les monkeys
1/535
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
536 Terms
Name the 3 rock types that make up the earth’s crust
Igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic
Describe 2 ways how sedimentary rocks are formed
Small particles which have been eroded, transported deposited in layers on the seabed
Or formed by the remains of plants and animals
2 examples of sedimentary rocks
Limestone, chalk
Describe how igneous rocks are formed
Created by volcanic activity when magma/lava cools, forming rocks made of crystals that are hard
1 example of igneous rocks
Granite
Describe how metamorphic rocks are formed
Existing rocks are changed under immense heat/pressure
Usually made up of layers/folds containing crystals
2 examples of metamorphic rocks
Schale, schist
What is the Tees-exe line
A theoretical line from the rivers Tees and Exe
To the south is predominantly sedimentary rock
To the north is shifting to igneous / metamorphic rock
Define weathering
The breakdown of rock on land / in Situ
3 types of weathering
Mechanical / physical / freeze thaw
Biological
Chemical
Describe mechanical / physical weathering / freeze thaw
Water enters cracks, freezes and expands
Describe biological weathering
Burrowing animals + tree roots break apart rocks
Describe chemical weathering
Acid rain dissolves rocks eg. limestone
Give an example of an upland landscape and where one can be found
Granite Tor, Dartmoor
Describe the formation of a Granite Tor (first 3)
Massive dome of magma formed underground, 250mil years ago
As it cooled and contracted, cracks aka joints formed
Freeze thaw weathering expanded joints (because water infiltrated)
Describe the formation of a Granite Tor (last 3)
Glaciation eroded nearby ground, leaving rock exposed
Mechanical + biological weathering eroded weaker joints of rock, while gravity caused mass movement
Blocks with fewer joints remain standing, surrounded by clitter slopes
Annotated diagram of how Granite Tor forms (all 6)

Give another example of an upland landscape and where one can be found
Limestone pavement, Malham Cove
Malham cove:
What is it
Where is it found
Malham cove is a large curved limestone rock
It can be found in yorkshire, 0.6 miles north of Malham village
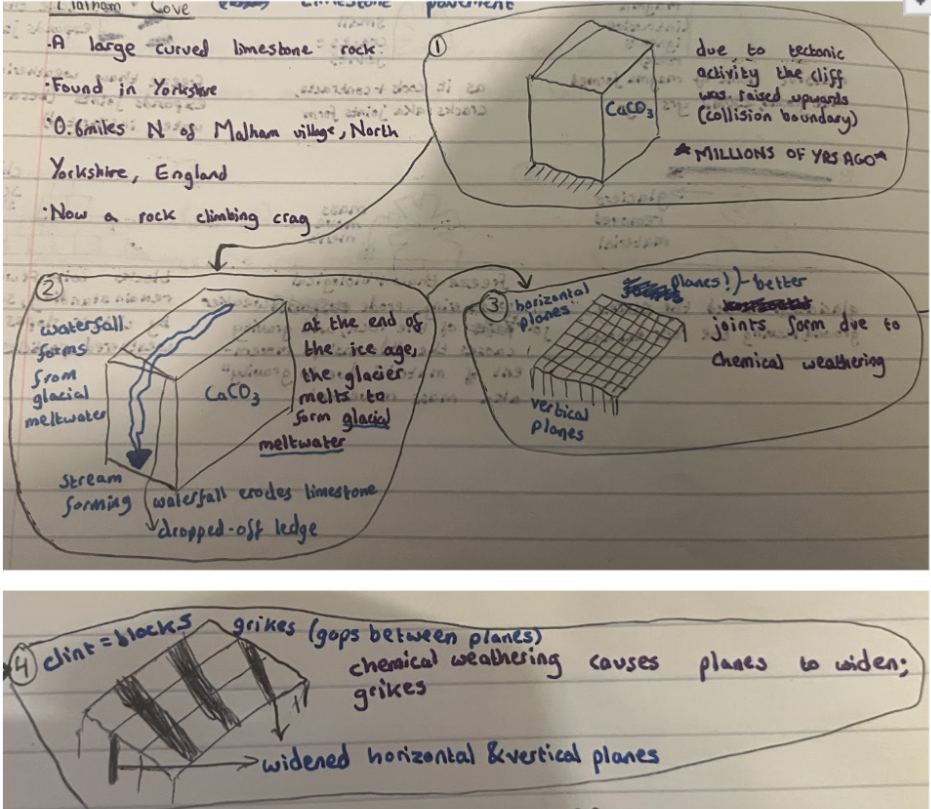
Describe the formation of a limestone pavement (first 2)
Over millions of years, due to tectonic activity, the softer rock was raised and became a limestone cliff
At the end of the ice age, glacier melts to form glacial meltwater. This formed a waterfall which eroded the cliff backwards to its current position
Describe the formation of a limestone pavement (last 3)
Along the top, carboniferous limestone is made of lines – planes and vertical joints
As rainwater passes through, chemical weathering widens the planes and joints
The deepening of cracks forms grykes, exposing blocks of limestone; clints
Annotated diagram of how limestone pavement forms (all 5)
Define an erratic
A rock which is geologically different to the surrounding rock
Describe how an erratic is formed
Glacier picks up chunk of rock and transports it away from where it came from
When glacier melts and retreats, rock is deposited and left
Give an example of a lowland landscape and where it can be found
Chalk escarpment, South downs national park
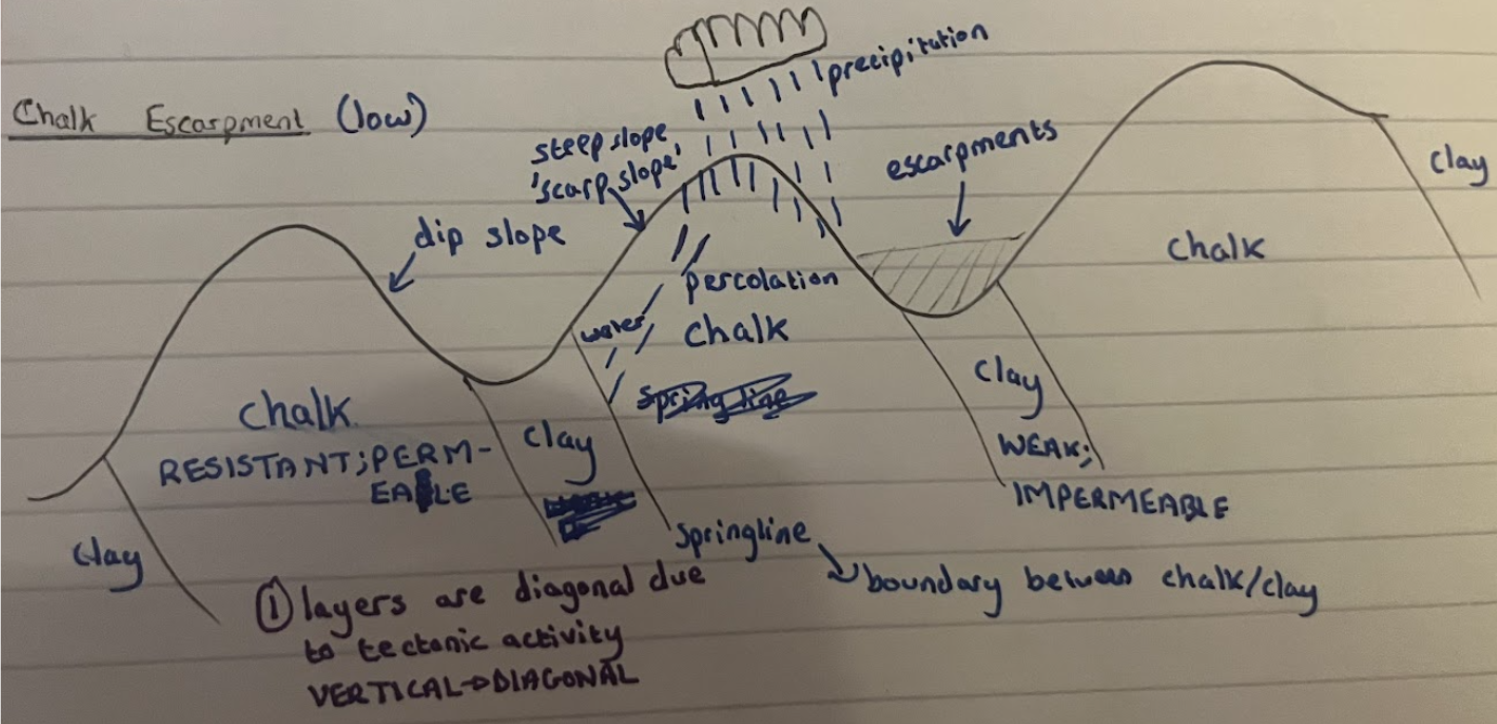
Describe the formation of a chalk escarpment (first 4)
Alternating layers of chalk and clay, which are diagonal due to tectonic activity
Chalk is more resistant to erosion, so erodes at slower pace, so more is left
Clay is less resistant to erosion, so erodes at faster pace, so less is left
Forming a scarp slope above chalk and a dip slope above clay
Describe the formation of a chalk escarpment (last 3)
Chalk is permeable so when water falls on it, water infiltrates the rock
Which flows down until it meets the clay, which is impermeable, so water flows as surface runoff
Forming a springline; a stream flowing between where the 2 types of rock meet
Annotated diagram of how chalk escarpment forms (all 7)
South downs national park:
Area
Population
Rocks
Nearby city
1672km2
108k population
Chalk, sandstone, clay
Brighton
3 aspects for south downs national park
Agriculture
Forestry
Settlement
SDNP agriculture:
What % of land is farmed
How many business farming
83%
1100 businesses
SDNP agriculture:
3 reasons why
Chalk grassland ideal for grazing sheep / training horses
Clay grassland ideal for dairy cows
South = arable farming
SDNP agriculture:
Income use +ve
Supports local economy
Businesses account for 6% of employment
SDNP agriculture:
Birds +ve
Contributed towards supporting rare bird species
Eg. corn bunting, grey partridge, skylark, stone curlew
SDNP agriculture:
Bats +ve
Hedgerows and field margins
Provide wildlife corridors for bats
SDNP agriculture:
Decline in arable farming -ve
Reduced presence of arable plants
Damaged wildlife habitats
SDNP agriculture:
Decline in traditional practices -ve
Eg. sheep grazing
→ scrub encroachment
SDNP agriculture:
Chemicals usage -ve
Decline in chalk grassland
SDNP forestry:
Which woodland
Area
Distribution
Human activity
Deciduous and coniferous mix
25.8% of SDNP or 38420 hectares
Unevenly distributed – more in W than E
Human activity increased
SDNP forestry:
Large % is ancient trees +ve
Provides habitats for wide range of wildlife
SDNP forestry:
Timber uses +ve
Valuable sustainable product
Growing markets in construction
Fuel for heating
SDNP forestry:
Removal of woodland for new developments -ve
Threatens some of ancient large-leaved lime woodland
SDNP forestry:
Trees no longer managed -ve
Many of hazel / chestnut coppices no longer managed
Overgrown
Decline in quality
Loss of biodiversity
SDNP settlement:
Escarpments
Make up the park, responsible for spring-like settlements
Built on naturally formed S slope
SDNP settlement: +ve
Population
Villages
Market towns
Most populated national park, 120k
Mostly live in urban towns and villages
Largest market towns of any NP
Eg. petersfield, lewes, midhurst
SDNP settlement: -ve
New developments which have not reflected local character in traditional design and materials
Loss of local distinctiveness
Historic features replaced eg. wooden to metal signage
Decline in local facilities eg. post offices, general stores, pubs, schools
Define coastal erosion
Action of waves wearing away rocks along coastline and removing sediments (occurs in sea)
4 types of erosion
Hydraulic action, abrasion, attrition, solution
Define hydraulic action
Power of water waves wearing away rock
Define abrasion
Waves throw rocks against coast
Define attrition
Rocks collide with one another, becoming smaller and rounder
Define solution (erosion)
Rocks / materials dissolving in water
Define weathering
Rocks are broken down at / near to surface of ground (occurs on land)
3 types of weathering
Mechanical, biological, chemical
Define mechanical weathering
Water enters rock cracks, freezes and expands
Define biological weathering
Animals burrowing / tree roots growing
Define chemical weathering
Acid rain melting away rocksDefine transportation
Define transportation
Eroded material’s movement along coastline by different processes, depending on its size and energy of waves (or water in river)
4 types of transportation
Traction, saltation, suspension, solution
Define traction
Large rocks roll along seabed
Define saltation
Rocks hop, skip and jump along seabed
Define suspension
Material is carried within the solution
Define solution (transportation)
Rocks / materials dissolved in solution
Define mass movement
Downslope movement of rocks + soil from top of cliff because of gravity (occurs on land)
3 types of mass movement for coasts
Rockfalls, landslides, flows
Define rockfall
Rocks from weathered cliffs falling
Why does rockfall often happen?
Cliff is undercut by wave action, leaving it unsupported and liable to collapse
Define landslides
Movement of material along a flat surface
Large amounts of rock and soil move downslope rapidly
Define flows
Usually after heavy rainfall, water seeps through permeable rocks
Where they meet impermeable rocks, saturated soil and weaker rock collapses
And slides in a rotational manner along a curved surface
Define deposition
When there isn’t enough energy to carry eroded material, so it’s dropped
When wind blows over the sea, waves are created due to..
Friction between the wind and surface of water creating ripples
Size and energy of a wave depends on 3 factors. Name them
Strength of wind
How long wind has been blowing for
The fetch (distance wind waves travel over)
Define swash motion
Water rushes up the beach
Define backwash motion
Water travels back to sea due to gravity
Constructive waves: strength of their swash and backwash
Strong swash, weak backwash
Constructive waves: height and frequency
Low in height, less frequent
Constructive waves: conditions
Calm conditions with little wind
Destructive waves: strength of their swash and backwash
Weak swash, strong backwash
Destructive waves: height and frequency
Tall and steep in height, closely spaced and frequent
Destructive waves: does what to the beach
Strong backwash removes sediment from beach
Define concordant coastline
Where folding / arrangement of rock types are parallel to coast
A concordant coastline means..
Alternating layers of hard and soft rock lay in same direction as coastline
Erode at similar speeds
Define discordant coastline
Where folding / arrangement of rock types are perpendicular to coast
A discordant coastline means..
Less resistant rocks erode at a quicker pase than more resistant rocks
Explain the formation of a headland and bay (3)
Discordant coastline where alternating layers of hard and soft rock lie perpendicular to coastline
Rocks eroded by erosion, eg. hydraulic action
Softer rock erodes more, forming bays
Harder rock erodes less, forming headlands
Diagram of formation of headland and bay
Explain the formation of a coastal stump (4)
On discordant coastline’s headland, crack opened up by erosion eg. hydraulic action
Crack grows into cave, then an arch
Land above arch becomes unstable due to chemical weathering eg. acid rain and collapses
Leaving a tall rock stack, which erodes into a stump
Explain the formation of a wave-cut notch and wave-cut platform (4)
Sea attacks base of cliff between high and low water mark
Wave-cut notch formed by erosion eg. hydraulic action – this is an undercut in the cliff
As notch increases in size, cliff becomes unstable and there is mass movement into the sea
Backwash carries away eroded material, leaving behind wave-cut platform
Diagram of formation of coastal stump
Diagram of formation of a wave-cut notch and wave-cut platform
Define longshore drift
Movement of material / sediment along coastline due to direction a prevailing wind hits coastline
Explain the process of longshore drift (3)
Prevailing wind hits shore at an angle of about 45 degrees
Waves (swash) move up beach at same angle, and move back down beach due to gravity, at 90 degrees
Within waves, sediment carried via transportation processes eg. traction, saltation along the beach
Explain the formation of a sand spit and salt marsh (3)
Prevailing wind hits shore at 45 degree angle, bringing waves with them
Angled swash and backwash transport material along coast via traction and saltation (longshore drift)
When encountering curve in coast, it’s “protected” from prevailing wind, so deposition occurs and spit is formed
Salt marsh formed behind due to sheltered nature
Explain the formation of a recurved sand spit and salt marsh (2)
(explain how a sand spit is formed)
If prevailing wind direction changes, so do direction of waves
Shift in deposition occurs, so recurved sand spit and salt marsh are formed
Explain how a bar and lagoon are formed (3)
Prevailing wind hits shore at 45 degree angle, bringing waves with them
Angled swash and backwash transport material along coast via traction and saltation (longshore drift)
Between 2 headlands, deposition occurs as constructive waves have little energy
Over time bar is formed across bay, which is now a lagoon
Explain the formation of a beach (3)
Eroded material that has been transported from somewhere else then deposited by the sea
Constructive waves build up beaches due to strong swash and weak backwash
Waves must have little energy so beaches form in sheltered areas eg. bays
5 factors relating to coastal erosion
Settlements, tourism, infrastructure, construction, agriculture
Are settlements impacted by, or impacting coastal erosion?
Impacted by
Explain how settlements are impacted by coastal erosion:
Coastal zone uk population
Eg. at ..
20mil in uk live within coastal zone
Eg. at holderness, over 29 villages lost due to coastal erosion in past millennium
Is tourism impacted by, or impacting coastal erosion?
Both impacted by and impacting