Kartlar: Lipid Bilayer and Membrane Proteins | Quizlet
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
cell membranes act as
selective barriers
plasma membrane
separates cell contents from the surrounding environment; found in bacterial and eukaryotic cells
plasma membrane is involved in
cell communication, import and export of molecules, ell growth and mobility, compartmentation, and energy transduction
lipid bilayer
flexible double-layered sheet that makes up the cell membrane and forms a barrier between the cell and its surroundings
Phospholipids
most abundant in the cell membrane
diglyceride (two fatty acids linked to a glycerol)
head group is X (small, polar molecule; phosphatidyl-)
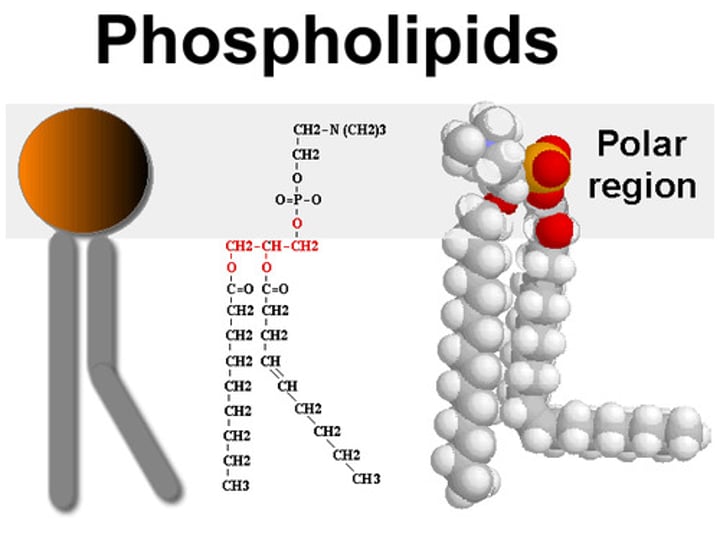
phospholipids are
amphipathic (polar head and nonpolar body)
types of membrane lipids
phospholipids, glycolipids, cholesterol
liposomes
Membrane-bound droplets that form when lipids are added to water.
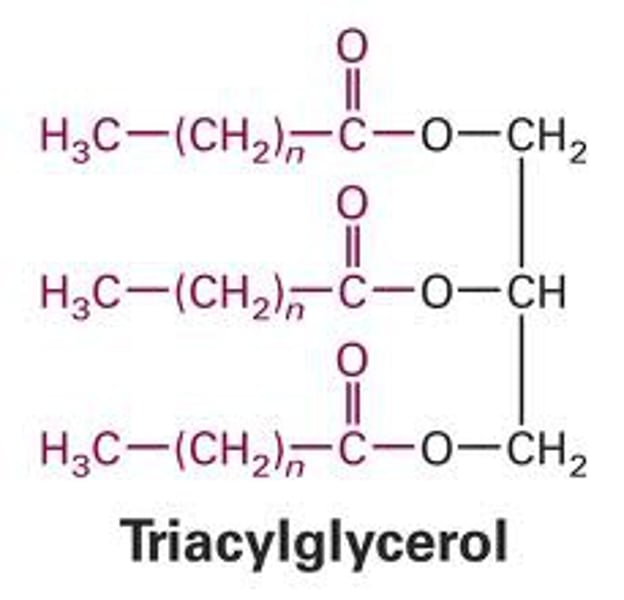
triacylglycerol
lipid consisting of three fatty acids linked to one glycerol molecule; also called a fat or triglyceride; storage lipids that are stored in lipid bodies; surrounded by monolayer
small nonpolar molecules
CO2, O2 N2, steroid hormones
Can go through the cell membrane easily,
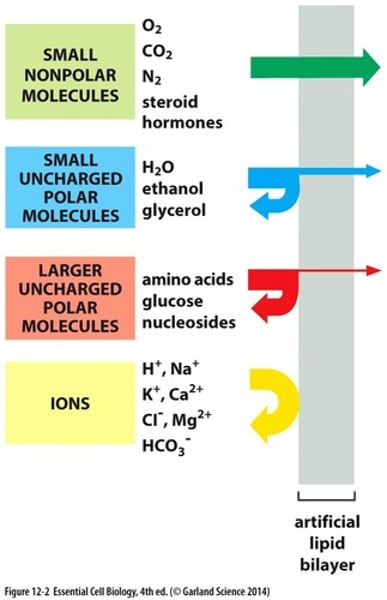
small uncharged polar molecules
H2O, glycerol, ethanol, permeable
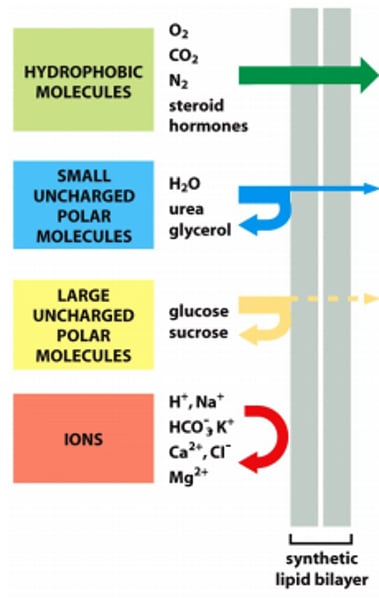
larger uncharged polar molecules
Only a tiny bit can diffuse through (amino acids, glucose, nucleosides)
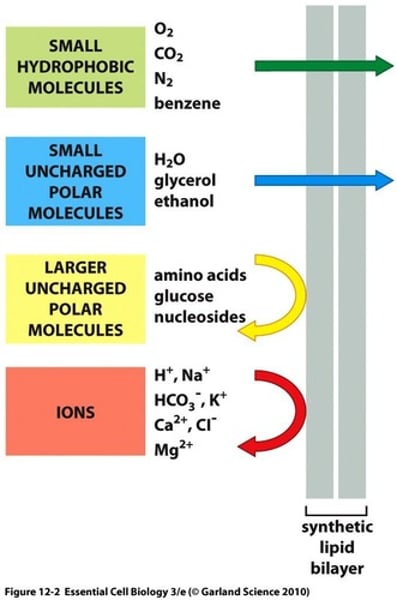
ions
cannot cross the membrane (H+, Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl-, Mg2+, HCO3-)
lipid bilayers are
highly fluid (able to move)
lateral diffusion, flexion, and rotation
occur easily
flipping sides within a bilayer is
very rare (non-spontaneous, needs help of enzymes)
factors that affect fluidity
increased temperature = increased fluidity
adding length to the chain = decreases fluidity
increase double bonds in a fatty acid chain = increases fluidity
increase cholesterol = decreases fluidity
Where does membrane assembly begin?
endoplasmic reticulum
what produces and inserts new phospholipids?
biosynthetic enzymes
Scramblase
randomly transfer phospholipids from one monolayer to the other
Flippase
in the golgi; selectively remove specific phospholipids from the noncytosolic monolayer and flip them to the cytosolic side
Where are glycolipids found?
non-cytosolic monolayer of lipid bilayer
where do glycolipids get there sugar group?
in the golgi (non-cytosolic half of the bi-layer)
membrane protein functions
Transporters and channels
Enzymes
anchors
receptors
transmembrane proteins
Integral proteins that span the membrane.
single alpha helix, multiple alpha helices and beta barrel
monolayer associated alpha helix
some membrane proteins are anchored to the cytosolic half of the lipid bilayer by an amphipathic alpha helix
Lipid-linked membrane proteins
protein covalently attached to a lipid
protein-attached membrane proteins
connected to a protein on either the EC or IC side; peripheral; non covalent
hydrophilic pore
can be formed by multiple transmembrane alpha helices
hydropathy plots
help identify possible transmembrane domains from the amino acid sequence
alpha helical transmembrane proteins
have sugars covalently attached to certain amino acid side chains out side the cell
S-S bonds outside cells
reduced SH groups in the cytosolic side
Bacteriorhodopsin
a membrane protein which functions as a light-driven proton pump
beta barrel
created when beta sheets are extensive enough to fold back on themselves; filled with water
porin proteins
proteins that form channels for the transport of small molecules across the outer membrane of gram-negative bacterial cell walls
detergents
amphipathic molecules that tend to form micelles in water (solubilize fats, oils, hydrophobic proteins)
Which detergents completely denature proteins?
Strong ionic detergents (SDS)
which detergents dissolve membranes but dont unfold proteins?
mild ionic detergents (Triton X-100)
what reinforces the plasma membrane?
cell cortex
cell cortex
Mesh of cytoskeletal elements under a plasma membrane; inside the cell
what restricts mobility of membrane proteins?
proteins can be tethered to the cell cortex or diffusion barriers can restrict proteins to a particular domain
FRAP attack
measures the rate of lateral diffusion
Glycoproteins
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to proteins.
Proteoglycans
a glycoprotein consisting of a small core protein with many carbohydrate chains attached, found in the extracellular matrix of animal cells.
Glycocalyx
carbohydrate coating on cell surface
function of cell surface carbohydrates
- Protect the cells from mechanical damage.
- Cell-cell recognition and adhesion.