Bio 1722 Exam 3 Flashcards
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
194 Terms
Virus
An infectious particle consisting of little more than one or more molecules of nucleic acid enclosed in a protein coat. Some also contain a membraneous (lipid) coat
Capsid
The protein shell that encloses the viral genome
Made up of subunits called capsomeres
What kind of genetic material does the viral genome contain
Either double/single stranded DNA or double/single stranded RNA
What is a Viral envelope
An envelope around viruses that help them infect hosts. Created by taking parts of the host cell’s membrane and using it to form their own membrane
Bacteriophages (Also called phages)
Complex viruses that infect bacteria
What kind of genetic material does COVID-19 contain
Single stranded RNA
Host Range
The number of host species that a virus can infect
T-Even bacteriophages
Use their tail apparatus to inject DNA into the bacterial host
Enveloped viruses
Enter host cells by fusing their viral envelope with the host’s plasma membrane
How do viruses replicate
By inserting their genetic material into the host cell’s genetic material and then replicating when the gene that the virus has inserted their genetic material into has been activated
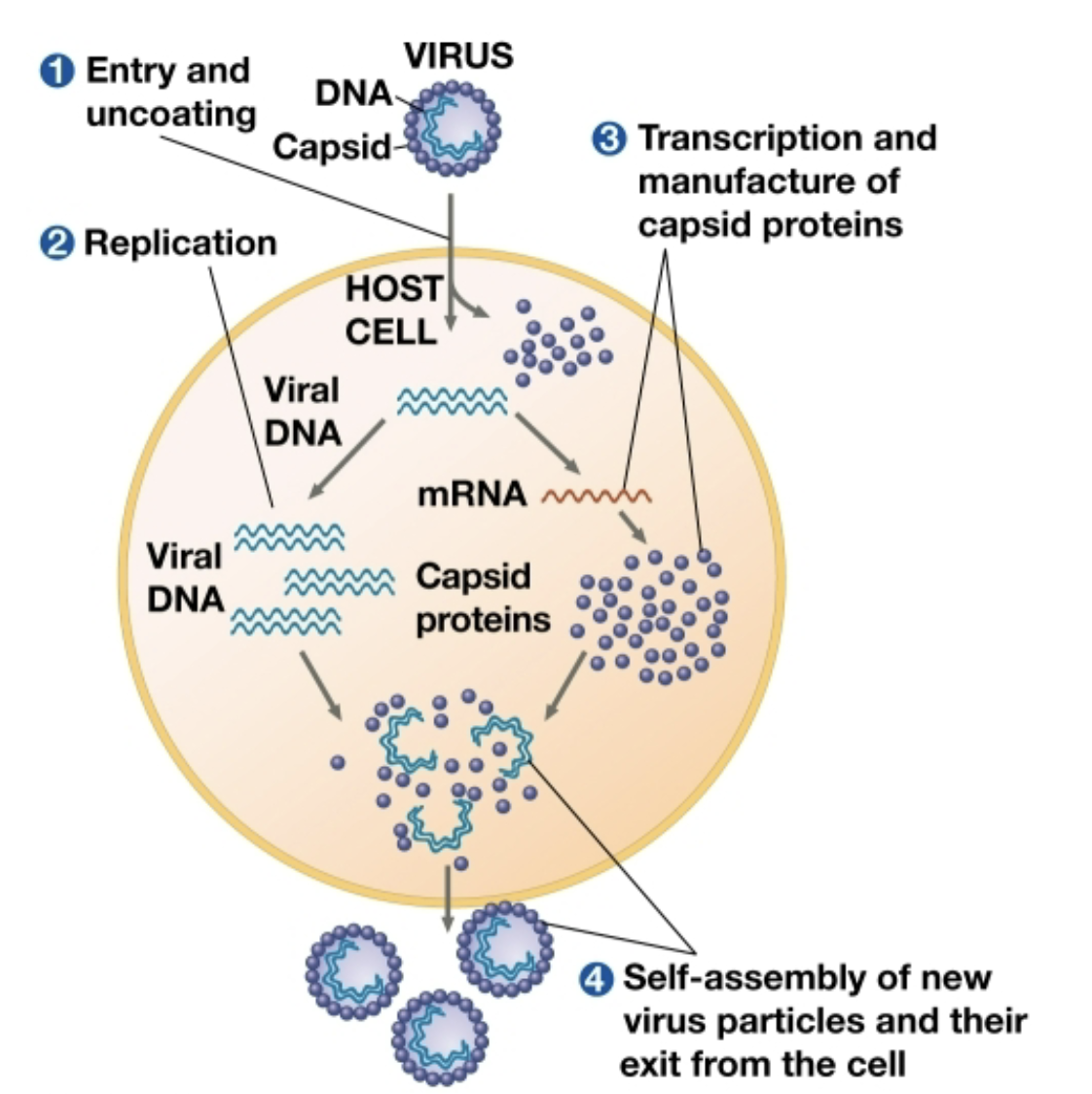
Lytic Cycle
A phage replicative cycle that culminates in the death of the host cell
Produces new phages and lyses the host cell wall, releasing the viruses and destroying the cell
Virulent Phage
A phage that reproduces only through the lytic cycle
Lysogenic Cycle
Phage genetic material is inserted into the host cell’s genetic material. Host cell often replicates multiple times to create many daughter cells from just one cell. Eventually, the phage’s genetic material is activated due to some kind of signal and the lytic cycle is activated which gives rise to many phages
Temperate Phages
Phages that use both the lytic and lysogenic cycles
Prophage
The viral DNA that is inserted into a host cell’s DNA
Bacterial defenses against phages
Natural selection favors mutant bacteria with surface proteins that are not recognized by a particular phage. Basically, natural selection favors bacteria that mutate to contain surface receptors that can’t bond with the receptors on viruses
Phage DNA is often identified as foreign and cut up by bacterial restriction enzymes
The bacterium’s own DNA is methylated in a way that prevents attack by its own restriction enzymes
Purpose of CRISPR-Cas (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic repeats and nuclease enzymes called Cas) system
To defend against phages. Works by transcribing the CRISPR region of DNA along with the phage DNA. Once it has been transcribed into RNA, it binds to a Cas protein that cuts out the phage DNA, leaving only the CRISPR DNA. The phage DNA is degraded and can no longer be used to replicate.
Basically cuts the phage RNA out of the RNA strand so that it can no longer be used to replicate phages
Characteristics that allow prokaryotes to thrive in diverse environments
Small size + rapid reproduction
High genetic diversity through mutation
Bacteria sharing plasmids with other bacteria to increase potential diversity
Rapid evolution of diverse adaptations
Prokaryotes
Single-celled organisms in the domains Bacteria and Archaea
Chemical + Physical processes on early Earth necessary for the synthesis of simple cells
Abiotic synthesis of small organic molecules
Joining of small molecuyles into macromolecules
Packaging of molecules into protocells, droplets with membrane that maintain consistent internal chemistry
Creation of self-replicating molecules
What did Oparin and Haldane do
They hypothesized that the early environment was a reducing environment
What did Miller and Urey do
They showed experimentally that abiotic synthesis of organic molecules was possible in a reducing atmosphere. Created a self-contained experiment simulating the conditions of the earth billions of years ago to see if they could create life from that.
Protocells
Fluid-filled vesicles enclosed with a membrane-like structure
Montmorillonite clay
Increases the rate of vesicle formation by concentrating molecules on its surface This is because lipids and other organic molecules can spontaneously form vesicles with a lipid bilayer in water so the higher the concentration of molecules on its surface, the higher the rate of vesicle formation
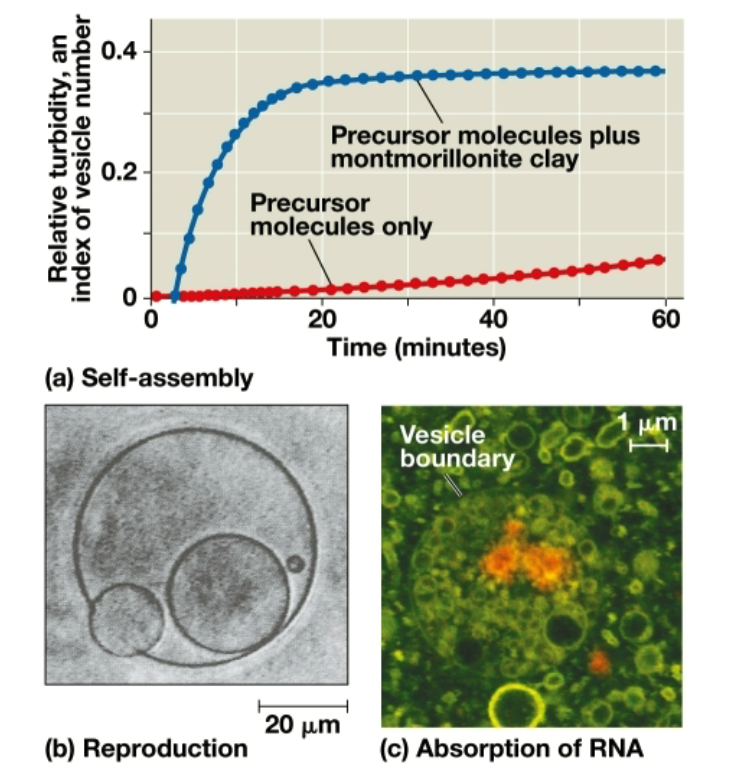
Ribozymes
RNA molecules that can catalyze reactions; some are also self-replicating
First genetic material
Likely RNA
Stromatolites
Layered rocks that formed from the activities of prokaryotes, formed by cyanobacteria and other photosynthetic bacteria
Size of prokaryotic cells
0.5-5 µm(micrometers)
Cell wall
Used to protect and maintain cell shape
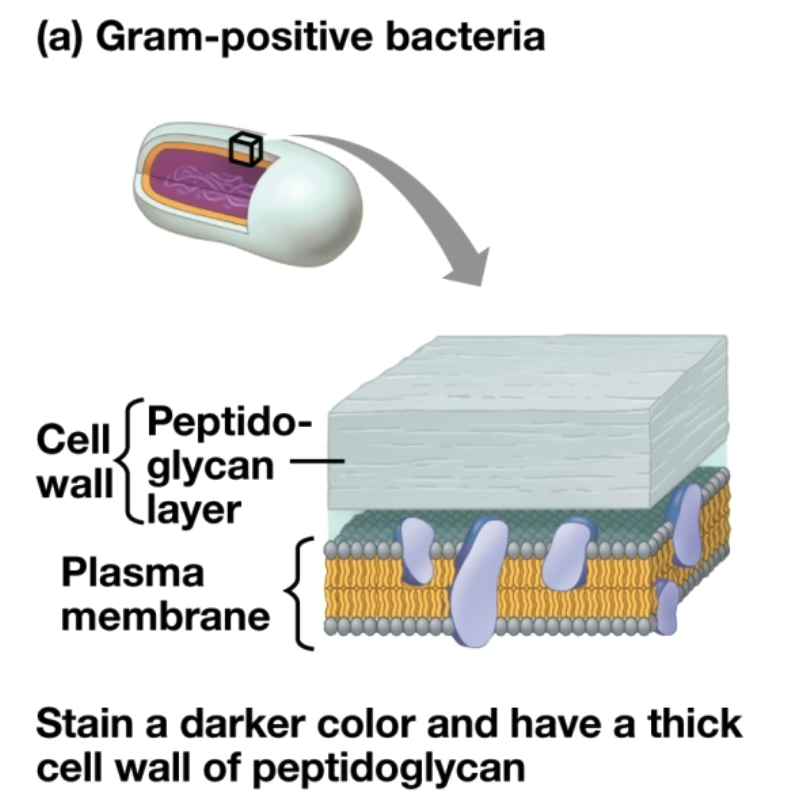
Bacterial cell walls
Contain peptidoglycan, a network of modified sugars and polypeptides
Archaeal cell walls
Contain polysacchardies and proteins but lack peptidoglycan
Gram-positive bacteria
Simpler cell walls composed of a thick layer of peptidoglycan
Stains a darker color
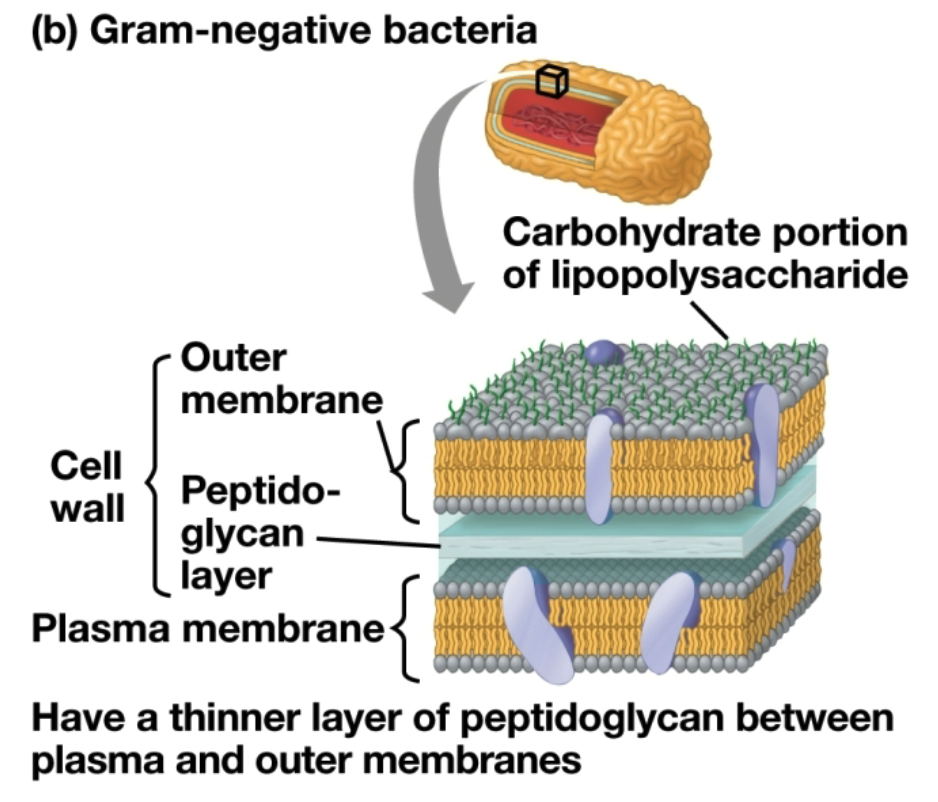
Gram-negative bacteria
They have less peptidoglycan and an outer membrane with lipopolysaccharide
Stains a lighter color
Why are some bacteria more resistant to antibiotics than others
Many antibiotics target peptidoglycan in a bacterial cell wall to destroy the bacteria however, the outer-membrane protects the peptidoglycan layer in gram-negative bacteria, increasing their antibiotic resistance by preventing the antibiotics from reaching the peptidoglycan
Capsule
A sticky, protective outer layer in prokaryotes that allow them to adhere to the substrate or each other
Endospores
Resistant cells developed by bacteria when water or nutrients are lacking so that the bacteria can survive
Dormant cells that can remain viable for centuries or survive extreme conditions
Fimbriae
Hairlike appendages used by prokaryotes to stick to the substrate or to other cells
Pili
Longer, less numerous appendages that are used to pull prokaryotes together during DNA transfer between cells
Endosymbiosis
When an ancestral cell engulfed an aerobic bacterium forming an early eukaryote
Basically where one life form engulfs another one and over time, the two cells merge and share the same functions
4 main supergroups that evolved using endosymbiosis from heterotrphic and photosynthetic eukaryotes
Excavata
SAR
Archaea
Unikonta
Examples of Endosymbiosis
Mitochondria being the descendant of some kind of ATP producing bacterium
Chloroplasts being the descendant of some kind of photosynthetic bacterium
Protist
Unicellular eukaryotes
Algae
Photosynthetic protists
Endosymbiont
Cell that lives within a host cell
Serial endosymbiosis hypothesis
The process that describes the repeated acquisition of endosymbionts, one after another, leading to the evolution of complex eukaryotic cells
ex. That mitochondria and plastids evolved sequentially with mitochondria evolving first and plastids evolving second
Secondary Endosymbiosis
When eukaryotic algal cells were ingested by heterotrophic eukaryotes
Steps in the Origin of Multicellularity
Involved many small steps
Transition to multicellularity involved having new ways of using proteins encoded by genes
Few novel genes actually had to evolve
Excavata
1 of the main supergroups of Eukaryotes
3 Clades - Parabasalids, Diplomonads and Euglenozoans
Includes parasites like Giardia intestinalis
SAR
1 of the main supergroups of Eukaryotes
Includes three diverse clades - Stramenopila Alveolata and Rhizaria
Includes important photosynthetic organisms like diatoms
Diatom are algae and contain a silica case
Ex. Plasmodium, which cause malaria
Archaeaplastida
Includes photosynthetic species of red algae, green algae and plants
Algae include unicellular, colonial and multicellular specias known as seaweeds
Ex. Volvox - A simple multicellular green algae that forms a ball of sterile cells surrounding groups of reproduction cells
Unikonta
Includes amoebas, animals, fungi and non-amoeba protists closely related to animals or fungi
Amoebas in this group have lobe or tube shaped pseudopodia
Ex. Amoeba proteus
Protists
Most are unicellular while others are colonial or multicellular
Most are aquatic but can be found anywhere were
Nutritionally diverse and consume food through photoautotrophy, heterotrophy and mixotrophy
Form the base of the food web
Producers
Use energy from light or inorganic chemicals to convert CO2 to organic compounds
Consumers
Depend on producers for food by eating hem or eating animals that eat them
Mycorrhizae
Symbiotic relationship between fungi and plants
Fungi help plants by increasing nutrient absorption, specifically the delivery of things like phosphate ions and other minerals, while the plant provides the fungi with organic nutrients like carbohydrates
Aided the transition of plants and fungi from water to land
How due fungi eat things
By secreting hydrolytic enzymes into their surroundings allowing them to break down molecules so that they can eat them
Hyphae
Branched filaments that make up the mycelium in mushrooms
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Endomycorrhizae)
Type of fungi that extend hyphae into root cell walls but don’t penetrate the membrane
Ectomycorrhizal fungi
Grow around the root surface and into the extracellular spaces of the root cortex
Plasmogamy
The union of cytoplasm from two different haploid mycelia (In fungi)
Karyogamy
Fusion of haploid nuclei to form diploid cells (In fungi)
Vascular tissue
COmposed of cells joined into tubes that transport water and nutrients throughout the plant
Bryophytes
Only living group of plants that lack vascular tissue
Also lack true roots or leaves
Contain a leafy bottom called a gametophyteand have a less dense protruding part
Gametophyte is dominant
Reproduce by releasing sperm that must swim through a film of water to fertilize an egg
The clades of Bryophytes
Liverworts
Mosses
Hornworts
Rhizoid
Root like structures in plants that anchor them to the substrate
Lycophytes
Type of a seedless vascular plant that reproduces through water
ex. Club mosses and their relatives
Sporophyte is dominant
Monilophytes
Type of seedless vascular plant that reproduces through water
ex. Fern and their relatives
Xylem
Type of vascular tissue that transports water and minerals
COnsists of dead cells
Phloem
Transports organic products like sugars or amino acids
Tracheids
Tube shaped cells that make up some of the xylem that conduct water and minerals
Lignin
Recalcitrant compound that strengthens xylem and doesn’t get broken down easily
Addition of this to vascular tissue provided the structural support for plants so that they can grow taller and have better access to sunlight or dispersal of spores
Roots
Absorb water and nutrients from the soil and anchor vascular plants to the group
Leaves
Promary photosynthetic organ of vascular plants
Microphylls
Small leaves with a single strand of vascular tissue and are only found in lycophytes
Ex. Krauss’s spikemoss
Megaphylls
Large leaves with a highly branched vascular ststem and are found in most other vascular plants
Ex. Tunbridge filmy fern
Seed
An embryo and its food supply contained within a protective coat
Wind or other long distance seed dispersal methods allowed seed to travel long distances and expand into new habitats on land
Gymosperms
Plants that have naked seeds that aren’t enclosed within chambers
ex. Sago palm or Douglass Fir
Angiosperms
Plants that have seeds that develop inside chambers called ovaries
Also produce reproductive structures called flowers or fruits
Pollination
Transfer of a pollen grain into the part of a seed plant containing the ovules
Pollen is generally transported by the wind or by attaching to the body of animals
Sepals
Part of the plant that encloses the unopened flower bud
Petal
Attracts pollinators with bright colors
Stamen
Contains an anther that produces pollen atop a fillament
Carpel
Produces ovules
Contains 3 parts - stigma (sticky top that catches pollen), styles (stalk) and an ovary at the base (contains ovules)
Retrovirus
A RNA virus that reproduces by transcribing its RNA into DNA inside a host cell using the enzyme reverse transcriptase. The DNA is then integrated into the host genome as a provius and becomes a permanent part of the host’s DNA
ex. HIV
Viroid
Circular RNA molecules that infect plants.
Lack a protein coat
Replicate within host plant cells and cause disease by disrupting gene expression
Prions
Infectious proteins that cause neurodegenerative diseases in animals. It is a misfolded form of a normal protein that can cause other normal proteins to misfold the same way
Vaccine
Works by injecting a harmless form or component of a pathogen like an inactivated or attenuated virus that triggers a response in the immune system which creates the appropriate memory cells and antibodies without actually causing the disease
They don’t cure an existing infection but provide immunity or a reduce in disease severity
Prokaryotes
Single Celled organisms without a nucleus
2 Domains: Archaea and Bacteria
Archaea
A type of prokaryote that thrives in extreme environments
Bacteria
A type of prokaryote that generally lives in normal temperatures
Nucleiod
A non membrane-bound region where DNA is concentrated in prokaryotes
Flagella
A structure of movement shaped like a thin rod
Taxis
A response to a stimuli seen in prokaryotes
Chemotaxis
Movement in response to chemicals
Binary Fission
Form of reproduction in prokaryotes where one cell divides into two identical daughter cells
Genetic Recombination - Transformation
Uptake of free DNA from the environment. A bacterium can absorb short fragments of DNA and incorporate them into its genome, altering its genotype
Genetic Recombination - Transduction
Transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another via bacteriophages (viruses)
Genetic Recombination - Conjugation
Direct transfer of DNA between two bacterial cells that are temporarily joined. Usually involves a donor cell with an F-plasmid forming a sex pilus to connect to a recipient cell. HOw antibiotic resistant genes spread
Phototrophs
Capture energy from sunlight
ex. Cyanobacteria performing photosynthesis
Chemotrophs
Obtain energy from chemical compounds