procedures
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:15 PM on 4/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
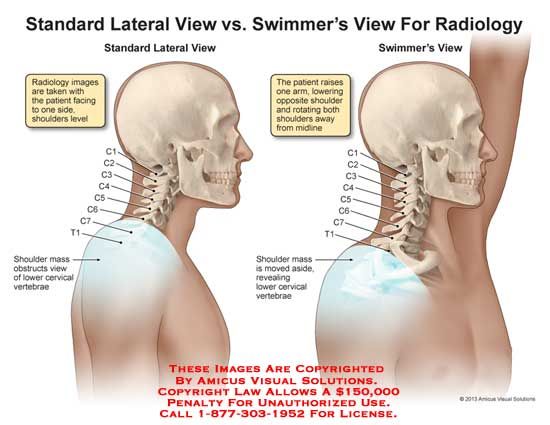
how should the patient’s arms be positioned for the swimmers projection?
* position the arm farthest from the IR down along the patient’s side with the shoulder depressed
* the arm closest to the IR should be elevated with the elbow flexed and the forearm resting on the patient’s head
(if supine, rest head on arm closest to the IR so that it is still out of the way)
* the arm closest to the IR should be elevated with the elbow flexed and the forearm resting on the patient’s head
(if supine, rest head on arm closest to the IR so that it is still out of the way)
2
New cards
two ways the CR can be directed in a swimmers technique
* perpendicular if the shoulder away from the IR is well depressed
* if not well depressed, 3-5° caudal angle
* if not well depressed, 3-5° caudal angle
3
New cards
Why would you flex the patient's hips for a T-spine AP projection?
to reduce the kyphotic curvature of the spine
4
New cards
respiration for an AP T-spine
suspended respiration at the end of full expiration
* this minimizes the air in the lungs, which results in less attenuation differences and more uniform exposure of the thoracic anatomy
* this minimizes the air in the lungs, which results in less attenuation differences and more uniform exposure of the thoracic anatomy
5
New cards
centering point for a T-spine AP projection?
* Perpendicular
* Midway between the jugular notch and xiphoid process (T7)
* Midway between the jugular notch and xiphoid process (T7)
6
New cards
How would you take advantage of the anode heel affect when taking an image of a chest or T-spine?
Put the cathode end of the tube toward the feet- so that the greatest percentage of radiation goes through the thickest part of the thorax
7
New cards
T7 landmark
level of the inferior angle of the scapula
8
New cards
Central ray centering for a T-spine lateral
perpendicular to T7 on the posterior half of the thorax
9
New cards
when positioning for a lateral T-spine, what should you do if the the thorax is not in a horizontal plane? (WM)
* women- 10° cephalad
* men- 15° cephalad -→ men have more broad shoulders. this is the reason for the larger angle
* men- 15° cephalad -→ men have more broad shoulders. this is the reason for the larger angle
10
New cards
For a T-spine AP projection in the supine position, Why should the patient's head rest directly on the table or on a thin pillow instead of on a thick pillow/foam
To avoid accentuating the thoracic kyphosis
11
New cards
Why is it preferable to place the patient in the left lateral position instead of the right lateral position for a T-spine
To place the heart closer to the IR - minimizing superimposition of vertebrae by the heart
12
New cards
For the lateral recumbent position, what is the purpose of placing a firm pillow under the patient's head
To keep the long axis of the vertical column horizontal
13
New cards
Where do you Center for an AP projection of the L-spine
* Perpendicular to L4 (Level of the iliac crest) To view lumbosacral (Both the spine and the sacrum)
* Perpendicular to 1 1/2 inches above the iliac crest for just the spine itself
* Perpendicular to 1 1/2 inches above the iliac crest for just the spine itself
14
New cards
Why would you ask the patient to flex their knees for the lumbar spine AP projection
to reduce the lordotic curvature
15
New cards
Where would you Center for a lateral projection of a L-spine
* Perpendicular to L4 (Level of the iliac crest) To view lumbosacral (Both the spine and the sacrum)
* Perpendicular to 1 1/2 inches above the iliac crest for just the spine itself
* Perpendicular to 1 1/2 inches above the iliac crest for just the spine itself
16
New cards
centering for the lateral lumbar spine projection
(L5/S1 junction)
(L5/S1 junction)
2 inches posterior to the ASIS and 1 1/2 inch inferior to the iliac crest
17
New cards
why should the patient empty the urinary bladder before the AP projection of the lumbar spine is performed
To eliminate superimposition caused by the secondary radiation generated with the filled bladder
18
New cards
lumbar articular facets for vertebrae L1-L4 form an angle of ______ __to__________
30 to 60 degrees
19
New cards
What is the importance of seeing the Scottie dog in an image
To show that the patient is properly positioned in an oblique
20
New cards
What is the ear of the Scottie dog
Superior articular process
21
New cards
What is the nose of the Scottie dog
Transverse process
22
New cards
What is the eye of the Scottie dog
pedicle
23
New cards
What is the neck of the Scottie dog
Pars interarticularis
24
New cards
What is the body of the spottie dog
lamina
25
New cards
What makes the feet of the Scottie dog
Inferior Articular process
26
New cards
What positioning error most likely occurred if the lumber zygapophyseal joint is not well demonstrated and the pedicle is quite anterior on the vertebral body
The patient was not rotated enough
27
New cards
What positioning error mostly likely occurred if the lumber zygapophyseal joint is not well demonstrated and the pedicle is quite posterior on the vertebral body
The patient is overrotated
28
New cards
How many degrees and in what direction should the central Ray be directed for a man and for females for the AP axial projection ( Ferguson method ) of the lumbosacral junction?
30° cephalad-men
35° cephalad- females
35° cephalad- females
29
New cards
What is the one a central projection for the SI joints
AP oblique
30
New cards
What is the angle of the body for the AP oblique of the SI joint
* The side of interest is elevated 25 to 30°
* the side being examined is furthest from the IR
* the side being examined is furthest from the IR