Geohazard
a geological condition that is dangerous or potentially dangerous to the environment and the people who live within it

Geohazards can be…
natural or artificial
long term or short term
large scale or small scale
frequent or infrequent
Examples of geohazards
landslides/mudslide/avalanche
sinkhole
flooding/tsunami
volcanoes/earthquakes
drilling/fracking in over-pressurized land
Focus
The point within the Earth where the earthquake originates
It occurs alongside a fault plane as one section of crust moves alongside another
Earthquakes do not actually originate from a single point but it is more convenient to think of it that way
Seismic waves radiate out from the focus
Depth of focus
Earthquakes are classified by their depth of focus…
Shallow focus 0 – 70 km
Intermediate focus 70 – 300 km
Deep focus 300 – 700 km
Shallow focus
0 - 70km
Intermediate focus
70 - 300km
Deep focus
300 - 700km
Why do earthquakes not occur deeper than 700km?
Earthquakes do not originate at greater depths because the greater temperatures lead to rocks behaving in a plastic rather than brittle manner
Epicentre
The point on the Earths surface directly above the focus
The epicentre is marked on surface maps to represent the position of the focus
The epicentre is where the greatest amount of damage is likely to occur
How do earthquakes occur?
Earthquakes can be dangerous because of the physical effects produced by ground acceleration
Relative movement of the bedrock on either side of a fault applies stress to the rock in the fault zone which undergoes strain.
This process transfers energy and increases the elastic strain energy stored in the rock
When the fault suddenly ruptures, elastic strain energy is reduced and the energy is released as movement on either side of the fault, as heat and as seismic waves
The energy transferred by P, S and L waves is around 1% of the work done by the earthquake
The greater the energy, the greater the amplitude of the earthquake waves
Wave terminology
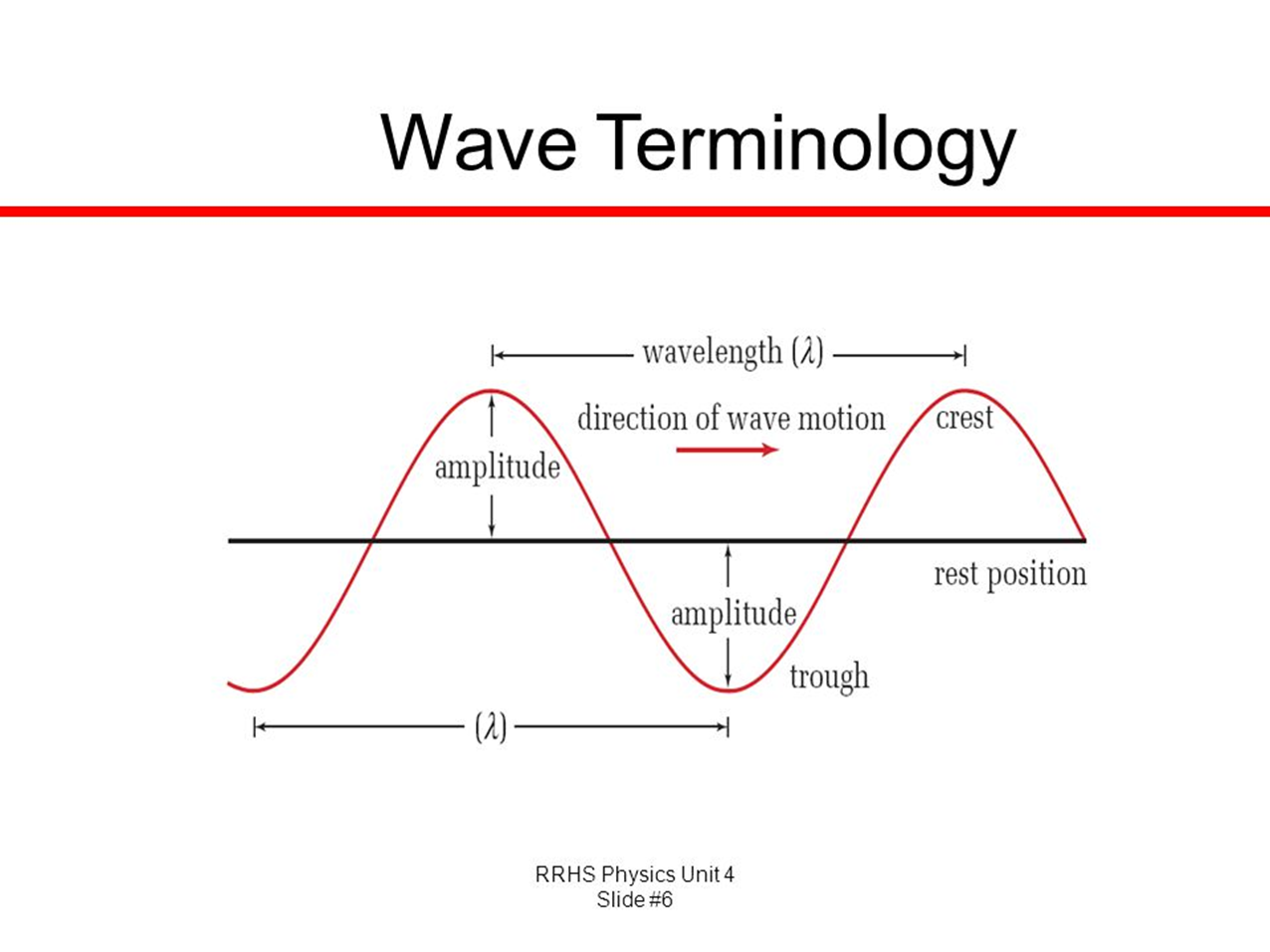
Amplitude
The maximum extent of an oscillation, measured from the position of rest (how high a peak measures)
Wave-length
How long a wave measures from peak-to-peak
Attenuation
The loss of energy experienced by a wave shown as a reduction in amplitude as it propagates through a material
Geometric Dispersion
What happens when pebble is tossed into a pond of water? Ripples spread out in circles
As the ripples increase in diameter, they spread out along a greater length
What happens to the amplitude of the waves? They get smaller
-
The amplitude also dissipates by attenuation
As the wave propagates through the rock, some elastic energy is transferred, near grain boundaries by friction and is transferred to thermal energy
Scattering of the waves by the grains accounts for some dissipation
The wave eventually disappears altogether
-
Competent rocks such as granite or limestone allow these vibrations to pass through them easily and attenuation is negligible
Weaker rocks such as clay or poorly cemented sandstone absorb some energy
Unconsolidated sands and gravels vibrate and move easily and attenuation may be ten times greater than in competent rocks
What do we use to measure seismic waves?
The amplitude of the wave (and therefore the amplitude shown on the seismogram) depends on the energy
Seismologists assess the amount of energy (E) released by the earthquake by measuring the maximum amplitude recorded on the seismogram
This is converted to a magnitude (M) scale to indicate the size of the earthquake
Energy
Energy is measured in joules (the energy transferred when a force of one newton acts through a distance of one metre)
For earthquakes this is a very small unit - a very small earthquake may transfer 109 joules of energy
On a logarithmic scale, this value for E is shown as 9, a much easier number to deal with
Now a number on a scale with no units…
Early magnitude scales were empirical, based on taking many readings from many earthquakes
A general relationship was established and used to define the term magnitude
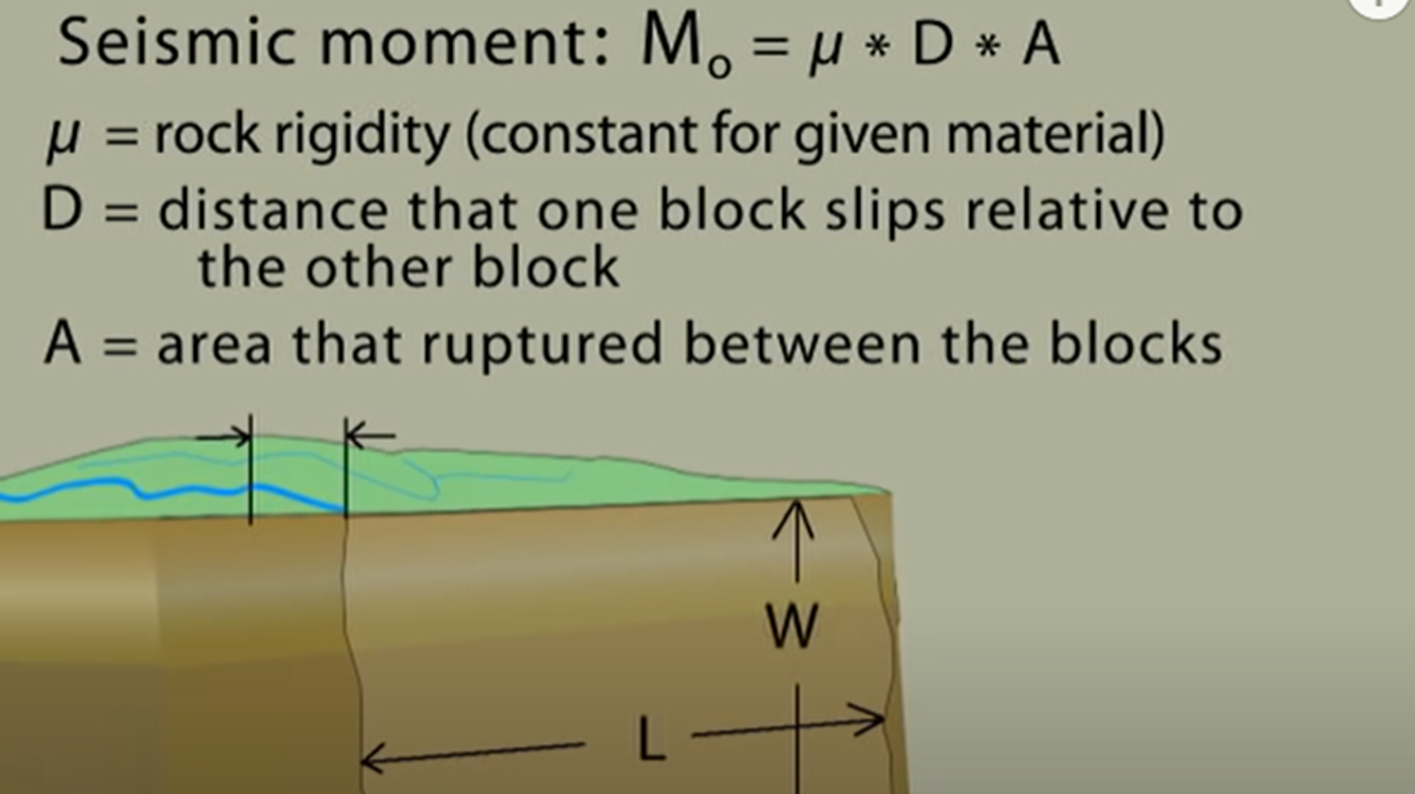
Fault geometry and seismic moment (Mo)
Magnitude scales are based on observation rather than maths. They do not measure a particular property of the earthquake. In 1979 a new scale, moment magnitude (Mw) was introduced
= Gives the most reliable magnitude for very large earthquakes because it is derived from factors that can be measured:
Size of fault rupture
Amount of displacement
Energy released
Seismic moment