Rivers
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Geography
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Hydraulic Action
When force of fast-flowing water hits the banks and river bed forcing water into the cracks which compresses air
Changes in air pressure weaken the channel
Vertically erodes upper course of the river
Laterally erodes lower course of the river especially when water hits a meander
Abrasion
Small boulders and stones scratch and scrape their way down a river during transport which wear down the river bed
Attrition
Affects rivers load. When stones first enter river they are angular and sharp but as they travel down they collide with each other and the river bed which makes the rocks smoother
Solution
Dissolving of rocks like chalk and limestone. Rivers travelling over these rocks will erode them this way
Suspension
Fine material is held up and carried with the rivers flow
Upper Course Characteristics
Steep V-Shaped Valley
Vertical erosion from hydraulic action
Narrow channel
Low velocity
Small discharge
Rough river bed due to large rocks from traction
Middle Course Characteristics
Less steep gradient
Lateral erosion more frequent via attrition and abrasion
Wide and deep channel
High velocity
High discharge
Less rough river bed and sediment is smaller and smoother
Lower Course Characteristics
Gentle gradient
Wide Valley
Lots of deposition
Wide and deep channel
High velocity & discharge
Smooth river bed
Only lateral erosion
Why does the river widen downstream
As gradient is less steep in middle course, river begins to meander and laterally erode into valley side
In lower course, deposition from floods build up flood plain and meanders migrate which builds up and widens the valley
Interlocking Spurs
Found in upper course in parts of high land that alternate from either side of valley
Steep gradient is separated from narrow valley floor
As river moves it erodes landscape through vertical erosion but it cant cut hard rock so winds around it
Land that sticks out between bends are called spurs
Because river weaves in and out around the spurs either side of valley, spurs interlock
Rapids
Fast flowing turbulent sections of river where bed has steep gradient
Upper course and found where there’s uneven river bed
Waterfalls
-Upper course
1). Found where there’s hard and soft rock but soft rock erodes
2). Splash back from water below causes hydraulic action to weaken rocks behind water
3). As soft rocks break off, a base is formed
4). Continued undercutting means hard rock loses support and overhangs the drop
5). As hard rock loses support and falls over, its caught in fast flowing water. Some rocks become trapped and drill into the bed creating a plunge pool
6). Undercutting continues creating new overhang and as more erosion happens, waterfall retreats upstream leaving gorge downstream
Gorge
Narrow steep sided valley with rocky walls
Found below waterfall
Boulders litter the river bed
As the waterfall retreats upstream gorge is formed and as overhanging cap breaks off, so does gorge
Meanders
On inside bank they are
-Curved, gentle convex slopes with sand, gravel and pebble sediment smoothened by attrition. Vegetation grows furthest from water
On outside bank they are
-Steep drop down into river, several meters high and composed of bare earth
Meander Formation
-Formed in middle-lower course of river in flat land where river has energy to move sideways
1). River begins to swing side to side following small differences in land or the obstacles creating bends
2). On outside of each bend, river flows faster with more energy causing lateral erosion by hydraulic action and abrasion cutting into riverbank forming river cliff
3). On inside of each bend, water is slower and shallower so there’s not enough energy to carry all it’s load so it deposits sand, silt and gravel forming slip-off slope
4). As erosion continues on outside, and deposition on inside, bends become more pronounced forming a meander
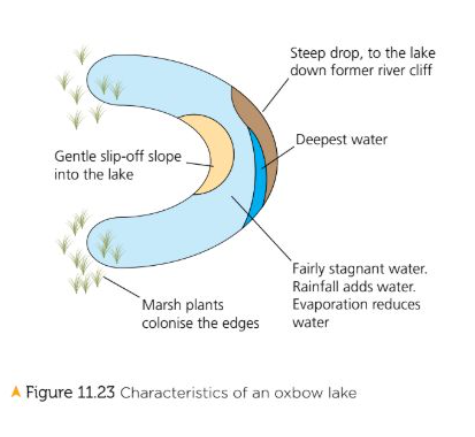
Oxbow Lake
Small, horseshow shaped lake which is found several meters from fairly straight stretch of river in its middle and lower courses
1). Overtime as meander gets more curved due to more erosion on outside bends, deposition builds up on inside bends
2). 2 outer bends of meander move closer forming narrow neck of land between them
3). During a flood, river has more energy and cuts straight through the neck carving a new channel. As this is the shortest path, the river takes it
4). Original meander is now cut off from main flow of river and becomes isolated U-Shaped body of water
5). Over time, sediment seals off ends of old meander loop and curved lake is left shaped like an oxbow
Levees
-Raised river banks made of gravel and stone
-Grade sediment with coarsest closest to river channel
-Steep-sided but steeper on channel side than land side
-Flat top covered by grass
1). When river bursts its bank, friction with land reduces velocity and causes deposition
2). Heavy sediment is deposited closest to river
3). Sediment size decreases with distance from river
4). With each flood, banks built higher. Overtime, river bed gains thick layer of sediment which raises river
Floodplain
-Large area of flat land either side of river prone to flooding
1). Width of flood plain is due to meander migration where outside bends erode sideways into valley
2). Position moves downstream cutting wider valley
3). When floods recede, floodplain is higher and more fertile due to deposits of silt and alluvium caused by flooding
Estauries
Tidal part of river where channel broadens and meets sea
High tidal range, wide, mudflats
-Tidal bores are huge waves that funnel up the river but travel so fast they damage river bank and nearby vegetation
1). Salinity increases towards sea as does sediment as it comes from sea and river
2). Sea level rises and falls with tide and when tide comes in, saltwater pushes up into river mouth
3). When tide comes out, freshwater flows into sea
4). As river reaches sea, it slows down and drops sediment.
5). As sediment forms mudflats and salt marshes on side of estuary areas are flooded at high tides and exposed at low tide
6). Constant actions of tides and deposition creates wide, funnel-shaped river mouth
Percolation
Water seeping deeper below the surface
Groundwater
Water stored in the rock
Throughflow
Water flowing through soil layer parallel to surface
Factors increasing flood risk
1). Depression- results in heavy rain which saturates soil so can no longer store water so surface runoff increases so rainwater enters river quicker so more discharge and floods
2). Sudden bursts of heavy rain resulting in infiltration rate being too slow to cope. Could occur after drought that has baked the soil. Surface runoff occurs so discharge increases causing flash floods
3). Too much light rainfall may cause floods if theres previous rainfall thats saturated soil
Human factors leading to flood risk
Urbanization- more infrastructure built with impermeable surfaces increasing flood risk
New Houses- Built on greenfield sites. Between 2001-2011, 72% increase in density of houses so multiple houses in spaces where there should be 1
People paving back gardens and concrete front areas to accommodate cars. 47% of UK households have 2 cars
How many tourists and revenue does Kielder Dam make
300,000 a year and $6M
How much electricity and water is Kielder Dam producing and how many trees planted around
6MW to serve town of 10,000
200M L of water
150M trees
Cost of Kielder Dam
$167M
How many trees and families removed
1.5M trees and 58 families
Effects of dam building
-Soil downstream becomes less fertile through lack of sediment from floods reducing crop yields
-Concrete dam affects path of migrating fish
-Algae collected behind dam which deoxygenates water
Channel straightening + Pros
-Meandering section of river is engineered to create wide, straight and deep course which improves flood risk
As its straightened, river moves water out of the area quicker as there’s less friction with bed and banks
Fast flowing water removes sediment that would be built up in height of river bed
Reduces length of river (Tees by 4km) which increased trade at (Stockton) port
Home owners will invest in properties as there’s less flood risk so less insurance
Channel straightening + Cons
-Doesn’t straighten entire river so still flood risk
-Dredging needs to be done to remove silt (costs $6M)
-Straightened river may have concrete lining which is unattractive and deprives burrowing river bank animals of habitat
-Causes pollution due to chemicals used
Embankments + Pros
Artificially raised river banks so more water stays in channel to reduce flood risk. Made by bulldozers which move mounds of impermeable soil into river banks to build up height
-Safer from flooding as channel has more capacity and less likely to burst
-Cheap, doesnt affect wildlife, provides walking paths
Embankments + Cons
-Harder for fishing + boating
-Not as reliable and could give false sense of security
-High maintenance costs due to constant repair and monitoring
-If embankment is breached, water lies on land for a while
Flood-relief Channel + Pros
Artificially made channel designed as a backup for river that frequently floods
Runs parallel to river and made by cutting out land using equipment then making a cut into river bank to join channels
-Removes risk of flooding from specific areas
-Exeter relief channels protected (3000) houses and built cycle tracks
-Calms the river
-More secure for houses and business
Flood-relief Channel + Cons
-People living in the path will have to be moved
-Settlements downstream will suffer from flooding as merging of water swells river
-Expensive
-Disturbs wildlife and looks bad
River Restoration + Pros
When river thats been hard engineered has been restored to natural channel
-Creates new habitats
-Increased water storage so less risk of flooding
-River Quaggy scheme stopped 600 houses from flooding
River Restoration + Cons
-Not always effective
-Loss of agricultural land and floods nearby crops
-Expensive (River Quaggy $11M)
Effects of Boscastle 2004
-3m wall of water flooded at 60km/h
-Cars swept away and destroyed buildings
-4 bridges washed away
-Economy ruined as 90% of income is from tourism
Why was flood so bad
-River was narrow at bridge
-Low bridges trapped boulders and trees
-Trees built next to river stopped water flow
How much did the scheme cost
$5M in 2008
What did the scheme include
-Widened bridge
-Widened river and deepened it to carry higher flows of water
-More drainage outfall
-Defence walls
-River level lowered by 75cm
-Replaced river channel next to RiverSide hotel
-Removed trees from river
-Land owners encouraged to maintain vegetation cover and remove dead trees
Effects of the scheme
-Reduced chance of flooding from 1:10 to 1:75
-Some felt it changed character of village replacing Elizabethan structures with metal poles