Things to go over for Quiz #1 (Lesson Content 1,2,&3 – 20 MCQ)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are the organs associated with the urinary system?
2 Kidneys, 2 ureters, 1 urinary bladder, and 1 urethra.
What are the functions of the kidneys?
Eliminate waste products
Regulate acid-base balance (pH)
Regulate composition and volume of body fluids
Produce hormones required for proper functions of bodily tissues and organs
Produce and excrete urine
filtering and cleansing the blood of harmful metabolic wastes, and excess ions
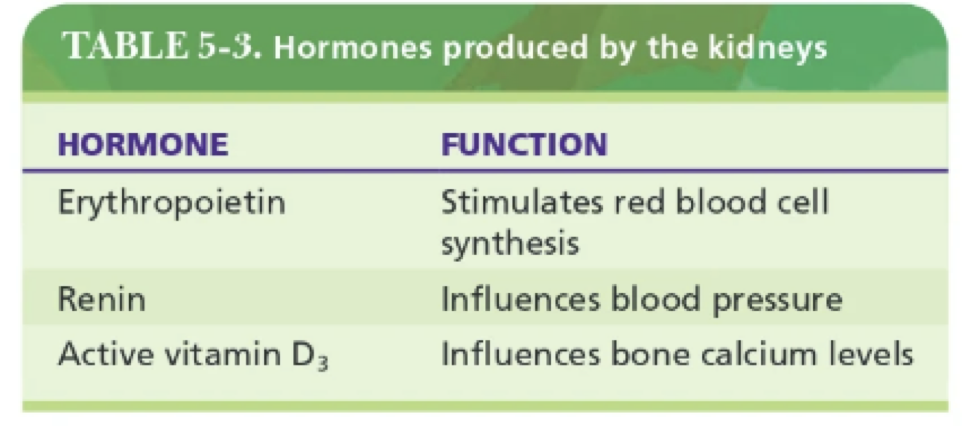
What are the three hormones produced by the urinary system and what are they for?
Erythropoietin (produces red blood cells), renin (regulates blood pressure), and calcitriol/Active vitamin D3 (increases bone calcium absorption levels).
What is the functional unit of the kidneys?
Nephron.
What is the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule?
The glomerulus is a network of capillaries involved in filtration; Bowman’s capsule encases the glomerulus and collects filtered fluid.
Quickly review how urine is produced.
Urine is produced through glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion in the nephrons. These processes ensure that only waste and excess water are removed from the body
On average how much urine do we produce in 24 hours?
between 750mL and 2 litres (L) of urine produced daily in a healthy adult
What is urine made of? - Include the percentage.
95% of urine is water and 5% is solutes (dissolved substances:urea, creatinine, electrolytes).
Routine urinalysis specimens that cannot be tested within 2 hours, what should we do with the specimen?
Refrigerate the specimen.
How long can we store urine in the refrigerator for?
Up to 24 hours.
What is the procedure for collecting 24-hour urine?
Collect all urine produced in 24 hours, starting from the first morning void to the next first morning void.
Once you receive 24-hour urine in the laboratory, what should you do?
Mix the specimen well and measure the total volume.
What is MSU urine? What is the procedure for it?
Midstream urine; collect urine after discarding the first few drops.
Why is clean-catch midstream urine collected? What is it used for and which department does it go to?
Its the most desirable for culture. Goes to the microbiology department. to be cultured
Which urine specimen is most concentrated? - What time of the day?
First morning urine.
What can we test for in 24-hour urine?
Protein, Creatinine, Urobilinogen
Calcium, Hormones, Amino acids
Metabolic products, Heavy metals, Drugs
What is the renal threshold for glucose?
Ranges from 160 to 180 mg/dL
Name the preservatives we can use for urine specimen.
Boracic acid, Formaldehyde (formalin), thymol, Toluene, Specialized additives (Nitric acid for mercury analysis, Sodium bicarbonate and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid for porphyrins, Sodium bicarbonate for urobilinogen analysis)
What is the pH of urine?
Ranges from 5.0 to 8.0.
What is the urine for cytology study and what is it trying to diagnose?
First Morning Urine. Studies cells in urine to diagnose cancer and other diseases.
What is chain-of-custody for?
To track the handling and storage of urine specimens for legal or forensic purposes.
When can we reject urine specimens?
If the specimen is contaminated, improperly labeled, or not collected properly.
Go over the physical, chemical and microscopic part of urine. Write down the related information for it.
Physical: color, clarity, odour; Chemical: pH, specific gravity, presence of proteins, glucose; Microscopic: cells, crystals, bacteria.
What is the normal color of urine? How does it get that color, due to what presence?
Normal color is pale yellow, due to the presence of urochrome.
What does acetest detect?
It detects ketones in urine.
What does Icotest detect?
It detects bilirubin in urine.
What is SSA for? What does it stand for?
SSA stands for Sulfosalicylic Acid; it detects proteins in urine.
What does Clinitest detect?
It detects reducing substances, primarily glucose.
How do you use a refractometer and what is it for?
Use it by placing a drop of urine on the prism to measure specific gravity.
What is a urinometer and what is its method?
A device for measuring urine specific gravity through buoyancy.
How, when, and what is the quality control for the urine reagent strips?
Perform quality control daily using known control solutions to ensure accuracy.
What type of semi-automated equipment can we use for reading dipsticks?
Automated urine analyzers, with color readings measured by photometry.
What is dipstick? – What can we read for dipstick?
A dipstick is a test strip for chemical analysis of urine; we can read for pH, proteins, glucose, and ketones.
For microscopic urine, what are we looking for under the microscope?
Cells, casts, crystals, bacteria, and any abnormal components.
How do we prepare the urine to be used for microscopic examination? What part do we use – the supernatant or the sediment to prepare the glass slide?
Centrifuge the urine, then use the sediment for microscope examination.