Chemistry 9 (all topics)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What is Chemistry?
The study of properties of matter and the changes that matter undergoes.
What is Alchemy?
The intrest in composition and properties of matter.
What was the goal of alchemists?
To change base metals into gold and find a cure for all diseases (Philosopher's Stone).
What is the scientific method?
A process of forming a hypothesis, collecting data, and analyzing results.
What is a hypothesis?
An educated guess, usually written as: If... then... because...
What's the difference between observation and inference?
Observation = what you see; Inference = what you think it means.
What are manipulated, responding, and controlled variables?
Manipulated = changed; Responding = observed effect; Controlled = kept constant.
What's the difference between a theory and a law?
Theory explains why; Law describes what happens.
What is Dalton's atomic model?
Atoms are solid, indivisible spheres.
What did J.J. Thomson discover?
The electron; created the Plum Pudding Model.
What did Rutherford discover?
The atom has a dense, positive nucleus.
What did Bohr add to atomic theory?
Electrons orbit in energy levels.
What is the current atomic model?
Electrons move in a cloud-like region around the nucleus.
What are Protons?
They are positively charges particles found in the nucleus of the atom.
What are Neutrons?
Neutral charged particles that are found in the nucleus of the atom.
What are Electrons?
Negatively charged particles that revolve around the nucleus in clouds.
What does the particle model of matter say?
Matter is made of tiny, moving, and attracted particles.
What happens to particles when heated?
They move faster and spread out.
What is a pure substance?
Made of one kind of particle; has fixed properties.
What is a mixture?
Made of different particles; can be separated physically.
Difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures?
Homogeneous = looks uniform; Heterogeneous = visibly different parts.
What's the difference between chemical and physical properties?
Chemical = how it reacts; Physical = what it's like (e.g., color, smell).
What are the types of Heterogeneous Mixtures?
Mechanical = Two or more visibly different materials Suspensions = Mixture of a solid in a liquid that will eventually settle
What are Colloids and Emulsions?
Heterogeneous mixtures whose solutes do not settle out.
What is the Periodic Table of Elements?
Shows all of the known elements in order of increasing atomic number. The table puts elements together in groups with similar characteristics.
What are Metals?
Elements that are good conductors of electric current and heat that are located on the Left of the Table. They lose electrons and become positive.
What are Non-metals?
Gases, liquids, or brittle solids that do not conduct heat or electricity that are located on the right side and include Hydrogen. They gain electrons and become negative.
What are Metalloids?
They are found on the border of the "staircase" and have properties of both metals and non-metals. They gain and lose electrons.
What are Alkali Metals?
The highly reactive metallic elements located in group 1 of the periodic table that tend to lose one electron.
What are Alkaline Earth Metals?
The reactive metallic elements located in Group 2 of the periodic table that tend to lose two electrons.
What are Halogens?
Highly reactive non-metals that tend to gain one electron.
What are Noble Gases?
Very un-reactive that are inert/stable.
What is Atomic Number?
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
What are Isotopes?
Different atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons.
What is Mass Number?
Sum of the number of protons and neutrons (nucleons)
What is Nuclear Notation?
Used to easily show the symbol of the element the mass number of the isotope and the atomic number.
What are Ions?
An atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
What is the trend for Ionic Charge?
+1, +2, (skip transition metals) +3, +4, -3, -2, -1, 0
What are valence Electrons?
Electrons that exist in the outer energy levels.
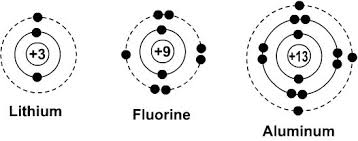
What are Bohr Diagrams? (SCIENCE 10)
Pictorial representation of atoms or ions that show valence electrons in its energy level.
What are Lewis Dot Diagrams? (SCIENCE 10)
Another pictorial representation of atoms that focuses on only the valence electrons. Is useful when thinking about reactivity.
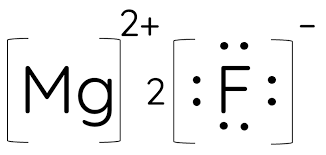
Ionic Compound
A compound formed from a metal and a non-metal through electron transfer.
Molecular Compound
A compound formed from non-metals through electron sharing.
Subscripts
Numbers in a chemical formula indicating the number of atoms of each element (e.g., H₂O has 2 H, 1 O).
Cation
A positively charged ion, typically a metal, that is named first in ionic compounds.
Anion
A negatively charged ion, typically a non-metal, that is named second in ionic compounds with the ending changed to '-ide'.
Multivalent Metals
Metals that can form more than one type of positive ion, indicated by Roman numerals in their names.
Common Polyatomic Ions
Ions that consist of multiple atoms and have a specific charge, such as sulfate (SO₄²⁻) and nitrate (NO₃⁻).
Naming Molecular Compounds
The process of naming compounds formed from non-metals using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms.
Diatomic Elements
Elements that naturally exist in pairs, represented by 'BrINClHOF' (e.g., Br₂, I₂, N₂).
Chemical Reactions
Processes where reactants are transformed into products, with mass conserved throughout the reaction.
Exothermic Reaction
A reaction that releases heat, resulting in an increase in temperature (e.g., combustion).
Endothermic Reaction
A reaction that absorbs heat, resulting in a decrease in temperature (e.g., photosynthesis).
Law of Conservation of Mass
A principle stating that mass is conserved in a chemical reaction; atoms are rearranged but not created or destroyed.
Physical Change
A change that does not result in a new substance being formed and is often reversible (e.g., melting, cutting).
Chemical Change
A change that results in the formation of a new substance and is often hard to reverse (e.g., burning, rusting).
Chemical Change Indicators
Signs that a chemical change has occurred, such as heat/light, gas formation, color change, precipitate formation, and new properties.
Properties of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are solid at SATP, have high melting points, are conductive when dissolved, and are hard and brittle.
Properties of Molecular Compounds
Molecular compounds can be solid, liquid, or gas, have low melting points, are usually non-conductive, and may be softer and have odors.
Prefixes in Molecular Naming
Terms used to indicate the number of atoms in molecular compounds, such as mono- (1), di- (2), tri- (3), tetra- (4), penta- (5), hexa- (6), and deca- (10).