DSA2: HAs - Osteopathic Considerations
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
SNOOP
-Systemic Sx
-Neuro Sx
-Onset sudden
-Onset under 5 y or after 50 y
-Pattern Change
What is the criteria to decide if a HA is secondary versus primary? What does it stand for?
Tension Type
Define Condition:
-Most common primary HA
-Bilateral pain
-Mild to Moderate intensity + tightness
-Can be infrequent, frequent, or chronic
-Due to muscular tension
-Tx = OMT, NSAIDs, Stretching, Biofeedback
-OA
-AA
-Suboccipital musc
-C2-C3
-Cranial
-Scalenes
-1st Rib
-Upper Thoracic Spine/Ribs
-Thoracoabdominal diaphragm
-Sacrum
What are common somatic dysfunctions seen Tension HAs?
Rectus capitis post major & minor have direct attachments to the cranial dura
Describe the "Biomechanical Model" behind Tension HAs
Nerves in the occipital triangle (Suboccipital, greater occipital, lesser occipital nn.) will become irritated when muscles around it are tightened/inflamed
Describe the "Neurologic Model" behind Tension HAs
Migraine
Define Condition:
-Unilateral HA
-Moderate to Severe intensity + Pulsatile quality
-May be due to neurogenic sensitization
-Assoc Sx = Nausea, Vomiting, Photophobia and/or phonophobia (+/- aura)
-Tx = OMT, Triptans, NSAIDs, Prophylaxis, Trigger Removal
trigeminal sensory afferents (aka Trigeminal nucleus & Trigeminal Ganglion + assoc nerves)
The development of migraine depends on the activation and sensitization of () that innervate cranial tissues --> creates tension depending on what nerve is irritated and what that nerve innervates
Where main part of Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) is located before it bifurcates into three branches; contains the temporal bone and sphenoid bone
Define Meckel's Cave
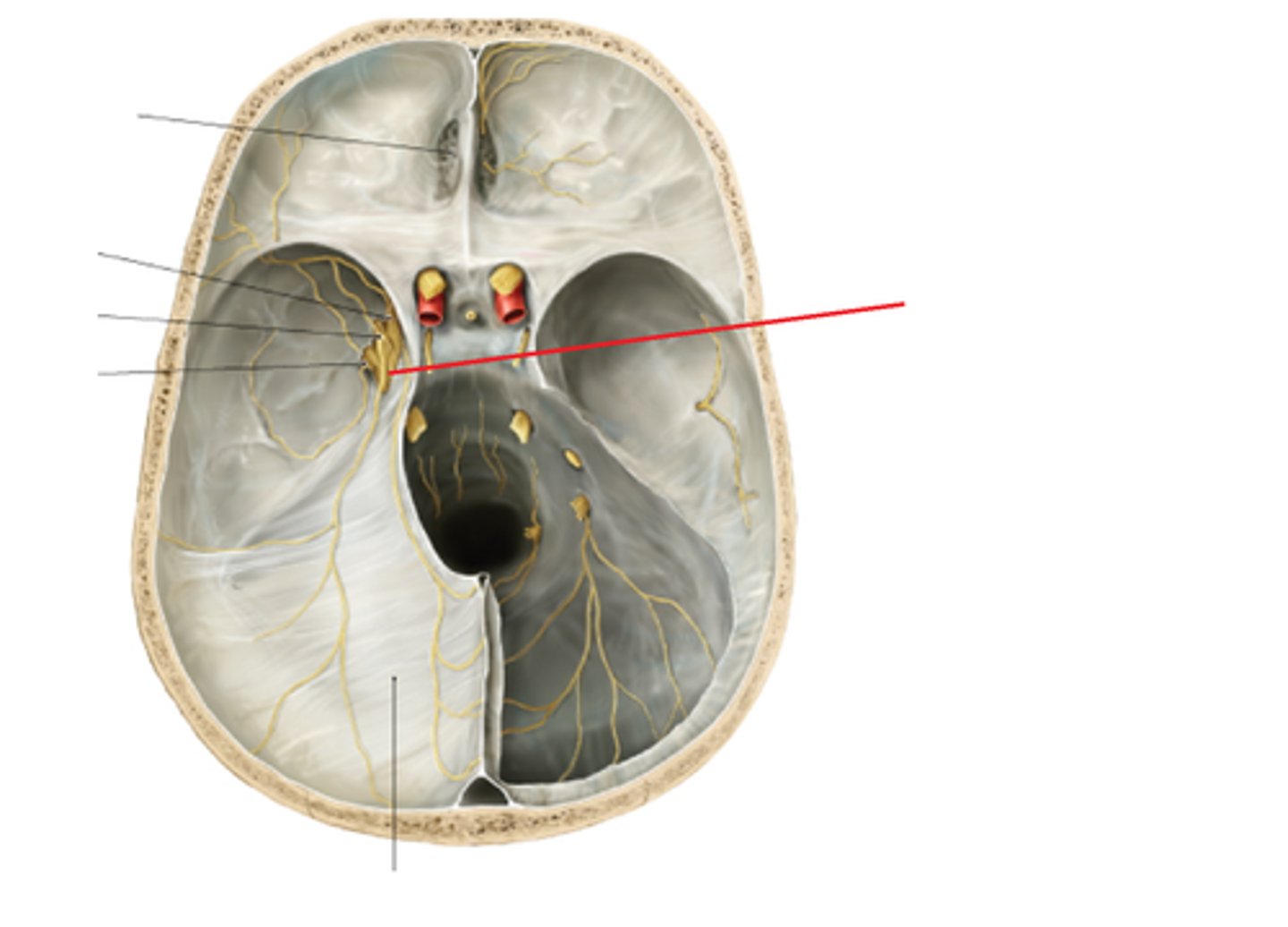
Focusing on the Trigeminal Nerve, Upper Thoracic/ribs, upper cervicals (pain fibers from C2-3) in Treatment
Describe the Neurological Model for Osteopathic Tx of Migraines
Focusing on cranial sutures/dura/musculature, Upp Cerv vertebrae/muscles/connective tissue and/or Sacrum
Describe the Biomechanical Model for Osteopathic Tx of Migraines
Focus on 1st rib/thoracic inlet
Or Venous SInus Drainage (w/n Dura Mater)
Or Brain Lymphatics
Describe the Respiratory Model for Osteopathic Tx of Migraines
Discover & Remove Triggers
Describe the Metabolic-Energy Model for Osteopathic Tx of Migraines
Psychological Support, Work Status
Describe the Behavioral Model for Osteopathic Tx of Migraines
OMT can trigger migraines
Why must caution be practiced with OMT for Migraines?
Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMJ)
Define Condition:
-Conditions characterized by pain in TMJ/surrounding tissues + clicking of joint during motion + limitations of mandible
-May be due to trauma, jaw clenching, teeth grinding, lip biting, etc
-Sx = Pain in jaw, head, neck, or ear + cervical spine dysfunction
-Tx = CBT +/- OMT, Physical therapy, NSAIDs, biofeedback
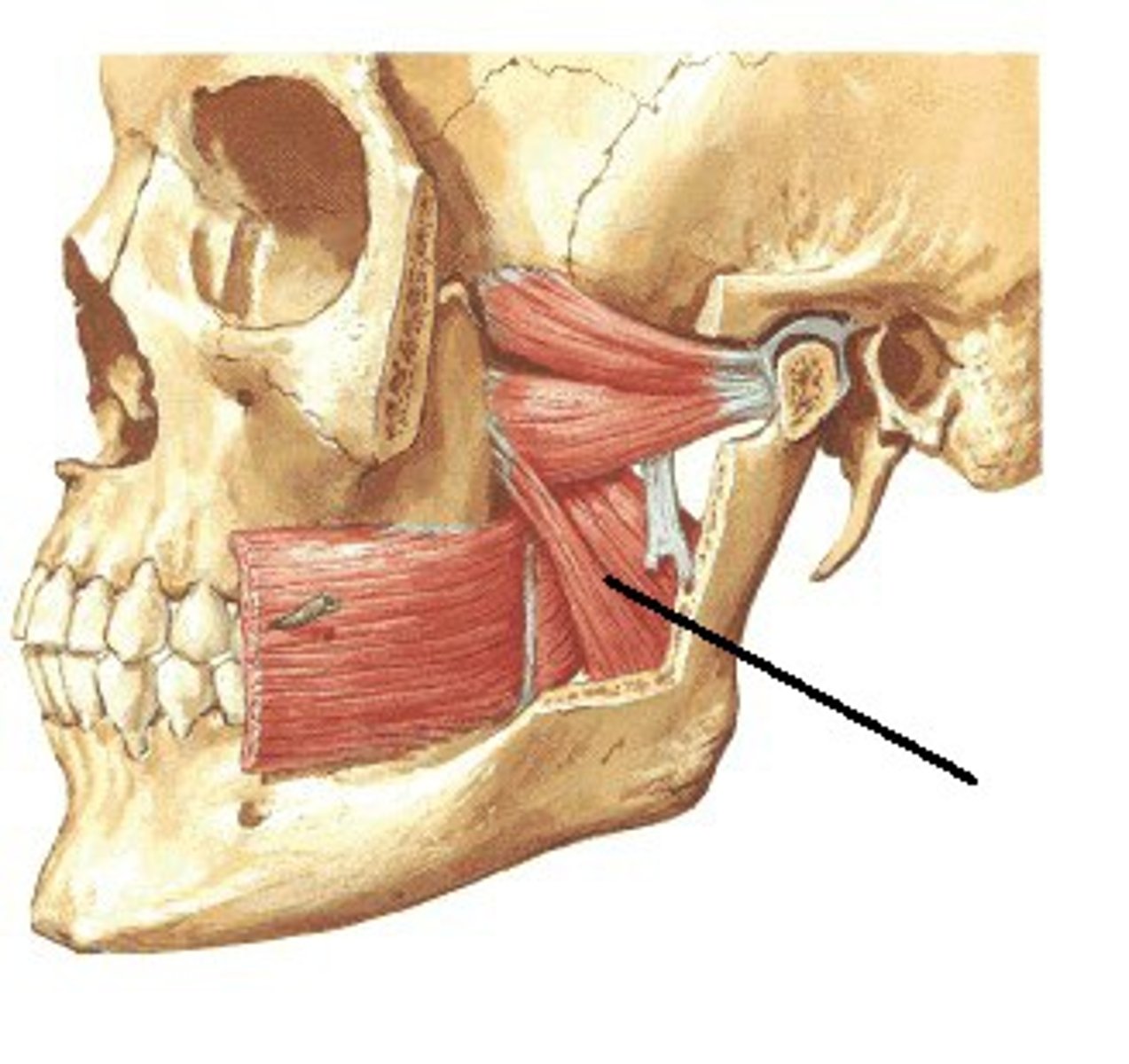
Medial Pterygoid
Which muscle within the TMJ attaches this way?
From the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate & adjacent maxilla to the medial aspect of the angle of the mandible
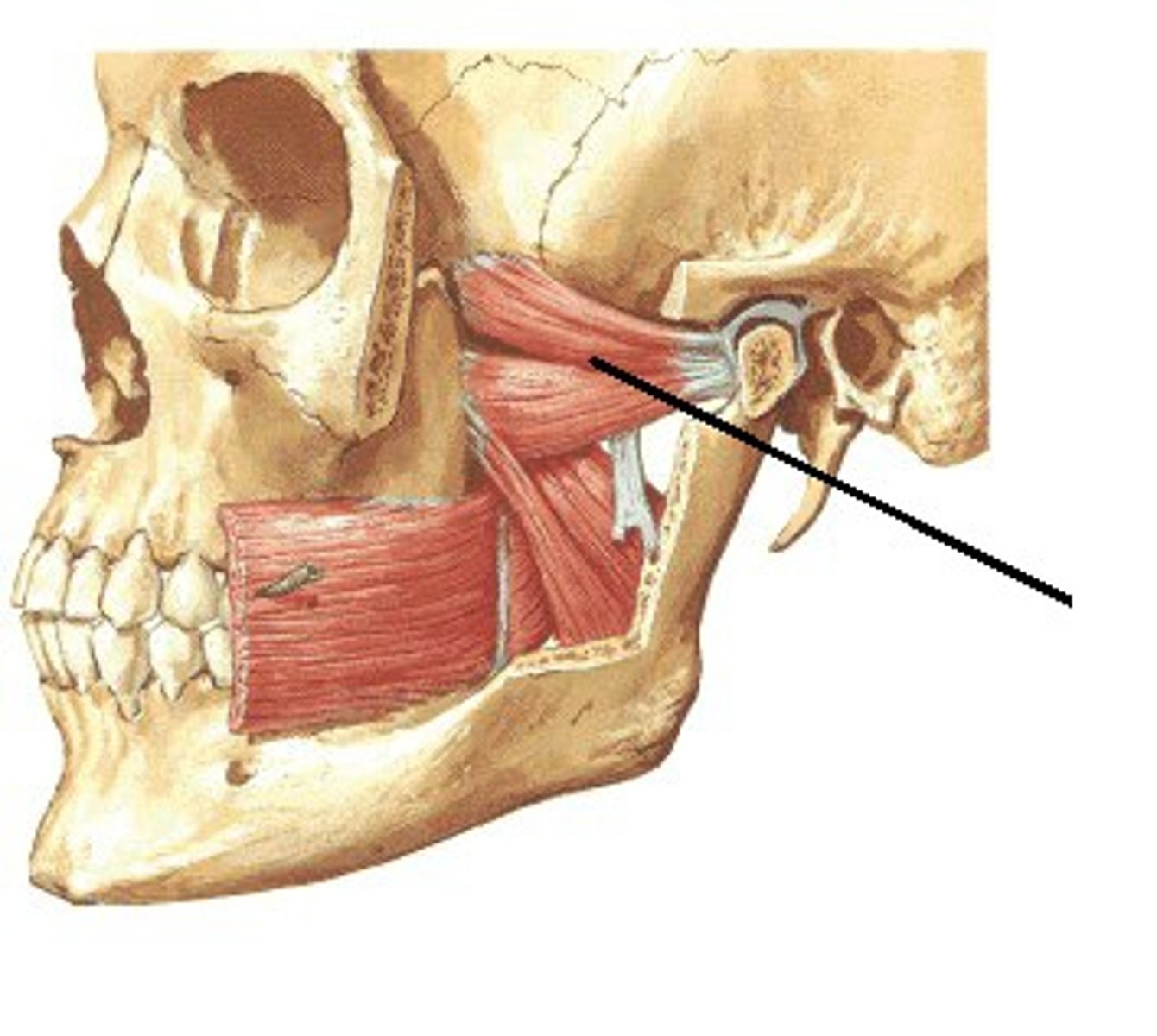
Lateral Pterygoid
Which muscle within the TMJ attaches this way?
On the lateral surface of lateral pterygoid plate and greater wing of sphenoid to neck of mandible and articular disc of TMJ
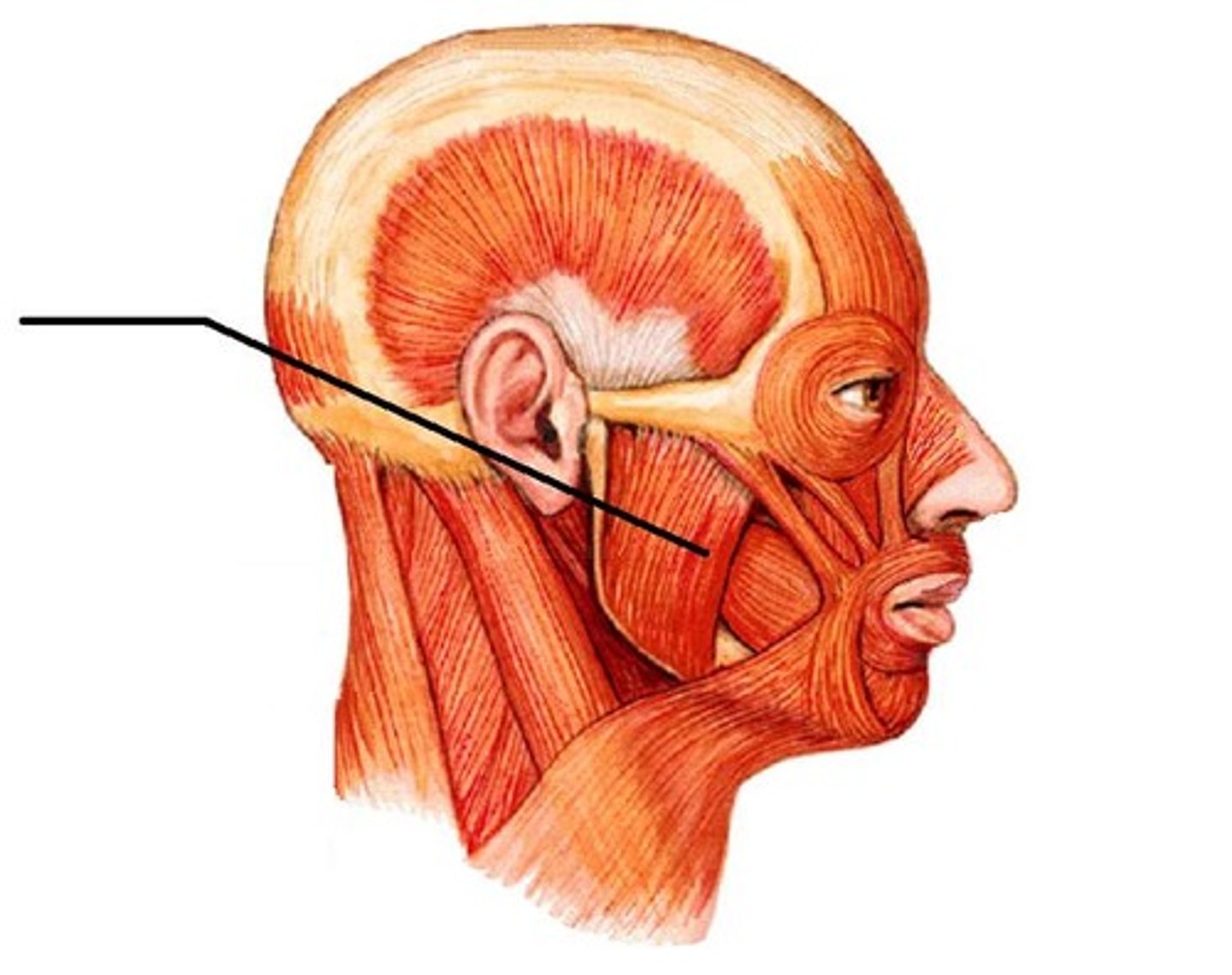
Masseter
Which muscle within the TMJ attaches this way?
From zygomatic arch to angle of mandible
–Mandible and musculature, upper cervicals, occiput (especially OM suture)
–Possibly: hyoid, anterior cervical fascia
–Consider Dental/Orthodontic referral for malocclusion, custom bite splint
Describe the Biomechanical Model for Osteopathic Tx of TMJ
–Decrease stress
–Change habits (clenching)
–OTC night guard
–Stretches, jaw/face self-massage
–Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Describe the Behavioral Model for Osteopathic Tx of TMJ
-Venous Sinuses + tributaries
-Dura mater
-Arteries
What are the Intracranial Pain Sensitive Structures of the Head?
-Skin, subcutaneous tissue,
-fascia, muscles, & arteries (includes TMJ)
-Eyes, ears, mouth, & nasal
-Cavities/sinuses
-Cranial periosteum (dura) and sutures
What are the Extracranial Pain Sensitive Structures of the Head?
is not
The brain parenchyma itself (is/is not) sensitive to pain
Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)
What nerve(s) provide(s) pain pathways for the following:
-Structures above the Tentorium cerebelli
-Frontal, Temporal & Parietal regions (+ TMJ)
Glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X), upper c-spine nerves
What nerve(s) provide(s) pain pathways for the following:
-Structures below the Tentorium cerebelli
-Occipital Region
-C1-C3 via greater & lesser occipital nerves for sensory information
sympathetic tone; trigeminocervical nucleus
Treating the upper thoracic spine can influence the () to the head.
Treating the upper cervical spine influences the input into the ().
T1-T4:
-Blood vessels
-Pupils
-Lacrimal gland
-Salivary glands
-Blood vessels
-Mucosal surfaces
Where is the sympathetic innervation to the head and neck located? What does it innervate?
Provides sympathetic innervation to head/neck --> Increased sympathetic tone leads to vasoconstriction and increased sensitivity to pain
Why might treating the Upper Thoracic Spine help in HA Tx?
neurologic sensitization and pain
Any structure innervated by trigeminal and/or upper cervical nerve roots can become irritated and contribute to () in the head
Somatic dysfunction in the occiput & cranium can disrupt venous drainage from the head (CSF, etc)
How can the Respiratory/Circulatory system be responsible for causing Headaches?
Increasing Omega-3s (anti-inflammatory) & Magnesium in diet
What are some natural remedies for HAs, as proposed by the Metabolic/Energetic Model?