Familes vocab for Exam 2
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Maternls chapter 1, 17-22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
abstience
abstening from having sexual intercourse eliminates the possiblity of sperm entering the vagina
coitus interrupts (withdrawl) (pull out and pray)
withdrawl of penis from vagina during sexual intercourse peior to ejaculation
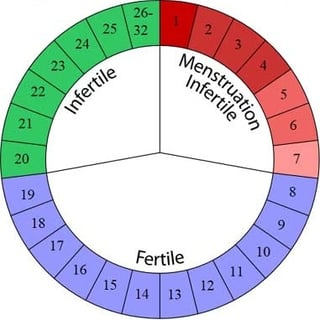
calender ryhthm model
tracking the menstaurl cycle
standard days method (cycle beads)
more modern version of calaendar rythm method
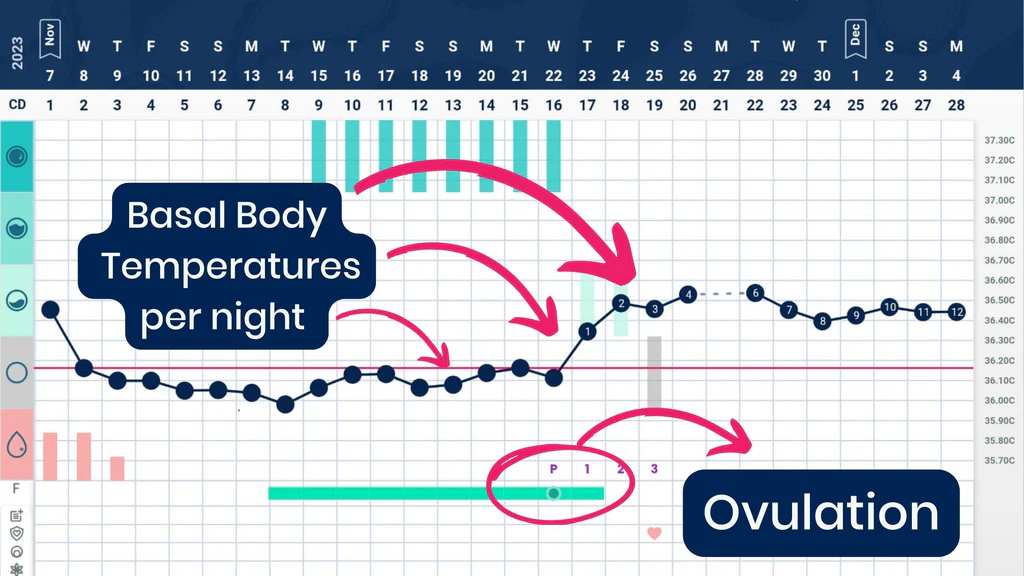
basal body temperature (BBT)
tempartre if the biday at rest, during ovulation as the progesterone raises some cloents experience rise of body temp
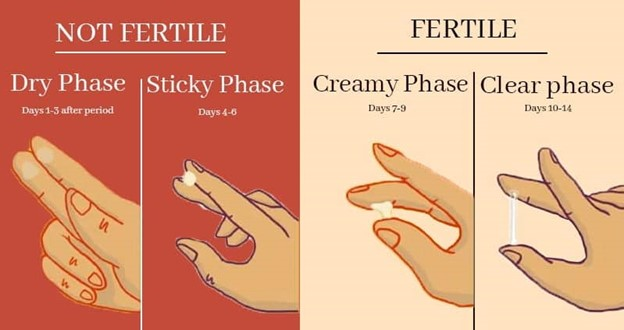
cervical mucus ovulation detection method
fertility awarness method, clinet anaylzes cervical mucous to determine ovulation
two day method
sx based method that involves checking for vaginal secertions daily, with o analysis ofs ecertions
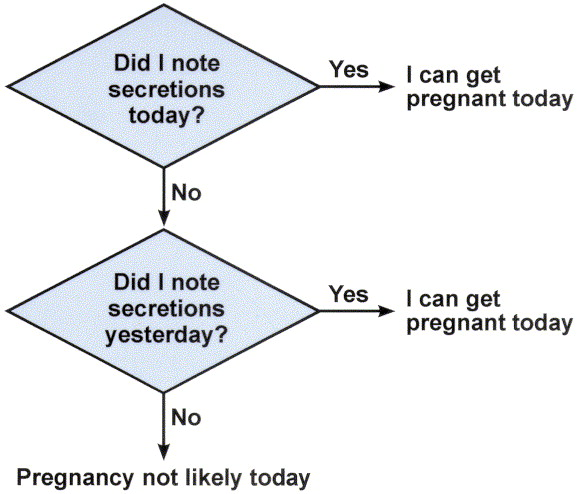
laceration amenorrhea method (LAM)
supression of ovulation and mensturation while breastfeeding
penile condom
thin sheath used to cover the penis during sexual intercourse as a cotraceptive or as protection against infection
vaginal condom
vaginal sheath made of nitrile, a nonlatex synthetic rubber with flexible rings on both ends that is pre-lubricated with a spermicdie
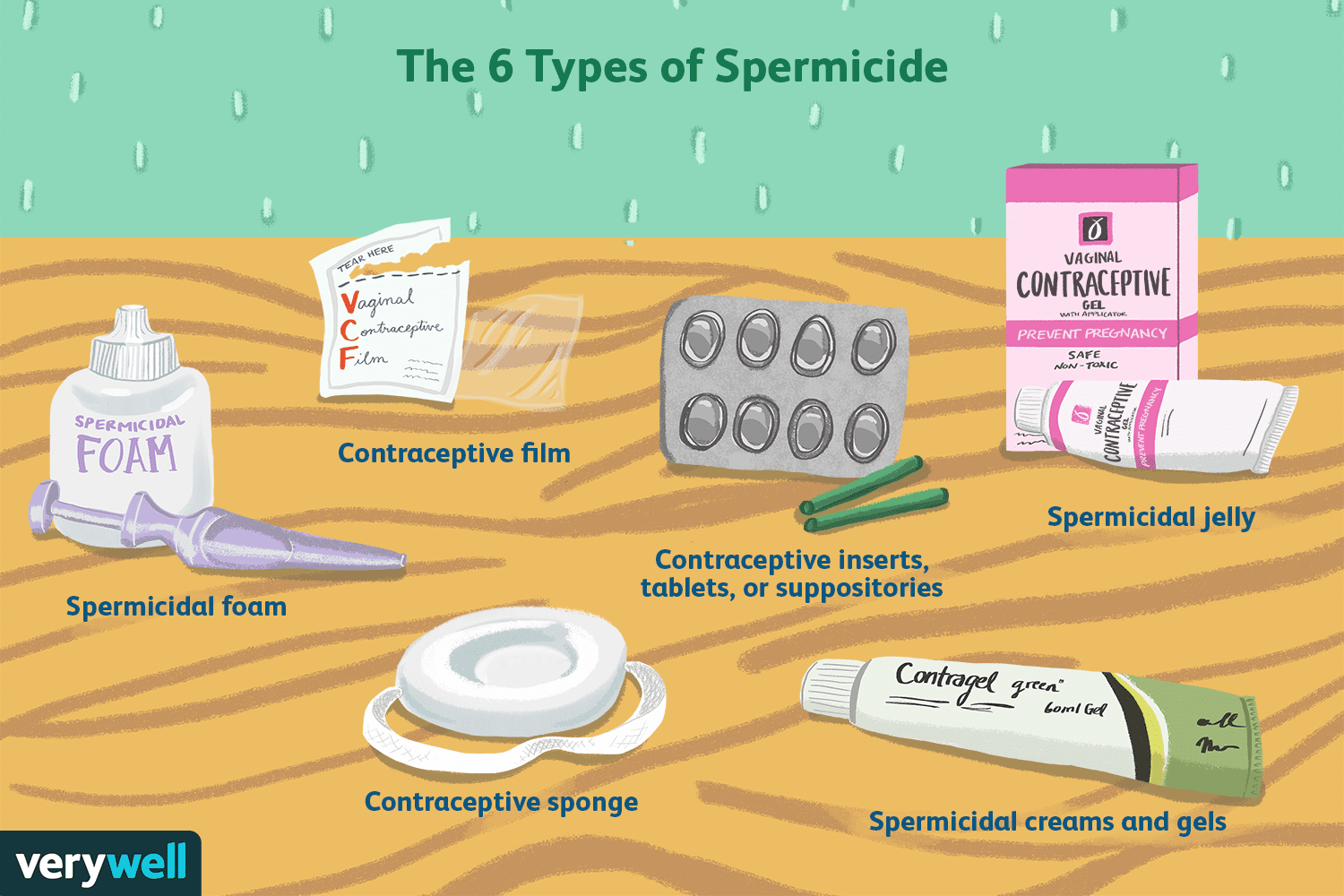
spermicide
chemical barrier that is available in a variety of forms and destroys sperm before they can enter the cervix, It causes the vaginal flora to be more acidic, which is not favorable for sperm survival
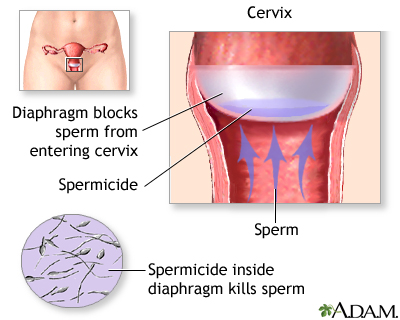
diaphragm
a dome shaped cup with a flexible rim made of silicone that fits snugly over the cervix, effectiveness is increased with the use of a spermicidal cream or gel placed into the dome and around the rim
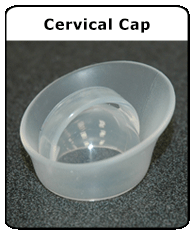
cervical cap
silicone rubber cap that fits tightly around the base of the cervix, serves as a physcial barrier against sperm entering the cervix, with spermicde icnreases its effectivess
combined oral contraceptives (COs)
estrogen and progestin, which acts by supressing ovulation, thickening the cervical musus to block semen and altering the uterine decidua to prevent implantation
progestin-only pills (minipill)
progestins provide the same action as combined oral contraceptives, which decreases the chance of fertilization and implantation
emergency oral contraceotives
morning after pill that prevents fertililzation from taking place by inhibitng ovulation and the transport of sperm
transdermal contraceptive patch
estrogen and progesterone or preogestin, which is dleivered a contiuns level through the skin into sub c tissuem inhibits ovulation by thickening cervical muscos
injectbale progestins
medroxyprogesterone is an intramuscular or sub c injection give to a femae every 11-13 weeks, inhibts ovulation and thickens cervical muscus
contraceptive vagianl ring
flexible sillicone ring that contains etongesterel and ethinyl estradiol, which are delivered at contuous levels vaginally
implantable progestin
small thin rods conissting of pregestin that are implanted by the provider under the skin of te inner upper part aspect of the arm
orevents pregancy by supressing the ovulatory cycle and thickening cervical mucus
intrauterine device (IUD)
chemically active t shapped device that is inserte through the cervix and placed in the uterus by the provdier, releases a chemical substance that dmages sperm in trnsit to the uterine tubes and prevents fetrillixation
most effective contraceptiv emethods, at prevnting pregancy
transcervical sterlization
insertion of small felxible agents througb the vagina and cervix into the fallopian tubes, results from scar tissue in the tubes, preventing conception
FDA caclled it
surgical= tubal ligation (bilaterla tubal ligation BTL)
severne and or burning or blocking the fallopian tubes to prevnt fertillization, at least 21
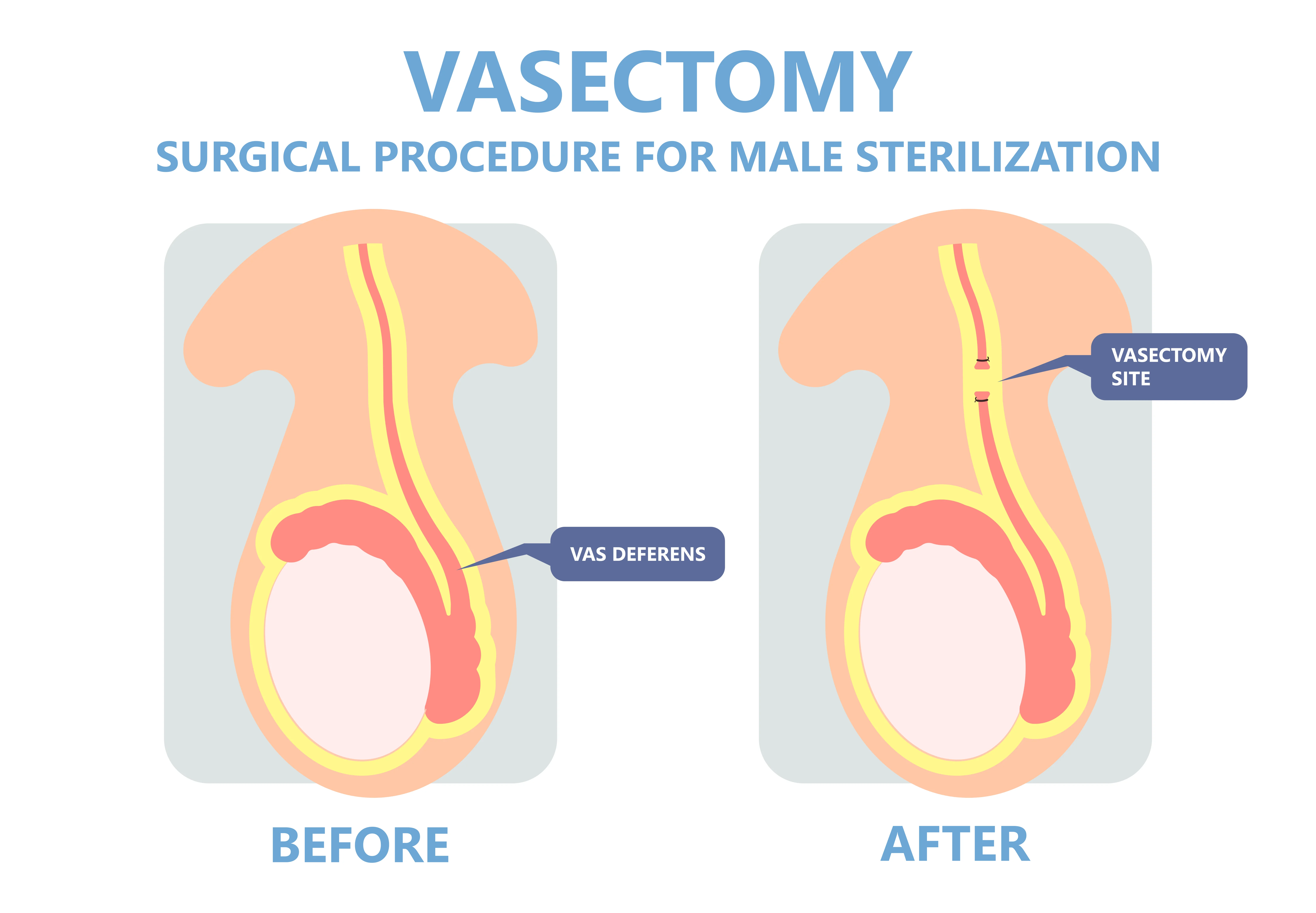
vasectomy
surgical procudure consisting if ligation and severeance of the vas defenrs, ehich prevents sperm from traveling
postpartum asses: BUBBLE
breats
utuerus
bowel
lochia
episiotomy
utuerus changes
involution which occurs with contractions of the uterine smooth muscle, wheaby the uterus returns to its perpragnst state
rapidly decreases from 1,000 g to 60-80g, fundal height decending 1cm per day
lochia
past birth uterine discharge that contains blood, musocus and uterine tissue
3 stages of lochia
lochia rubra
lochia serosa
lochia alba
rubra= dark red color, bloody constsitency, fleshy odor
serosa= pinksh brown color and serosangiunois consistency
alba= yellowish white creany color
dependet role attainment
taking in phase
24-48 hr, meeting personal needs, excite and talkative
dependent-independent role attainment
taking-hold phase
day 2/3, last 1o days to several weeks, focus on baby care and imporving caregiver competency, take charge but need appprovale, expericnes baby blues
interdependent role attianment
letting go phase
focus on famly as unit, resumption of role
expectation and intention transition
desries to be deeply and emotionally connected with the infant
confrontity reality transition
reality dosent always meet exoectaion, feeling sad, frustrated, jealous, unable to talk with the other parent, who is consumend with infant caregiving and their own transition to parenthood
creating thw role of the invlved co parent
become activeky involved in the care of the newborn
reaping rewards
include newborn smiles and a sense of completeness and meaning
idipoathic throbocytopenic purpura (ITP)
coaugulpathy that is an immune disorder in which the life span of platelts is decreased by antiplatel antiboides, result is sevre hemoragge follwing a c section or lacertaions
disseminated intravsucalar coagulation (DIC)
caogulapthy in which clotting and anticlotting mechnaisms occur at the same time, clien tis risk for both the internal anad external bleeding, as well as dmage to organs resulting form ischemia cause by microclots
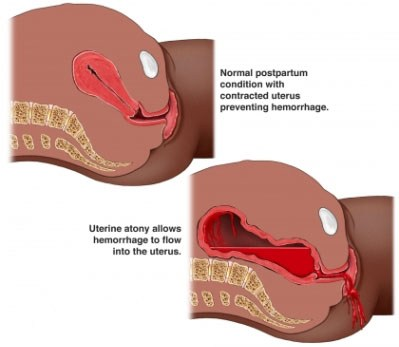
uterine atony
inability if the uterine muscle to contract adequetly after birth, can lead to postpartum hemorrhage
subinvolution of the uteurs
when th euterus remianes enlarged with contiuned lochial discharge and can result i postpartum hemorrhage
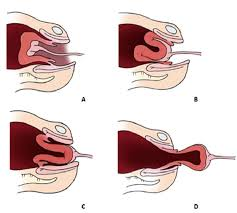
inversion of th euteurs
turning inside out of the uteurs and can be partial or complete, emergecy sitauion
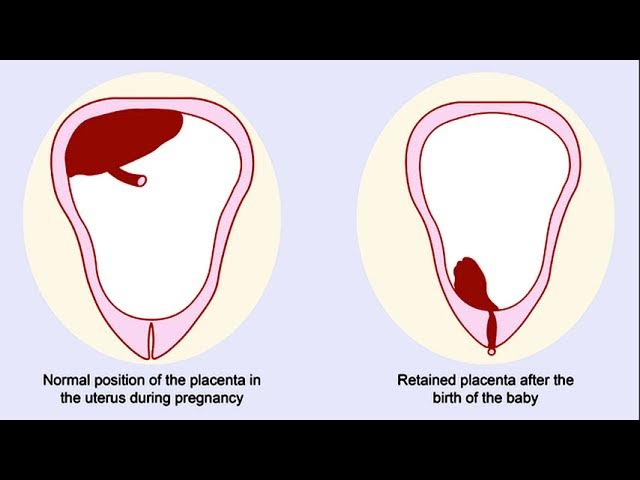
retained placenta
placneta or fragments if the placneta remian in the uteurs an dprevent te utueres from contracting, wgich cna lead to uteirne atony or subinvolution, a placenta that has not been delievred within 30 minutes of the birth is a reatined placenta
uterine infection (endometrisosi)
infection of the uterine lining or endometurium
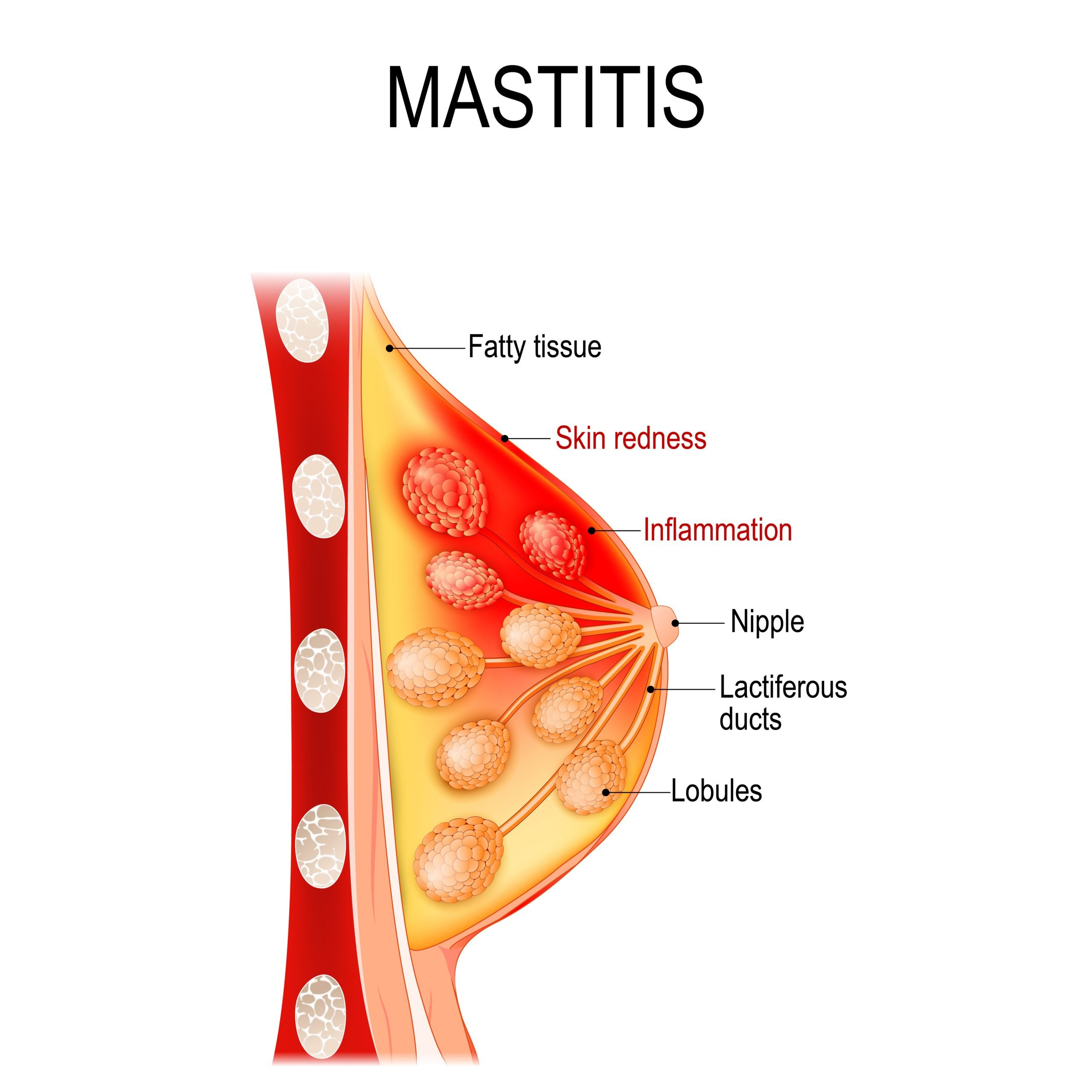
mastitis
infection of the breast involving the nterlobular connective tissue and is usally unilateral