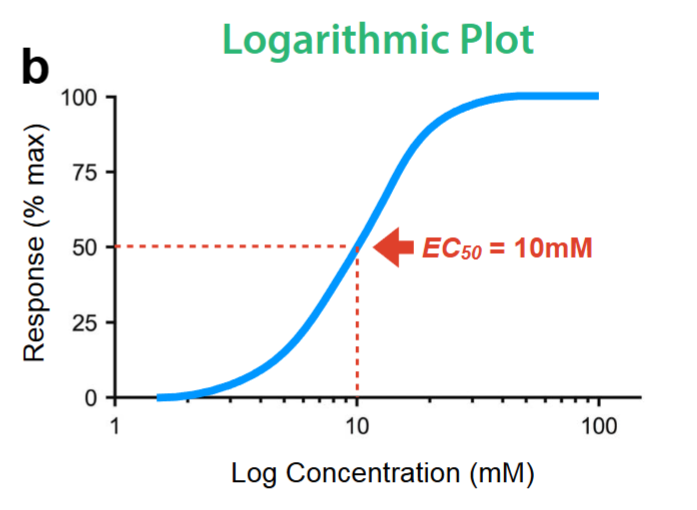
what is the EC50 value?
the concentration that produces 50% of the response
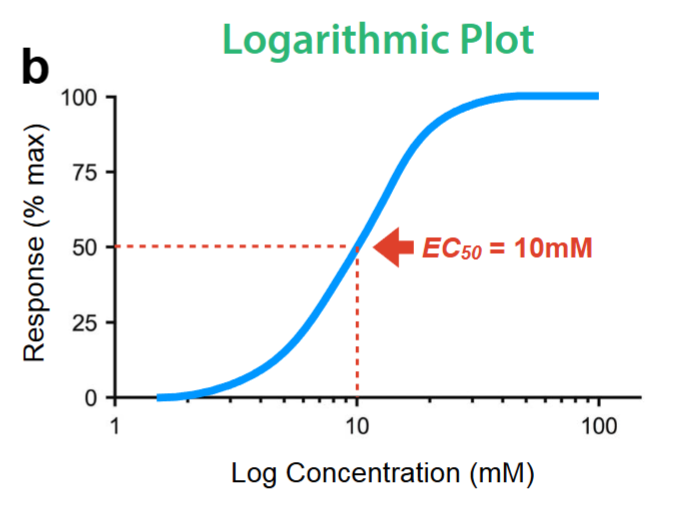
how is potency measured?
EC50 value (smaller= more potent)(excitatory concentration)
how is efficacy represented?
Emax

how does a partial agonist differ to a full agonist?
has less of an effect (can still be more potent than a full agonist)
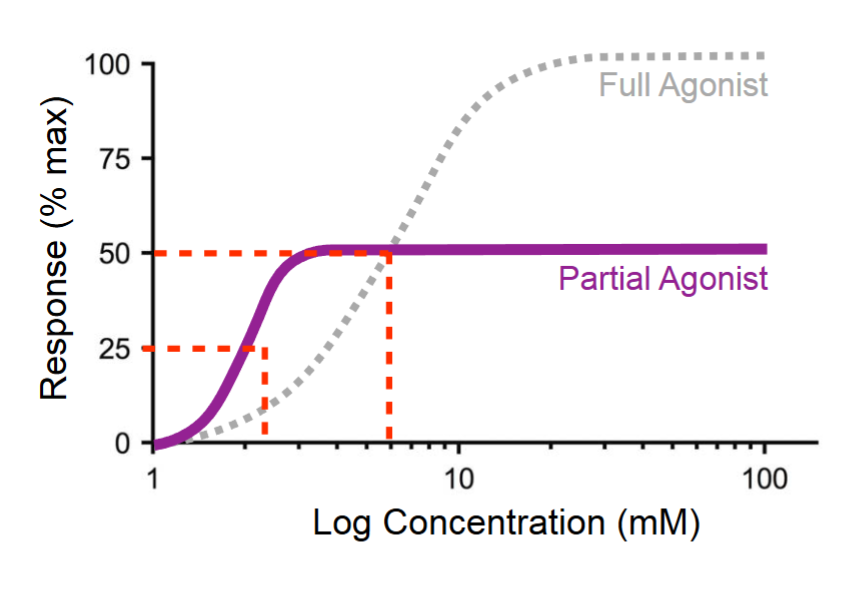
how can a partial agonist act as a functional antagonist?
if in presence of full agonist then it can compete with it and act as an antagonist, as it reduces the full agonists ability to create full effect
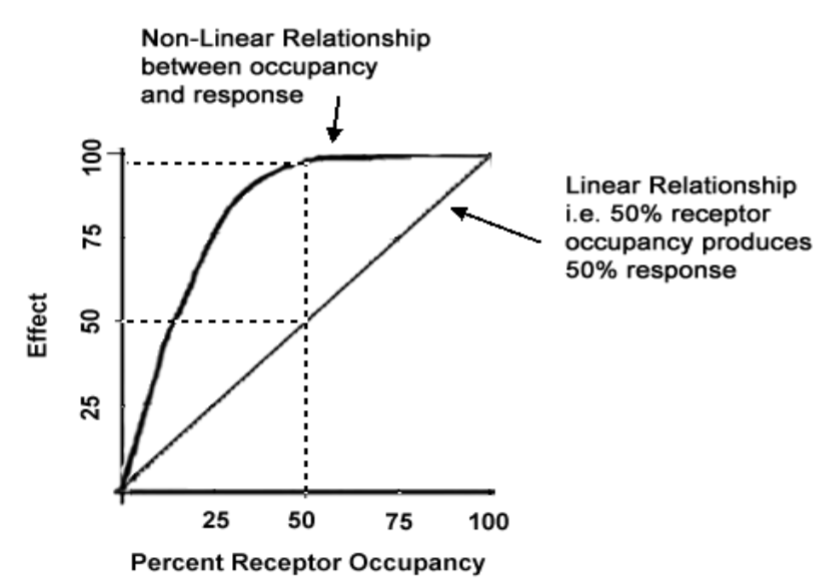
what is the difference between linear and hyperbolic relationships between response and receptor binding?
linear= Max response is created by Max binding of receptors
hyperbolic (in most mammals) = Max response can occur before all receptors bound (spare receptors)
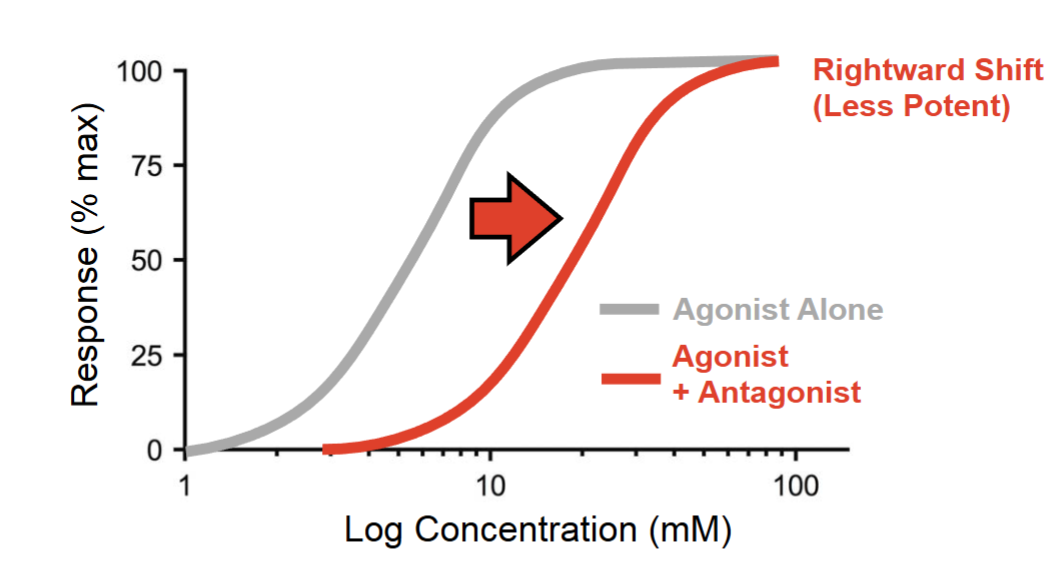
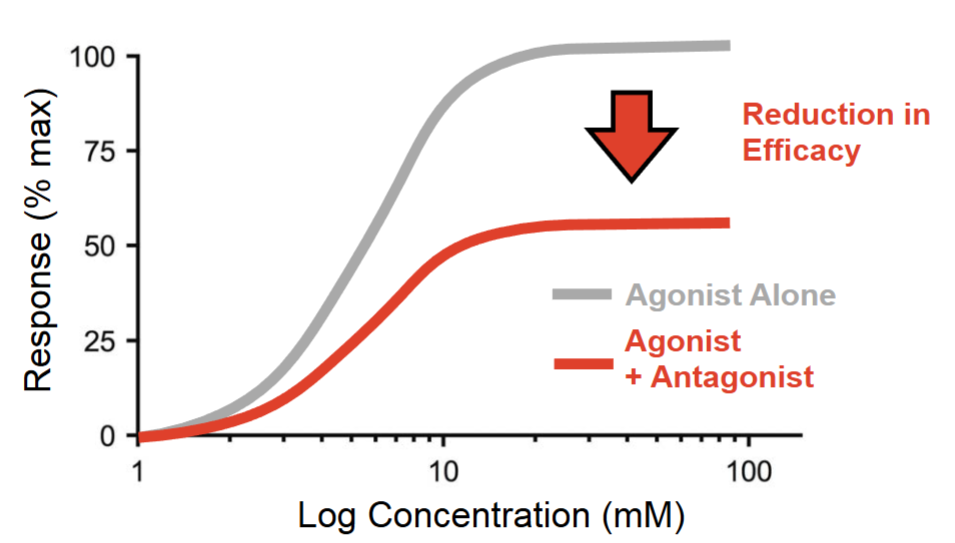
what type of antagonist is this?
competitive
what type of antagonist is this?
non-competitive
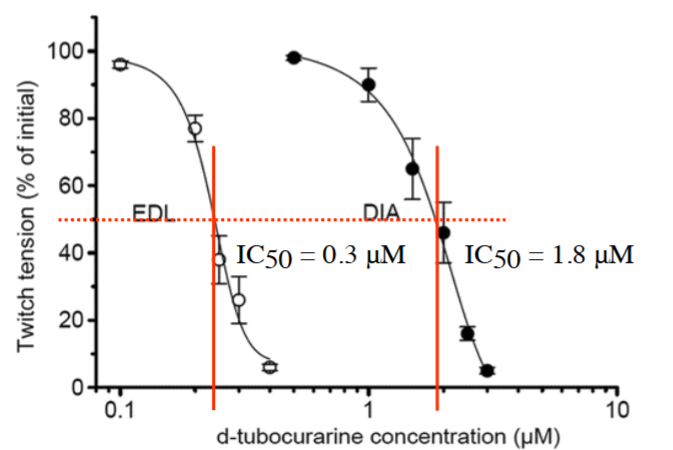
what is IC50?
half the conc needed for half the inhibition of an effect
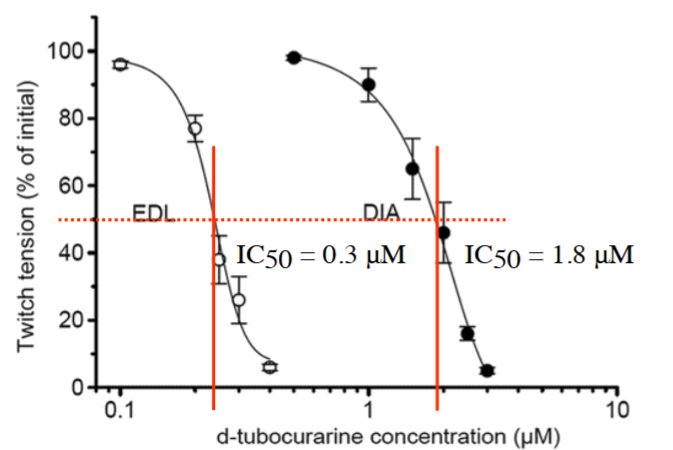
how can IC50 be quantified?
keep agonist conc constant and change conc of antagonist.
describe Otto Loewi’s experiment that came to him in a dream?
he took the liquid from one heart and put it on another frog heart (it induced APs in the 2nd heart proving transmission is chemical)
what are the 5 steps in ligand testing in neuropharmacological tests?
-choice of test system (in vivo or in vitro)
-route of ligand delivery (depends but could be microiontophoresis, bath incubation)
-equilibration (penetration, distribution)
-testing and establishing dose/response relationships (electrophysiology/ imaging)
-reverse/ washout / control experiments (specificity of effect)
what are the steps of microiontophoresis?
prepare micropipettes from glass capillary tubes (5mm tail ideal)
backfill micropipette with Ach (or other), place into a micro manipulator, position adjacent to site of interest
negative retaining current is set to prevent leaking of Ach
positive current given to eject Ach (set duration and intensity (min 5V))
set up software to start recording fluorescence, diameter or arteriole as soon as TTL pulse given
patch clamp and gigaseal formation: what are the variations?
cell attached
inside out patch
outside out patch
whole cell patch
(also special pokemone, perforated patch)
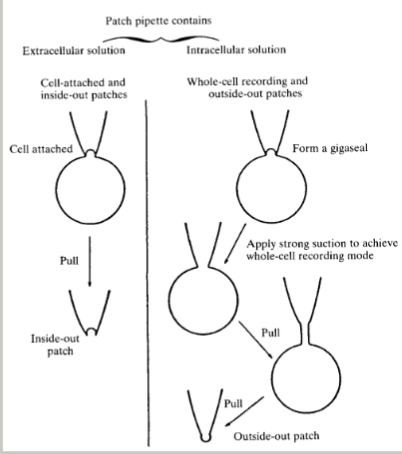
what is the size of intracellular vs extracellular micropipettes?
extra- 30-20 micrometers, intra- 1micrometer
what are the 3 paths of the trisynaptic hippocampus?
entorhinal cortex to the dendate gyrus granule cells (via perforant pathway)
dendate gyrus to the pyramidal cells of CA3 (via mossy fibres)
CA3 to CA1 granule cells (via schaffer collaterals)
in vivo vs in vitro vs in situ?
in situ- in organ/ organism? (slices of hippocampus)
in vitro- plate of cells? (outside normal environment)
in vivo- in living organism
what type of memory is the maintenance and (second phase) LTP in the hippocampus involved in?
spatial memory (one day or older)