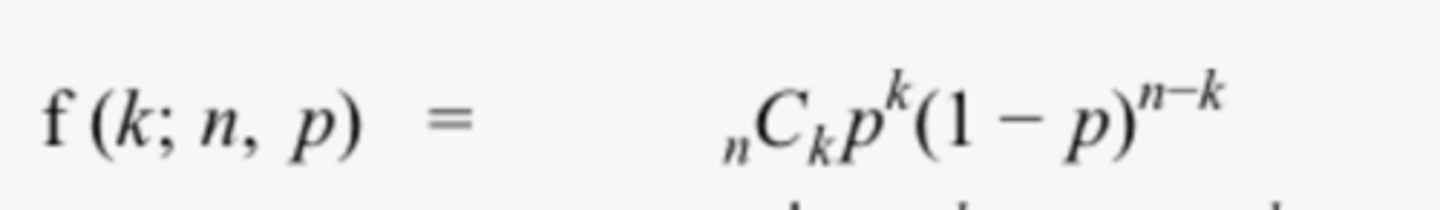Level 3 stats distributions
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What does Poisson distribution give us
the probability of a certain number occurring
What are the Poisson distributions conditions?
RIPS
what does the R stand for in RIPS
random occurrence at a constant rate
what does the I stand for in RIPS
Independence of occurrences
what does the P stand for in RIPS
Probability of occurring is proportional
what does the S stand for in RIPS
simultaneous events are impossible
what is PPD and BPD used for
the exact number
what is PCD and BCD used for
a group of numbers eg more than or less than
P(x≤4)
up to 4
P(x≤3)
less than 4
1- P(x≤4)
more than 4
1- P(x≤3)
at least 4
P(x≤4) - P(x≤1)
between 2 and 4
what is x
number of occurrences
what is λ
average rate of occurrences
what is in this image
the inverse poisson formula
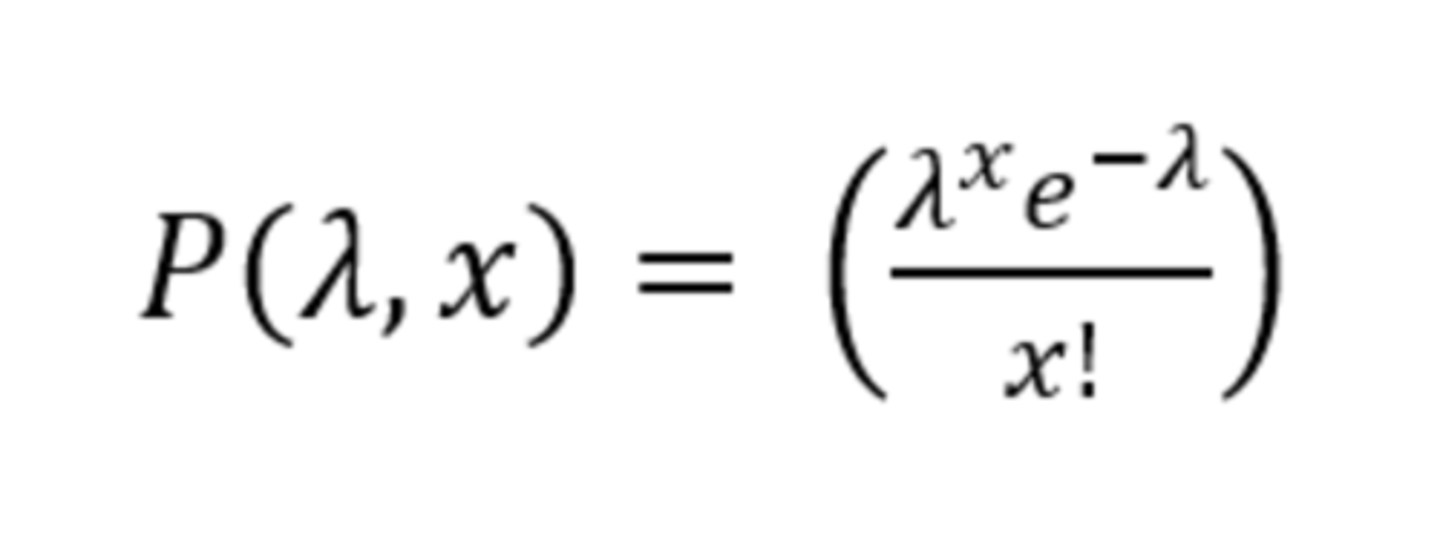
what distributions are continuous
Triangular, Uniform, Normal
what distributions are discrete
binomial, poisson
Triangular Distribution
the distribution has a maximum and a minimum x-vaule and the highest point is the mode
height at x on left of mode
2(x-a)/(b-a)(c-a)
height at x on right of mode
2(b-x)/(b-a)(b-c)
height at mode
2/b-a
how do we justify triangular distribution
there is a maximum and minimum x-value
we have the mode
the distribution is continuous
the distribution is often skewed to one side
for uniform distribution every x-value has the same height...
same probability of occurring
justify uniform distribution
there is a maximum and minimum x-value
all possible x-values have the same probability of occurring
the distributions is continuous
for normal distribution use...
NCD
justify normal distribution
the mean median mode are in the middle
almost all values are within 3 S.D of the mean
the distribution is symmetrical
there is no maximum or minimum x-value
continuous variables are.... and rounding makes the variable....
mesurable, discrete
when to use binomial distribution
discrete variable
two possible outcomes
fixed number of trials
When to use poisson distribution
discrete variable
rate of occurrence
no upper limit on number
When to use normal distribution
continuous variable
central mean median mode
symmetrical bell curve
uses standard deviation
when to use Triangular distribution:
continuous variable
maximum and minimum
clear mode
When to use uniform distribution
continuous variable
maximum and minimum
same probability for all x
comes from counting the number of successes in a fixed set of trials
binomial distribution
what are the binomial conditions?
PITT
what does the P in PITT stand for
probability of success is fixed
what does the I in PITT stand for
independence of trials
what does the first T in PITT stand for
two possible outcomes of trials
what does the second T in PITT stand for
trial number is fixed
if events are independent
P(AnB) = P(A) x P(B)
calculating conditional probability
P(A|B)=P(AnB)/P(B)
probability of someone having a dog knowing they have a cat is
P(dog|cat) = P(dog n cat)/P(cat)
what is this image
inverse binomial problems