Clinical Signs Cutaneous 2
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Disease and clinical signs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
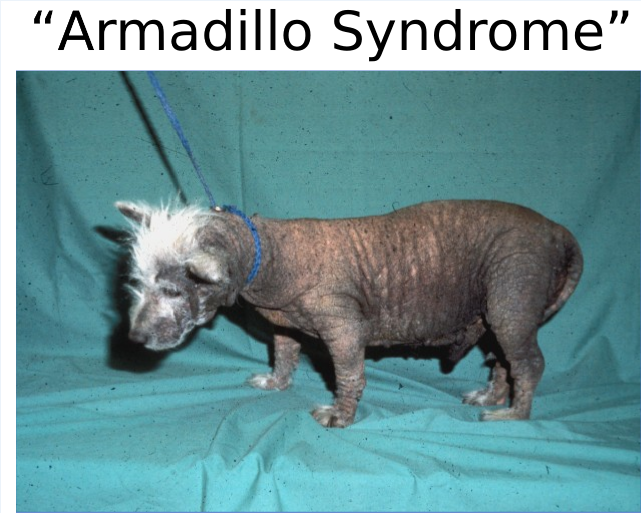
Malassezia
Pruritic, erythematous patches, moist, greasy, malodorous skin.
Hyperpigmentation, lichenification, brown staining on nails.
Commonly affects: ventral neck, interdigital region, perioral region, and chin.
Otitis externa
Frequent head shaking
Rubbing/scratching of ear
Discomfort or pain
Otic exudate and odor
Otitis Media
Facial paralysis
Horner’s syndrome
Otitis Interna
Vestibular syndrome and head tilt
Hallmark Feature Malassezia
Sudden increase in pruritus, often associated with allergies or primary skin disease.
Malodor and greasy texture
Atopic Dematitis
Pruitus, erythema, Secondary infection (pyoderma, malassezia)
Food Allergy
Non-seasonal peritus, GI signs (vomiting, diarrhea)
Environmental allergies
seasonal or non-seasonal pruritus; localized erythema
Alopecia Areata
Circumscribed alopecia without inflammation or pain
Hallmark Alopecia Areata
Spontaneous resolution, lymphatic follicle damage
Alopecia X
Symmetrical alopecia, hyperpigmentation, dull coat
Hallmark Alopecia X
Flame follicles on histopathology, hyperpigmented alopecia
Black Hair Follicular Dysplasia
Localized black hair loss, scaling
Hallmark Black Hair Follicular Dysplasia
Black hair affected, pigment clumping
Color Dilution Alopecia
Progressive alopecia, recurrent skin infections
Hallmark Color Dilution Alopecia
Diluted coat color, recurrent pyoderma
Diluted coat color, recurrent pyoderma
Symmetrical alopecia, thin skin, comedones, recurrent infections
Hallmark Diluted coat color, recurrent pyoderma
Thin skin, calcinosis cutis, recurrent pyoderma
Hypothyroidism
Hallmark Hypothyroidism
Post-Clipping Alopecia
Delayed or patchy regrowth after shaving
Hallmark Post-Clipped Alopcia
Telogen hair follicles, delayed regrowth
Seasonal/Cyclical Flank Alopecia
Symmetrical flank alopecia, seasonal regrowth
Hallmark Seasonal/Cyclical Flank Alopecia
Seasonal pattern, polycyclic lesions, spontaneous regrowth
Sebaceous Adenitis
Alopecia, scaling, follicular casts, oily coat
Hallmark Sebaceous Adenitis
Sebaceous gland loss, follicular casts
Cutaneous Vasculitis
Petechiae, ecchymoses, erythematous/purplish skin, crateriform ulcers, skin sloughing, pain, pitting edema, cyanosis, panniculitis.
Hallmark Cutaneous Vasculitis
Non-blanching petechiae/ecchymoses, leukocytoclastic vasculitis on histopathology ("nuclear dust").
Vaccine-Induced Vasculitis
Alopecia and hyperpigmentation at the vaccine site, appearing weeks to months post-vaccination. Lesions may remain static, resolve, or spread.
Hallmark Vaccine-Induced Vasculitis
Focal alopecia and hyperpigmentation at vaccine sites.
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE)
Depigmentation, erythema, ulcerations, crusting, and loss of nasal cobblestone architecture.
Hallmark Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE)
Photo-induced depigmentation and nasal planum changes with absence of systemic signs.
Pemphigus Foliaceus
Pustules, erosions, crusting, alopecia, and scales; primarily affects face, ears, footpads; may become generalized.
Hallmark Pemphigus Foliaceus
Subcorneal pustules with acantholytic cells; wave-like eruptions of pustules.
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Vesicles, bullae, ulcers, and angular erosions; oral mucosa affected in >90% of cases; painful lesions.
Hallmark Pemphigus Vulgaris
Severe mucosal involvement, particularly oral; vesicle and ulcer formations.
Erythema Multiforme (EM)
Occurs due to drugs, infections, or neoplasia; idiopathic in some cases; seen in various species.
Hallmark Erythema Multiforme (EM)
Erythematous macules, target lesions, plaques, vesicles, and mucosal involvement; systemic signs like fever.
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
Widespread epidermal sloughing, painful ulcers, systemic illness, and potential life-threatening complications.
Hallmark Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
Massive epidermal sloughing resembling burns; rapid onset.
Lipoma
Common in older dogs.
Rarely cause clinical issues.
Found in areas of high mobility (axillary, inguinal regions).
Hallmark Lipoma
Benign with a well-defined, soft mass.
Intermuscular Lipoma
Located between muscle bellies (e.g., semimembranosus/semitendinosus).
May feel firm due to overlying muscle stretching.
Can cause limb discomfort.
Hallmark Intermuscular Lipoma
Firm mass in deeper soft tissues; prone to seroma formation after excision.
Infiltrative Lipoma
Locally aggressive; may infiltrate muscle or fascia.
Prone to recurrence.
Hallmark Infiltrative Lipoma
Does not metastasize but invades surrounding structures.
Soft Tissue Sarcoma (STS)
Solitary, slow-growing masses that may become large.
Frequently adhered to underlying tissues.
Overlying skin may be taut, ulcerated, or necrotic.
Hallmark Soft Tissue Sarcoma (STS)
Highly locally invasive, appearing pseudoencapsulated but infiltrating deeply.
Non-STS Sarcomas
Includes hemangiosarcoma, lymphangiosarcoma, osteosarcoma, etc.
Varies in behavior (metastatic or locally invasive).
Hallmark Non-STS Sarcomas
Behavior depends on subtype, but often aggressive.
Feline Injection Site Sarcoma (FISS)
Develops 3 months to 3 years after injection.
Firm mass, adherent to underlying tissues.
Overlying skin may be ulcerated.
Hallmark Feline Injection Site Sarcoma (FISS)
Highly locally invasive; requires WIDE surgical margins (5 cm laterally, 2 fascial planes deep).
Staphylococcus spp.(deep pyoderma)
Deep Pyoderma
Painful nodules and draining tracts.
Plaques and furuncles (nodules that rupture to form draining tracts).
Localized swelling with potential lymphadenopathy.
Lameness may occur if affecting paws (e.g., interdigital furunculosis).
Secondary systemic signs (fever, lethargy) in severe cases.Rupture of hair follicles leading to pyogranulomatous inflammation (furunculosis).
Draining tracts and chronic non-healing wounds.
Hallmark Deep Pyoderma
Rupture of hair follicles leading to pyogranulomatous inflammation (furunculosis).
Draining tracts and chronic non-healing wounds.
Blastomycosis
Nodules with draining tracts.
Pulmonary signs (cough, dyspnea).
Ocular and bone lesions in systemic disease.
Cutaneous lesions may be localized or systemic.
Hallmark Blastomycosis
Broad-budding yeast with thick cell walls on cytology or histopathology.
Sporotrichosis
Ulcerative nodules, commonly on head and extremities.
Dissemination common in cats (fever, systemic involvement).
Localized lesions in dogs and horses.
Hallmark Sporotrichosis
Thin-capsuled yeast in tissue or cytology.
High organism burden in cats, increasing zoonotic risk.
Cryptococcosis
Swelling and nodules on the face and nose (nasal form in cats).
Multifocal cutaneous nodules.
Systemic signs (neurological or respiratory involvement).
Hallmark Cryptococcosis
Thick-capsuled, narrow-budding yeast seen on histopathology.
Latex agglutination test for diagnosis.
Atypical Mycobacterium Infection
Non-healing wounds with draining tracts.
Firm nodules or pockets containing purulent material.
Common in obese cats and those with puncture wounds.Fast-growing organism requiring specific culture techniques
Hallmark Atypical Mycobacterium Infection
Fast-growing organism requiring specific culture techniques
Sterile Nodular Panniculitis
Deep-seated nodules extending into the subcutaneous fat.
Ulceration with greasy or milky exudate.
Systemic signs: fever, lethargy, inappetence.
Hallmark Sterile Nodular Panniculitis
Pyogranulomatous panniculitis with no infectious agents found.
Diagnosis requires exclusion of infectious causes via macerated tissue culture.
Hallmark Reactive Histiocytosis
Proliferation of histiocytes associated with immune dysregulation.
Reactive Histiocytosis
Multiple firm, non-ulcerated nodules.
May involve mucosal surfaces in severe cases.
Non-painful and typically non-pruritic.
Plasma Cell Pododermatitis
Soft, swollen, ulcerative nodules on paw pads.
Discomfort and secondary infection common.Plasma cell infiltration of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue.
Hallmark Plasma Cell Pododermatitis
Plasma cell infiltration of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue.
Interdigital Furunculosis (Misnomer: Interdigital Cysts)
Nodules between the toes, often rupturing to drain purulent material.
Swelling and pain leading to lameness.
Hallmark Interdigital Furunculosis (Misnomer: Interdigital Cysts)
Pyogranulomatous furunculosis due to ruptured hair follicles.
Frequently associated with comedones on the palmar/plantar surfaces.
Neoplastic Nodules
Single or multiple firm nodules, often progressively enlarging.
Systemic signs depending on malignancy and metastasis.
Hallmark Neoplastic Nodules
Single or multiple firm nodules, often progressively enlarging.
Systemic signs depending on malignancy and metastasis.
Sarcoids
Occult, Verrucous, Nodular, Fibroblastic, Mixed, Malevolent
Occult Sarcoid
Flat areas of alopecia with scaling.
Mild and often unnoticed.
Sarcoid Verrucous
Wart-like lesions with raised, lichenified surfaces.
Rough texture.
Nodular Sarcoid
Firm, well-defined subcutaneous masses.
Can remain stable for extended periods.
Fibroblastic Sarcoids
Ulcerated, fleshy, and infiltrative masses.
Rapid growth and bleeding may occur.
Mixed Sarcoids
Combination of the above types in one lesion.
Varied presentation.
Malevolent Sarcoids
Aggressive and spreads along fascial planes.
Often painful with significant local tissue damage.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Non-healing ulcerated areas or proliferative growths.
Bleeding, crusting, or discharge may be present.
Lesions are often found in unpigmented areas, including:
Periorbital region (around the eyes).
Penis and prepuce.
Anus and perineum.
Muzzle.
Secondary infection can exacerbate signs.
Discomfort or irritation at the site may occur.
Melanomas
Black, round, firm masses, often smooth in texture.
Enlargement and coalescence of masses over time.
Common locations:
Ventral tail.
Anus and perineum.
Muzzle.
Parotid salivary gland.
Prepuce.
Usually painless and slow-growing.
Advanced or malignant melanomas may cause:
Obstruction of adjacent structures (e.g., anal opening).
Secondary infections or discomfort.
Insect Hypersensitivity
Pruritus, alopecia, excoriations, seasonal pattern.
Atopic Dermatitis EQ
Pruritus, urticaria, alopecia, secondary infections.
Food Hypersensitivity EQ
Pruritus, urticaria, alopecia, +/- secondary infections.
Alopecia Areata
Well-circumscribed alopecia without inflammation.
Dermatophytosis
Crusted alopecic lesions with sharp borders, ring lesions.
Dermatophilosis
Painful crusted lesions with underlying erythema.
Pemphigus Foliaceus
Fragile pustules, crusts, systemic signs (e.g., fever).
Eosinophilic Granuloma
Nodular lesions, occasional abscesses.
Habronemiasis
Granulomas on skin or wounds, pruritus.
Pythiosis
Large ulcerative granulomas with necrotic debris.
Pastern Dermatitis
Scaling, crusting, or moist lesions; lower legs often affected.
HERDA (Hereditary Equine Regional Dermal Asthenia):
Hyperextensible skin prone to tearing and scarring.