MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BONES
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Functions of the skeletal system
Support, protection, assistance in movement, mineral homeostasis, haematopoiesis, triglyceride storage
Skeletal system: support
Structural framework for the body by supporting soft tissues and providing attachment points for tendons
Skeletal system: protection
Protects the most important internal organs from injury
Skeletal system: Assistance in movement
Skeletal muscles attach to bones, pulling on them during contraction to produce movement
Skeletal system: Mineral homeostasis
Stores several minerals especially Ca and P which contribute to bone strength. 99% of calcium here and can release and distribute minerals to maintain mineral balance
Skeletal system: Haemopoiesis
Red bone marrow creates RBC, WBC, and platelets. It consists of developing blood cells, adipocytes, fibroblasts, and macrophages within a network of reticular fibres. Found in developing bones of the foetus and axial bones of adults
Skeletal system: Triglyceride storage
Yellow bone marrow consists mainly of adipose cells and act as a chemical energy reserve. Found in appendicular bones of adults
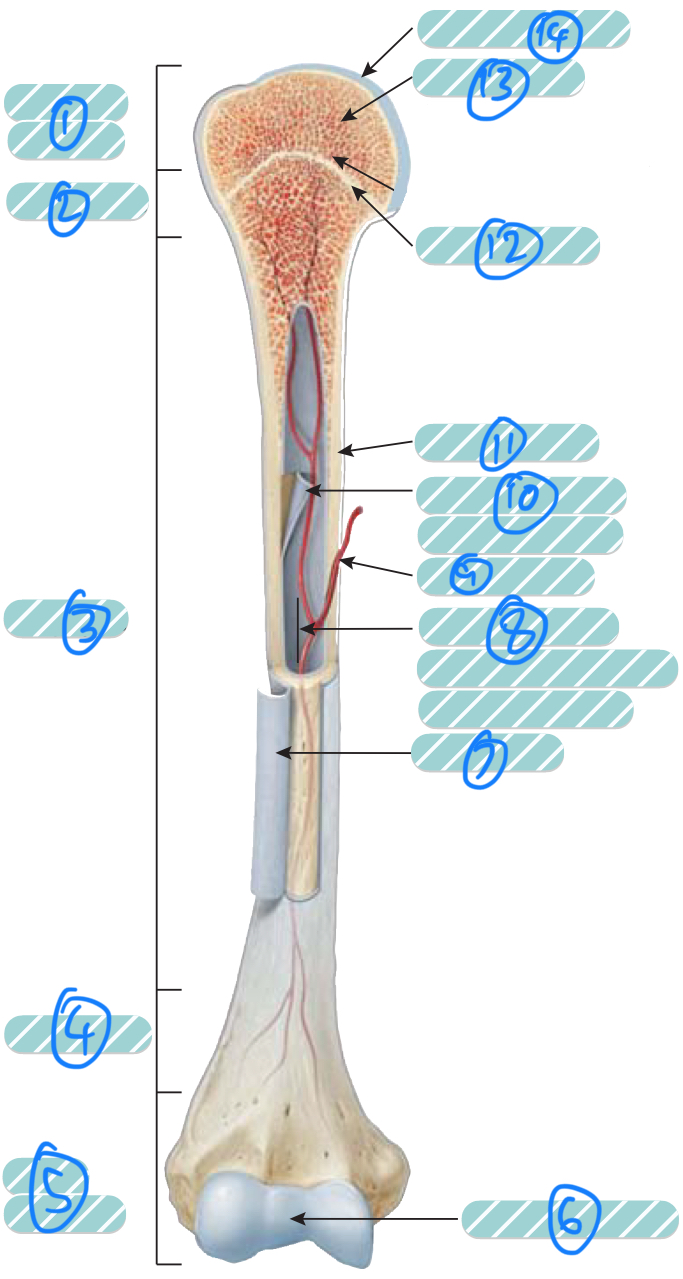
What is the label 1?
Proximal epiphysis. As it is closer to the axial skeleton, it is more likely to contain red bone marrow
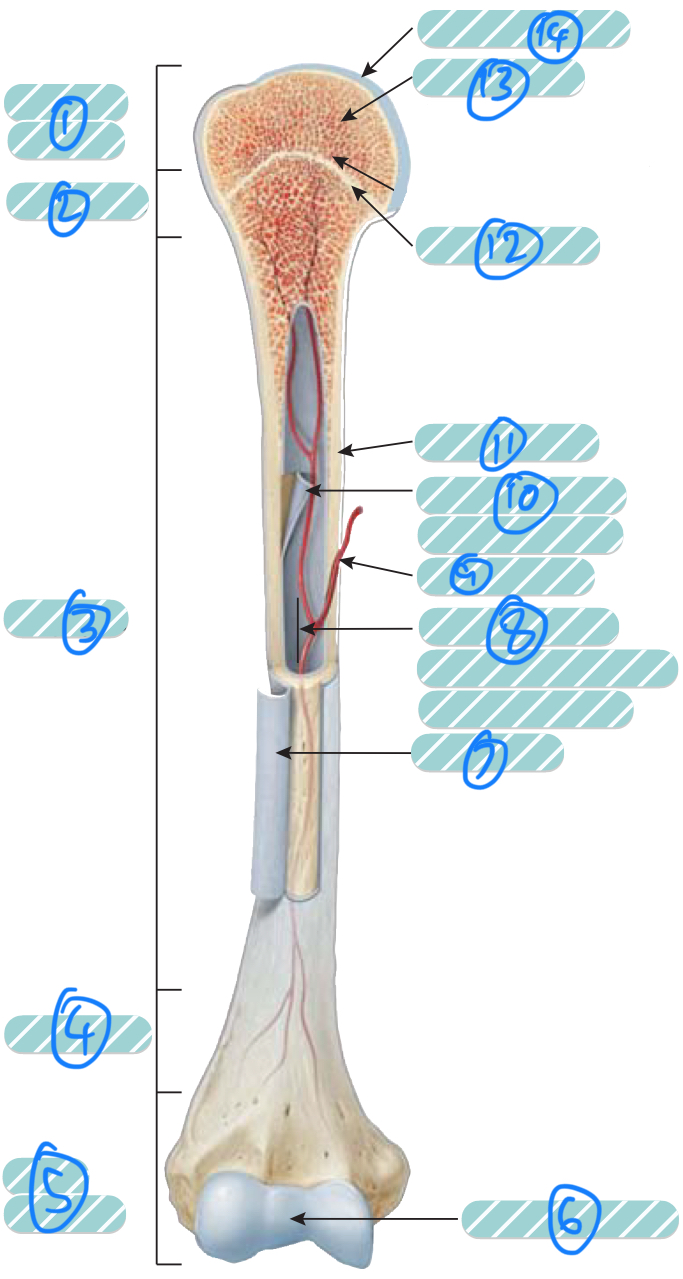
What is the label 2 and 4?
Metaphysis which transitions the epiphysis into the diaphysis and vice versa
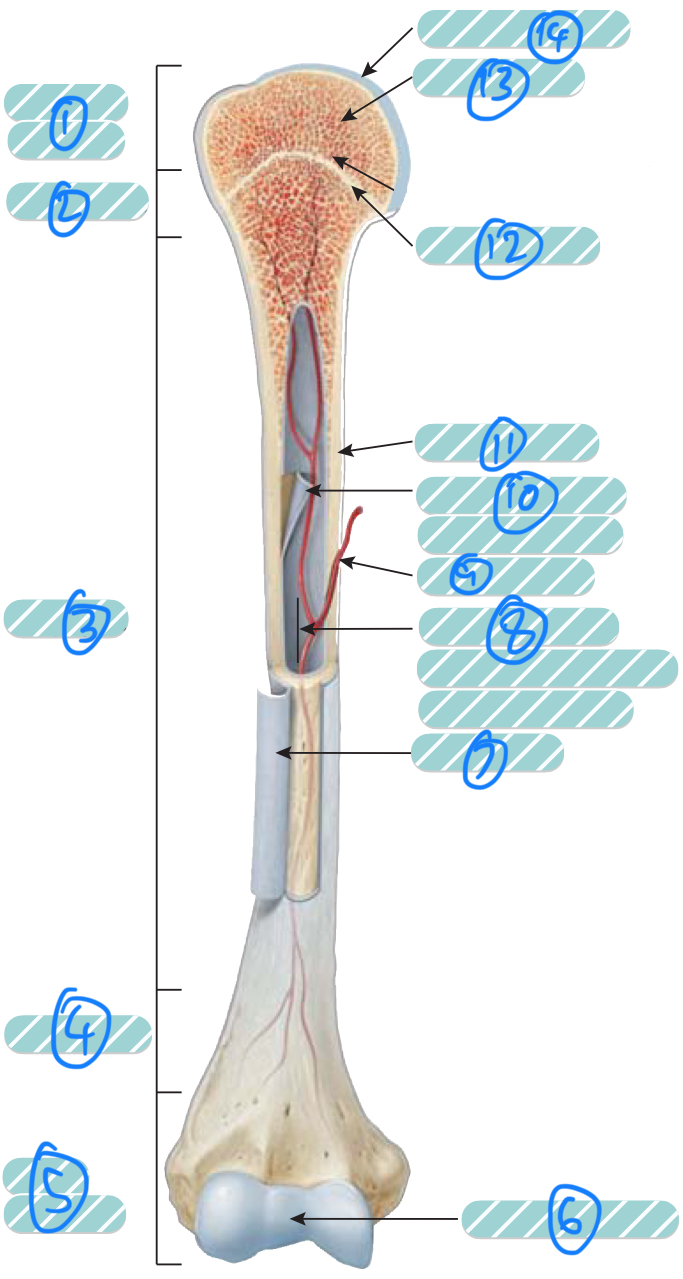
What is the label 3?
Diaphysis
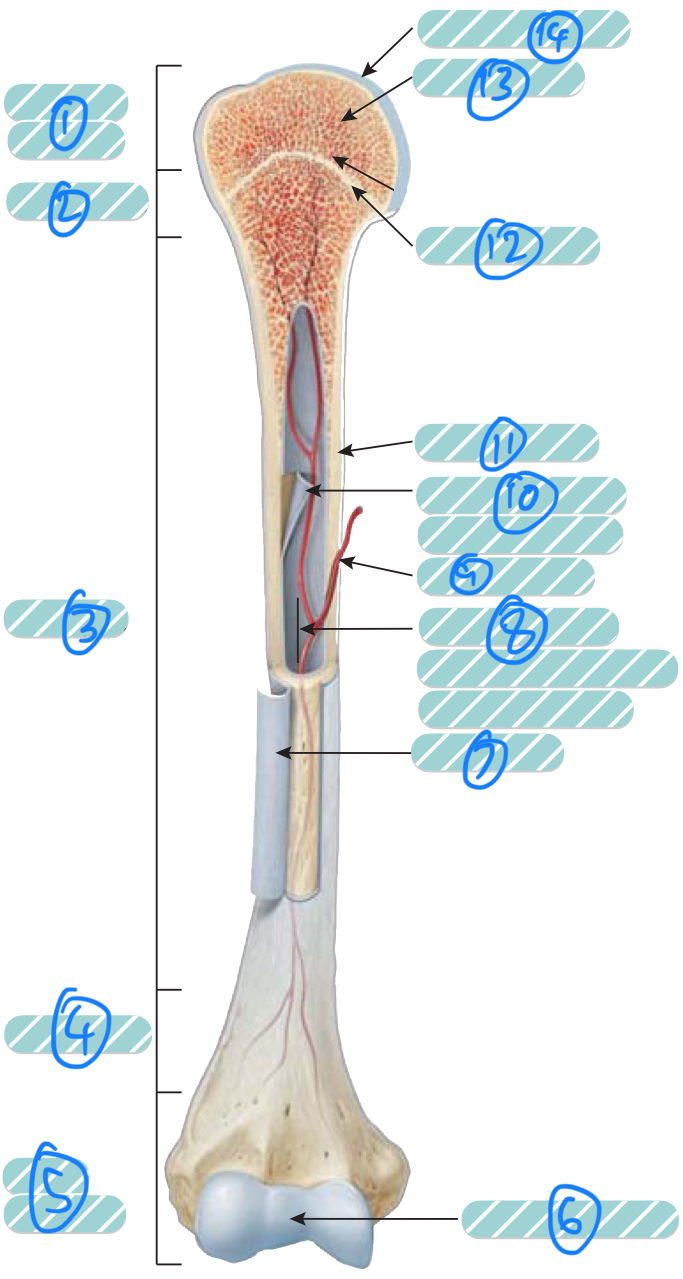
What is the label 5?
Distal epiphysis. As it is farther from the axial skeleton, it is more likely to contain yellow bone marrow
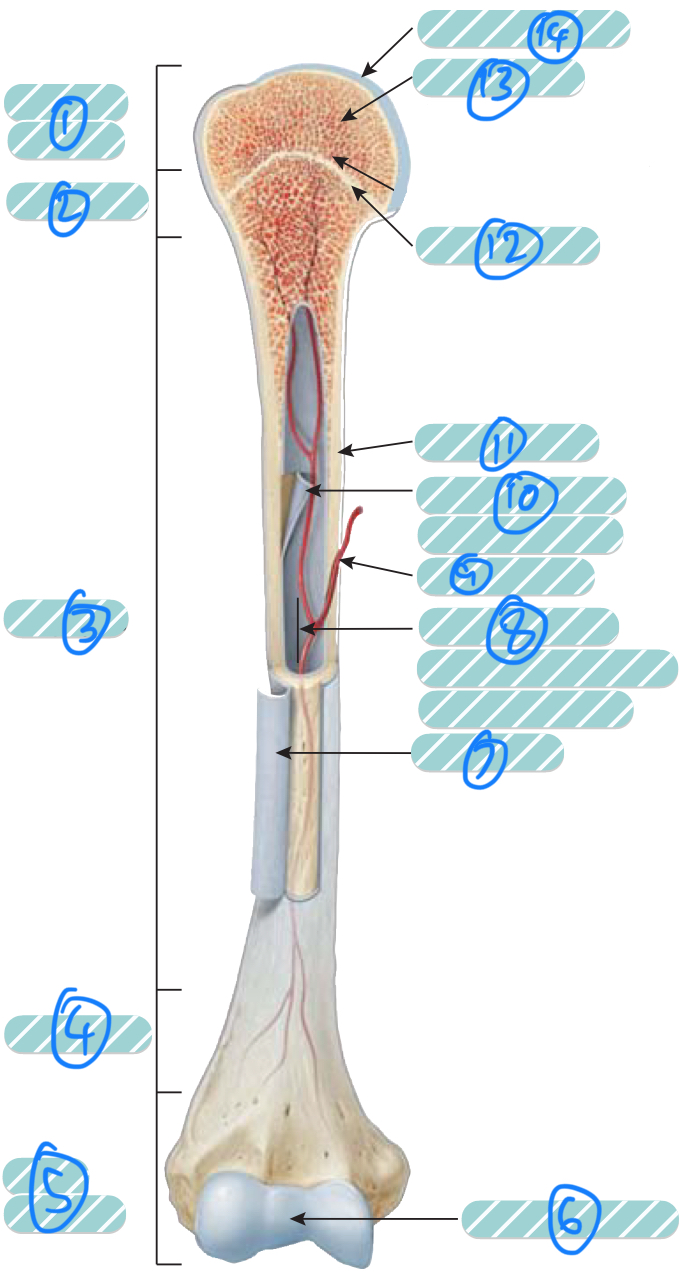
What is label 6 and 14?
Articular cartilage. Thin layer of hyaline cartilage at the articulation of a bone with another bone to reduce friction and absorb shock. It lacks a perichondrium and blood vessels so repair is limited
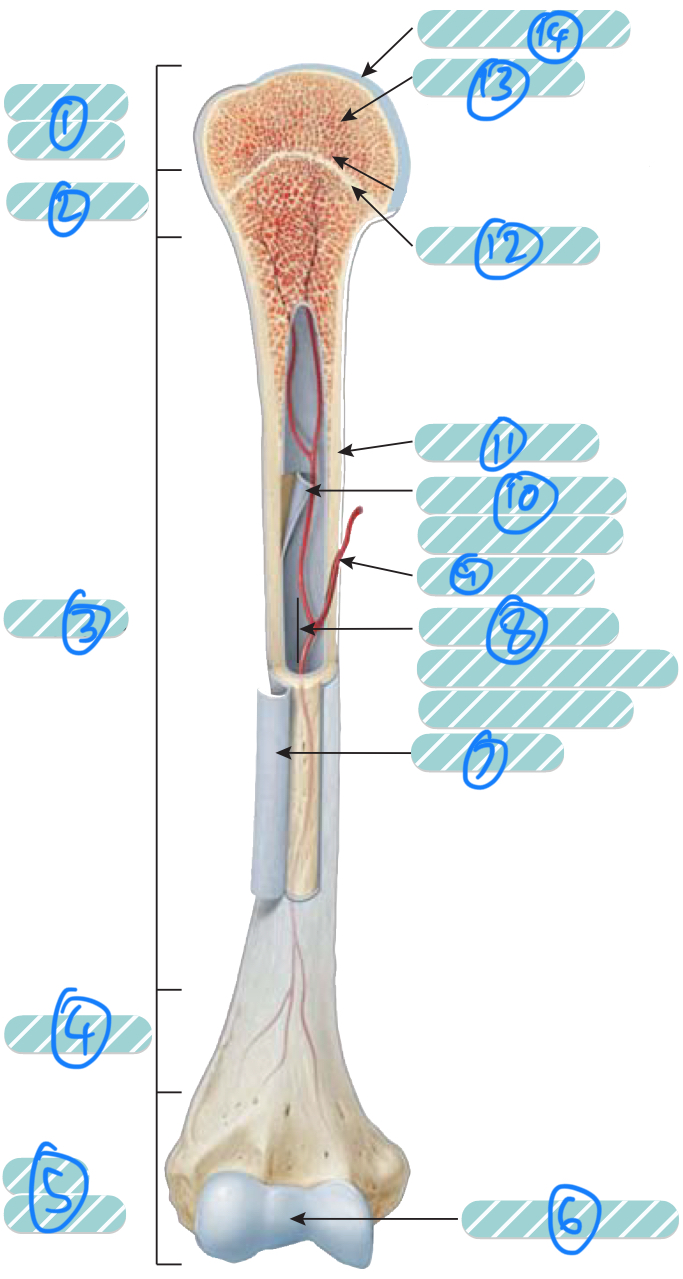
What is label 7?
Periosteum. Outer layer of bone that supplies the inner bone with blood vessels and nerves and has an outer fibrous layer and an inner osteogenic layer. It protects the bone, assists in fracture repair, nourish bone tissue, and serves as an attachment point for ligaments and tendons. Attached to underlying bone by perforating fibres
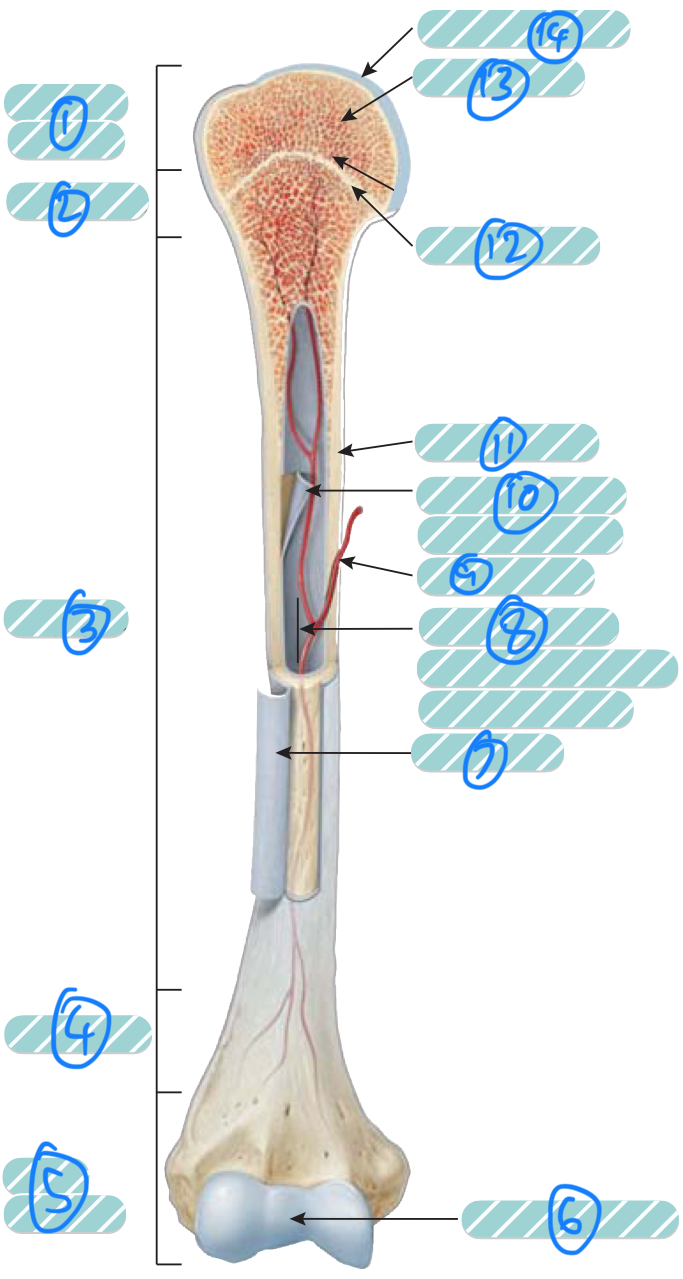
What is label 8?
Medullary cavity. Contains either red or yellow bone marrow depending on the bone is axial or appendicular. It minimises weight of the bone by reducing density

What is label 9?
Nutrient artery
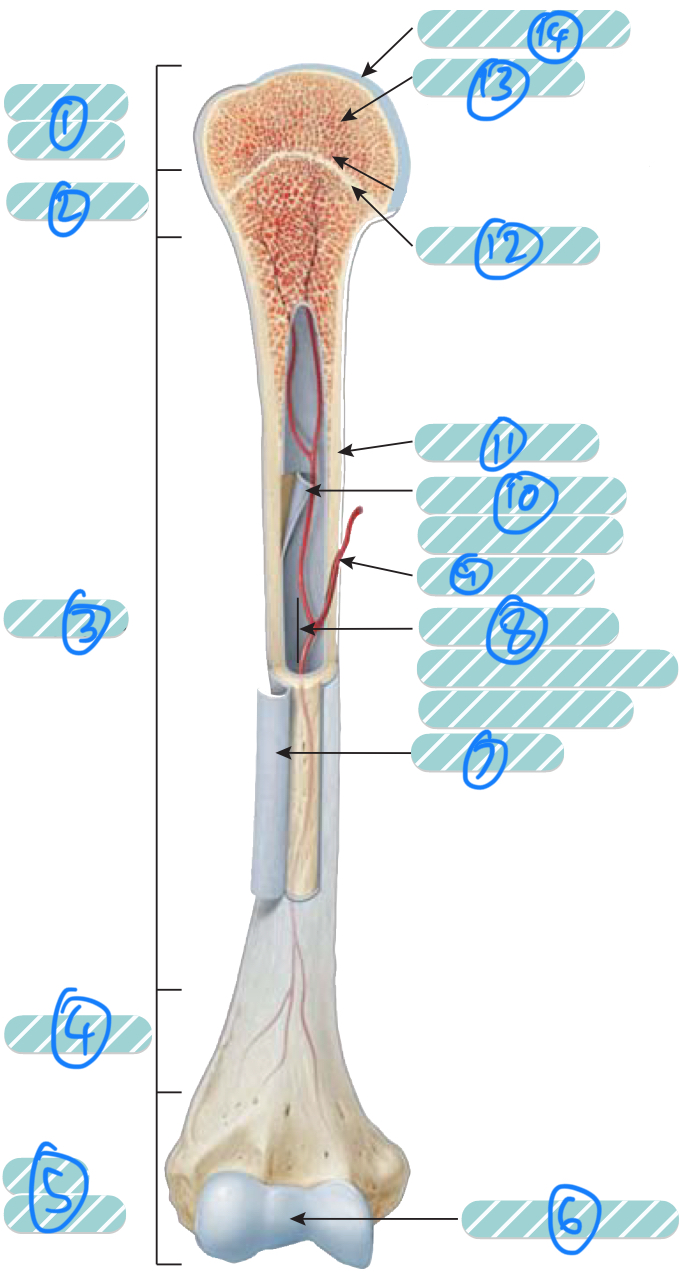
What is label 10?
Endosteum. A thin membrane that lines the medullary cavity and contains a single later of bone-forming cells and a small amount of connective tissue
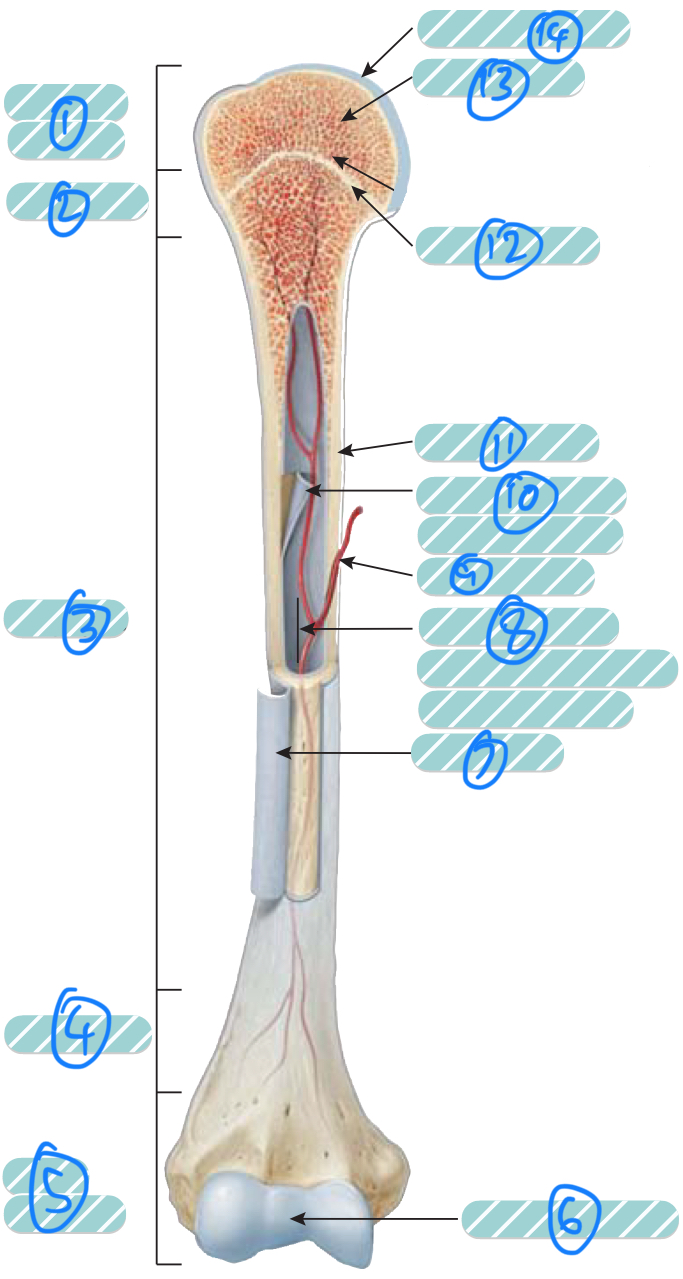
What is label 11?
Compact bone
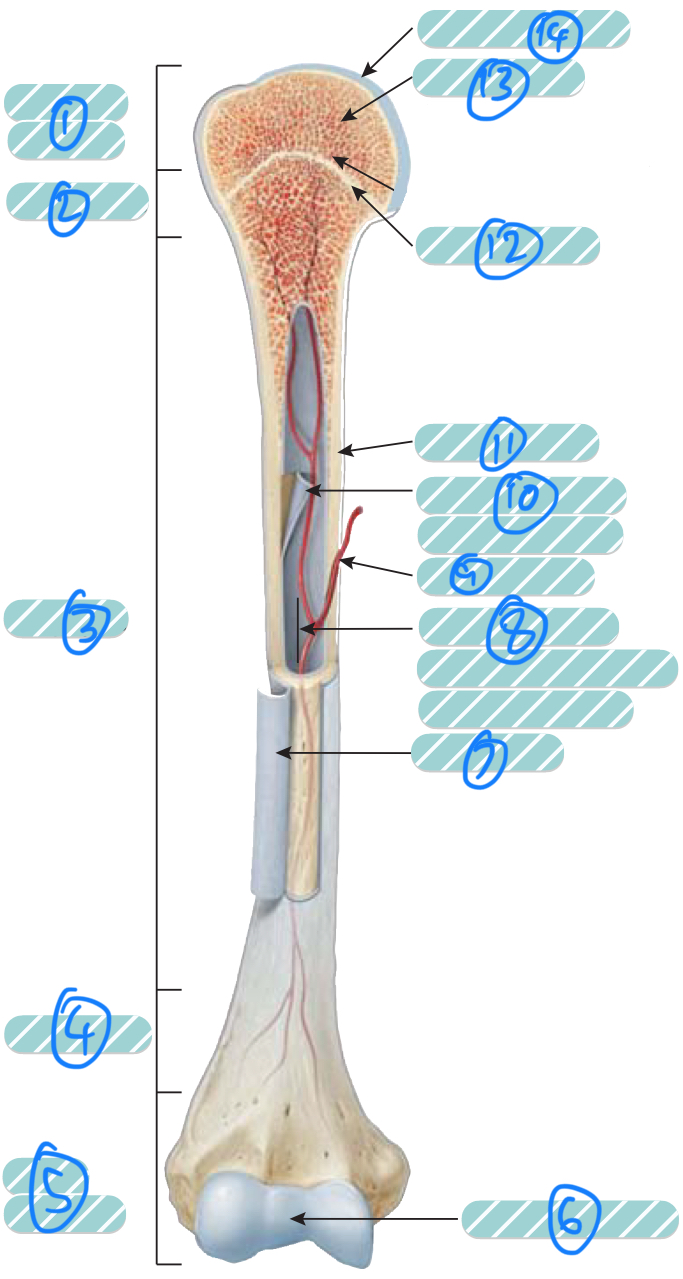
What is label 12?
Epiphyseal line. Bone that replaces the cartilage in the epiphyseal plate
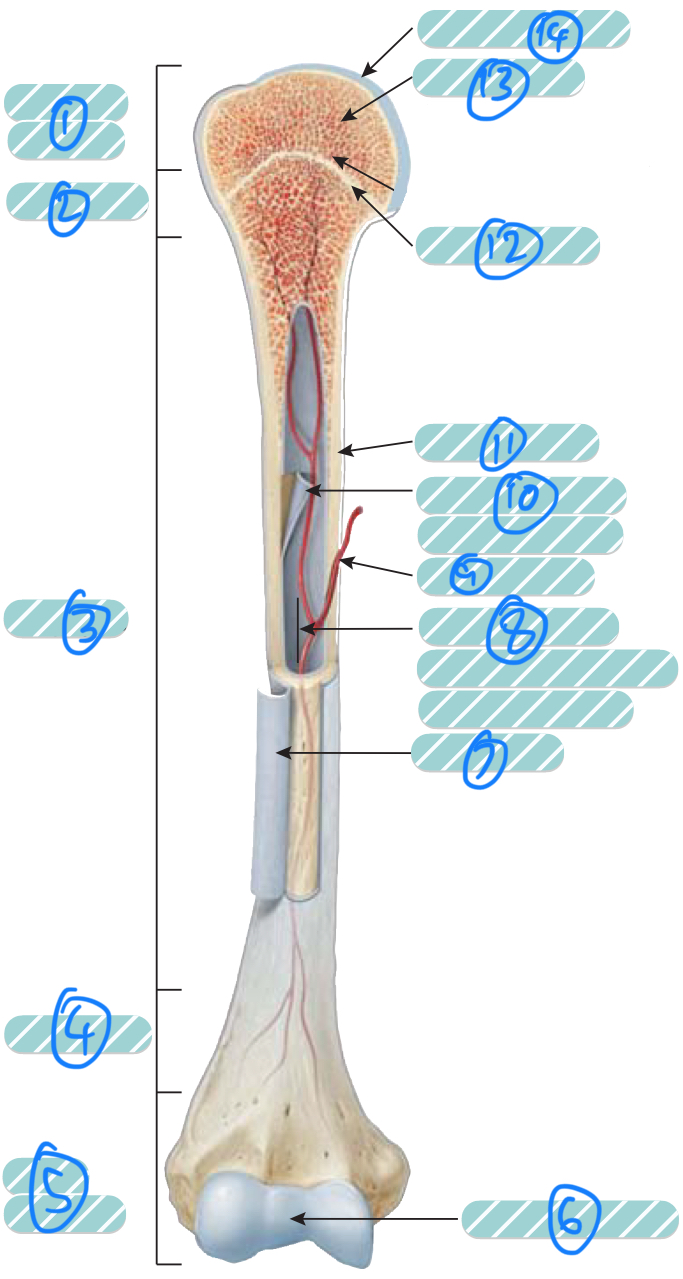
What is label 13?
Spongy bone
Epiphyseal plate
A layer of hyaline cartilage that allows the diaphysis of the bone to grow in length (ages 14 - 24)
Perforating fibres
Sharpey’s fibres. Thick bundles of collagen that extend from the periosteum into the bone ECM
Calcification
The formation and crystallisation of hydroxyapatite (calcium phosphate + calcium hydroxide) and combining with other mineral salts (calcium carbonate, ions such as magnesium, fluoride, potassium, and sulphate). It is deposited in the required collagen fibre framework of ECM and hardens
Osteogenic/Osteoprogenitor cells
Unspecialised bone stem cells that come from mesenchyme. They undergo cell division which results in osteoblasts. Found along the inner portions of the periosteum, in the endosteum, and canals