CHM 256 Final
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
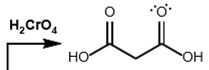
aldehyde + H2CrO4
oxidized into carboxylic acid and carbonyl
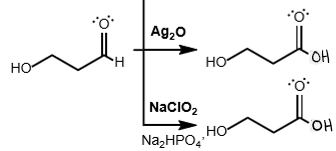
aldehyde + Ag2O (OR) NaClO2
oxidized into carboxylic acid
ketone tautomers
keto tautomerized into enol
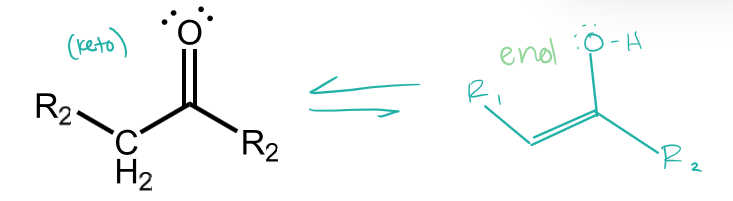
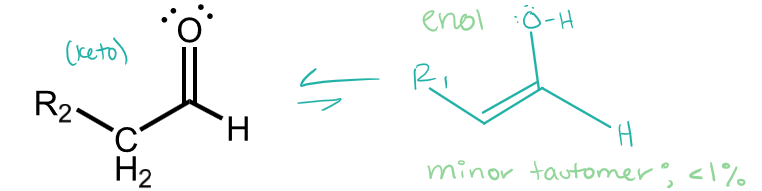
aldehyde tautomers
keto (major) and enol (minor)
ketones are more acidic than alkanes because
enolates are resonance-stabilized
carbonyl has strong inductive effect
enols are electronically similar to alcohols
enolates formed by strong bases (LDA, NaH)
reaction is irreversible
enolates formed by weaker bases (NaOR, NaOH)
reaction is reversible
enolate + D2O →
addition
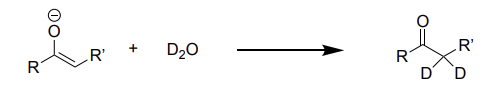
enolate + Br2 →
halogenation
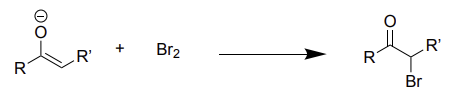
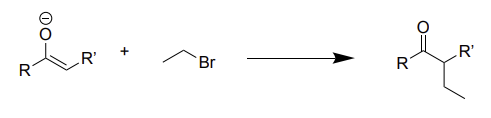
enolate + alkane →
alkylation
enolate + aldol → (WU)
aldol addition

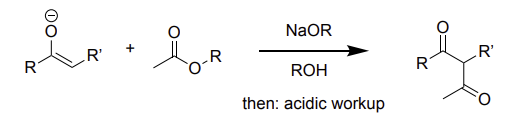
enolate + ester → (NaOR & ROH, then acidic WU)
Claisen condensation
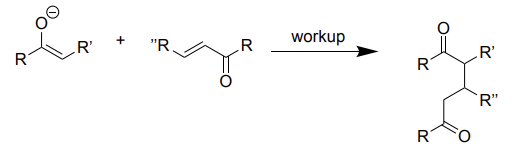
enolate + 1,4 carbonyl alkene → (WU)
phenol + K2Cr2O7 & H2SO4 →
para quinone
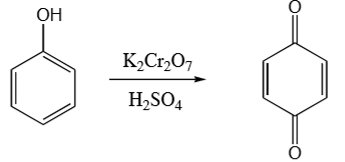
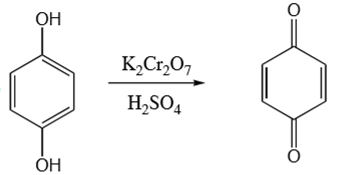
para position phenol + K2Cr2O7 & H2SO4 →
para quinone
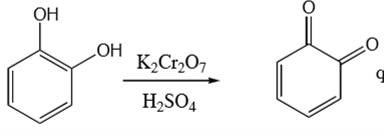
ortho position phenol + K2Cr2O7 & H2SO4 →
ortho quinone
reducing quinones back to phenols
Na2S2O4 & H2O
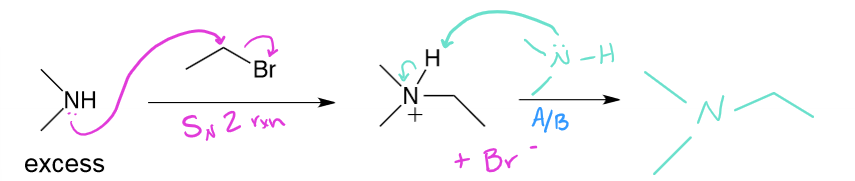
excess amine + alkyl halide →
SN2 rxn, then A/B rxn → 2° aliphatic to 3° aliphatic
halide + sodium azide (NaN3) → 1. LiAlH4 2. H2O →
reduced to primary amine
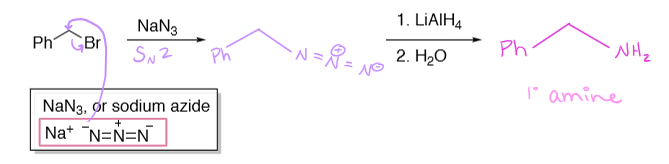
molecules with 4n + 2 pi electrons are
aromatic
molecules with 4n pi electrons are
antiaromatic
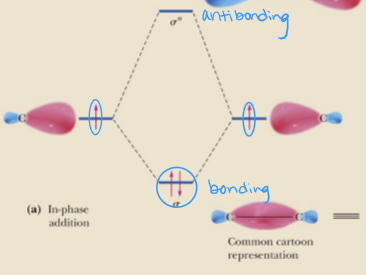
molecular orbitals at lower energy than atomic orbitals are called
bonding
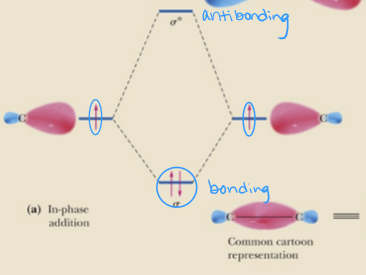
molecular orbitals at higher energy than atomic orbitals are called
antibonding
molecular orbitals at equal energy than atomic orbitals are called
nonbonding
coenzyme Q
carrier of electrons in oxidative phosphorylation, anchored to the mitochondrial membrane
menadione
synthetic Vitamin K replacement
alkane pKa
~50
Ester pKa
23-25
Ketone pKa
20-22
Aldehyde pKa
17-19
Alcohol pKa
16-17
HDA (from LDA) pKa
35
water pKa
15.7
malonate pKa
13
Strong base and large molecule
LDA
Strong base but small molecule
NaH
Weaker base
NaOH or NaOR