Microbial Evolution exam 1
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
what is evolution?
change in genetic composition of a population with the passage of each generation
changes in allelic frequency in populations over time
time + generation + genetic composition =
Microevolution
small divergence
adaptation
ex/ bacteria changing to become resistant
Macroevolution
Big divergence
Speciation
ex/ beak shape
Sources of Genetic Diversity
Mutation
Gene flow
Genetic drift
Selection (natural and artificial)
Characteristics of all living things (organisms)
metabolism
organization (cells)
reproduction
growth/develop (more than one stage of life)
Adaptation
Homeostatsis
Asexual Reproduction
the organism is producing more of itself without the assistance of any other organism
ex/ bacteria and microbes
Sexual Reproduction
there are two types (male and female) of an organism that come together in some way and produce another organism like themselves
Viruses
a NON-living thing that is able to grow inside another organism and form more of itself
it can not grow without the help of living organism
acellular microorganisms, extremely small
What are microbes when is comes to the domains of life?
everything but plants and animals plus viruses
LUCA
Late Universal Common Ancestor
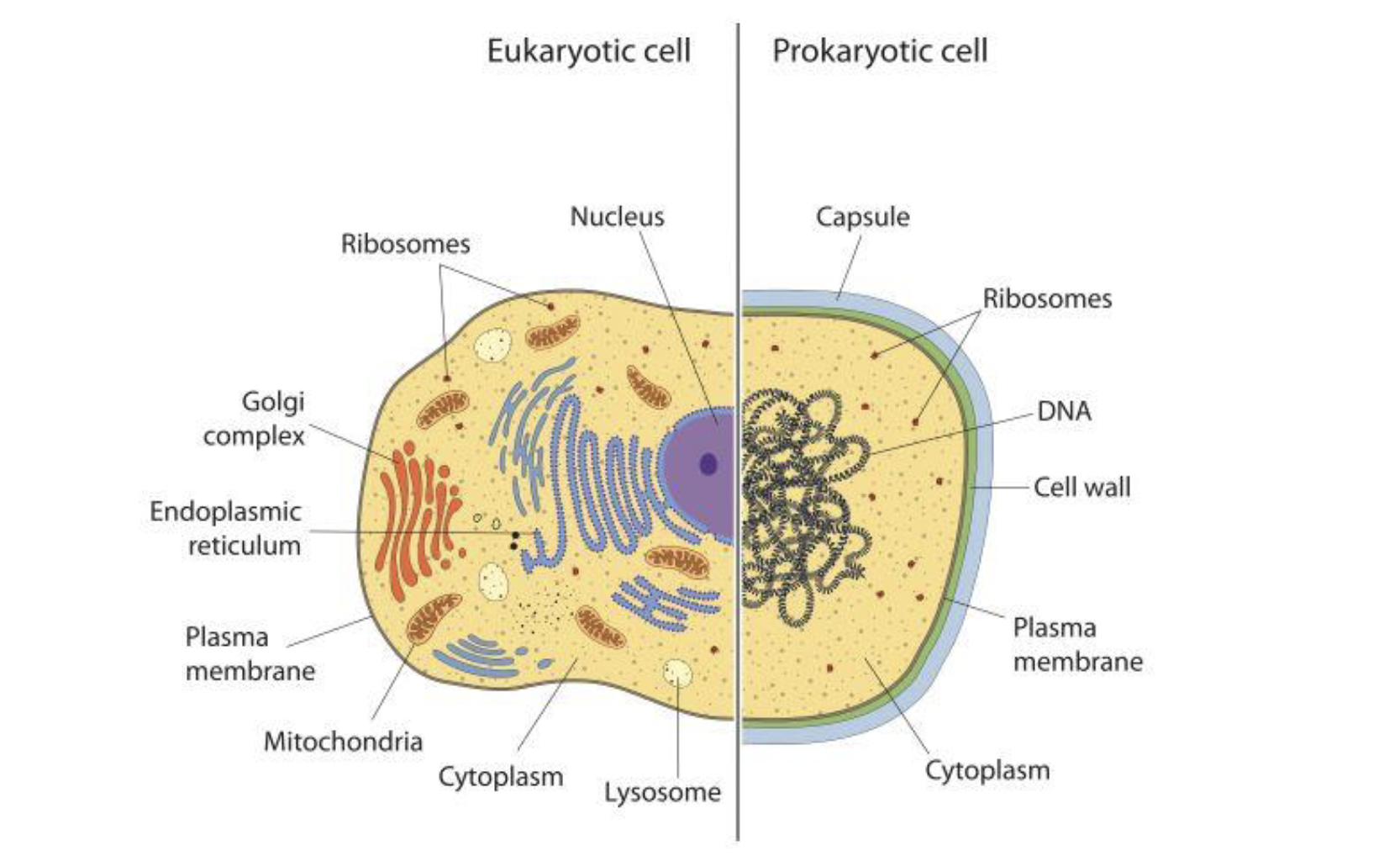
Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic
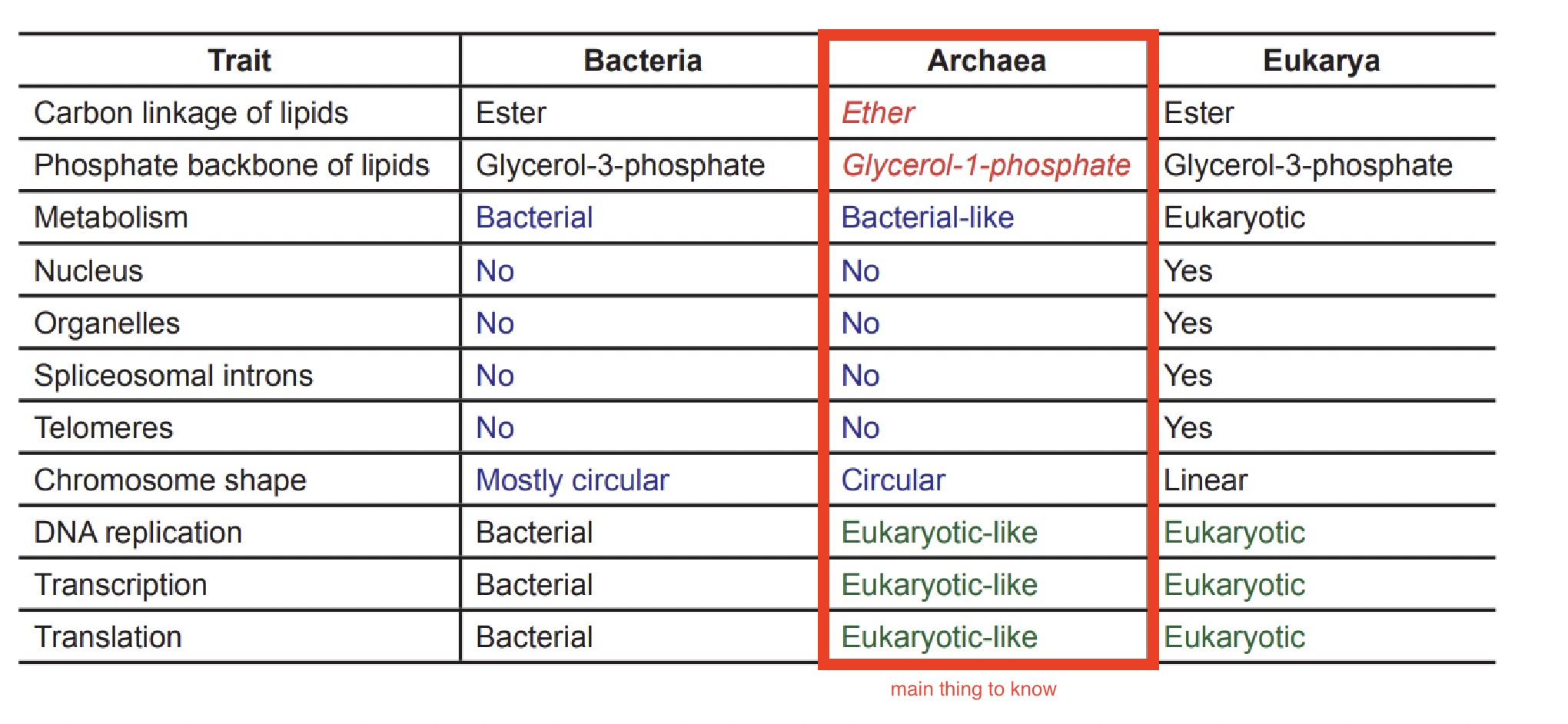
Comparison of a few traits of bacteria, archaea, and eukarya
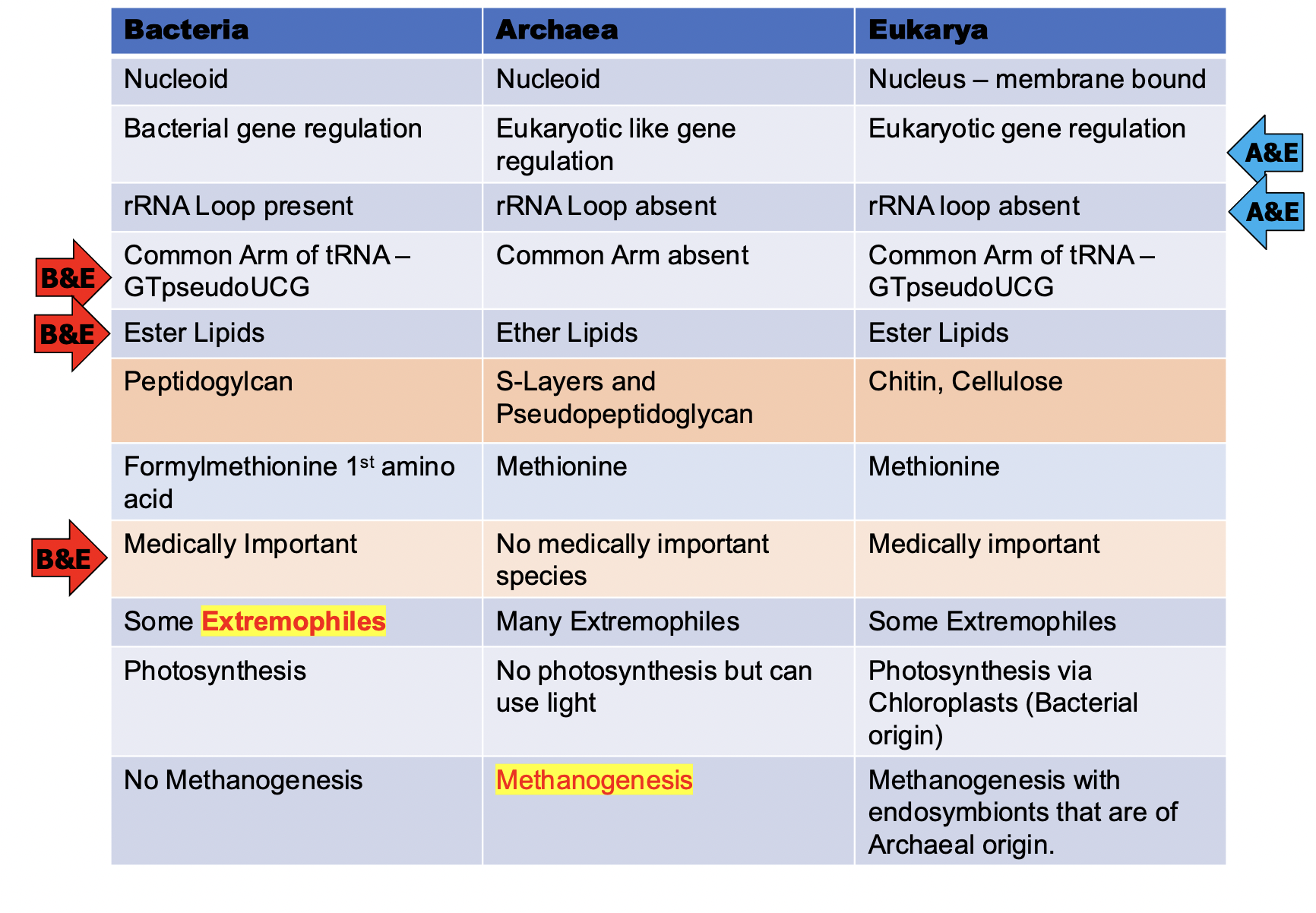
Know the arrow and highlighted parts
Microorganisms
mostly exist as single cells, clusters of cells that can independently carry on all of the necessary processes of life to grow and divide
Biomass
weight after water is removed
Subsurface bacteria
no oxygen, lots of pressure, cold, and dark
vast majority of bacteria are thought to be subsurface (over 80%)
Microbial Diversity
Morphological Diversity
Genetics Diversity
Functional Diversity
Habitat Diversity
Grouping of Organisms/Microbes
life→domain→kingdom→phylum→class→order→family→genus→species
Species
Operational taxonomic unit that has an ANI (Average Nucleotide Identity) of less than 3% or (5%) different at the DNA level in the conserved genes
Population genetics
field of biology that studies allele frequencies in populations and how they change overtime
Population
group of organisms of the same species that are found in the same area and can interbreed
gene pool
a population consists of all copies (alleles) of all the genes in that population
allele frequency
how common an allele is in a population
Mutation
a heritable change in the nucleotide sequence of an organism’s genome
if a mutation is evolution a change must occur
sexual reproduction is the most important driver for different mutations (crossing over)
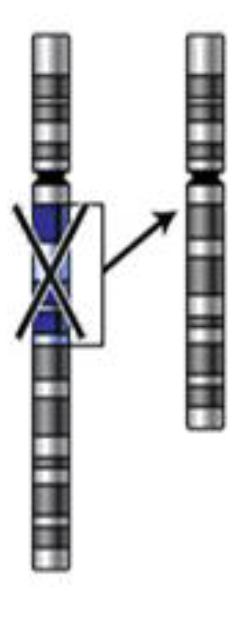
Mutation: Deletion
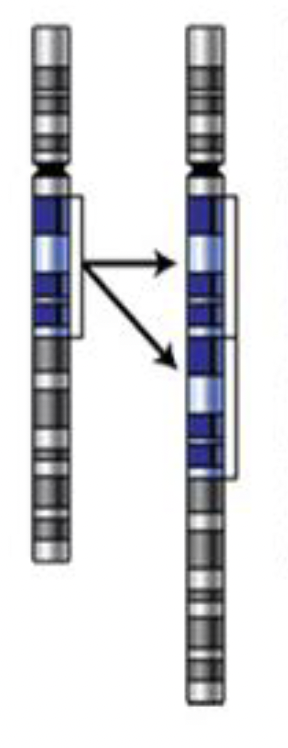
Mutation: Duplication
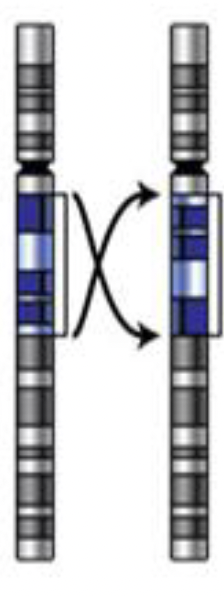
Mutation: Inversion
Mutation: Insertion
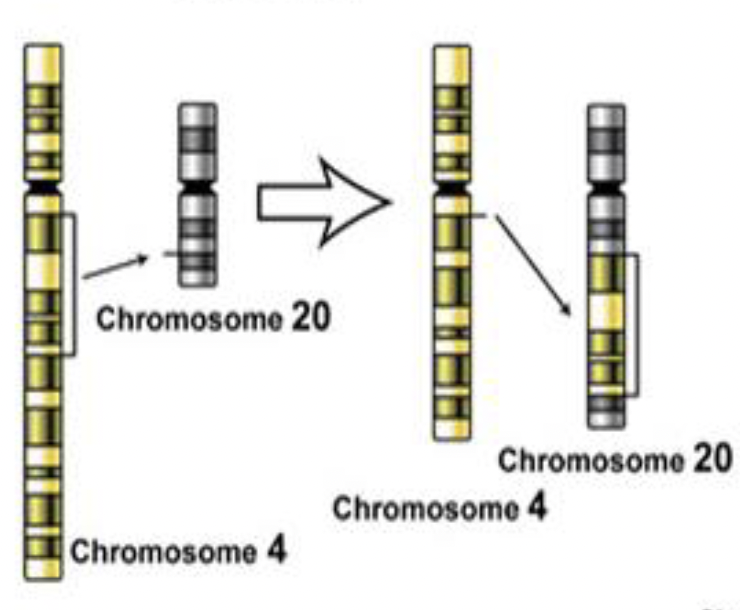
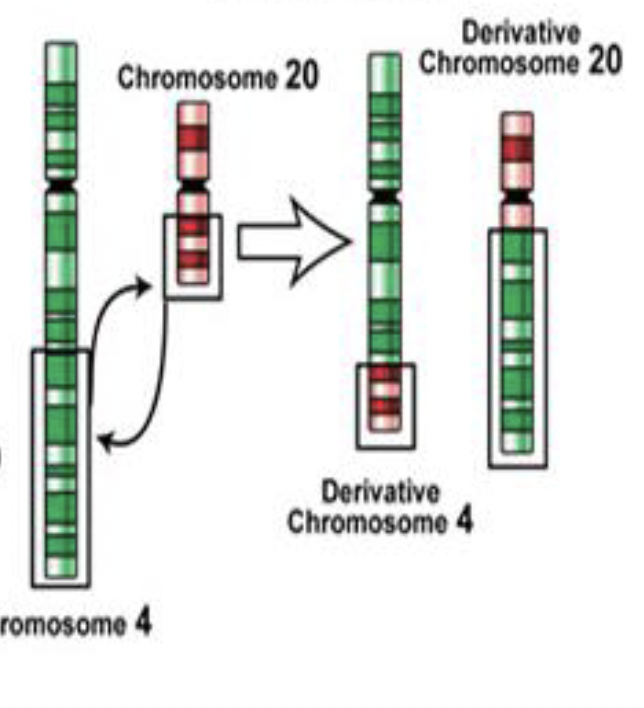
Mutation: Translocation
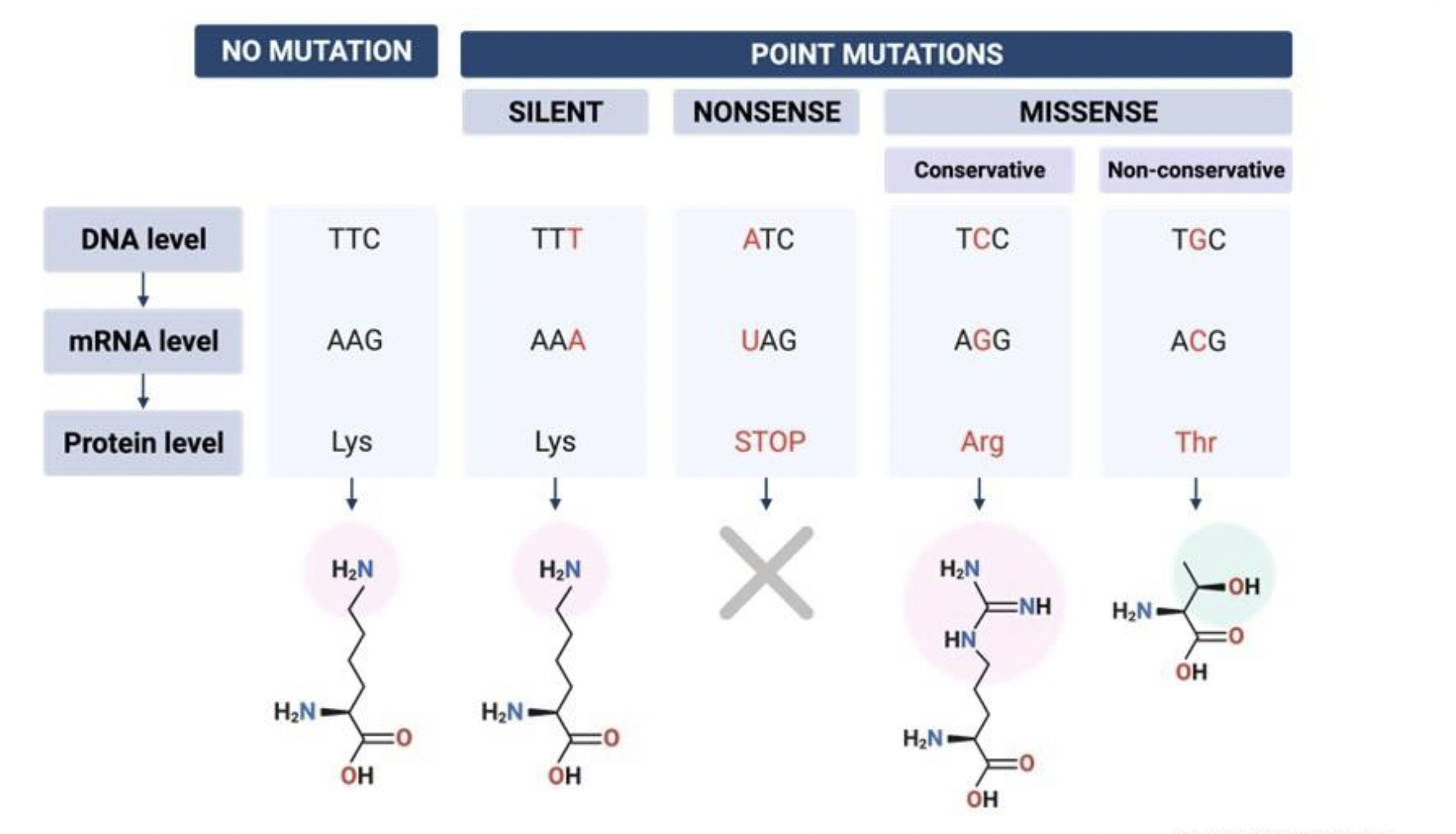
Point Mutations
Gene flow
the movement of alleles into, or out of, a population as a result of immigration or emigration
Gene Flow in bacteria
genetic transfer processes like horizontal gene transfer, allow DNA to pass between organisms without the need for sexual reproduction
Horizontal Gene Transfer (HGT)
the movement of genetic information across normal mating barriers, between more or less distantly related organisms (no new generation)
Genetic Drift
change in the composition of a gene pool as a result of chance or random events
Natural Selection
which more advantages traits are likely to be passed down
Three Requirements:
different individuals in a population have different traits
traits are heritable
some traits help individuals that possess them survive and reproduce better than other traits
doesn’t cause mutations or adaptions- they arise randomly, and it selects beneficial ones
fitness
an individual’s ability to produce viable offspring
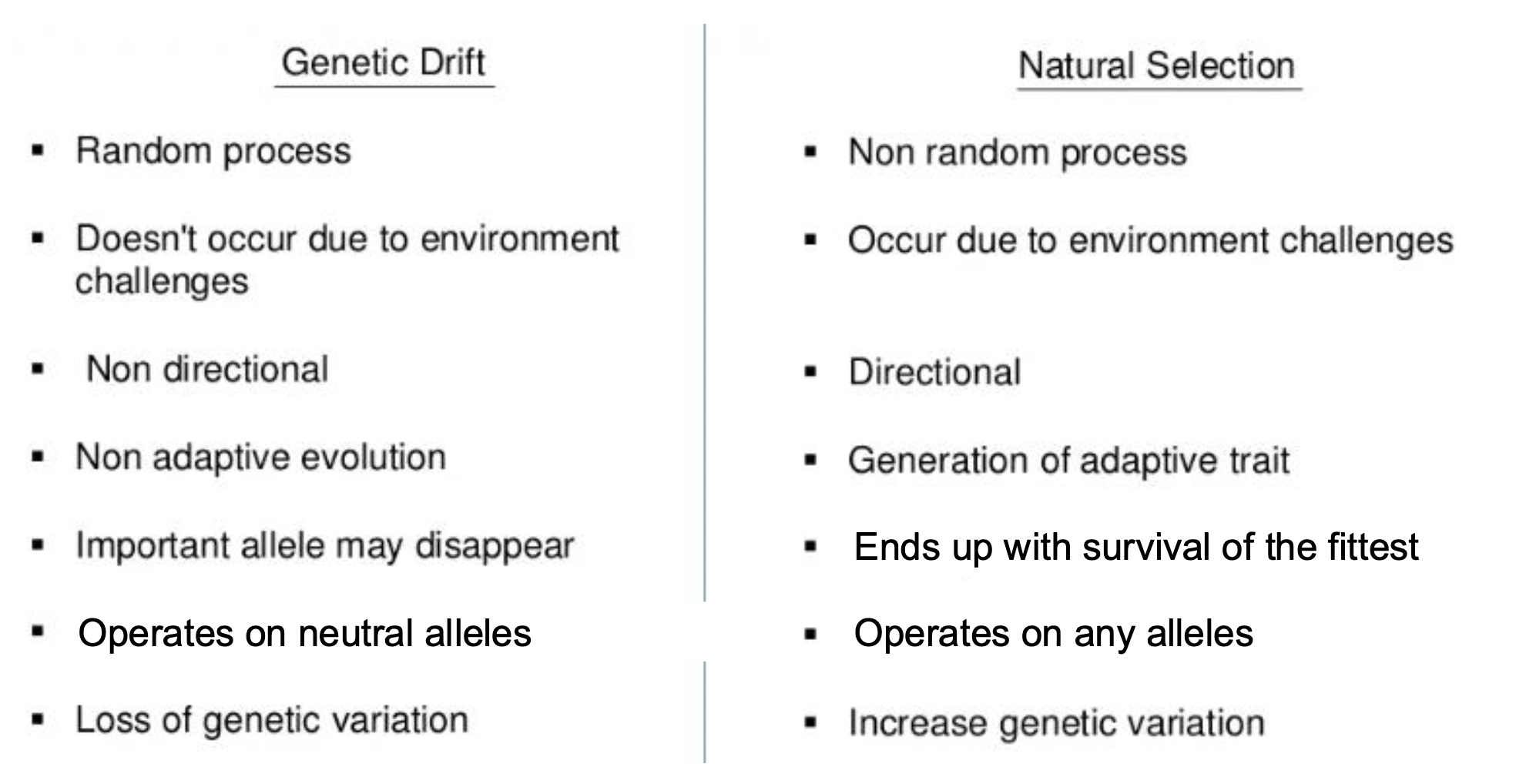
Genetic Drift vs. Natural Selection
Bottlenecks effect
an event reduces population size by an order of magnitude
surviving population has less genetic variability than before
The newly developing gene pool will be divergent from the original
Founder Effect
when a small group breaks away from a larger population to colonize a new territory
differs from bottleneck in that original population remains largely intact
Systematics
study of the diversity of life, with focus on relationships between organisms
taxonomy
science of classifying organisms
for microbes, based on phenotype, genotype, and phylogeny
Phylogeny
study of evolutionary relationships between organisms
study using molecular sequence comparsions
Phylogenetic tree
shows evolutionary relationships between organism/classes of organisms
Homologous genes
originated from common ancestor
Orthologs
homologs with same functions
Paralogs
homologs with different function
rooted tree
shows branch/node for last common ancestor of all organisms on the tree
unrooted tree
doesn’t show last common ancestor
Microbial species (commonly accepted definition)
group of strains with similar genetics and characteristics that share a recent common ancestor
core genome
genes all strains of that species have
pan genome
genes that only one or some strains of that species have
Two main kinds of information inherent to any tree
topology
branch lengths
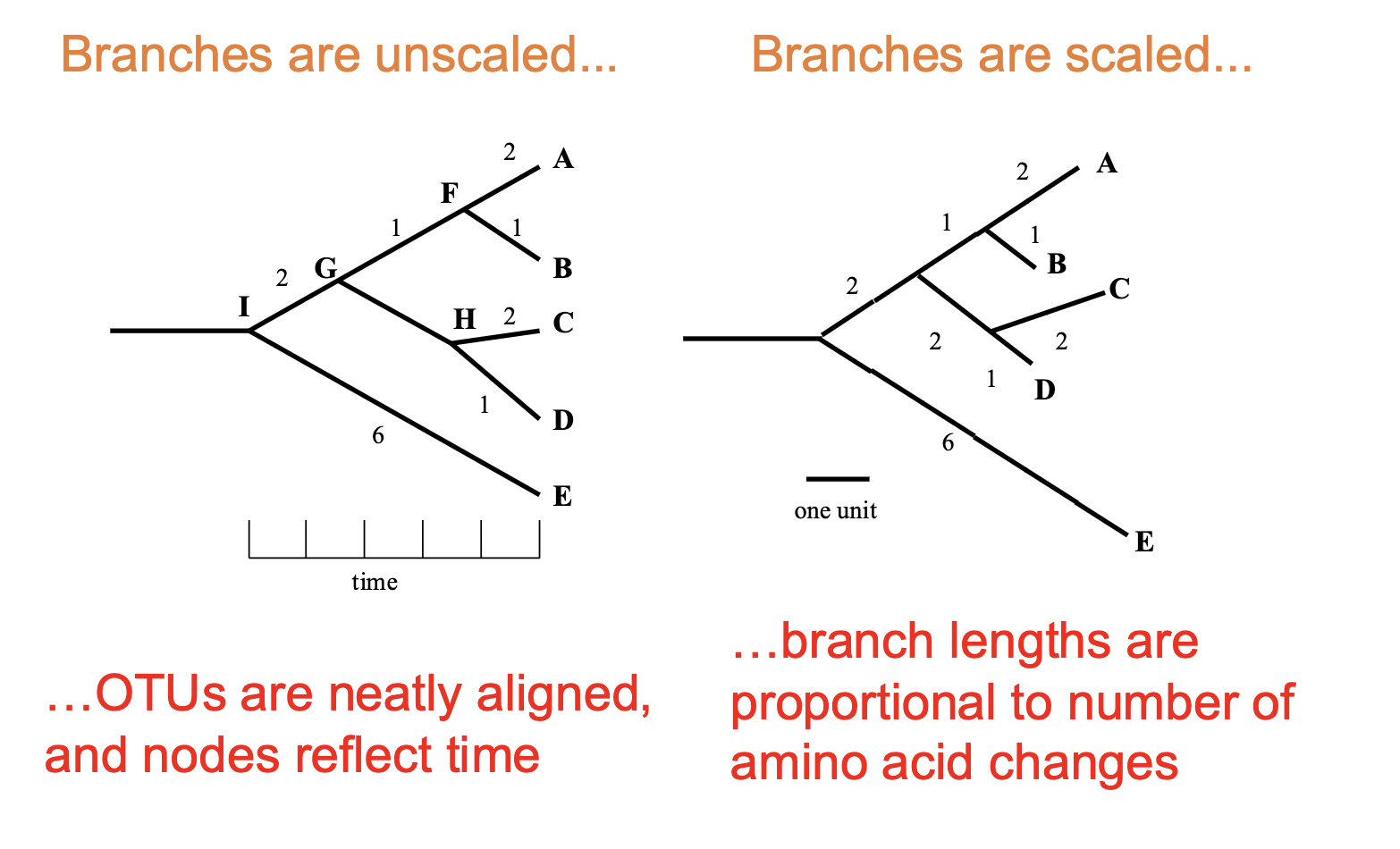
chronogram
allows you to look at chronology
how long in the past they separated
can treat a genetic distance that is larger as the same as one that is smaller
Phylogram
focuses on genetic distance
branch lengths all directly correlate to genetic distance
visually less pretty
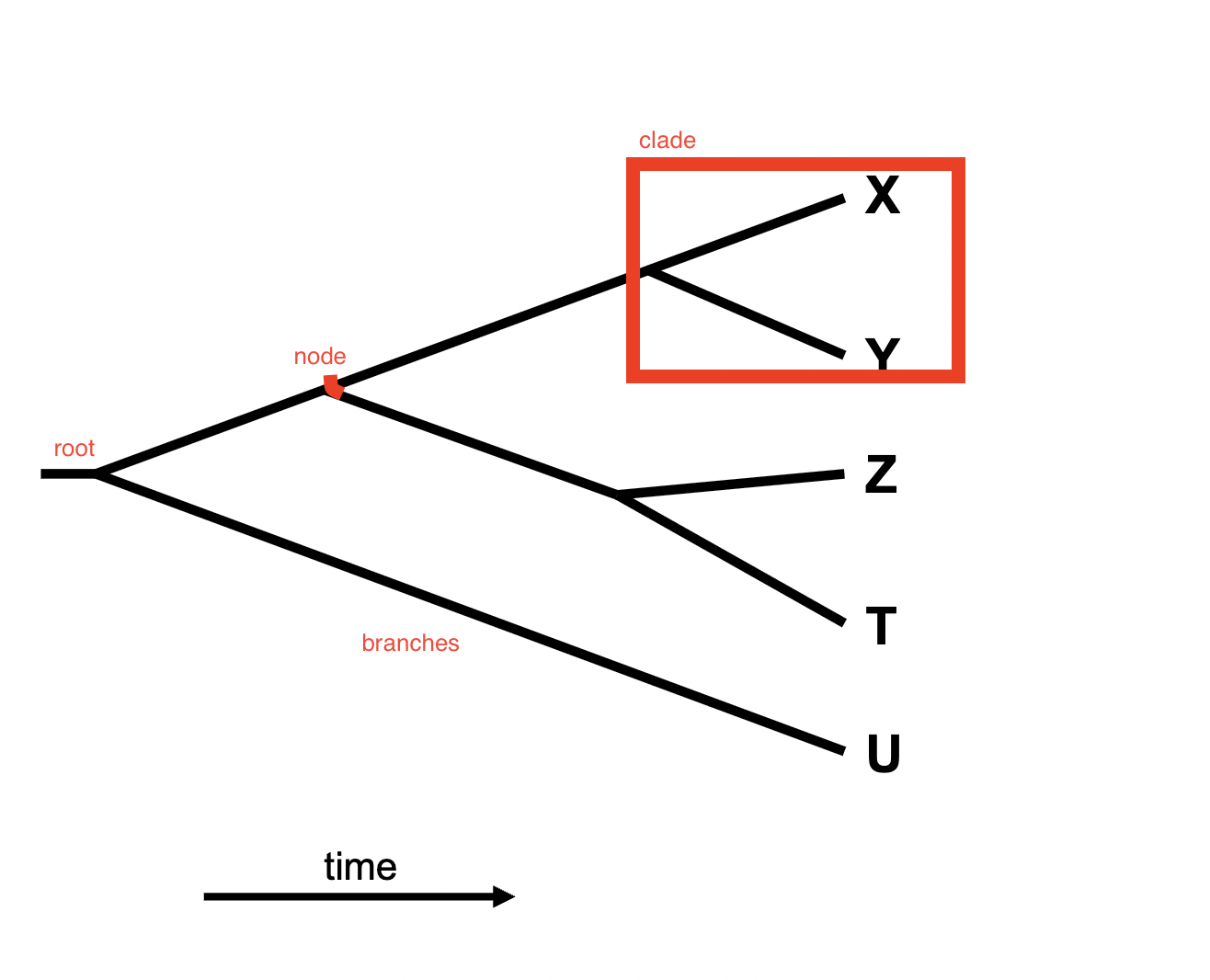
Taxon
an organism that exists as a distinct population
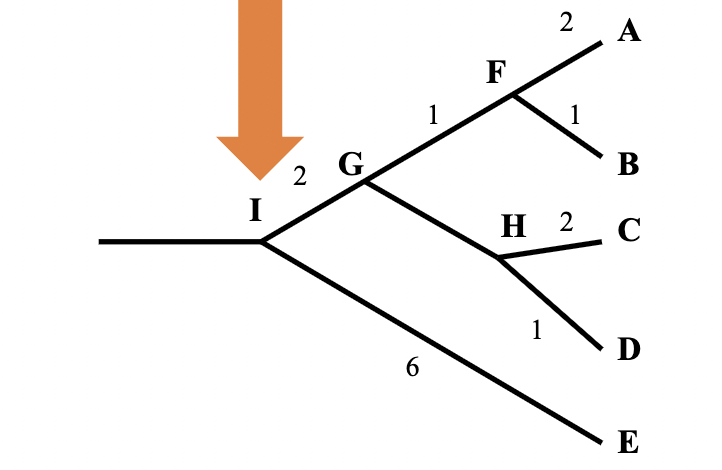
Operational taxonomic unit (OTU)
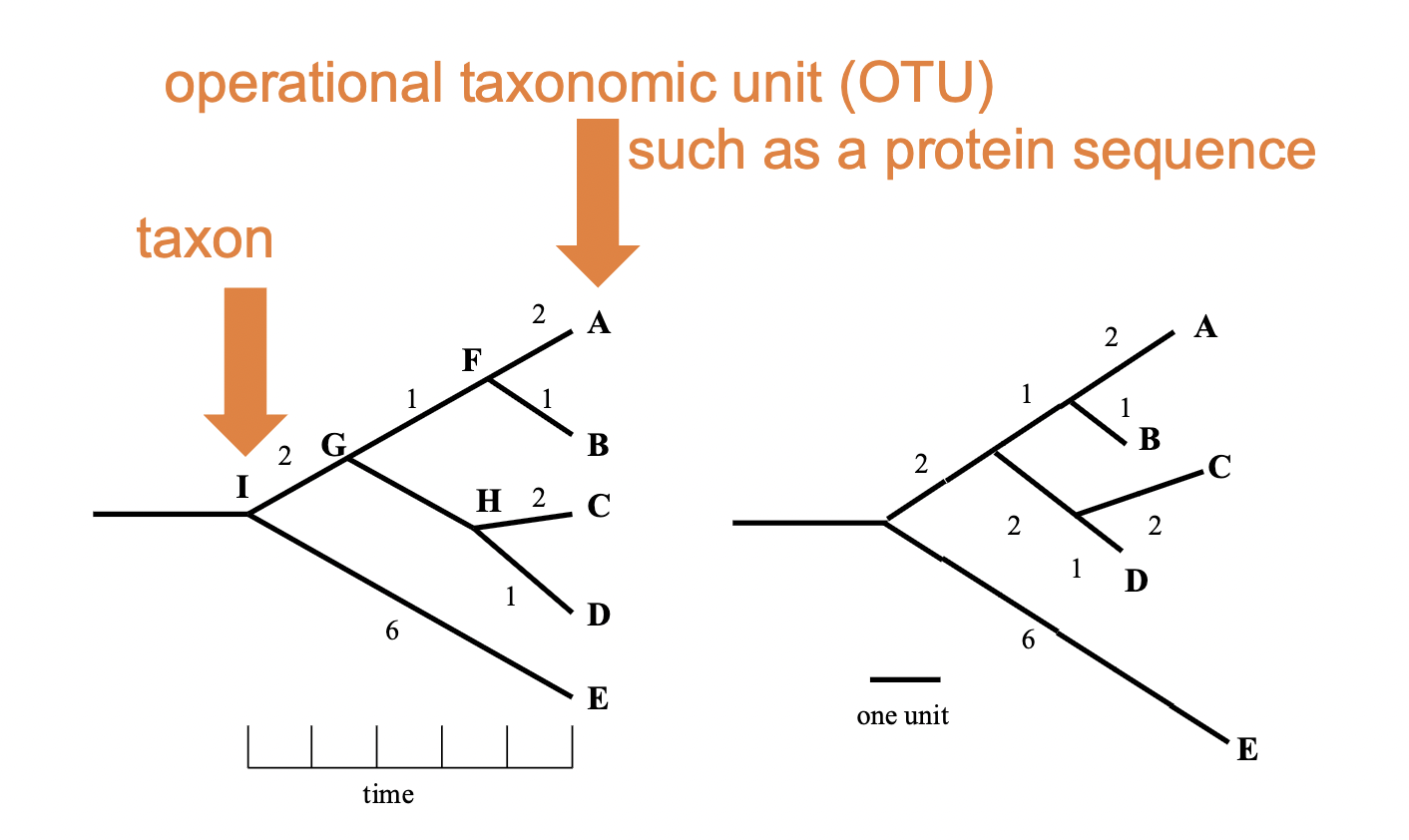
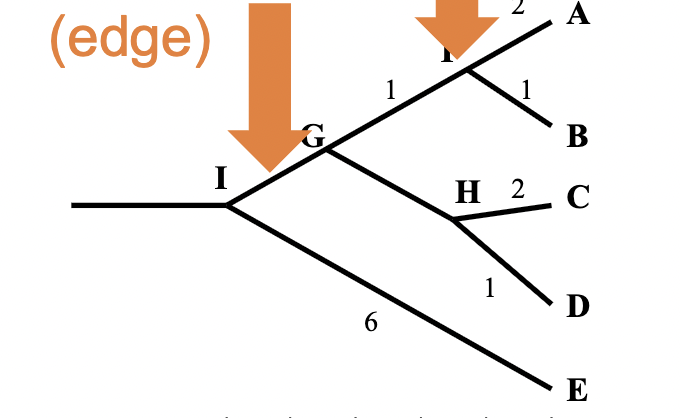
branch
branch length is very important
if branch length is set to match the change, it can tell you the genetic distance visually (not in a chronogram)
Unscaled vs Scaled branches
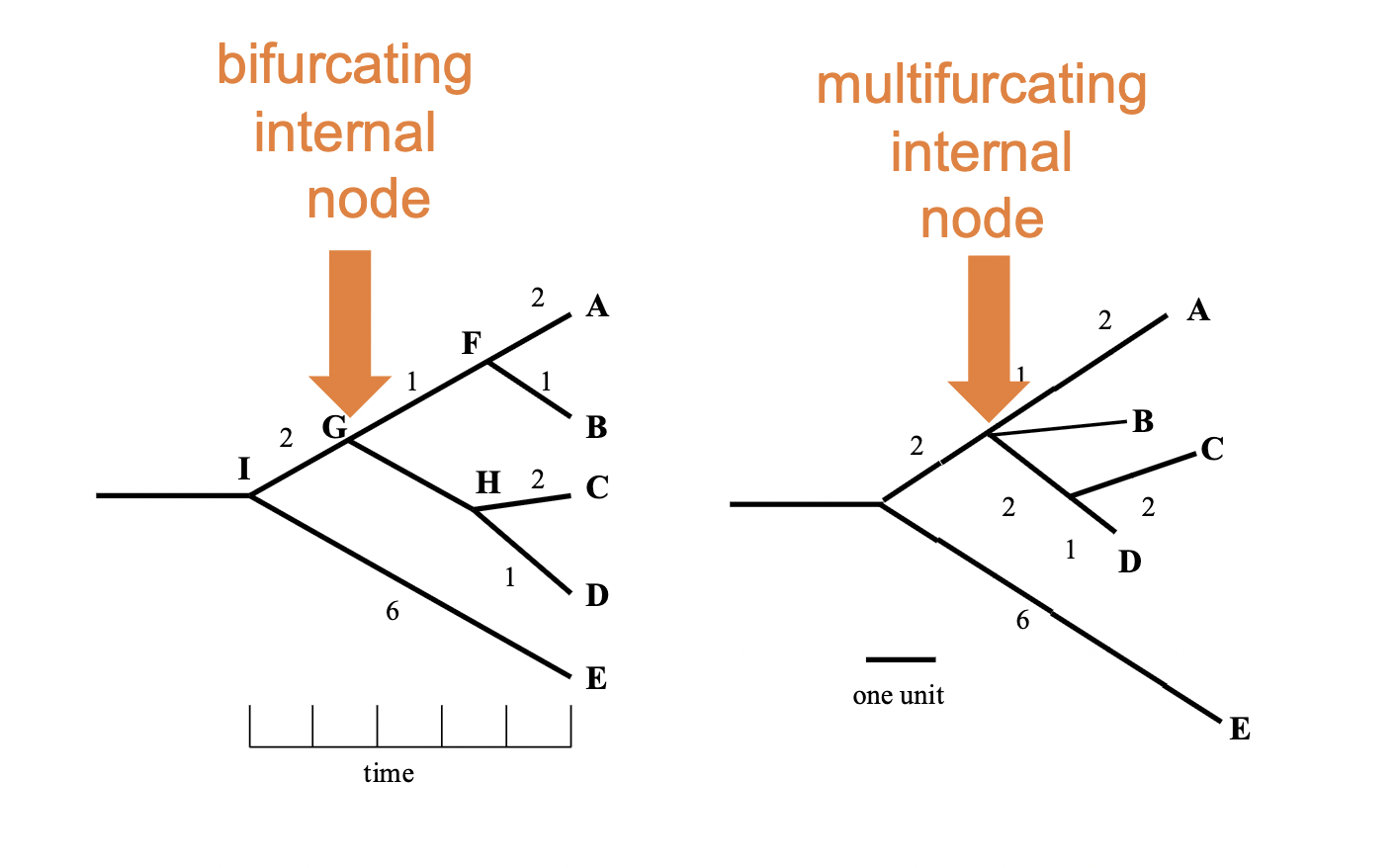
bifurcating vs multifurcating
monophyletic
consists of a common ancestor and all its descendants
Clade ABF- A and B are descendants of F
Outgroup
more distantly related used as a reference point
formula for possible arrangements
2^N-1
tree growth
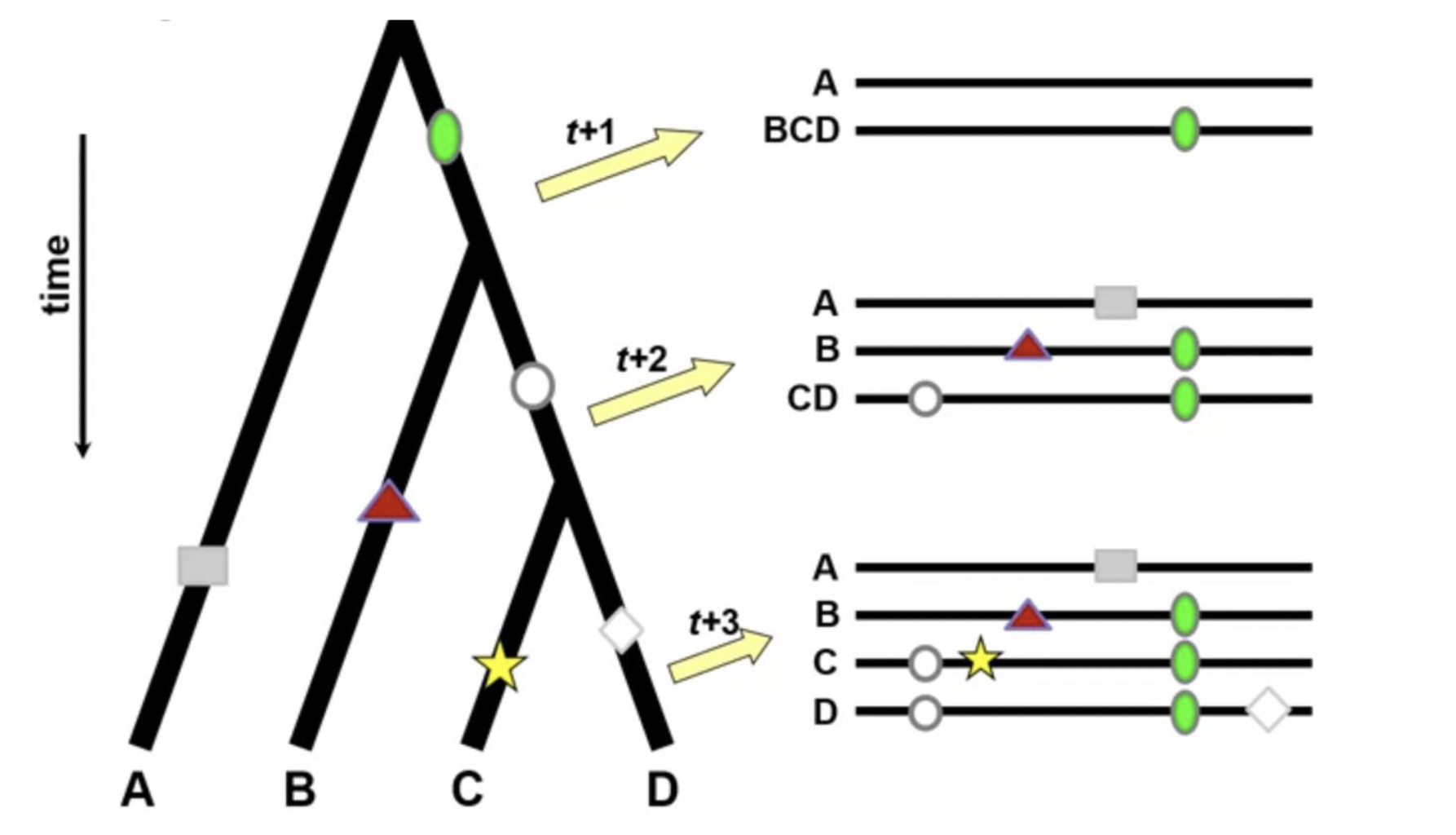
tree anatomy
Homoplasy
similarity due to parallel evolution, convergent evolution or secondary loss
Homology
similarity due to common ancestry
Parallel evolution
independent evolution of same character from same ancestral state
Convergent evolution
independent evolution of same character from different ancestral states
Secondary loss
Reversion to ancestral state
this is your reminder to look at substation matrices (ppt 4 slides 19-32)
YOU’VE GOT THIS
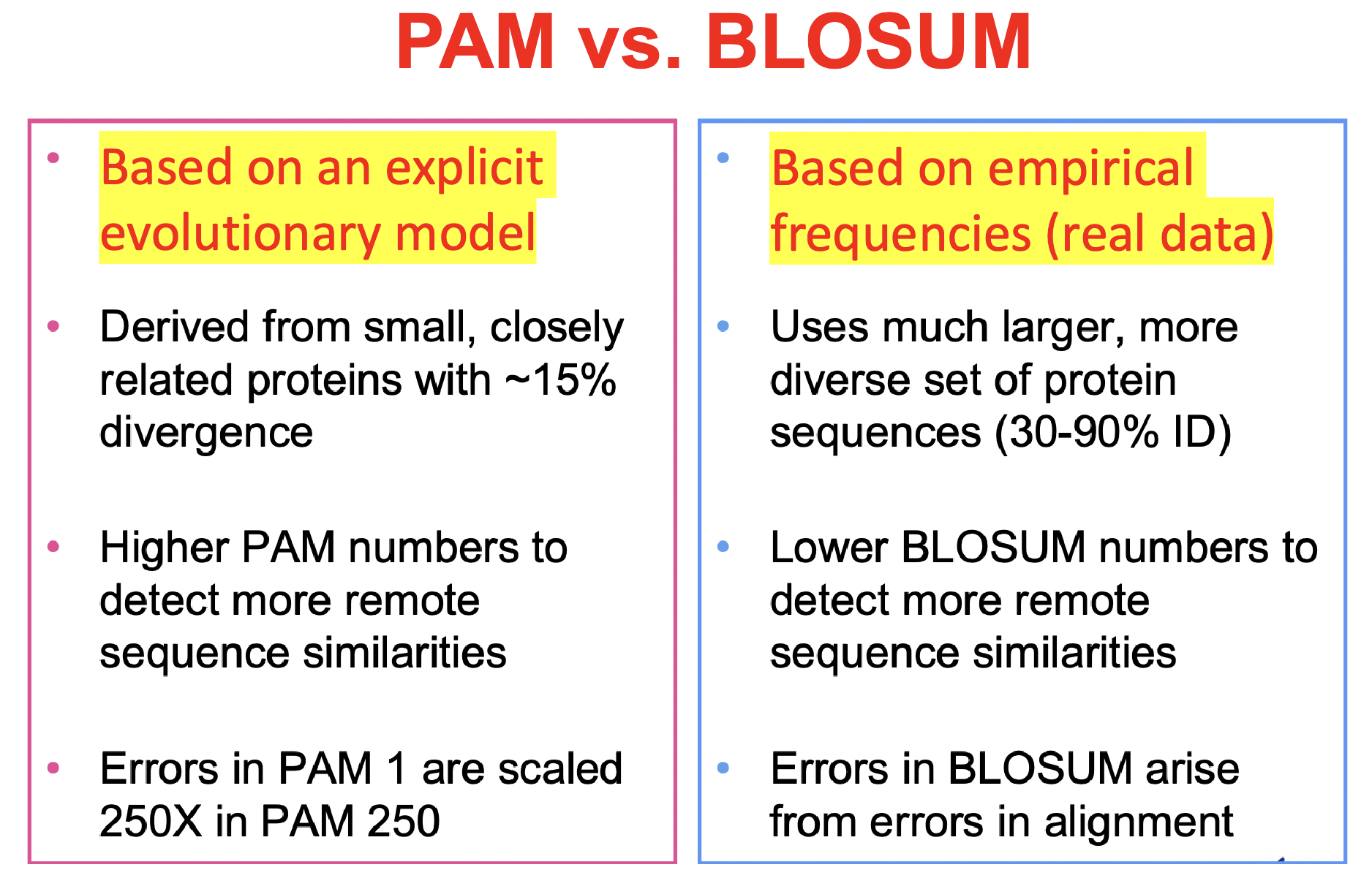
PAM
Point Accepted Mutations (ppt 5 slides 6-13)
BLOSUM
blocks amino acid substitution matrices (ppt 5 slides 14-18)
PAM vs BLOSUM