Anaerobic Respiration
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
What is anaerobic respiration?
Respiration in the absence of oxygen.
Under anaerobic conditions, what stage of respiration can only occur?
Glycolysis.
Why can’t the link reaction and Krebs cycle take place under anaerobic conditions?
The reduced NAD cannot become reoxidised, and therefore be made available to pick up more hydrogen, so the link reaction and Krebs cycle cannot take place.
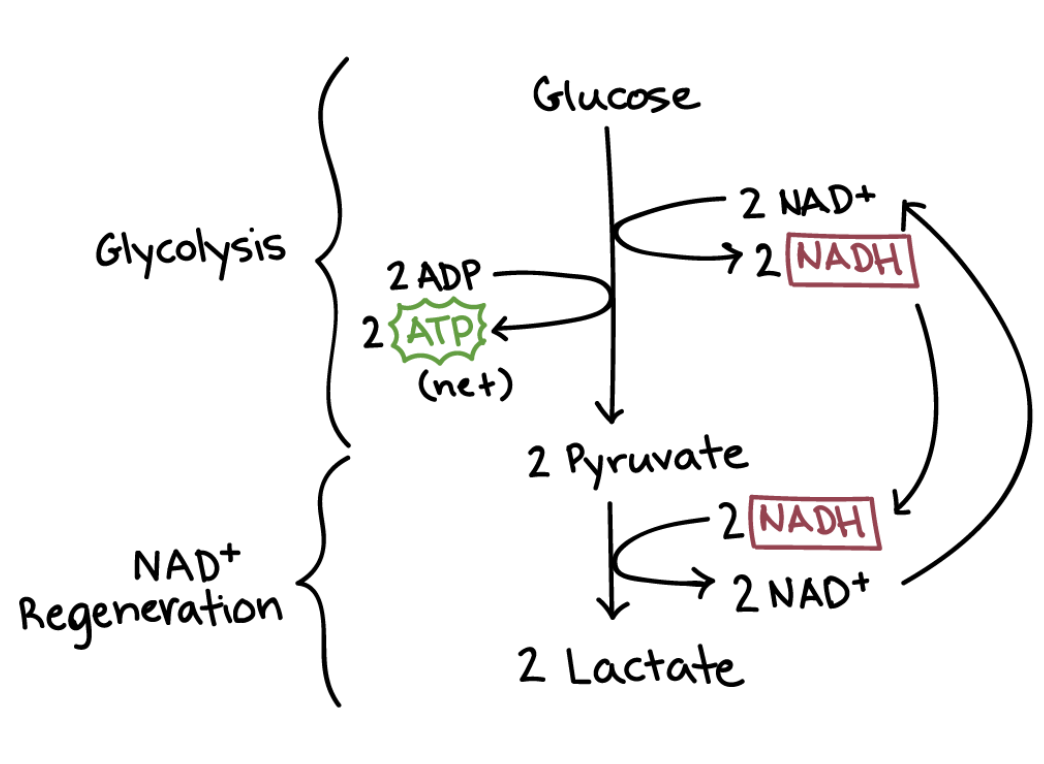
What must happen for glycolysis to continue?
Pyruvate and hydrogen must be removed, and NAD must be regenerated.
This is achieved by the pyruvate molecule accepting the hydrogen from the reduced NAD.
What are the 2 different anaerobic pathways to remove hydrogen?
In animals, pyruvate is converted to lactate / lactic acid (lactic acid fermentation).
In micro-organisms, such as yeast, pyruvate is converted to ethanol ( alcoholic fermentation).
Describe the process of lactic acid fermentation.
The reduced NAD transfers the hydrogen to pyruvate to form lactate/lactic acid (the pyruvate is reduced to lactate).
Lactic acid production is reversible if oxygen becomes available – the amount of oxygen needed to remove the lactic acid is called the oxygen debt.
This reaction mostly occurs in the muscle tissues during rigorous exercise.
Describe the process of alcoholic fermentation.
The pyruvate is first decarboxylated to form ethanal. Carbon dioxide is lost.
The reduced NAD passes the hydrogen to ethanal, forming ethanol.

Under anaerobic conditions, what is the yield of ATP molecules per molecule of glucose?
2 ATP molecules.