Chapter 8: Transport Across Membranes
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Channel the transport of water
Aquaporin
Hydrophilic in nature so it can promote the transport of the polar water
Inner region
Hydrophobic because they are exposed to the hydrophobic interior of the plasma membrane
Outer region
How many aquaporins are there in one RBC?
200,000
Glucose is transported inward by a
glucose transporter (GLUT, GLUT1)
An integral membrane protein with 12 transmembrane segments (12 passes), which form a cavity with hydrophilic side chains
GLUT1
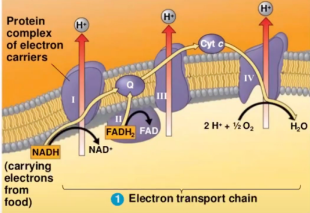
Involved in ETC. Establishing Electrochemical Gradient
Protein Complex of Electron Carriers
TRUE OR FALSE:
Sometimes we need to have an imbalance environment to push other cellular processes forward
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
Concentration of proton pumps (H+) will establish a gradient, which will push the synthesis of ADP
False
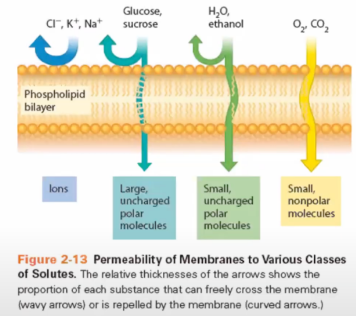
Ions have a difficulty in crossing the membrane because the cells have a lot of water, surrounding by the
sphere of hydration
Can go through, O2, CO2
Small, uncharged solutes
Glucose, sucrose. Can go through but to a lesser extend. Can use GLUT1 or tranpsorters
Large, uncharged solutes
Uses ATP. Needs energy. Movement is from the lower electrochemical gradient to higher concentration
Active Transport
Movement DOWN to the concentration movement (higher to lower)
Diffusion
Movement UP to the concentration movement (lower to higher)
Active transport
Diffusion where no membrane proteins needed to pass through like O2, CO2
Simple diffusion
Diffusion where it uses protein channels to pass through
Facilitated Diffusion
Diffusion where it is a movement up to the concentration gradient
Active transport
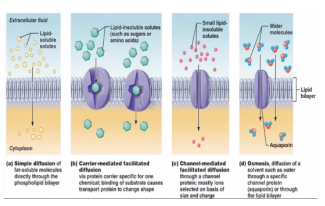
What would happen if O2 and CO2 diffusion will need membrane diffusion?
Difficulty in respiration
Change in conformation, Pushing the molecules inward
Carrier Membrane Proteins
Always open
Facilitated and Osmosis
How will the drug enter the plasma membrane? (Kinetics)
Transport mechanism
Small vesicles forming a closed, spherical lipid bilayer lacking proteins
Liposomes
Discovered that when lipids from cell membrane are dispersed in water, they form liposomes
Bangham
TRUE OR FALSE:
Solute molecules that are dissolved in water do not disrupt the interactions that normally occur between water molecules
False
TRUE OR FALSE
Water thus moves from regions of high to low solute concentration
False
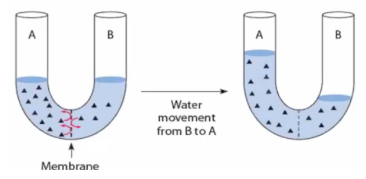
Diffusion involving water
osmosis
Exposing the cell to very high concentration of solute outside the cell. Solute concentration is high outside the cell. Movement of water is from inside to outside of the cell. Animal cell will shrink
Hypertonic solution
Exposing the cell to so much solute outside. Solute will go inside
Hypotonic solution
FILL IN THE BLANKS:
The movement of an ion is determined by its ________________, the combined effect of its concentration gradient and the charged gradient across the membrane
electrochemical potential
FILL IN THE BLANKS:
The movement of an ion is determined by its electrochemical potential, the combined effect of its _________________ and the charged gradient across the membrane
concentration gradient
FILL IN THE BLANKS:
The movement of an ion is determined by its electrochemical potential, the combined effect of its concentration gradient and the _____________ across the membrane
charged gradient
Carry oxygen from the lungs to the body tissues, and to carry carbon dioxide (waste product) away from the tissues and back to the lungs
RBCs
An important protein in RBCs that carries oxygen from the lungs to all parts of our body
Hemoglobin (Hgb)
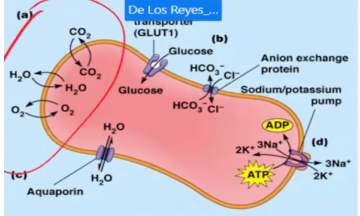
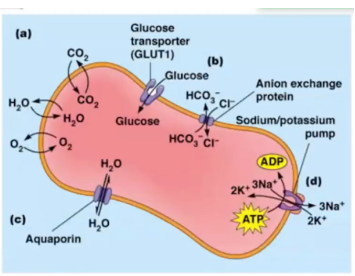
Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water diffuse directly across the plasma membrane in response to their relative concentrations inside and outside the cell. No transport protein is required
Simple Diffusion
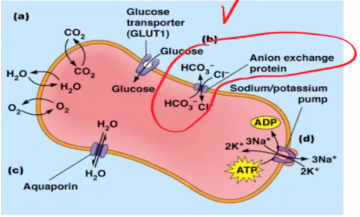
GLUT1 transports glucose into the erythrocyte, where the glucose concentration is lower. An anion exchange protein transports chloride (Cl-) and bicarbonate (HCO3) in opposite directions
Facilitated Diffusion
This channel proteins can facilitate the rapid inward or outward movement of water depending on the relative solute concentration on opposite sides of the membrane
Aquaporin
Push the transport from lower to higher concentration (movement up to the concentration gradient). Driven by the hydrolysis of ATP, the Na+/K+ pump moves sodium ions outward and potassium ions inward, establishing an electrochemical potential across the plasma membrane for both ions
Active Transport Using ATP-requiring Pumps
Oxygen gas traverses the lipid bilayer readily by
simple diffusion
TRUE OR FALSE:
Erythrocytes take up oxygen in the lungs where oxygen concentration is high and release it in the body tissues where oxygen concentration is low
True
When this happens, RBC through Hgb will deliver O2, collect metabolic waste through CO2, and CO2 will be converted to bicarbonate (HCO3-) ions
Depleted O2
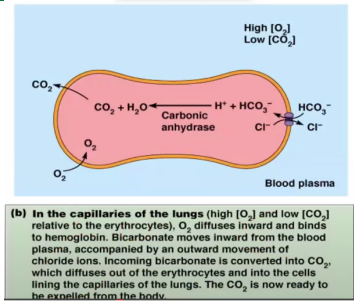
Why is there a need to immediately convert CO2 to bicarbonate?
RBC can collect more CO2
Diffusion depends on these 3
Solute Size, Polarity, Charge
Lipid bilayers are more permeable to small molecules such as water, oxygen, CO2 than larger ones
Solute Size
Lipid bilayers are more permeable to nonpolar substances than to polar ones
Polarity
A simple measure of the polarity (or non- polarity) of a solute. Which is the ratio of its solubility in an organic solvent (such as vegetable oil or octanol) to its solubility in water
partition coefficient
The relative impermeability of polar substances, especially ions, is due to their associations with water molecules
Charge
The molecules of water form a this around polar substances. Ions will have a hard time to get inside the plasma membrane, repelled
sphere of hydration
TRUE OR FALSE:
The rate of simple diffusion is directly proportional to the concentration gradient
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
Facilitated diffusion is hypobolic because membrane proteins will help them to make the reaction faster
False
From hydrophobic channels through the membrane to provide a passage route for solutes
Channel Proteins
Transporters or permeases. Bind solute molecules on one side of a membrane, undergo a conformational change, and release the solute on the other side of the membrane
Carrier proteins
Sometimes are not selective. As long as the molecules are polar, the let them pass
Ion Channels
Provides a shield/protection against hydrophobic interior of the interior of the membrane to the solute passing through the membrane
Interior of the channel and carrier protein
Carrier protein. Proceeds with conformational change. Alternating conformational change
GLUT1
Membrane proteins behave like
enzymes
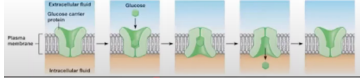
Involves binding a substrate on a specific solute binding site
Facilitated diffusion
When a carrier protein transports a single solute across the membrane, the process is called?
uniport
A carrier protein that transports a single solute is called a?
uniporter
When two solutes are transported simultaneously, and their transport is coupled, the process is called
coupled transport
Coupled transport in the same direction
Symport
Coupled transport in the opposite direction
Antiport
a uniport carrier for glucose
Glucose Transporter (GLUT1)
an antiport (coupled) anion carrier for Cl- and HCO3-
Anion exchange protein
Both the GLUT1 and Anion exchange protein can be found in the what of erythrocytes
plasma membranes
TRUE OR FALSE:
As the concentration of bicarbonate rises it moves out of the cell, coupled with uptake of CL- to prevent a net charge imbalance
True
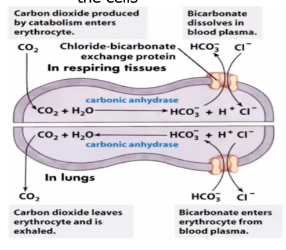
By having this, bicarbonate will go out for balancing. Entry of Cl- ions will level of balance the ionic charges within the cells
Anion exchanger
Channel proteins from this that allow specific solutes to cross the membrane directly
hydrophilic transmembrane channels
Transmembrane channels that allow rapid passage of water. Movement of water across cell membranes in some tissues is faster than expected given the polarity of the water molecule
Aquaporins
Aquaporin was discovered when?
1992
TRUE OR FALSE:
Aquaporins allow rapid passage of water through membranes of erythrocytes and kidney cells in animals, and root cells and vacuolar membranes in plants
True
Transmembrane proteins that allow rapid passage of various solutes. The pores are formed by multipass transmembrane (as beta barrels) proteins called?
Porins
FILL IN THE BLANKS:
The beta barrel has a _________ pore at its center
water-filled
TRUE OR FALSE:
In porins, non-polar side chains line the inside of the pore, allowing passage of many hydrophilic solutes
False
TRUE OR FALSE:
In porins, the outside of the barrel contains many nonpolar side chains (amino acids) that interact with the hydrophobic interior of the membrane
True
FILL IN THE BLANKS:
All aquaporins are ___________ integral membrane proteins
tetrameric
TRUE OR FALSE:
The channels of aquaporin, lined with hydrophobic side chains (amino acids), are just large enough for water molecules to pass through one at a time
False
Transmembrane proteins that allow rapid passage of specific ions. Tiny pores lined with hydrophilic atoms are remarkably selective
Ion Channels
TRUE OR FALSE:
There are separate proteins needed to transport Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Cl-, etc
True
FILL IN THE BLANKS:
Most ion channels are ________, meaning that they open and close in response to some stimulus
gated
When Ca2+ enters the heart muscles, during heartbeat, it contributes to the electrical signal that coordinate the heart’s function
Calcium Ion Channels
They open and close in response to some stimulus
Gated Ion Channels
Ion channels that change their structure in response to voltage (changes in membrane potential) are called?
voltage-gated ion channels
The difference in total charge between the inside and outside of the cell is called the?
membrane potential
Regulate the relative concentrations of different ions inside and outside the cell. Opens and close in response to changes in membrane potential. Can regulate the relative concentration of ions
Voltage gated Ion channels
Triggered by the binding of certain substances to the channel protein
Ligand-gated channels
A molecule in the extracellular part of the cell (signalling molecule)
Ligand
Respond to mechanicals forces acting on the membrane
Mechanosensitive channels
Ranging from thermal molecular agitation to potentially destructive cell swelling caused by osmotic pressure gradients
Mechanical stimuli
TRUE OR FALSE:
Ion channels play roles in many types of cellular communication such as muscle contraction and electrical signaling of nerve cells
True
A chloride ion channel that helps maintain the proper Cl- concentration in the lungs. Defects in the protein cause cystic fibrosis.
cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)
If there’s irregularity in CFTR, there will be?
cystic fibrosis
Controls the flow of water and salts such as chloride ions into and outside the lung cells
CFTR
TRUE OR FALSE:
When Chloride is transported outside, promotes transport of water in the same direction. As a result, it will not have thickened mucus because it is diluted by water that is transported along with the Chloride
True
Muscle contraction starts with the release of neurotransmitter called what which will go in the cell via the ion channel receptors
acetylcholine
For the muscles contract, the acetylcholine neurotransmitters need to pass through the?
neurotransmitter receptors
To propagate nerve impulses across the neuromuscular junction between a nerve cell and muscle cell. Attaches to the receptors on the muscle cells and resulting to muscle contraction
Acetylcholine
Down the concentration Gradient
Passive
Up the concentration gradient, ATP requiring
Active
A type of active transport that is directly coupled with ATP to drive the transport forward
Direct