Unit 3-1: Cultural Patterns and Processes - AP Outline
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Centrifugal Force
A force that threatens the cohesion of a neighborhood, society, or country; any factor that tends to divide, destabilize, or weaken a state (country)
Examples of Centrifugal Forces
Ethnic, language, or religious differences
Economic inequality (disparities in wealth, resources, or job opportunities between regions or groups in a country
Physical geography/spatial factors - such as mountains or rivers that separate people or inhibit communication and transportation.
Political instability/corruption - weak, ineffective or corrupt central government
Centripetal Force
Any factor that unifies and strengthens a state, promoting political stability and national cohesion
Examples of Centripetal Forces
Political/Institutional Factors - nationalism/patriotism, strong/legitimate government
Cultural Factors - common language, shared religion or ethnicity, national sports/events
Economic/Infrastructure Factors - effective infrastructure (transportation/communication), equitable economic development, forward capital
Contagious Diffusion
Form of expansion diffusion where a cultural trait, idea, or innovation spreads rapidly outward from its hearth (origin) to nearby places or people; widespread and rapid
Examples of Contagious Diffusion
Disease - contagious diseases that pass through physical proximity and personal contact (flu, common cold, Ebola, cholera)
Ideas/Trends - Viral internet meme or TikTok trend
Creole (Creolization)
Language that results from the mixing (blending) of a colonizer's language with the language(s) of the people being dominated, which has become nativized (the first or native language of a generation of speakers)
Examples of Creole Languages
Haitian Creole, Tok Pisin, Louisiana Creole, Gullah
Cultural Relativism
Evaluating a culture or practice from its own perspective and standard
Promotes tolerance, empathy, and a complete understanding of why a trait exists in a specific culture
Cultural Landscape - helps explain why a particular practice or landscape feature exists in a specific location by tying it to that culture’s beliefs, environment, and history
Ethnocentric Approach (Ethnocentrism)
Belief that one's own culture or ethnic group is superior to others and is the standard by which all other cultures should be measured
Evaluating a culture or practice based on the standards of one's own culture; often leads to prejudice, misunderstanding, judging another culture as inferior, or conflict
Hierarchical Diffusion
Form of expansion diffusion where an idea, innovation, or trend spreads by passing first among the most connected individuals or places, then trickling down to the rest of the population or lower levels of the urban hierarchy
Often skips (leapfrogs) over less influential people or smaller places in the initial stages
Examples of Hierarchical Diffusion
Fashion Trends (starts in major cities)
New Technology (starts with high-income/wealthy)
Music Genres (starts in major cities)
Company Decisions (starts with owner or CEO)
Lingua Franca
Language systematically used to facilitate communication between people who speak different native languages. It is a common language adopted for trade, diplomacy, science, and other international purposes
Examples of Lingua Franca
English - Colonization by Britain (historical); Internet (contemporary)
Spanish - Trade in Latin America
Arabic - Religion (Islam) and trade in the Middle East
Swahili - Trade and communication in East Africa
Traditional Architecture
Building style that reflects the cultural, historical, and environmental conditions of a small, cohesive, and homogeneous group of people
Features of Traditional Architecture
Local Materials - use materials available in the environment
Climate Adaption - designed for the local climate conditions
Cultural and Religious Beliefs - incorporate symbols and practices significant to the community's heritage
Slow Diffusion - Passed down through generations and likely only through relocation diffusion

Multiculturalism
A set of policies that promote the active participation and inclusion of minority groups in national histories, national politics, and cultural institutions with the goal of embracing difference with society;
Presence and active support of multiple, distinct cultural groups coexisting within a single society (cultural pluralism)
Examples of Multiculturalism
Ethnic Enclaves/Neighborhoods
Bilingual or Multilingual Signage
Diverse Architecture
Diverse Cuisine (restaurants and grocery stores)
Placelessness
Refers to the loss of unique identity and character of a place, resulting in landscapes that look and feel the same regardless of their location; diminishes regional variation and eliminates the unique meanings associated with specific locations
Causes of Placelessness
Globalization and Economic Uniformity
Mass Communication and Popular Culture
Standardized Architecture and Urban Planning
Increased Mobility and Connectivity
Visualization on the Cultural Landscape
Retail and Commercial Spaces (shopping malls and big-box stores)
Housing - “Cookie-Cutter” suburban housing
Infrastructure - Standardized highway systems, rest stops, and chain hotels/restaurants

Placemaking
Process that involves the deliberate design and management of public spaces to create environments that are vibrant, functional, and meaningful to the local community
Key Characteristics and Goals of Placemaking
Community Engagement - Involving residents in the planning process
Place Attachment - Fostering emotional connections between people and their environment
Cultural Expression - Reflecting local culture and history in the design
Sustainability - Promoting environmental responsibility and social equity
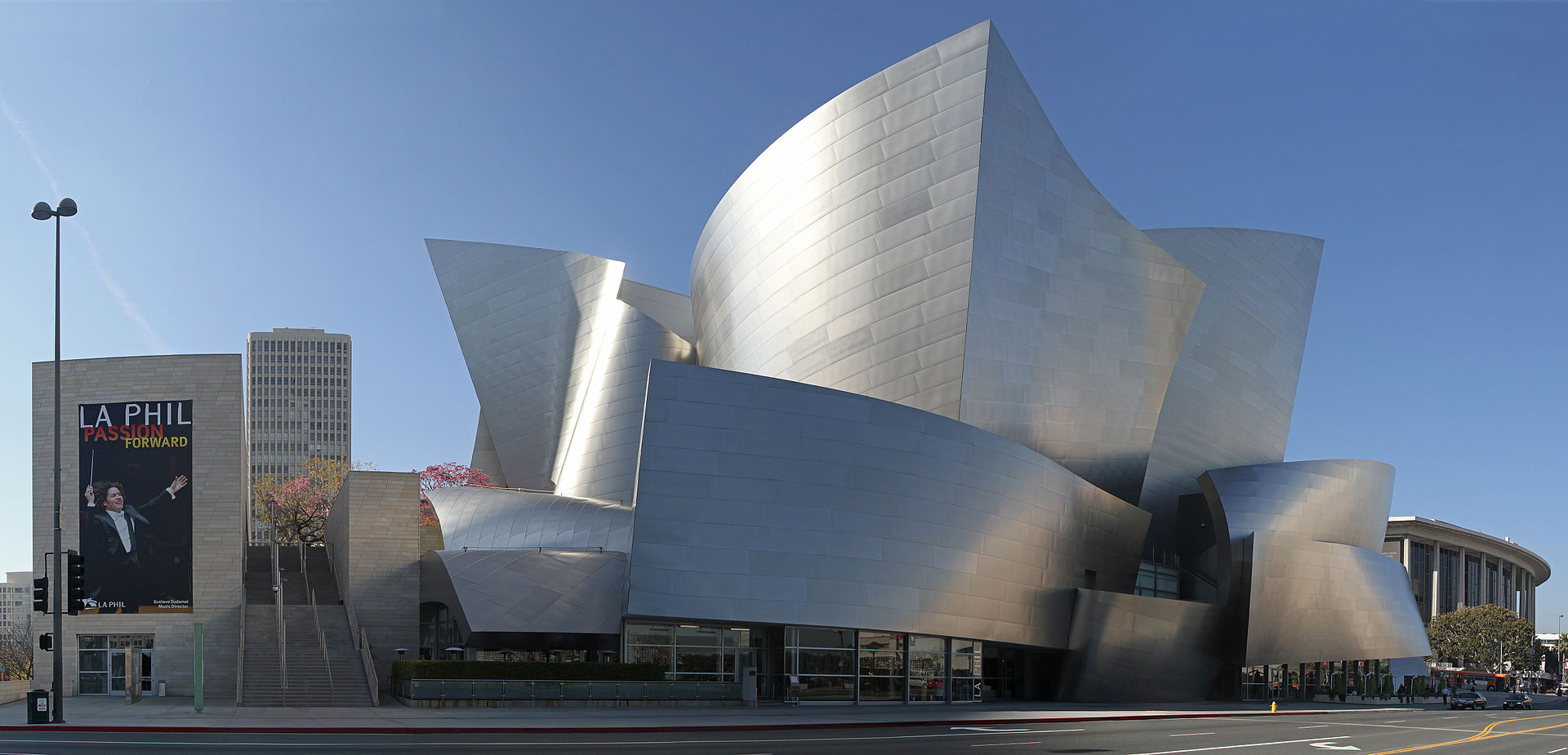
Postmodern Architecture
Style that is unique and nontraditional - as a reaction against the perceived uniformity, austerity, and rigid focus on function of modern architecture
Key Characteristics of Postmodern Architecture
Eclecticism and Historicism - use of historical architectural styles (columns, arches) with modern materials and technology
Ornamentation and Decoration - use of decorative elements, embracing color, patterns, and surface ornamentations
Contextualism - attempt to use more local context, culture, and history of the place where being built
Whimsy and Irony - use of playful, unconventional forms, exaggerated proportions, and even metaphorical shapes

Sense of Place
Refers to the emotional and subjective connections people have with a specific geographic location. It is the feeling, meaning, and character that a place is perceived to have, which is shaped by human experience, memory, and culture
Components of Sense of Place
Physical Attributes - Unique natural and built features of a place (ocean, mountain range, local architecture)
Human Attributes - Culture, history, language, traditions
Personal Experience - Memories and emotional bonds
Stimulus Diffusion
Form of expansion diffusion where the underlying principle or idea of a cultural trait spreads, even though the specific original characteristic or trait itself does not diffuse
Key Characteristics of Stimulus Diffusion
Core concept adopted, but specific item is rejected or cannot be implemented in the new environment
Idea adapted to local conditions, resources, or cultural values, creating a new, unique, yet related trait
Usually the result of barriers (cultural, economic, or environmental) that prevent adoption of original item
Cultural Landscape
Visible imprint of human activity on the natural environment. It shows how human practices, beliefs, and values shape and modify the physical surroundings. ANYTHING humans do to modify/change the landscape/environment
Key Characteristics of Cultural Landscape
Physical and Built Features - buildings, roads, monuments, infrastructure - the built environment
Agricultural and Industrial Practices - factories/manufacturing, farms
Religious and Linguistic Characteristics - Churches, mosques, temples, cemeteries, and language visible on signs or place names (toponym)
Culture
Comprises the shared practices, technologies, attitudes, and behaviors transmitted by a society
The beliefs, values, practices, behaviors, and technologies shared by a society and passed down from generation to generation
Gendered Spaces
Areas or environments that are socially constructed to be primarily associated with, restricted to, or designed for a specific gender
Spaces reflect and reinforce societal gender roles, expectations, and power structures by influencing how different genders are expected to behave, work, and interact within a given location
Types of Gendered Spaces
Public-Private divide - historically private spaces are often female-associated and public space is male-associated
Physical and Structural Design - design of built environment can intentionally (or unintentionally) accommodate or restrict certain groups (schools or places or worship)
Sequent Occupancy
Notion that successive societies leave their cultural imprints on a place, each contributing to the cumulative cultural landscape
Cultural Imprints
Architecture and Infrastructure - distinct building styles, road patterns, and historic structures left by past societies
Land Use - changes in agricultural practices, resource exploitation, and urban development over time
Place Names (Toponyms) - names of cities, rivers, and streets reflect the language of former groups
Social and Cultural Practices - enduring traditions, religious sites, and foodways that have been passed down or blended
Commodification
Process of transforming a good, service, idea, or cultural artifact that previously was not regarded as an object to be bought or sold into a commodity that has monetary value and can be traded in a market economy
Cultural Appropriation
Unauthorized adoption or use of elements from one culture by members of a different and typically dominant culture, often without consent, proper credit, or a deep understanding of the elements' original context and significance
Examples of Cultural Appropriation
Fashion - major retailer mass-producing and selling designs inspired by Indigenous or marginalized cultures without proper acknowledgment
Symbolism - non-native individuals wearing Native American headdresses as fashion statements without understanding their cultural significance
Language/Music - taking phrases or musical styles (blues/jazz/rap) from African American vernacular
Cultural Trait
Single, distinguishing characteristic of a culture. It is the smallest element that can be recognized, learned, and transmitted from one person to another - includes such things as food preferences, architecture, and land use
Ethnic Enclave
A geographical area where a particular ethnic group is spatially clustered and socially and economically distinct from the majority group
Key Characteristics of Ethnic Enclave
Cultural Preservation - “safe space” where immigrants can maintain their language, religion, foodways, and social customs without pressure to assimilate into host culture
Cultural Landscape - create a distinct cultural landscape using unique architecture, bilingual signs (toponyms), and ethnic shops
Examples of Ethnic Enclave
Chinatown - cities like San Francisco, New York City, and Chicago
Little Havana - Cuban Americans in Miami
Koreatown - Korean Americans in Los Angeles and Chicago

Relocation Diffusion
Spread of an idea through physical movement of people from one place to another
When people migrate they bring aspects of culture with them (language, religion, food, dress, architecture, etc.)
Modern Architecture
Functional, rational, and orderly architecture that used simple, geometric forms (rectangular, box-like), new materials (glass, steel, concrete), flat roofs, with a lack of ornamentation and an emphasis on open spaces and natural light

Material Culture
Refers to the physical objects, resources, and spaces that a group of people uses to define their culture (comprised of artifacts)
Key Characteristics and Examples
Architecture and Shelter - housing places of worship, monuments, and commercial buildings
Tools and Technology - infrastructure (transportation, communication, utilities)
Clothing and Adornment - traditional dress, uniforms
Foodways - specific food and utensils
Art - paintings, sculptures, pottery
Nonmaterial Culture
Refers to the intangible concepts, ideas, beliefs, and values that shape a society. It is the part of culture that cannot be seen or touched but profoundly influences human behavior and interactions such as norms, customs, languages, and rituals
Colonialism/Imperialism
The policy and practice of extending a country's power and influence through colonization, military force, or other means, often resulting in the domination and exploitation of a territory and its people and the establishment of control over foreign lands and resources
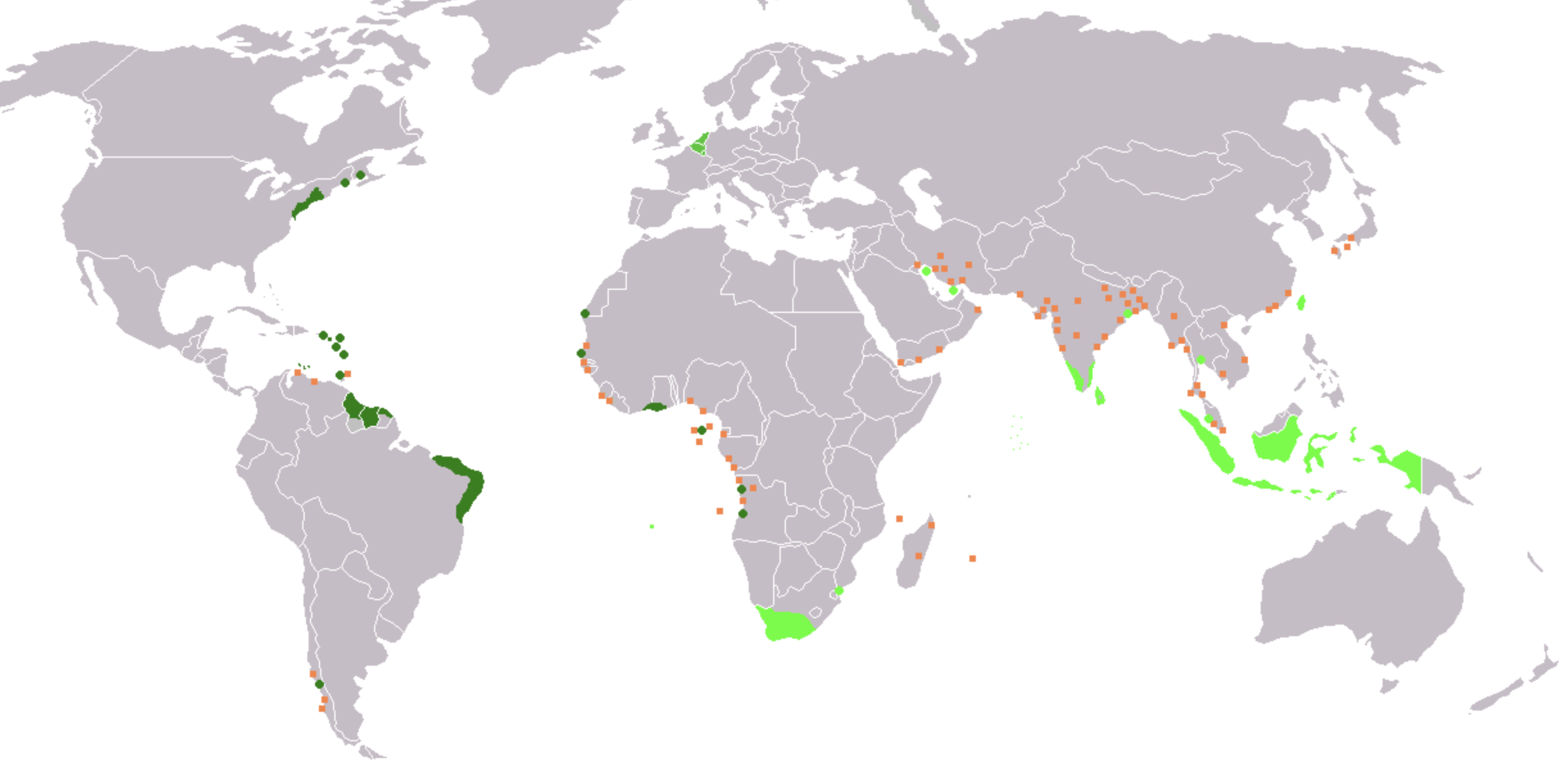
British Colonization
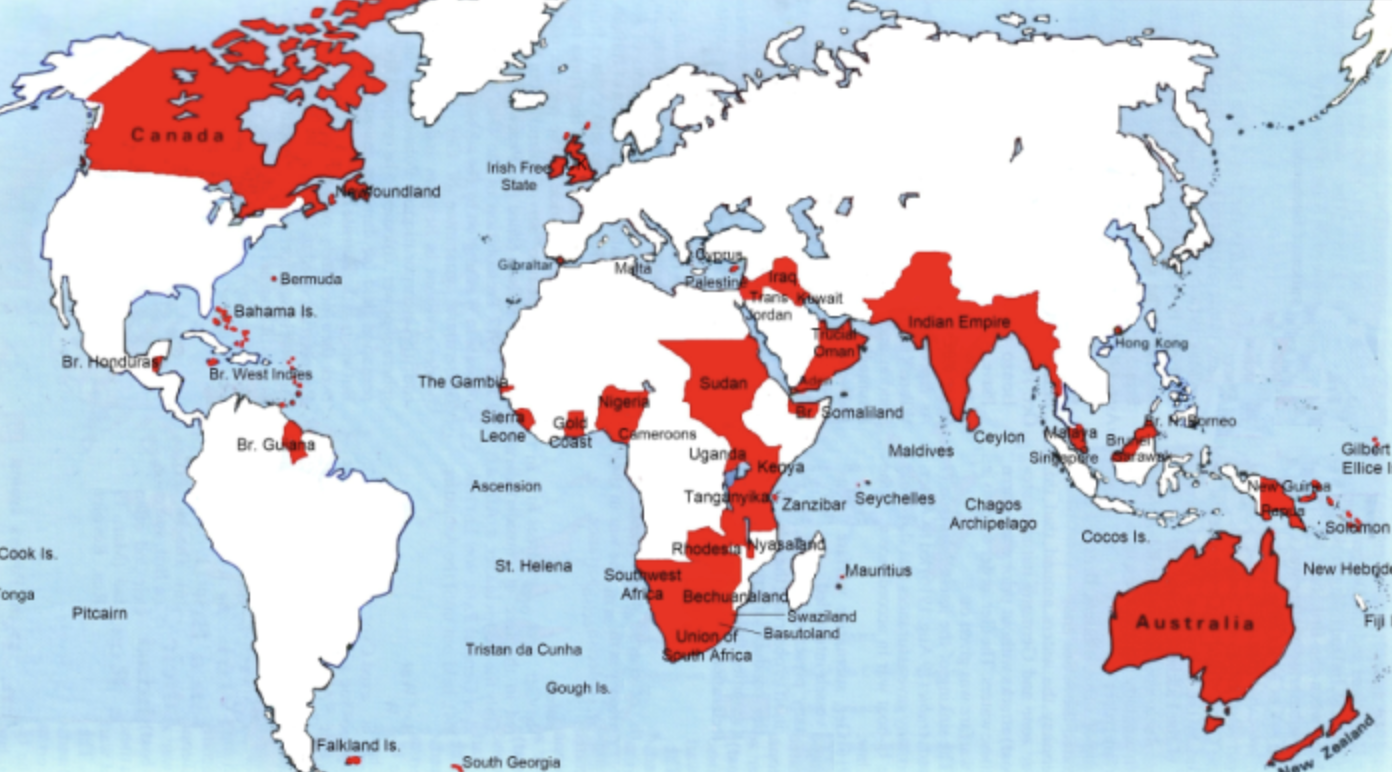
French Colonization
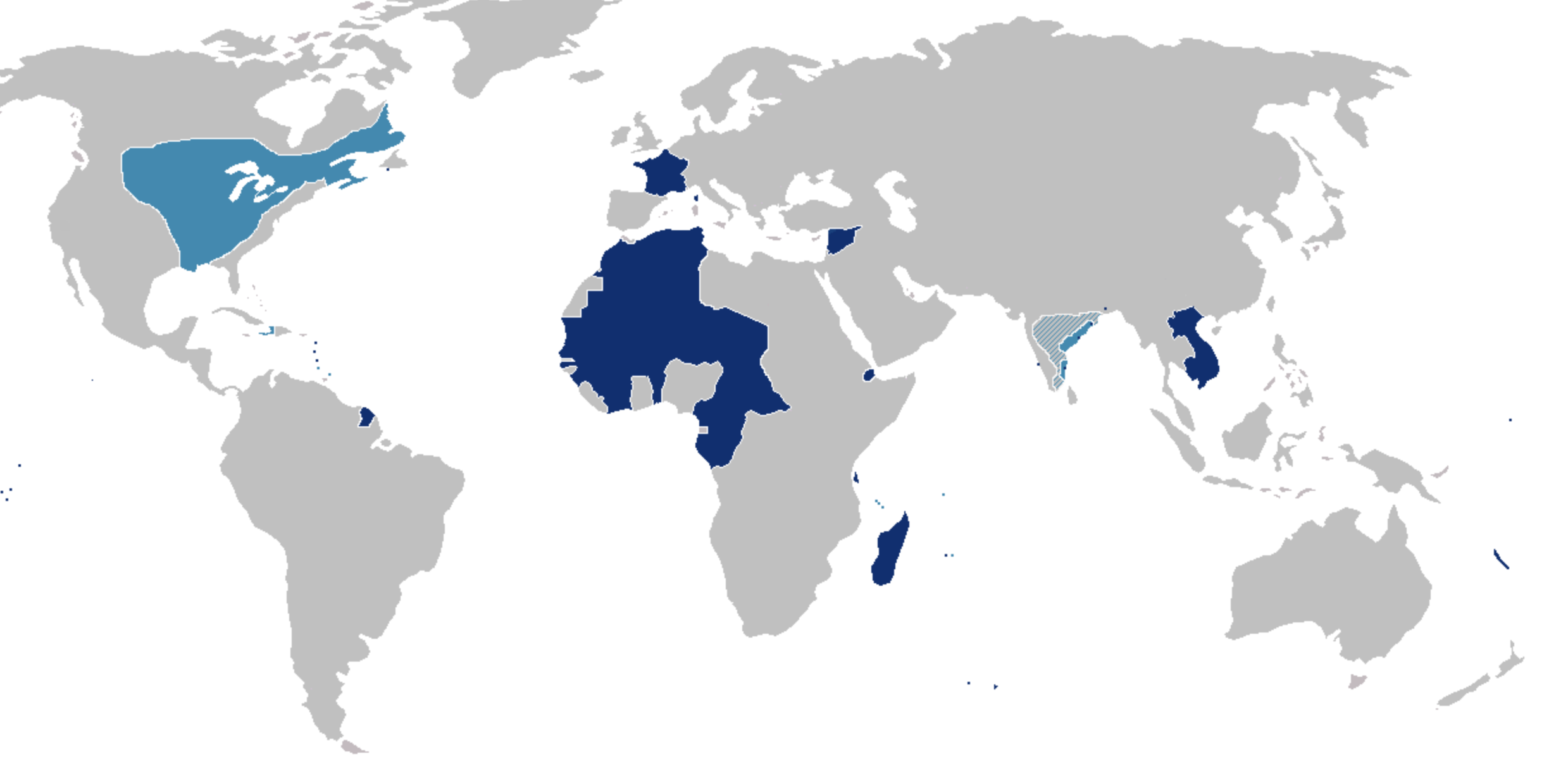
Spanish Colonization
Portuguese Colonization
Dutch (Netherlands) Colonization