Unit 5 and 6 Geometry 25-26 IHS Sem 1 Online
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
equilateral triangle
three congruent sides
iscoleces triangle
two congruent sides
-vertex: b/w 2 congruent sides
-leg: two congruent sides
-vertex angle: angle between legs
-base: opposite of vertex, non congruent side
-base angle: angles opposite of the legs, always congruent to each other. sides of base angles are also congruent
-can use TST and isosceles triangle theorem to find missing angles and sides
converse of iscosceles triangle theorem
If the base angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite those angles are congruent
scalene triangle
triangle with no congruent side lengths
acute triangle
all 3 angles are acute
obtuse triangle
one obtuse angle
right triangle
one right angle
hypotenuse
opposite of right angle
equiangular
all right angles are congruent
-has to be acute and equilateral
-have to be 60 degrees
Triangle Sum Theorem
3 angles add up to 180
Pythagorean Theorem
a²+b²=c²
-for right triangles only
-hypotenuse: longest side of right triangle
-3-4-5 triangle
-used to find missing sides
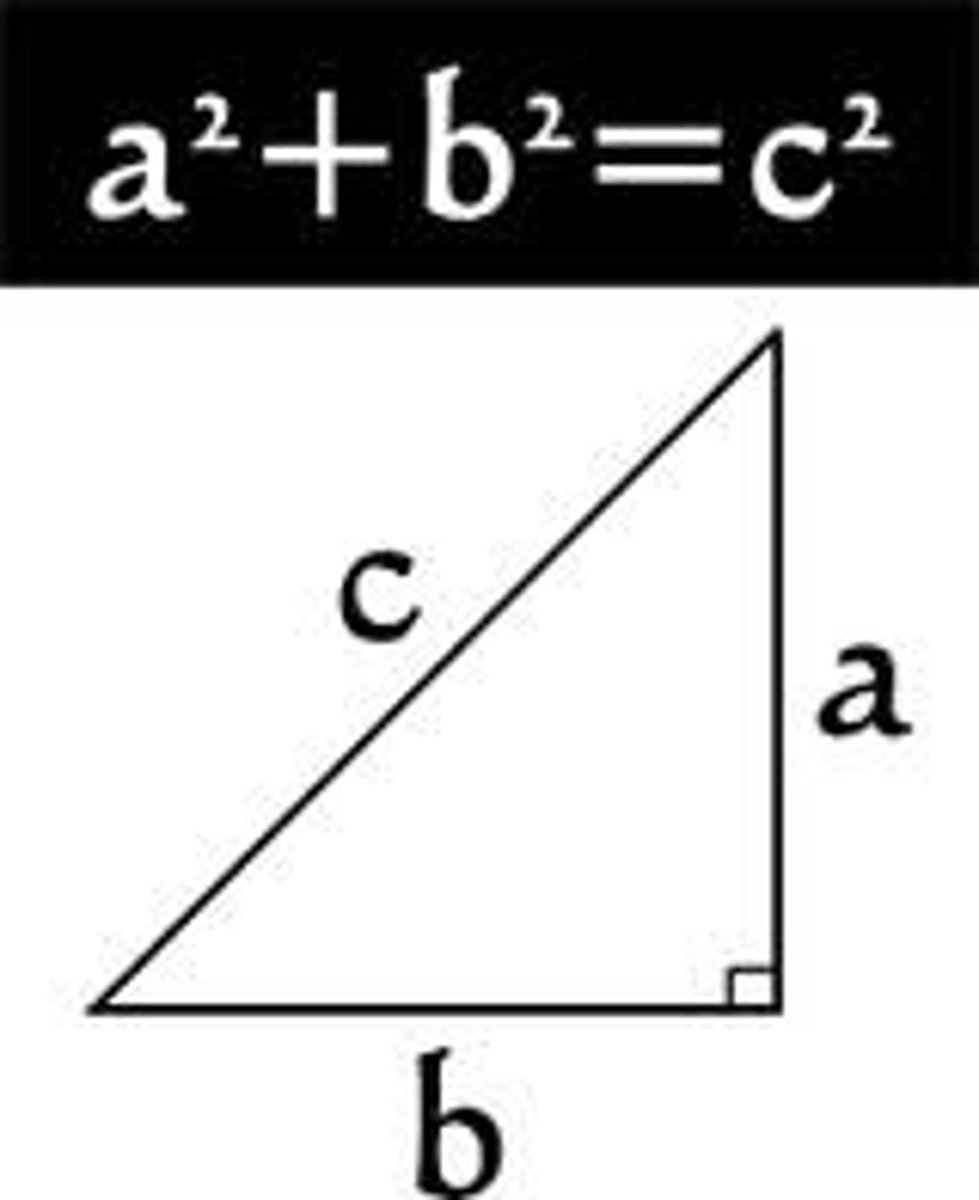
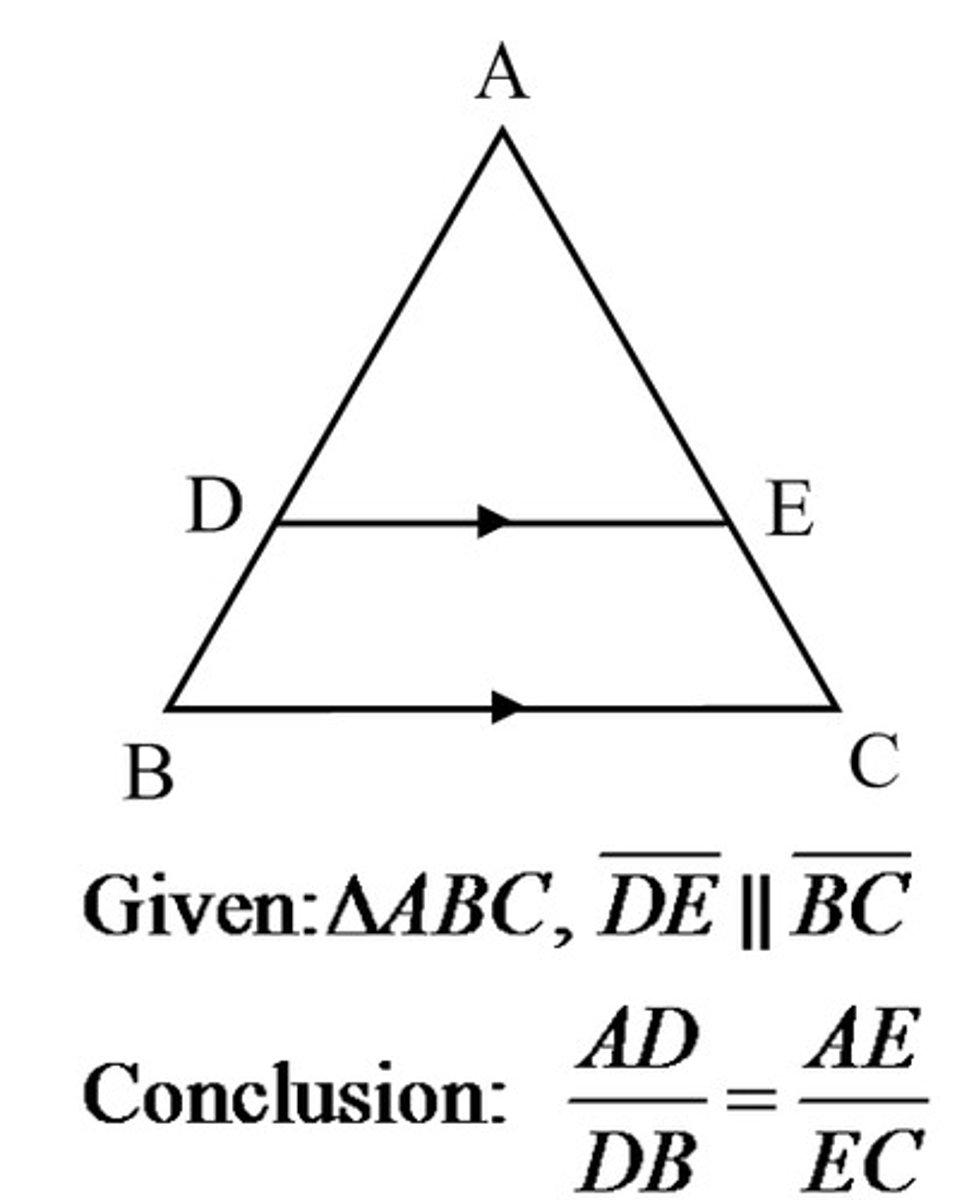
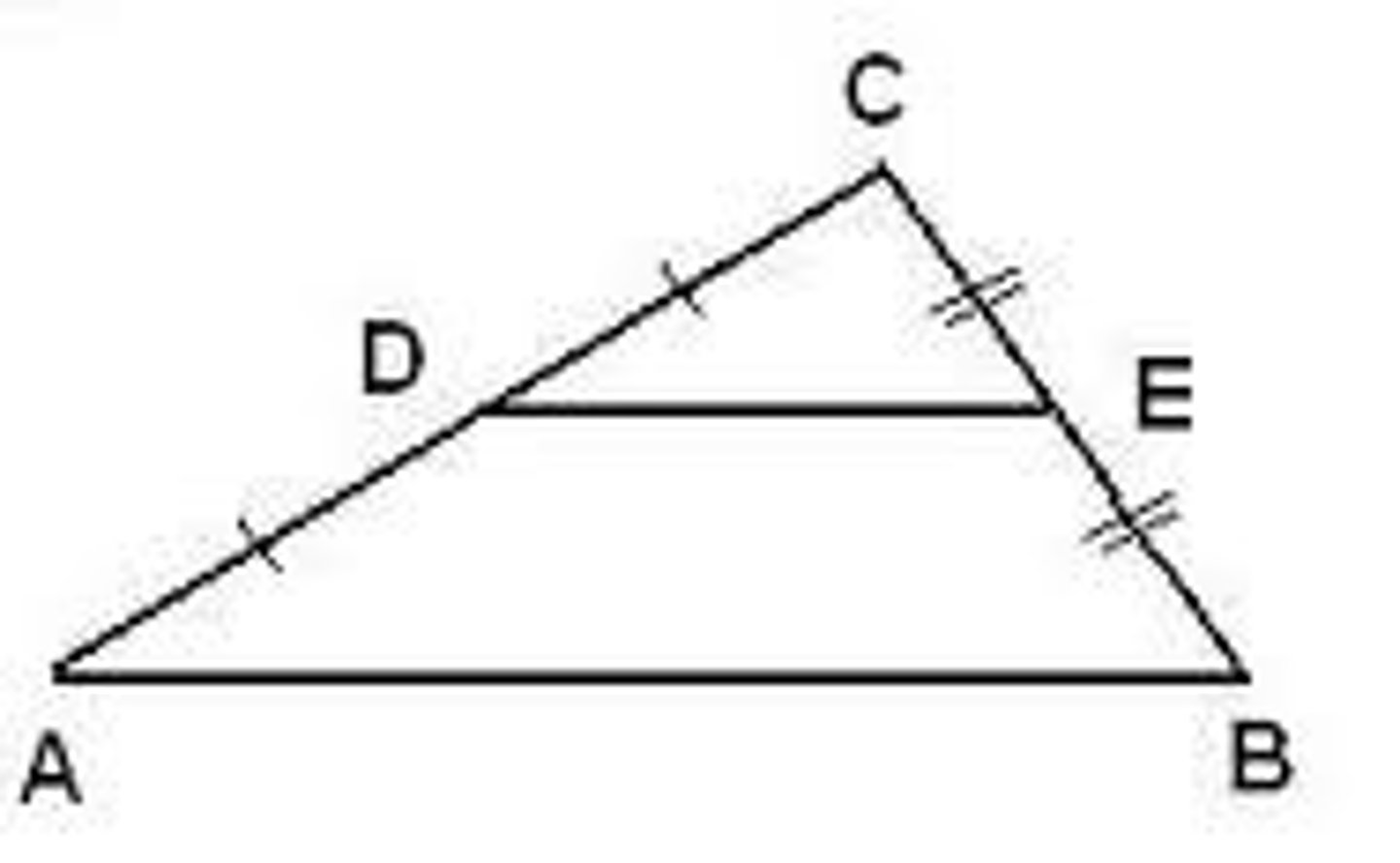
triangle proportionality theorem
If a line parallel to one side of a triangle intersects the other two sides, then it divides the two sides proportionally
-Set up the proportion. a/b=c/d Then solve the proportion using the cross product method.
median
connects vertex to midpoint
-Each triangle has 3 medians that will intersect in the middle, creating a centroid
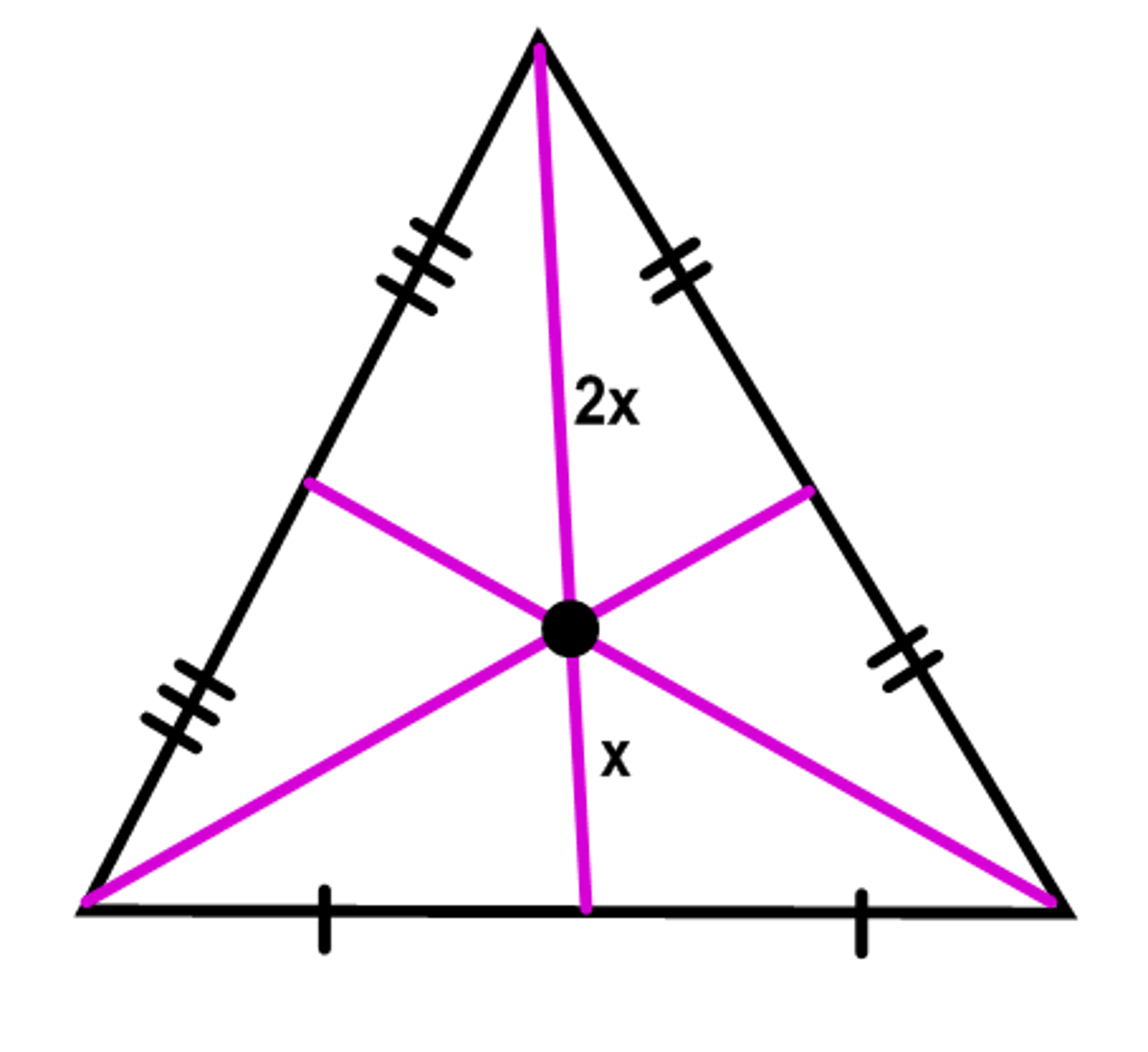
Centroid
exactly 2/3 of the distance from each vertex to midpoint of the opposite side, center of triangle

midpoint formula
(x₁+x₂)/2, (y₁+y₂)/2
altitude
height of object
-runs perpendicular to opposite side
-triangles have 3 altitudes
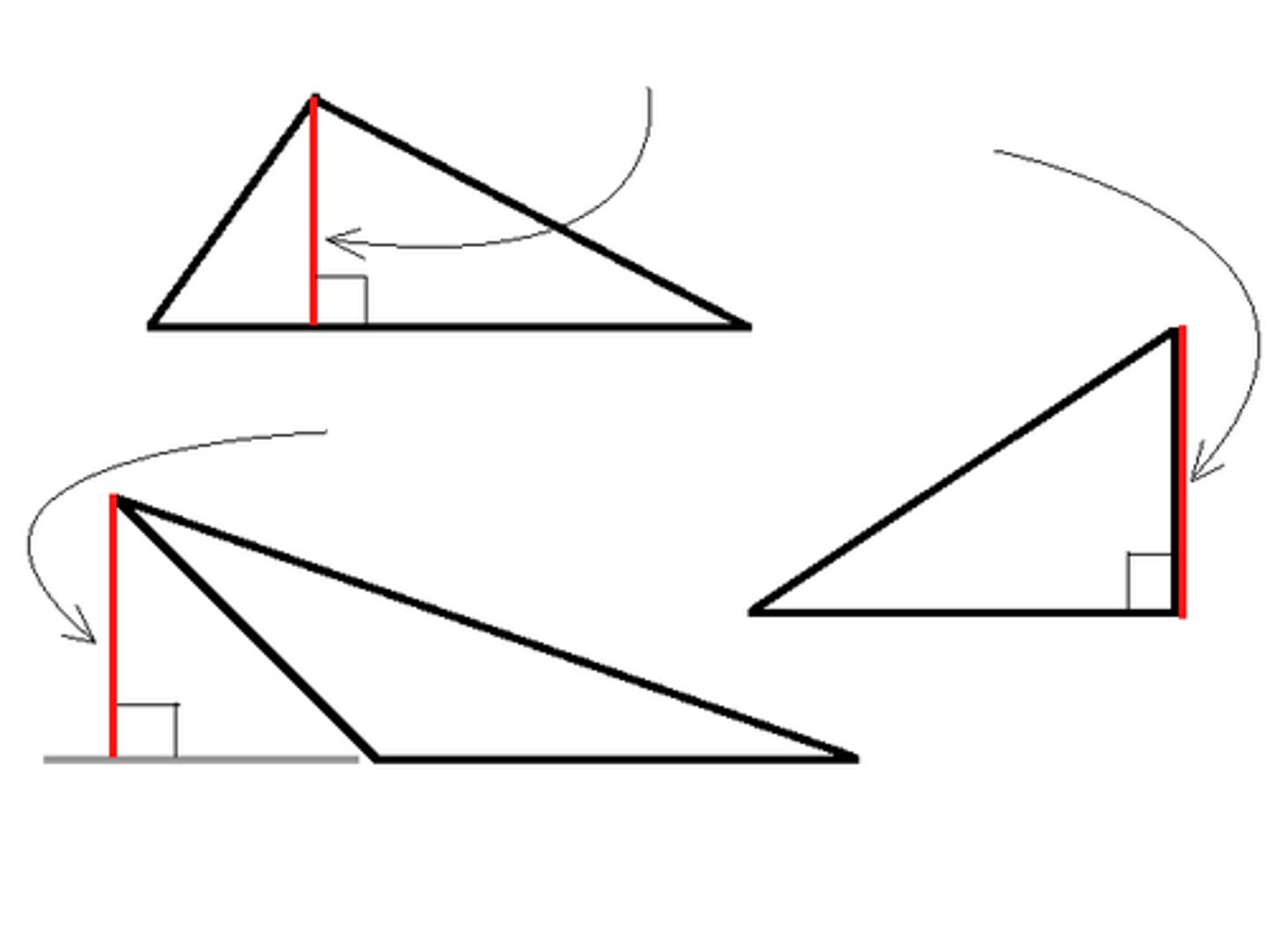
orthocenter
point of concurrency of the altitudes
-off center
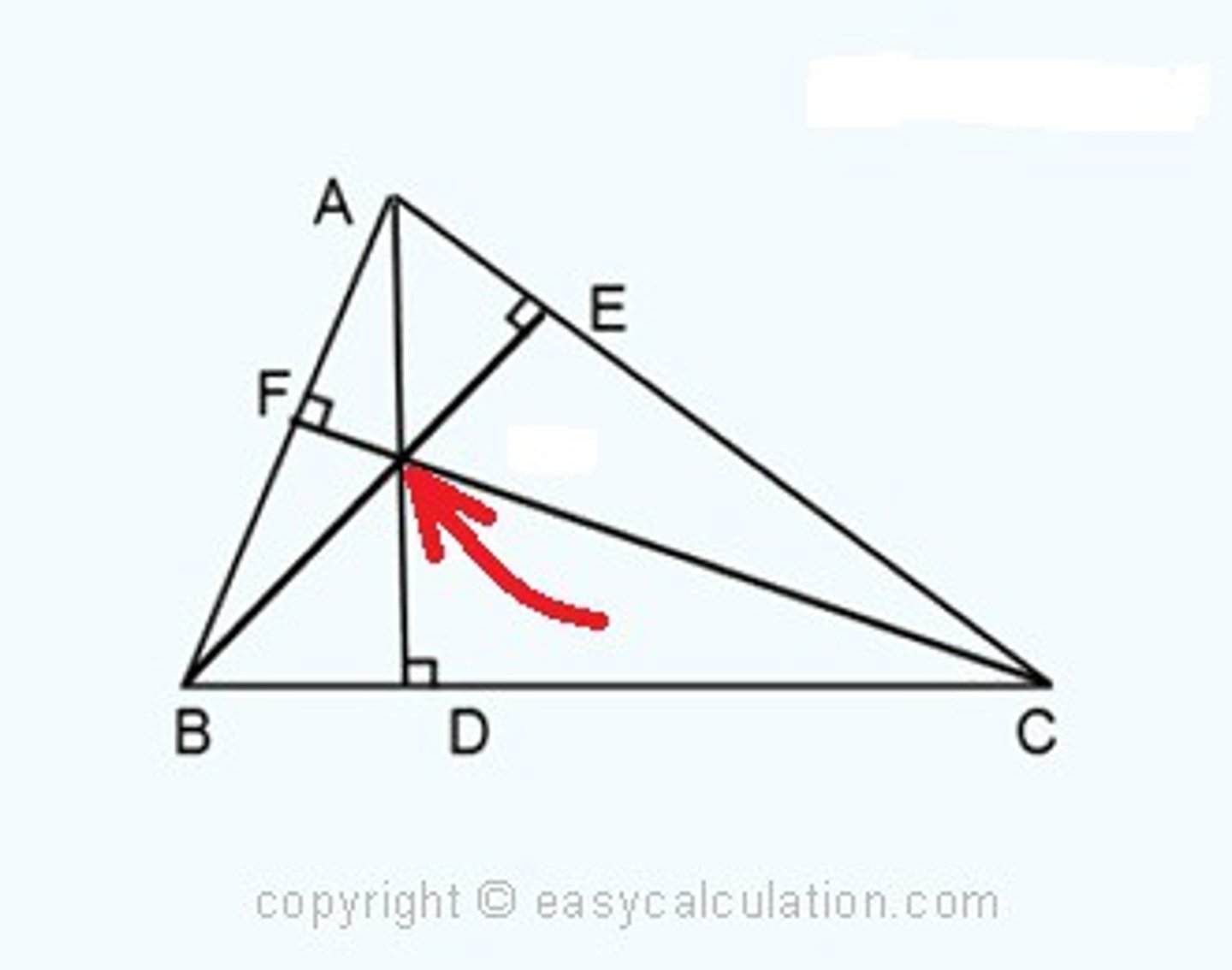
concurrent
intersect at one point
fulcrum
anchor point that connects two sets of legs
midsegment
finite line with two end points
-two endpoints are midpoints
-every triangle has 3 midsegments
distance formula
d = √[( x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²]
Midsegment Theorem
segment connecting the midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half as long
-same slope
-1/2 as long

slope
amount of incline/slant in an object
-pos, neg, or 0
-y2-y1 over x2-x1 if same slope = parallel
trapezoid
A quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides
-nonparallel sides: legs
-parallel sides: bases
-altitude: perpendicular distance between bases
-median: connects opposing legs, 1/2 of the sum of the bases
Midsegment Trapezoid theorem
The midsegment of a trapezoid is parallel to the bases and its length is equal to the average of the lengths of the two bases.
triangle inequality theorem
any side of a triangle must be shorter than the sum of the lengths of the other two sides
- x < 14 + 10, x must be less than 24
- 1051 < x + 979, x must be greater than ___ and less than __
triangle inequality theorem equations
AC < AB + BC
BC < AB + AC
AB < BC + AC
converse of triangle inequality theorem
In a 3 sided shape, if any side is shorter than the sum of the other two sides, then a triangle exists
triangle inequality theorem for angles
The largest angle in the triangle will be opposite the longest side, and smallest angle in a triangle will be opposite the shortest side
triangle inequality theorem for angles converse
The longest side in a triangle will be opposite the longest angle and the shortest side will be opposite the smallest angle
indirect proofs
assume opposite is true and then makes an absurd point
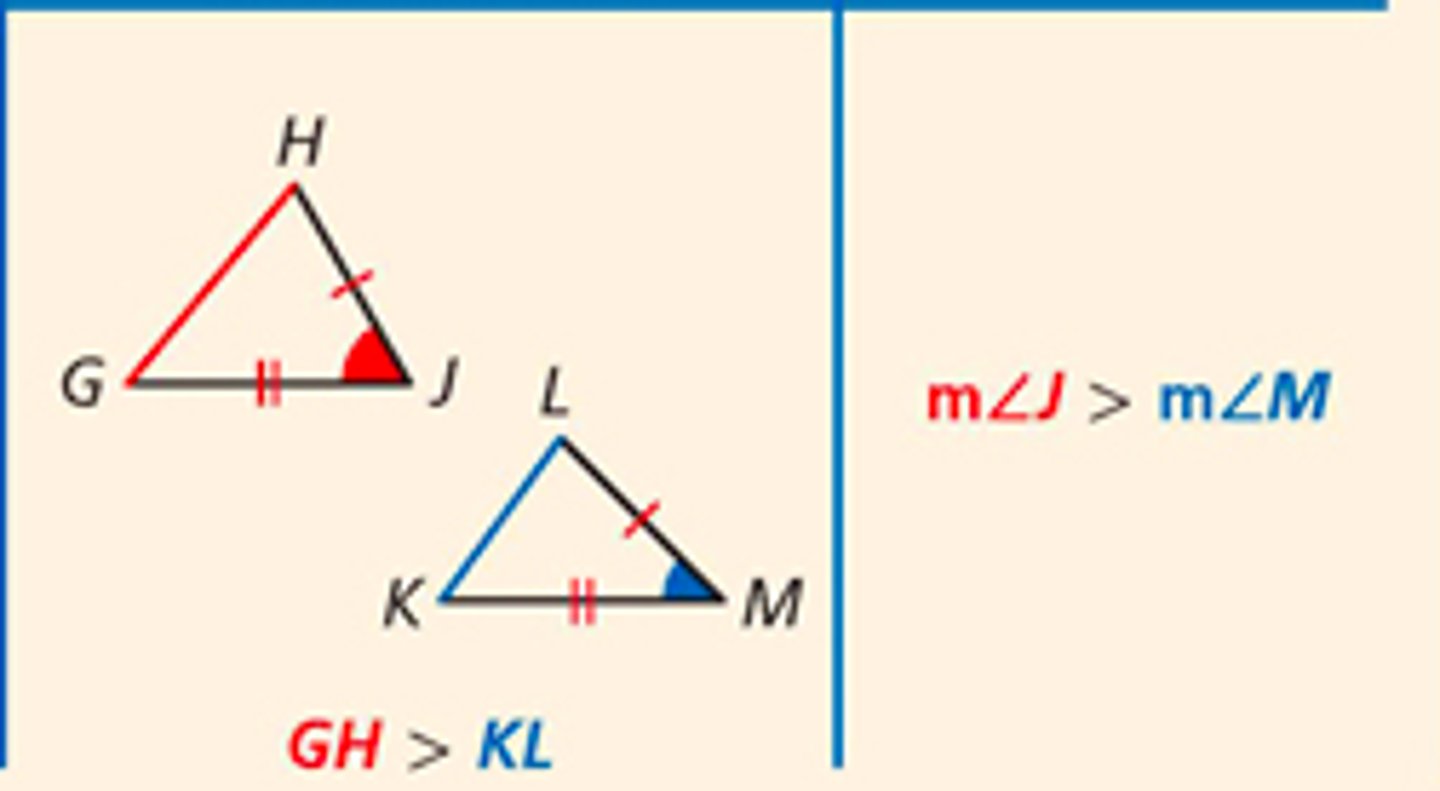
Hinge Theorem
If two sides of one triangle are congruent to two sides of another triangle, and the included angle of the first is larger than the included angle of the second, then the third side of the first is longer than the third side of the second.
-Also known as SAS Inequality theorem
Converse of Hinge Theorem
If two sides of one triangle are congruent to two sides of another triangle, and the third side of the first is longer than the third side of the second, then the included angle of the first is larger than the included angle of the second.
-Also SSS Inequality theorem
proportional triangles
parts of similar objects are corresponding parts
<--> means corresponding
- fraction = part / whole
proportion
mathematical expression that equates two ratios
- a/b = c/d
-ad are extremes, cb are means
-can rewrite by flipping the fractions
-b/a = d/c
geometric mean
3/x = x / 12
3(12) = x^2
square root to find x which is the geo. mean
-special ratio that relates the sides of similar right triangles
altitude rule
The altitude to the hypotenuse of a right triangle is the mean proportional between the segments into which it divides the hypotenuse
-altitude: line segment that extends from 1 vertex to form a right triangle with the opposite side
-part of hypotenuse / altitude = altitude / other part of hypotenuse
Leg Rule
the length of each leg of a right triangle is the geometric mean between the length of the hypotenuse and the length of the adjacent hypotenuse segmnet
- hypotenuse / leg = leg / projection
Congruency properties
SSS, Sas, ASA, ASA, AAS, HL
triangle applications
-Hinge Theorem: use main theorem for side lengths, converse for angles
-Similarity problems will have two triangles formed. Can involve right triangles with altitude, geometric mean, leg rule, and altitude rule
-Problems may include medians and altitudes
right triangles
-one right angle and two acute
-hypotenuse is opposite right, longest side
-each acute angle has an adjacent leg and opposite leg
similar triangles
congruent corresponding angles
-proportional corresponding sides
geometric mean
nth root of the N #s
two rules for similar triangles
-Altitude from right angle of right triangle is geometric mean of two segments formed by altitude
-The length of either leg of triangle is geometric mean of the hypotenuse and segment from altitude to leg
45-45-90 triangle
hypotenuse = x√2
-x = leg
-side ratio: 1:1:square root of 2
30-60-90 triangle
-1:2:to square root of 3
-side opposite 30: x
-hypotenuse: 2x
-side opposite 60: x√3
tangent ratio
tanx = opposite/adjacent (adjacent, not hypotenuse)
-for acute angles of right triangles
-tells us X and Y coordinates of a circles radius on a Cartesian plan
-0 with a slash = theta
applying tangent ratio
use DRG mode and use "tan" on calc
SOH
opposite over hypotenuse
toa
opposite over adjacent
cah
adjacent over hypotenuse
formula to find area with sin
A = 1/2absinC
a and b are sidelengths, sin C is an angle measure
Law of Sines
sinA/a=sinB/b=sinC/c or flip it
-two triangles angles are known and 1 side
-press 2nd to get inverse of sine and cosine
-ASA, SAA use law of sines
height of triangle
h=bsinA
One triangle
Angle a is acute and a=h. If angle is acute/obtuse, a > h
two triangles
if angle A is acute and h < a < b, then two triangles are created
no triangles
if Angle A is acute and a < h, if angle A is obtuse and a < b or a = b
-if it is SSA, it will be an ambiguous case
steps for using law of sines
1, check for ambiguous case
2. draw a triangle if not given
3. write a proportion based on law of sines
4. solve equation to find unknown side or angle
-use inverse after proportion when solving for an angle
Law of cosines
a²=b²+c²-2bcCosA
c²=a²+b²-2abcosC
b²=a²+c²-2acCosB
-use when SAS and SSS
Formula for the area of an acute or obtuse angle
Make a right triangle: 1/2bh
Use the other formula 1/2absin(c)
Right triangles in rectangles
Use 2 congruent triangles to make a rectangle
Diagonal of a rectangle
d= √l^2+w^2
-can use sine, cosine, and tangent ratios
-can use leg ratios
2d distance formula
d = √[( x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²]
3d distance formula
d=√(x2-x1)+(y2-y1)+(z2-z1)