Schizophrenia- Krysiak
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Describe the 4 major dopaminergic pathways involved in schizophrenia:
what kind of symptoms are involved with each?
mesolimbic: positive sym
mesocortical: negative sym
nigrostriatal: EPS, movement
tuberoinfundibular: prolactin release
Result of D2 receptor antagonism on the mesolimbic area:
decreased positive symptoms
Result of D2 receptor antagonism on the mesocortical area:
production of secondary negative symptoms
may/may not worsen cognitive or affective symptoms
Result of D2 receptor antagonism on the nigrostriatal pathway:
EPS
Result of D2 receptor antagonism on the tuberoinfundibular pathway:
hyperprolactinemia
PRACTICE:
Which dopamine pathway is involved with positive symptoms of
schizophrenia?
A. Mesocortical
B. Nigrostriatal
C. Mesolimbic
D. Tuberoinfundibular
C
Schizophrenia is a chronic disorder of __________ and __________.
thought and affect
List positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms:
Positive | Negative | Cognitive |
|
|
|
What are the time frames for each of the following:
brief psychotic episode
schizophreniform
schizophrenia
chronic schizophrenia
brief psychotic episode: <2w
schizophreniform: ≥2w and <6m
schizophrenia: ≥6m
chronic schizophrenia: >2yrs
How is schizophrenia diagnosed according to DSM-V:
characteristic symptoms: 2 or more of the following
delusions*
hallucinations*
disorganized speech*
grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior
negative symptoms
each symptom must persist for a significant portion of at least a 1-month period
MUST have at least one the symptoms with an *
PRACTICE:
Which of the following is a negative symptom of schizophrenia?
A. hallucinations
B. delusions
C. avolition
D. disorganization
C.
is schizophrenia curable?
no
Nonpharm for schizophrenia:
psychosocial rehab programs
case management, education, targeted therapy, basic living and social skills, work programs, housing
assertive community treatment (ACT)
teams available 24/7—> help with meds, crises, and daily living
List the typical or first gen antipsychotics:
also say whether they are high, mid, or low potency
Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)- low
Thioridazine (Mellaril)- low
Perphenazine (Trilafon)- mid
Loxapine (Loxitane, Adasuve Inhaled Powder)- mid
Thiothixene (Navane)- high
Trifluperazine (Stelazine)- high
Molindone (Moban)- high
Haloperidol (Haldol, Haldol-D)- high
Fluphenazine (Prolixin, decanoate)- high
MOA of FGAs:
DA receptor antagonists—> high affinity to D2
What FGA has a REMS program due to risk of bronchospasm, pulmonary distress, and pulmonary arrest?
Loxapine
Loxapine Staccato (Adasuve) is what kind of dosage form? indication?
inhaled powder
indication: acute agitation associated with schizo and BPD
List the SGAs:
Aripiprazole (Abilify, Abilify Maintena, Abilify Aristada, Initio, Asimtufii, MyCite)
Asenapine (Saphris, Secuado)
Brexpiprazole (Rexulti)
Cariprazine (Vraylar)
Clozapine (Clozaril)
Iloperidone (Fanapt)
Lumateperone (Caplyta)
Lurasidone (Latuda)
Olanzapine (Zyprexa, Zydis, Relprevv)
Paliperidone (Invega, Invega Sustenna, Invega Trinza, Invega Hafyera)
Pimavanserin (Nuplazid)
Quetiapine (Seroquel, XR)
Risperidone (Risperdal, M-Tab, Risperdal Consta, Perseris, Uzedy)
Ziprasidone (Geodon)
How do SGAs effect each of the following:
mesolimbic
mesocortical
nigrostriatal
tuberoinfundibular
limbic: decreases DA= relieves + sym
cortical: increases DA= relieves - sym
nigro: increase DA= less chance of EPS
tube: less prolactin release
MOA of SGAs:
which have greater affinity for 5HT2A receptors > D2 receptors
which are partial agonists?
ALL HAVE UNIQUE PROPERTIES!!!!!!!!!!!!
In common: 5HT2 and D2 antagonism
ALL SGAs have greater affinity for 5HT2A >D2 EXCEPT aripiprazole and brexipiprazole
Partial D2 agonists: Aripiprazole, brexipiprazole, cariprazine
two “pips” and a “rip”
List the SGA for each of the following questions:
What SGA is sublingual only and no food/drink 10min after admin?
Due to a long half-live steady state with what SGA is not reached for several weeks?
Which SGA needs care with dosing in CYP2D6 slow metabolizers?
Which SGA’s bioavailability is increased by 9% when administered with high fat meal?
Which SGA’s bioavailability is increased when administered with food?
Asenapine
Cariprazine
Iloperidone
Lumateperone
Paliperidone
What 2 SGA’s must be taken with food?
Lurasidone
Ziprasidone
Which SGA has a REMS program for neutropenia/agranulocytosis?
what is defined as severe neutropenia?
At what ANC level can it be initiated?
Clozapine
severe neutropenia is ANC <500
ANC ≥1500 it can be initiated
Which SGA is avoided in first episode because of weight gain?
olanzapine
PRACTICE:
In addition to dopamine blockade, second generation antipsychotics as a class
have a mechanism of:
A. Dopamine agonism
B. Serotonin antagonism
C. Alpha blockade
D. Histaminergic blockade
B.
Side effects associated with Aripirazole?
akathisia (movement disorder)
others: HA, anxiety, lower risk of weight gain
When is clozapine indicated? advantages and disadvantages of use? BBW?
only if pt. fails 2 treatments
advantages: lowest risk of EPS, very effective tx
disadvantages: side effect profile
BBW:
neuropenia/agranulocytosis—> REMS
myocarditis/cardiomyopathy
orthostatic hypotension
seizures
other ADRS: severe weight gain, constipation, drooling
C/I of lurasidone?
strong CYP450 3A4 inhibitors/inducers
Paliperidone is the active metabolite of ____________.
Risperidone
BBW with Zyprexa?
Zyprexa Relprevv (ER injection formulation)—> BBW for sedation and delirium following injection
Quetiapine XR is oral only and taken when?
at night WITHOUT food
Ziprasidone is C/I in what?
QT prolongation
PRACTICE:
At what ANC level may clozapine be initiated?
A. 900
B. 1000
C. 1200
D. 1500
D.
PRACTICE:
When educating a patient on a new prescription for lurasidone, which statement would be considered the most appropriate regarding taking the medication?
A. Take the dose prior to bedtime for full effect
B. Avoid grapefruit and grapefruit juices
C. All side effects are short lived
D. Take dose on an empty stomach
B. (bc it’s contraindicated with 3A4 inhibitors/inducers)
PRACTICE:
A patient presents to your clinic and is found to have hyperprolactinemia from his risperidone. What additional antipsychotic should be avoided?
A. Clozapine
B. Olanzapine
C. Paliperidone
D. Quetiapine
C.
ALL ANTIPSYCHOTICS HAVE WHAT BBW?
increased risk of mortality if used for dementia-related psychosis
What endocrine ADRs are seen with antipsychotics?
prolactin elevation (bc of DA antagonism in tuberoinfundibular tract)
weight gain (bc of antihistamine, antimuscarinic, and blocking 5HT2C)
Type 2 DM (increases insulin resistance and impairs b-cell fxn)
What CV ADRs are seen with antipsychotics?
orthostatic hypotension (bc of a-adrenergic blockage)
ECG changes (bc of anticholinergic and alpha affects)
QT prolongation, reflex tachycardia
d/c if QTc interval exceeds 500msec
myocarditis (mainly w/ clozapine, <1% of pts.)
lipid changes (increased appetite and weight gain contributes, elevated TGs and CHO)
Describe the CNS ADR seen with antipsychotics called EPS.
prevention?
EPS—> extrapyramidal system, term used to describe anti-psychotic induced movement disorders
includes:
dystonia (involuntary movements/spasms)
akathisia (Unbearable inner restlessness with compulsive movements (pacing, foot-tapping, inability to sit still))
parkinsonism (Bradykinesia, rigidity, and resting tremor mimicking idiopathic Parkinson’s disease)
tardive dyskinesia (Involuntary, repetitive movements (tongue writhing, lip smacking, grimacing) that develop after months/years of antipsychotic use)
prevent by
initiating at low dose, and titrating up slowly
choose antipsychotic with low EPS risk
PRACTICE:
A 67yo patient that has been taking risperidone 0.5 PO BID x 4 weeks presents to your outpatient clinic with bradykinesia and tremor at rest. What is the most likely EPS the patient is experiencing?
A. Akathisia
B. Dystonia
C. Tardive dyskinesia
D. Pseudoparkinsonism
D.
PRACTICE:
Which of the following is a black boxed warning of clozapine? SATA
A. Constipation
B. Myocarditis
C. Agranulocytosis
D. Death with dementia related psychosis
B, C, D
What drugs can be used to prevent tardive dyskinesia (an ADR of antipsychotics)?
What is the MOA?
ADRs?
C/Is?
Valbenazine and Deutetrabenazine
MOA: VMAT2 inhibitors
ADRs: somnolence
C/Is: Deute in hepatic impairment
Treating parkinson’s and psychosis is difficult because it’s a balancing act between dopamine and acetylcholine.
What drug can be used for psychosis in Parkinson’s Disease?
MOA?
Warnings?
SE?
drug: Pimavanserin (Nuplazid)
MOA: inverse agonist and antagonist at 5-HT2A receptors
Warnings: not for dementia related psychosis, QT prolongation
SE: peripheral edema, confusion
Describe the CNS ADR seen with antipsychotics called NMS.
treatment?
NMS—> neuroleptic malignant syndrome, disruption of thermoregulatory process or excess heat production second to muscle contractions
tx:
D/C ALL DOPAMINE blockers
supportive care
DA agonists: bromocriptine
Dantrolene for skeletal relaxation
What Derm ADRs are seen with antipsychotics?
BBW on what drug?
DRESS—> drug reaction with eosinophilia and systematic symptoms
BBW on olanzapine
photosensitivity
REVIEW:
Answer the following about FGAs and SGAs and ADR risk:
SE/Risk | Meds |
EPS | lowest risk: highest risk: |
Metabolic | lowest risk: mod risk: highest risk: |
QT prolongation | highest risk: |
Hematological | highest risk: |
increase prolactin | highest risk: |
seizure | highest risk: |
Cerebrovascular events | highest risk: |
SE/Risk | Meds |
EPS | lowest risk: quetiapine, clozapine highest risk: FGAs, risperidone, paliperidone |
Metabolic | lowest risk: aripiprazole, ziprasidone, lurasidone, asenapine mod risk: risperidone, paliperidone highest risk: clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine |
QT prolongation | highest risk: thioridazone, haloperidol, ziprasidone |
Hematological | highest risk: clozapine |
increase prolactin | highest risk: risperidone, paliperidone |
seizure | highest risk: clozapine |
Cerebrovascular events | highest risk: risperidone |
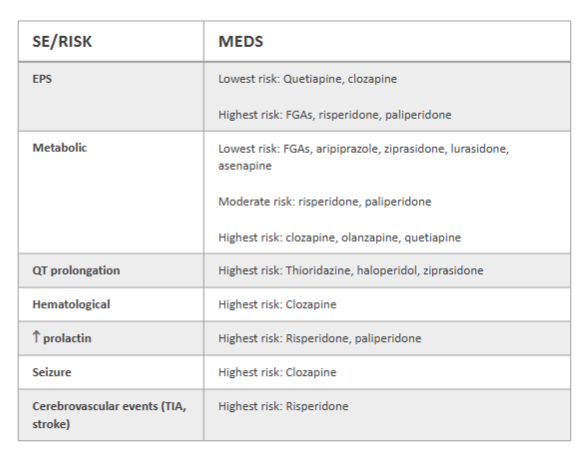
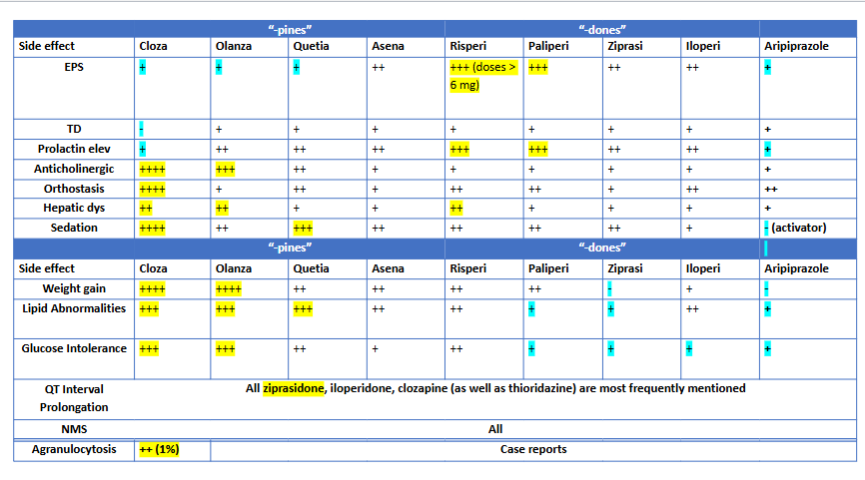
Another review table for ADRs krysiak gave us:

Smoking induces what enzyme? what SGA interacts then?
smoking—> CYP1A2—> can increase clozapine levels = increased seizure risk
For initial treatment of schizophrenia:
1st episode pts. should be started at ___% of normal dose range
adequate trial is how long?
after tx of first psychotic episode, pt. should continue on medication for at least __ months after remission
1st episode pts. should be started at 50% of normal dose range
adequate trial—> 4-6 weeks
after tx of first psychotic episode, pt. should continue on medication for at least 18 months after remission
What dosage form can a pt. take that may help with adherence in schizo pts.?
long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIA) or Abilify MyCite (a biosensor inside a tablet)
List the FGAs and SGAs that come in long-acting injectable form:
FGAs:
Fluphenazine decanoate
Haloperidol decanoate
SGAs
Risperidone IM (Risperdal Consta, Rykindo)
Risperidone SQ (Perseris, Uzedy)
Paliperidone (Sustenna, Trinza, Hafyera)
Aripiprazole (Maintena, Aristada, Asimtufii, Initio)
Olanzapine (Zyprexa Relprevv)
remember BBW with it
What is the definition of treatment-resistant schizophrenia?
What is the only antipsychotic that has shown superiority in tx for this?
def: persistent symptoms despite 2 different antipsychotics at adequate dosage for at least 6 weeks
clozapine