BIOL 300 Discussion Mobile Genetic Elements
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Are transposons found in prokaryotes or in eukaryotes?
Both; first found in bacteria
What are several possible mutations caused by transposons?
Gene distruption when inserted in an important gene
Can transposons infect other hosts other than a host in which they are found?
No
Can transposons make copies of themselves?
Yes
Can transposons move from one location to another within the same genome?
Yes
What is the difference between a retrovirus and other DNA or RNA viruses?
Retroviruses have reverse transcriptase and includes RNA/DNA in its life cycle
Why is the DNA stage necessary in the retrovirus life cycle?
In order to integrate itself into host
What is a difference between (+) and (-) strand of viral RNA?
Message is (+) while template is (-)
What serves as a primer for RTase during retroviral infection?
tRNA
What enzyme is required for the integration of a dsDNA retroviral genome into the host genome?
Integrase
What is an additional gene that could be carried by a retrovirus?
Genes to transform a normal cell to a cancer cell
Why can genes in a viral geneome quickly become mutated?
They go through transcription which does not have proof reading activity
When a retrovirus integrates into DNA, does it generate extra direct repeats just as transposons do?
Yes
What are the activities of RTase?
RNA (+) and DNA (-), RNA/DNA to dsDNA, and degradation of RNA (RNase H')
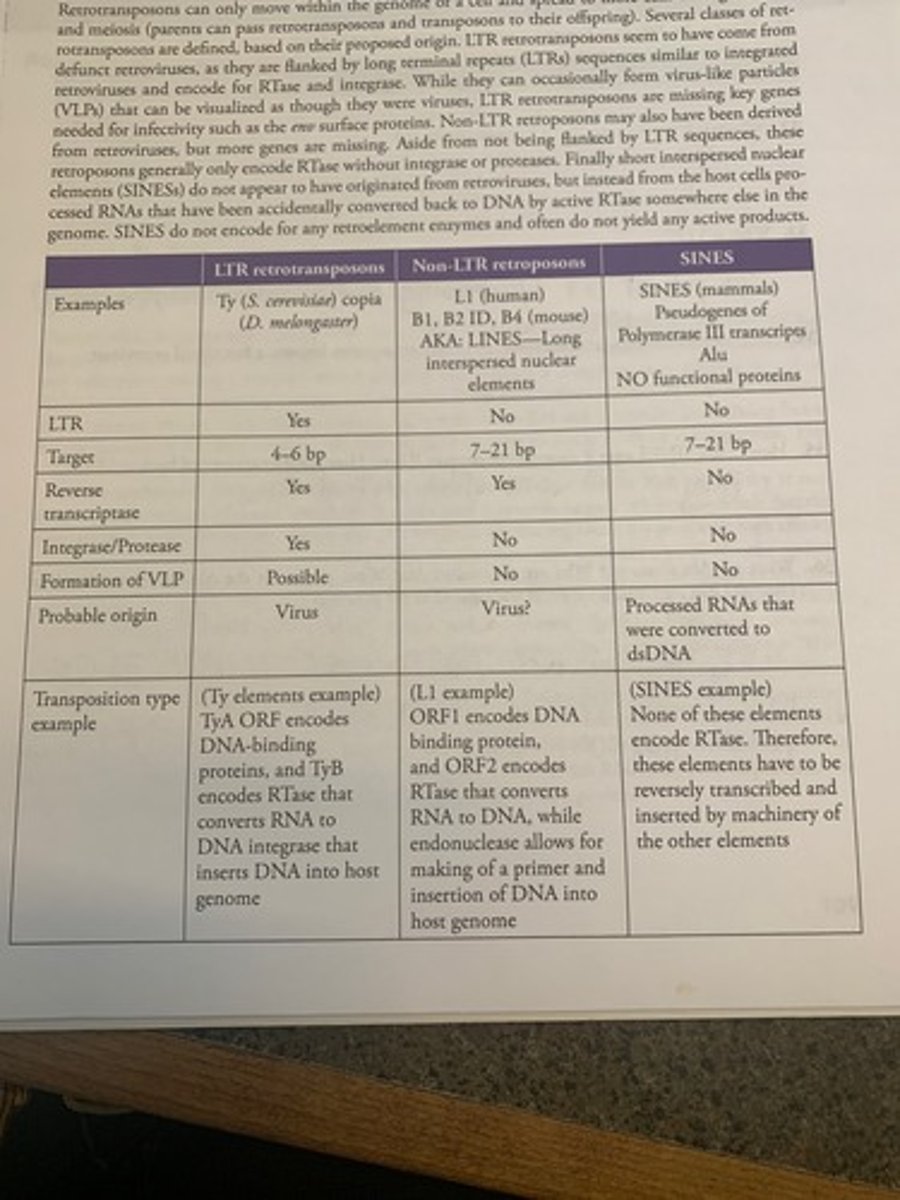
What are retrotransposons?
Genetic elements that can amplify themselves using RNA intermediate
What is the difference between a retrotransposon and retrovirus?
A retrotransposon cannot move from cell to cell or organism to organism
Where is RTase encoded in LTR retrotransposons?
Coded in retrotransposon
What is VPL?
virus like particle
it looks like a retrovirus but it cannot get out of cell b/c missing Env, protein for packaging and infection
If supplemented with extra enzymes, can a retrotransposon become a functional retrovirus?
Yes
How could SINES arise if they do not contain RTase? How are they converted back to DNA?
They need some sort of RTase
What are Alu elements? Why are they called Alu? What RNA are the Alu elements related to? How did Alu elements become so widespread in the genome?
SINES most well known b/c it contains restiction sites for Alu restiction enzyme.
75rRNA
75 have been reverse transcribed to DNA by some reverse transcriptase
What are some strategies that an organism uses to deal with transposons?
Silencing
1) Act on DNA directly by methylation of DNA (prevents transcription)
2) RNA interface
Are sequences for new transposition insertion random?
Not always, target sites can be chosen
can be a consensus sequence, or DNA structure
Are transposable elements common in many organisms?
Yes
Why are composite transposons called "composite?"
They contain other genes besides just transposons and flanked by IS
In most cases what proteins are responsible for choosing the target sequence for a transposon?
Transposase
Where is the gene for transposase located?
Within the transposon
What does it mean to be "autonomous?"
Contains genes for transcription
Can transposons exist in genomic DNA and plasmids?
yes
Can one organism have more than one type of transposon?
Yes
How are the ends of IS elements different from the target sequence?
Target sequences are direct repeats while IS terminal repeats are inverted
What is the differece between transposons and defective elements?
Transposons code for transposase
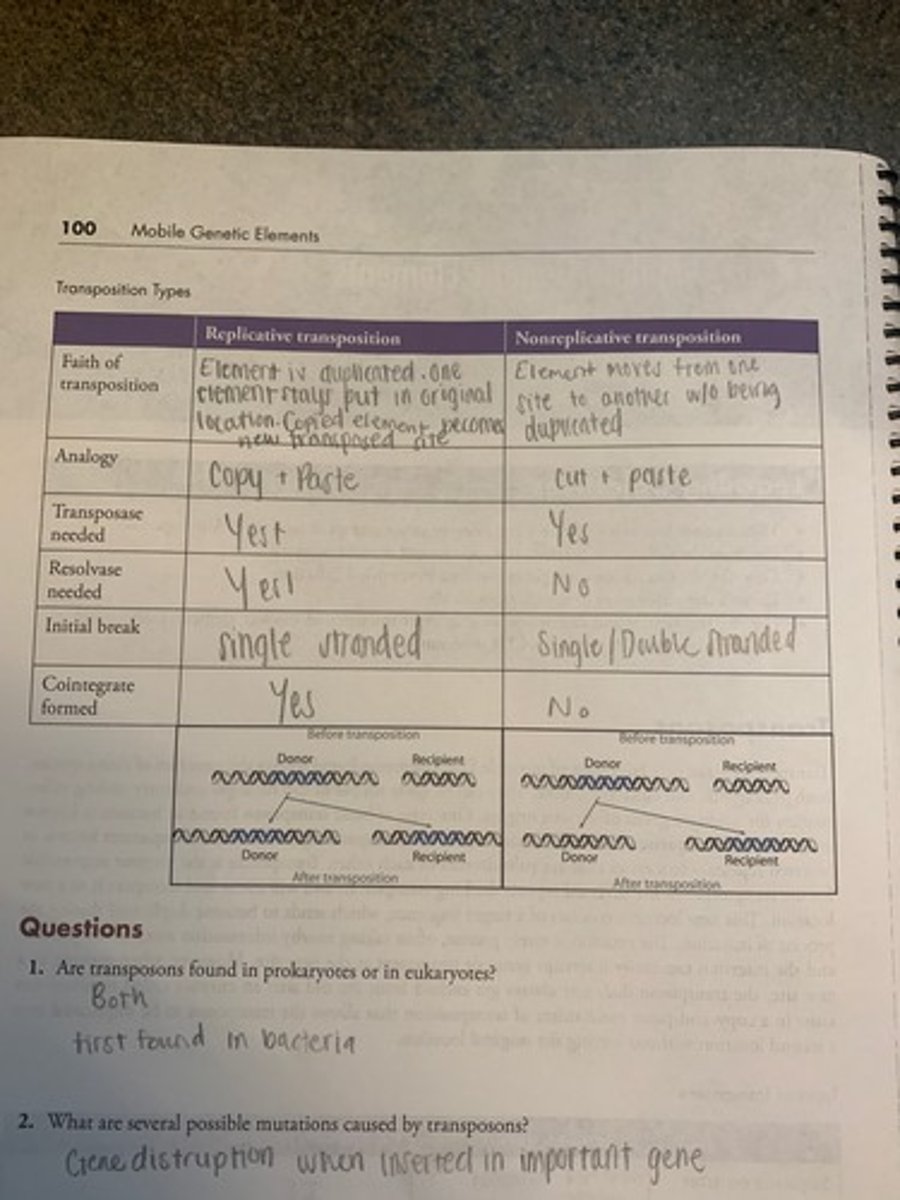
What is the result of the target sequence after transposistion?
Duplicated
Why is resolvase needed in replicative transposition?
Cointegrate is formed and nedds to be resolved
When a transposon is removed from one location and transposed to another, is the "cutting out" precise?
Not always, only a rare occurence
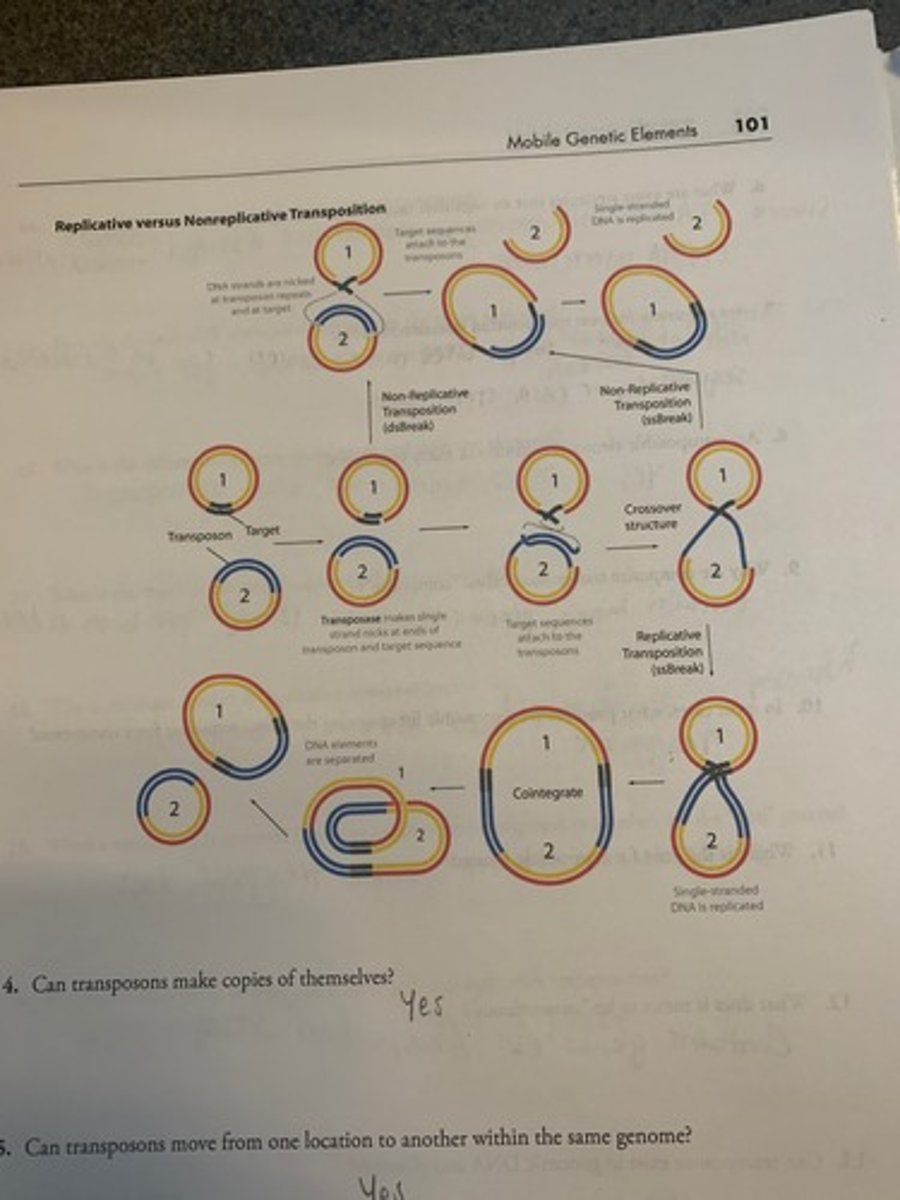
What is the difference between replicative and nonreplicative transposition?
Copy + paste; cut + paste
Insertion sequence
The simplest kind of transposable element, consisting of inverted repeats of DNA flanking a gene for transposase, the enzyme that catalyzes transposition.
replicative transposition
to copy and paste
nonreplicative transposition
to cut and paste
Genes inside of a virus
-gag
-polymerase
-env
Types of Transposons Chart

Transposition types chart
Replication be Nonreplicative Transposition
Genes inside of a virus

Reverse transcription

Retrotransposons Chart