psychology learning
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
learning
a relatively permanent change often of behaviour that occurs as a result of experience or practice.
stimulus response
learning occurs due to a response to a specific stimulus in the environment. meaning that an environmental stimulus will lead to a certain behavioral response
behaviorists
theorists who use the stimulus response model believing that all behavior is learned from response to the environment
classic conditions
behavioural procedure in which a potent stimulus is paired with a neutral stimulus to elicit a conditioned response. two or more things paired together (salt and pepper)
stimulus
an object or event that can be detected by the senses
response
the resulting behavior from a given stimulus
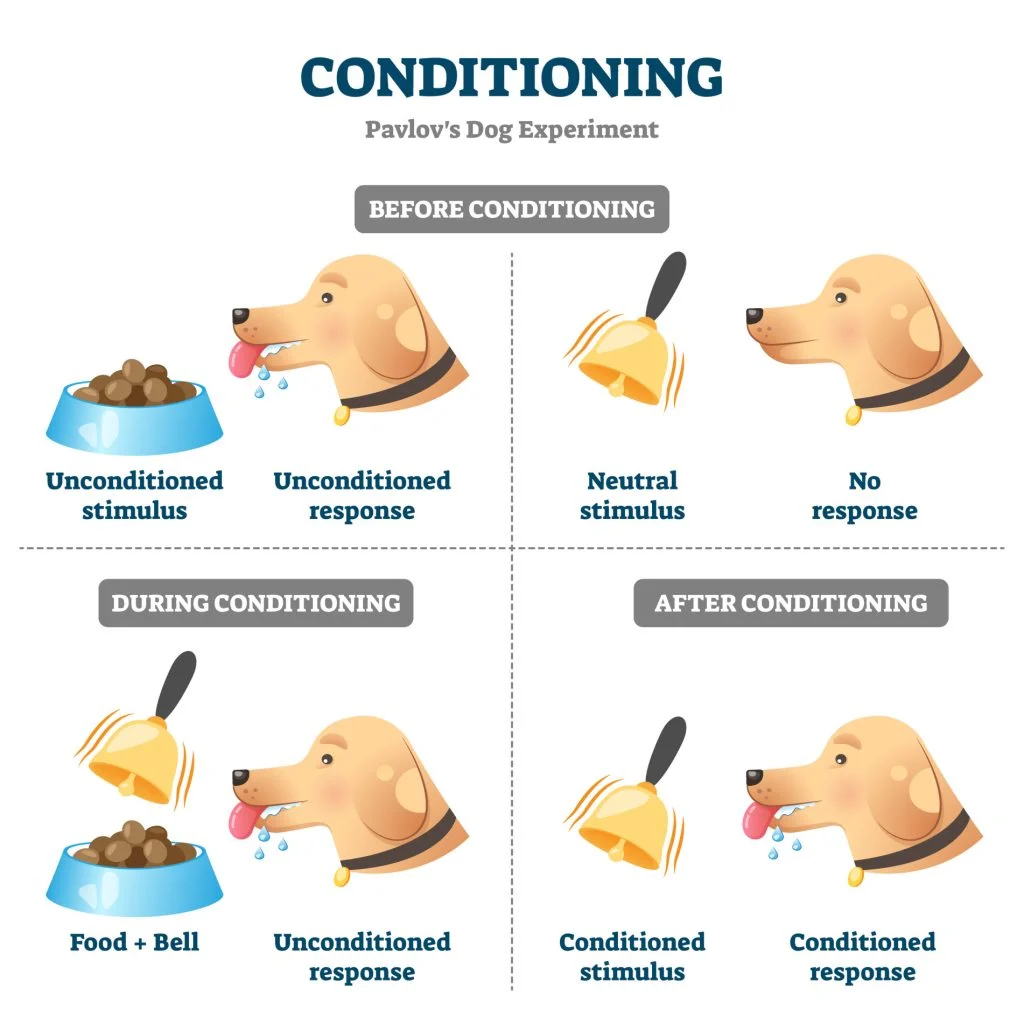
unconditioned stimulus
a natural stimulus that results in a natural responsewithout prior learning or conditioning.
e.g the smell of cooking meat
unconditioned response
a natural response to the natural stimulus e.g salivation and stomache rumbling
neutral stimulus
a stimulus that does not evoke a responce e.g sound of the bell
conditioned stimulus
a previously neutral stimulus that, is associated with a conditioned responce
e.g bell assoicated with smell of meat
conditioned responce
the same response as the unconditional responce but it occurs following the conditioned stimulus not just the unconditioned stimulus
e.g salivating at the sound of a bell after it has been paired with food.
classical conditioning
A learning process in which a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a meaningful stimulus, leading to a conditioned response. This process was famously demonstrated by Ivan Pavlov in his experiments with dogs.
behaviorism method
method 1 we learn by association - one thing with another thing- classical conditioning
method 2 we learn by consequences of what we do (the effect of our behaviour)-operant conditioning
operant conditioning
a specific voluntary behavior employs awards and punishments for behavior
antecedent
the environmental stimulus that precedes the specific behaviour and therefor influences the occurance of the behaviour and indicates the consequence
e.g small group at school
behaviour
voluntary activity that occurs in the presence of the antecedent stimulus.involves activity that has an affect on the environment form of a consequence that allows it
e.g tells bad jokes
consequences
environmental event that occurs immediately after the behaviour and has an effect on the occurance of the behaviour
reinforcement
increases the frequency of desirable behaviour
punishment
decreases the frequency of an undesirable behaviour
positive
+a stimulus
negative
-a stimulus
positive reinforcement
Favourable stimuli presented after the behaviour in positive reinforcement situations a response or behaviour is strengthened but the addition of something consdiered pleasant
positive punishment
presents unfavourable stimulus in order to weaken the response it follows. In these situations a response is weakened by the addition of something considered unpleasant
negative reinforcement
Removal of an unfavourable stimulus after the display of a behaviour in these situations a response is strengthened by the removal of something considered unpleasant
negative punishment
Favourable stimulus is removed after a behaviour occurs in these situations a response is weakened by the removal of something considered pleasant
stimulus generalization
the tendency for another stimulus that is similar to the original conditioned stimulus to produce a response that is similar to the original conditioned stimulus to produce a response that is similiar but not necessarily identical to conditioned responce the greater the similiarity between stimuli greater possibility of generalisation.
e.g pavlons dogs the dogs may also salivate in responce to ringing of a doorbell however the amount they salivate may differ
stimulus discrimination
occurrs when a person or animal responds to conditioned stimulus only but not too aby other similair stimulus
e.g pavlons dogs salivating only in responce to the sound of the experimental bell and not any other sounds
extinction
gradual decrease in the strength or rate of a conditioned responce that occurs when the unconditioned stimulus is no longer presented. it is said to occurr when a conditioned responce no longer occurrs following presentation of the conditioned stimulus.
spontaneous recovery
the reappearance of a conditioned response when the conditioned stimulus is presented following a rest period after the conditioned response appears to have been distinguished often short lived and cr returns typically weaker when spontaneous recovery eventually when it doesn’t occur the cr has disappeared all together
pavlovs dogs hypothesis
that if a particular stimulus in the dogs surroundings was present when the dogs where given food then that stimulus could be associated with food and cause salivation on its own.
pavlov’s dogs weakness
methodical - low generalizability
ethical - harm to animals (starving)
pavlovs dogs strengths
able to infer cause and effect due to his control over variable and precise instruments
pavlovs dog dependent variable
the amount of salivation the dogs exhibited when they heard the bell (conditioned stimulus).
pavlovs dog independent variable
The factor that is manipulated or changed by the researcher. In Pavlov's experiment, this was the neutral stimulus (like a bell) that was paired with the food (unconditioned stimulus).
operant 3 phase model
skinners beleif that all behaviour can be anaylised and explained by the relationship between the behaviour, its antecedents (what happens just before it) and its consequences.
law of effect - thorndikes
behaviours with satisfying outcomes are more likely to happen again while those with unsatisfying outcomes are less likely to reoccur
behaviorism definition
theory that learning occurs through observational behaviors and response to external stimuli primarily through conditioning
fixed ratio schedule
animal received pellet after pushing lever certain amount of times
variable ratio schedules
where animals receive reinforcement after a random number of responces
fixed interval schedule
animals given pellets after designated time period e.g every 5 minutes
variable interval schedules
animals receive reinforcement at random- once data has been obtained researchers can look at rate of responce depending on schedule
phobia
an irrational fear of a specific object or situation
the anxiety must be out of proportion to the actual danger
fear vs phobia
some fears are healthy some fears can turn into phobias when the source of anxiety comes from an actual threat to our safety its a fear. however when the person expeirnaces intense anxiety in the presence of the item or situation or even when thinking about it fear is so strong that it interferes with everyday activity