Chapter 4: Cytology
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Ribosomes
Cytoplasmic organelles where proteins are synthesized
Plasma membrane
Composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins that encloses the cell contents
Separates the body’s two main fluid components:
Intracellular space (inside the cell)
Extracellular space (outside the cell)
Plasma membrane - Cholesterol
A steroid that stabilizes the membrane’s structure in the face of changing temperatures
Plasma membrane - Integral proteins
Span the width of the membrane
Plasma membrane - Peripheral proteins
Located on only one face of the membrane
Plasma membrane - Glycoproteins and glycolipids
Cell recognition
Microvilli
Tiny projections on the free surface of some epithelial cells, increases surface area for absorption
In parts of the body where rapid absorption is necessary the plasma membrane is folded into…
Projections called microvilli
Which type or organelle contains its own DNA and ribosomes?
Mitochondria
Golgi Apparatus
Membrane-enclosed sacs system close to the cell nucleus that packages protein secretions for export, packages enzymes into lysosomes for cellular use, and modifies proteins destined to become part of the cellular membrane
Ribosomes
Cytoplasmic organelles composed of proteins and RNA (ribosomal RNA) where proteins are synthesized
Not enclosed by a membrane
Peroxisome
Membranous sacs in the cytoplasm containing powerful oxidase enzymes that use molecular oxygen to detoxify harmful or toxic substances such as red radicals
Also synthesize phospholipids that are critical for normal functioning of the nervous system
Cytosol
Viscous, semitransparent fluid substance of cytoplasm in which other element are suspended
Contains water, solutes, RNA, enzymes, and other proteins
Mitochondria
Responsible for ATP (energy) generation for cellular activities (the powerhouse of the cell)
Lysosome
Organelles that originate from the Golgi Apparatus and contain strong digestive enzymes (catalyze reactions that digest particles brought into the cell, worn-out organelles, and even the cell itself)
Nucleus
Control center of the cell that contains the genetic material
Cytoskeleton
An elaborate series of rods running through the cytosol, supporting cellular structures and providing the machinery to generate various cell movements
Cytoskeleton - Intermediate filaments
Rodlike structures that maintain the shape of organelles and the nucleus and give the cell mechanical strength
Cytoskeleton - Microtubules
The largest filaments
Hollow tubes that maintain the shape of the cell, hold organelles in place, move substances within the cell, and function in cell division
Cilia
Small, hairlike extensions that beat rhythmically together to propel substances past the cell
Act like tiny brooms, removing debris that has been inhaled and trapped in mucus
Flagella
Single extensions that propel the cell itself (sperm cells are the only flagellated cells in the human body)
Centriole
Paired organelles found near the nucleus of the cell, active in cell division
Microtubule organizing centers and are important in facilitating the assembly and disassembly of microtubules
Centrosome
Central area of the cell
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Lacks ribosomes
Breakdown of stored glycogen
Detoxification of drugs, certain pesticides and carcinogens
Absorption, synthesis, and transport of fats
Synthesis of steroid-based hormones such as sex hormones
Stores calcium ions
Lipid synthesis
Lipid metabolism, cholesterol synthesis, and synthesis of the lipid components of lipoproteins
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Performs some of the final steps of protein synthesis, modifying proteins the ribosomes have made
• Particularly integral membrane proteins and proteins secreted from the cell
Nucleolus
“Birthplace” of ribosomes
Dense spherical body in the cell nucleus involved with ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosomal subunit assembly
Chromatin
A ball-like mass of tightly coiled DNA and proteins; RNA; and the nucleolus
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane that surrounds the nucleus
Nuclear pores
Holes in the nuclear envelope
Extracellular fluid
Fluid located outside the cells; includes interstitial fluid, blood plasma, and cerebrospinal fluid
Cytokinesis
The division of cytoplasm that occurs after the cell nucleus has divided
Plasma membrane structure
Phospholipids form a bilayer
Why do phospholipids form a bilayer in the plasma membrane?
The hydrophilic heads of the phospholipids are attracted to the water, while the hydrophobic tails are repelled by it. To minimize contact between the hydrophobic tails and water, they arrange themselves into a bilayer, with the tails facing each other in the interior and the heads exposed to the water on both surfaces.
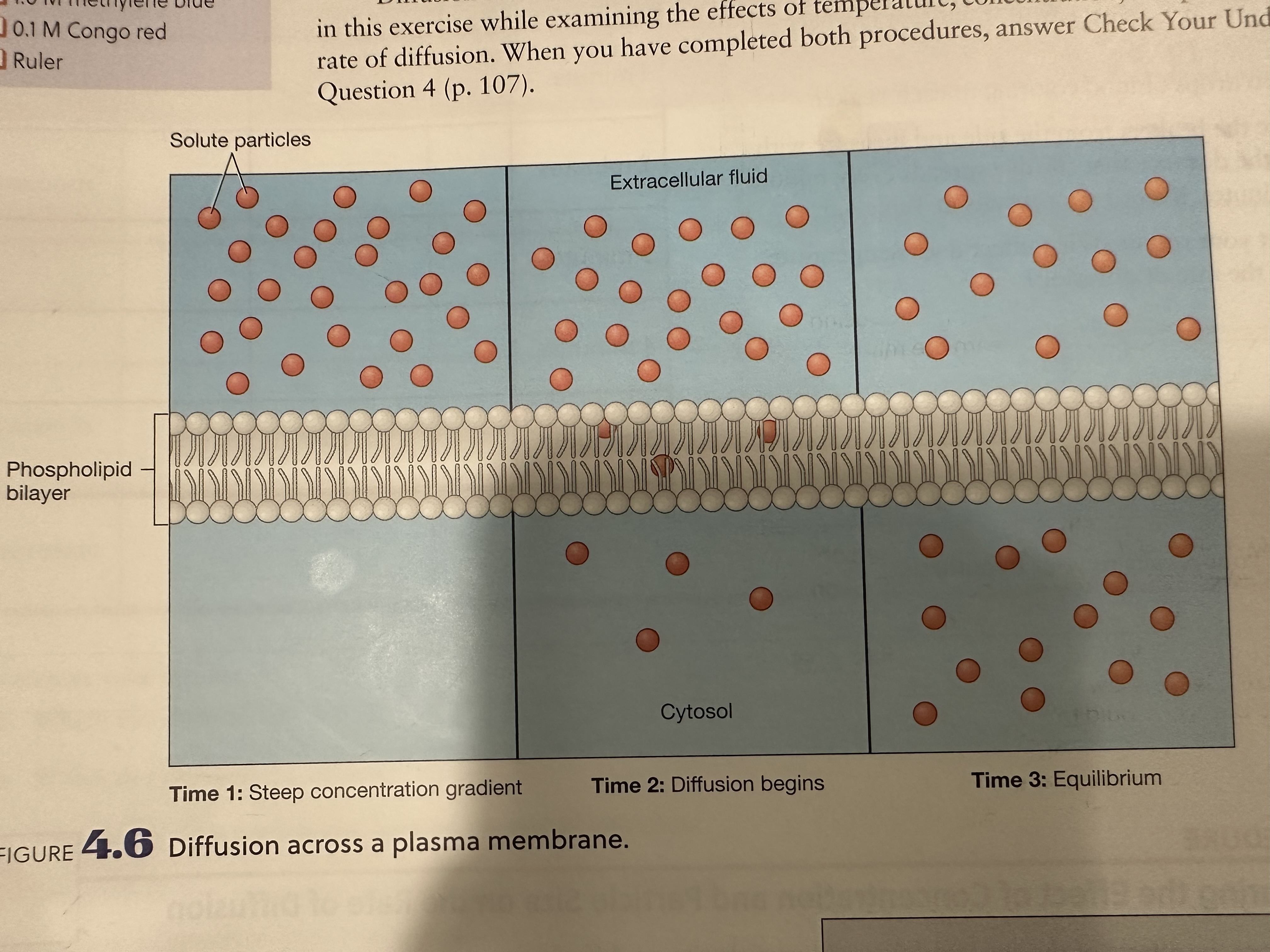
Diffusion
The movement of solute particles from a HIGH solute concentration to a LOW solute concentration until a state of equilibrium is reached
Passive process - requires no net input of energy by a cell
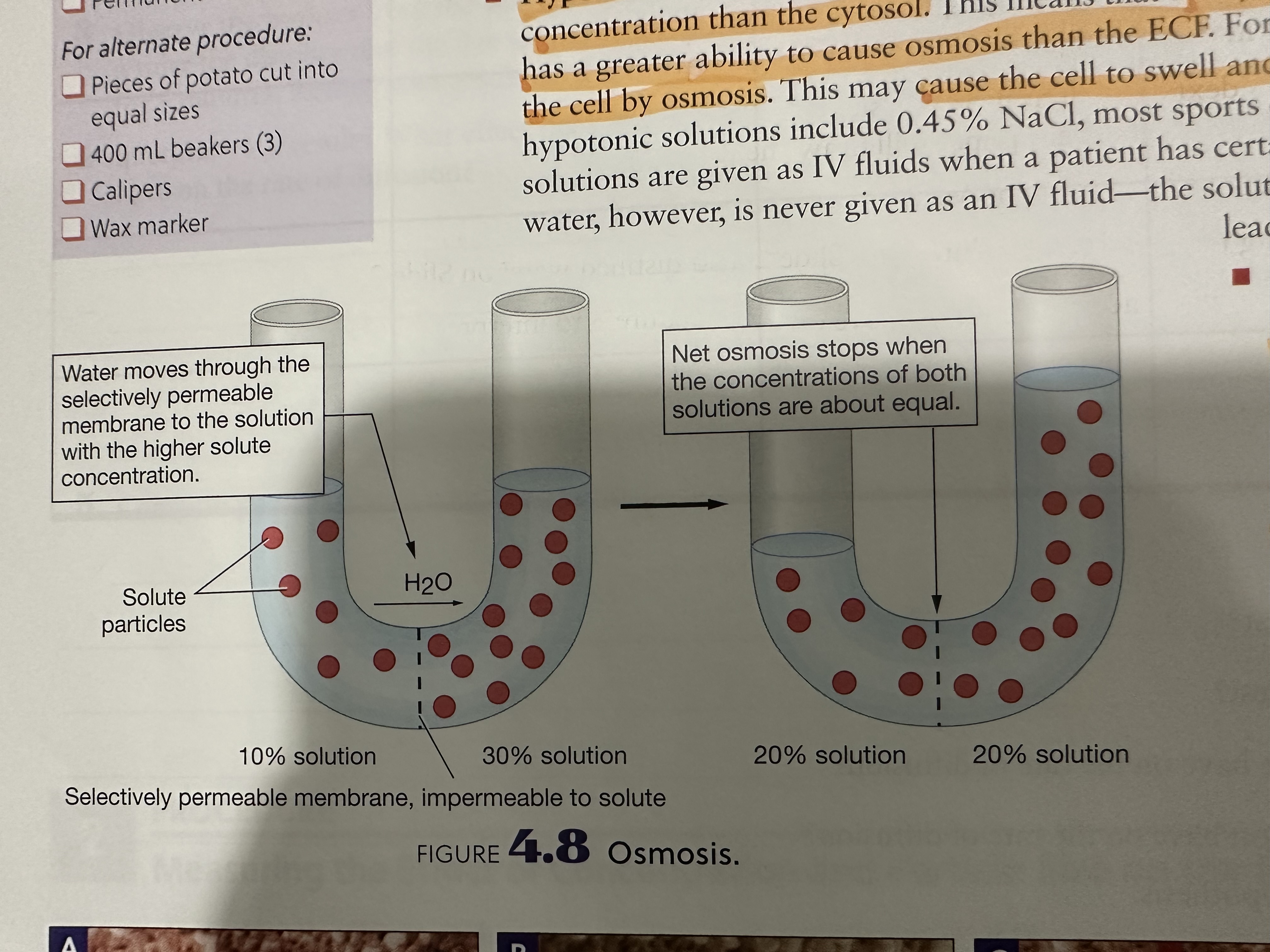
Osmosis
The movement of solvent from a LOWER solute concentration to a solution with a HIGHER solute concentration
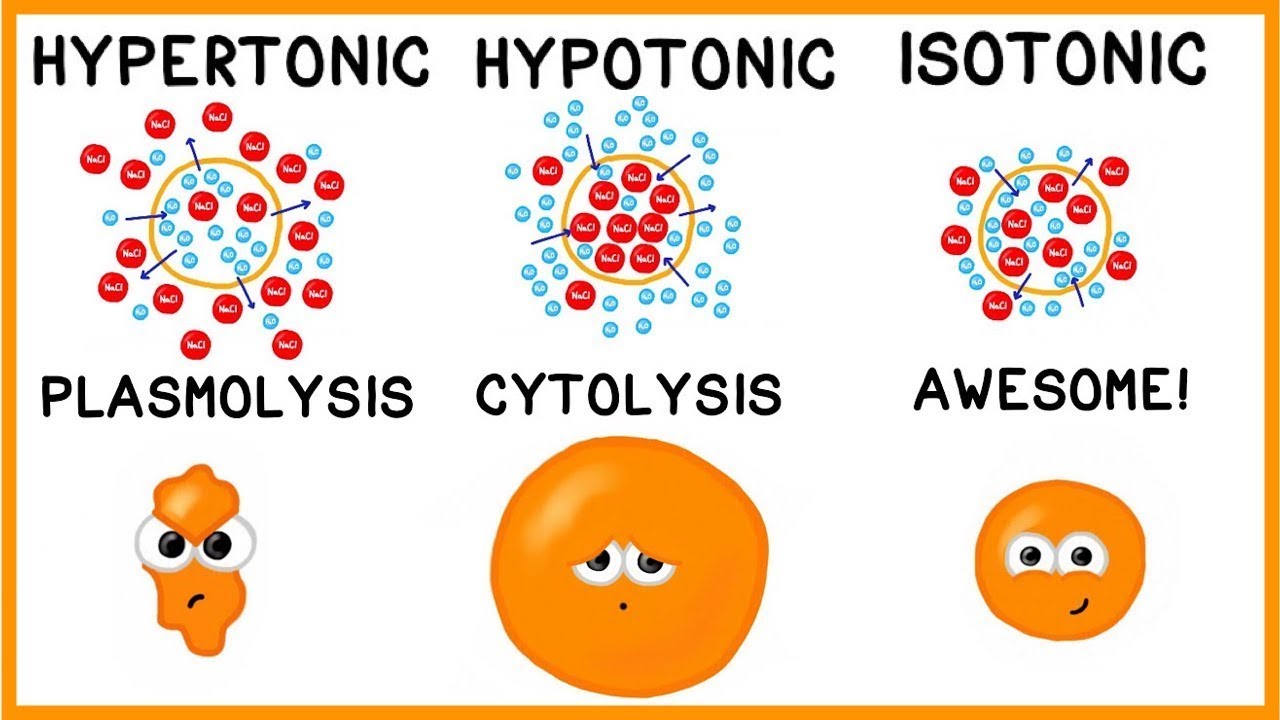
Isotonic
Iso = “same”
Extracellular fluid (ECF) has the same solute concentration as the cytosol
Both have equal ability to cause osmosis
No net movement of water into or out of a cell
Solutions given by intravenous (IV) administration are almost always isotonic
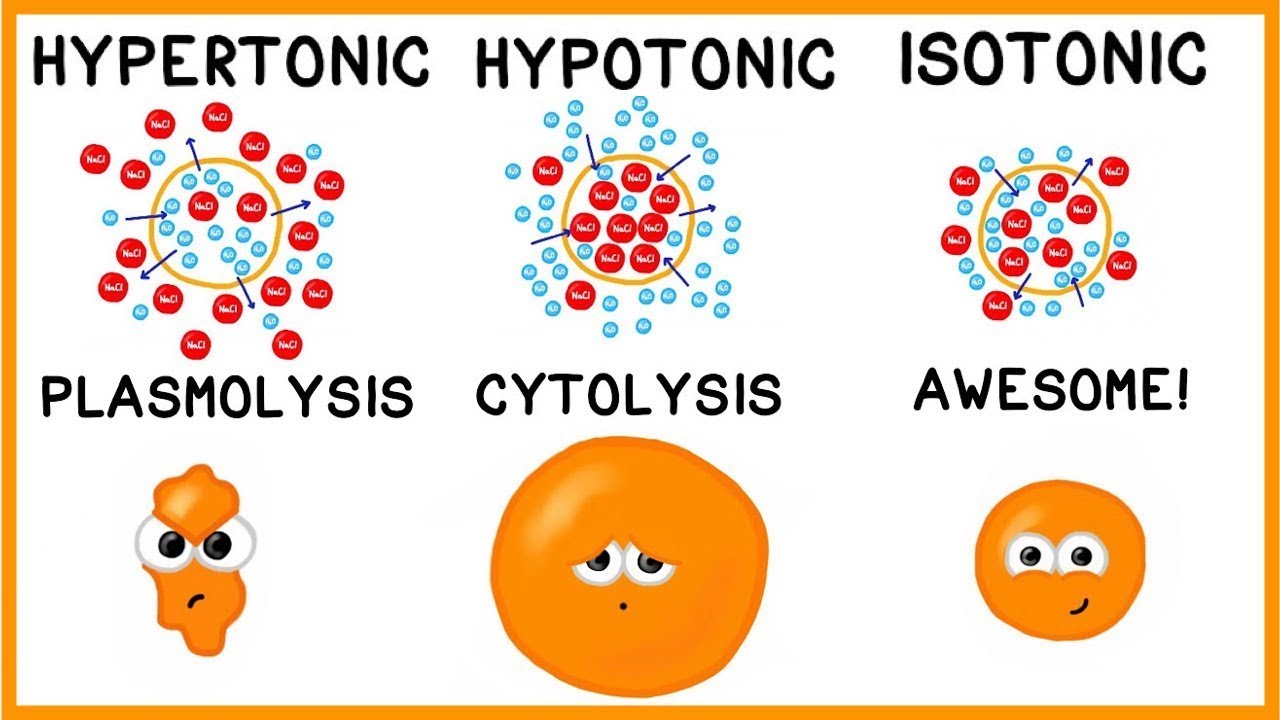
Hypotonic
Hypo = “below”
Extracellular (ECF) has a lower solute concentration than the cytosol
Cytosol has more solute particles, and has a greater ability to cause osmosis than the ECF
Water will move into the cell by osmosis
May cause cell to swell and burst
Given as IV fluids when a patient has certain types of dehydration
Hypertonic
Hyper = “above”
ECF has a higher solute concentration than the cytosol
ECF has a greater ability to cause osmosis
Causes ECF to pull water molecules out of the cytosol by osmosis
May cause cell to shrivel or crenate as it loses water to the ECF
Only ever given by IV under very specific conditions
Interphase
When the cell is NOT dividing:
G1
S
G2
Interphase - G1
Initial growth phase
Cell grows, develops, and carries out activities specific to that cell type
Interphase - S
Cell’s DNA is replicated
“S” stands for synthesis
Interphase - G2
Second growth phase which the cell makes its final preparations for division (mitosis)
Mitosis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Prophase
Nuclear membrane starts to degenerate
Chromatin condenses into individual chromosomes
Mitotic spindle organizing around centrioles
Centrioles have reaches opposite poles of the cell
Spindle fibers emanate from each side of the mitotic spindle and attach to the centromere (one single fiber attaches to each side of the centromere)
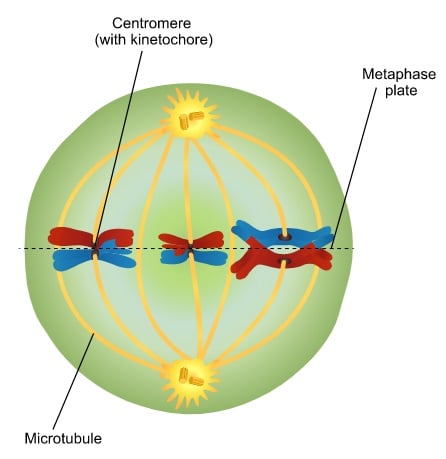
Metaphase
Sister chromatids line up along the equator of the cell
Anaphase
Spindle fibers shorten which pulls sister centromeres apart
Sister chromatids migrate toward the opposite poles of the cell
Cytokinesis begins
Telophase
Cleavage furrow forms between the two cells
Cell is pinched into two identical daughter cells and cytokinesis is completed
Nuclear membrane begins to reassemble
Mitotic spindle becomes less visible
DNA returns to its chromatin form
Mitotic spindle
Made up of microtubules that facilitates the separation of chromosomes
Ensures accurate chromosome segregation
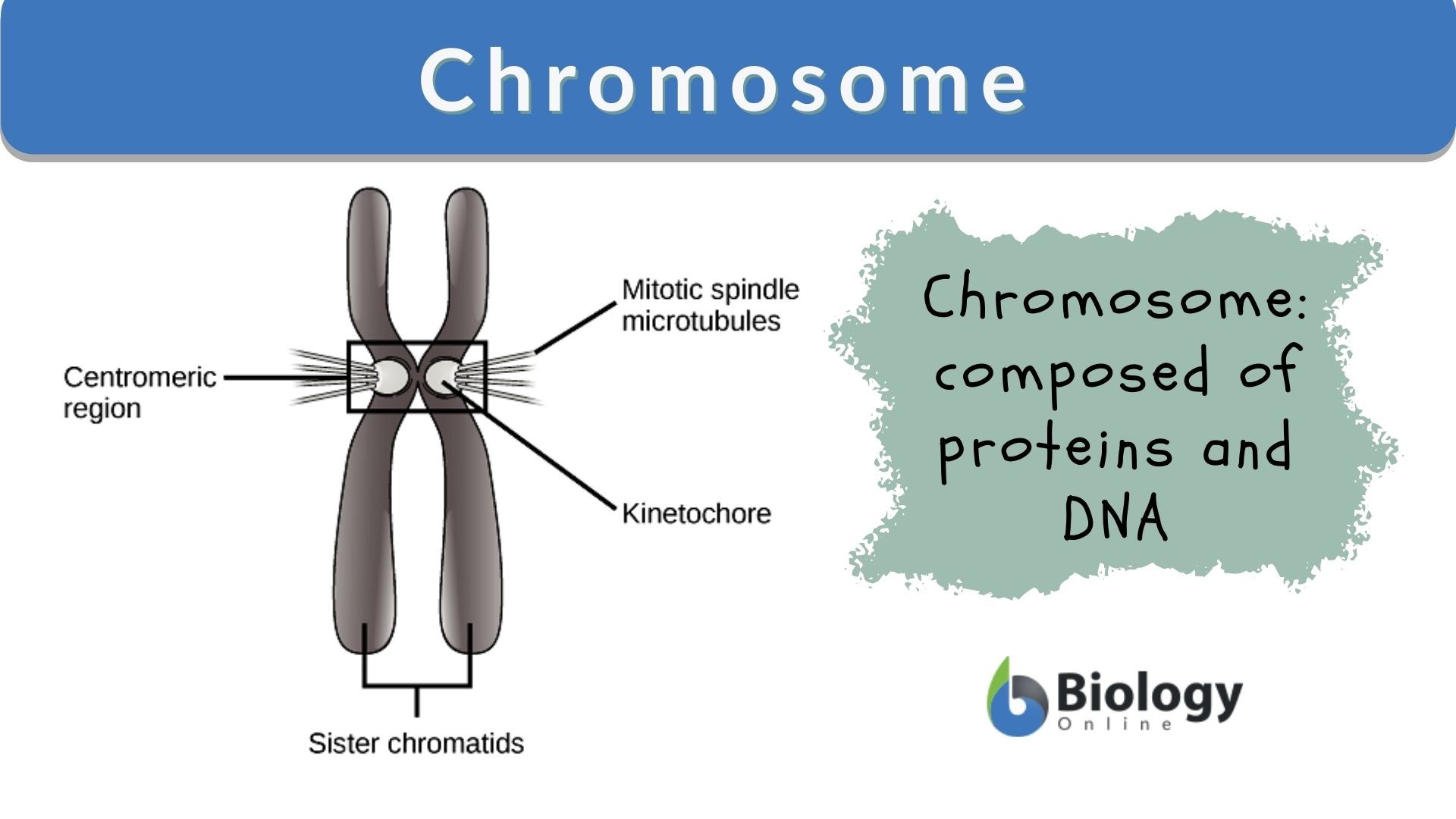
Centromere
The point where sister chromatids are joined and where spindle fibers attach during cell division
Ensures that sister chromatids are properly aligned and separating
Ensuring each new cell receives the correct number of chromosomes
Metaphase plate
An imaginary line that runs across the cell, dividing the cell into hemispheres
Chromosome
Thread-like structure made of DNA and proteins
Ensures accurate chromosome that the correct instructions are available for cell function and genes are passed down from one generation to the next
Centriole
Small, cylindrical organelle
Forms spindle fibers that pull chromosomes apart
Spindle fibers
Long strands of protein that extend toward opposites sides of the cell
Chromatid
One of the two identical halves of a chromosome that has been replicated in preparation for cell division
The two “sister” chromatids are joined at the centromere
Active Transport
Requires ATP to move
Brownian movement
Solute
Soluble
Solvent
Active transport
Filtration
Pinocytosis
Endocytosis
Semi-permeable membrane
Insoluble
Phagocytosis
Solution