NUR 215 Cumulative final
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What are the 3 main factors for TNM staging system?
Tumor (T): This indicates the size and extent of the primary tumor. It ranges from TX (tumor cannot be evaluated) to T4 (large tumor with extensive involvement).
Nodes (N): This describes the extent of spread to nearby lymph nodes, from NX (nodes cannot be evaluated) to N3b (extensive lymph node involvement).
Metastasis (M): This shows whether cancer has spread to other parts of the body, with M0 indicating no distant metastasis and M1-M3 indicating increasing levels of metastasis.
What are the 4 types of Neutropenic precautions?
Room environment
Restricted visitors
Hygiene practices
Patient care.
What are some examples of Room environment for neutropenic precautions?
Keep the door closed at all times.
No flowers, plants, fresh fruits, or vegetables are allowed in the room to prevent exposure to potential pathogens.
What are some examples of patient care for neutropenic precautions?
Patients should wear a basic isolation face mask when leaving the room.
Dietary restrictions include avoiding raw meats, seafood, deli foods, and partially cooked eggs.
What are some examples of hygiene practices that are used for neutropenic precautions?
Wash hands thoroughly when entering and exiting the room.
Visitors with infections or colds should not visit.
What are some dietary precautions for neutropenic precautions?
Dietary restrictions include avoiding raw meats, seafood, deli foods, and partially cooked eggs.
No fresh fruit or vegetables are allowed.
What is Hyperplasia?
is an increase in the number or density of normal cells. Hyperplasia occurs in response to stress, increased metabolic demands, or elevated levels of hormones.
What is Metaplasia?
is a reversible change in which one adult cell type, such as epithelial, is replaced by another adult cell type.
EX: in the lungs of smokers, where normal ciliated epithelium may be replaced by a squamous stratified epithelium known as squamous metaplasia.
What is Dysplasia?
disturbed cell growth of specific tissue.
Ex: changes in the cervix in response to continued irritation, such as from the human papillomavirus, and leukoplakia on oral mucous membranes in response to chronic irritation from smoking.
What is anaplasia?
is the regression of a cell to an immature or undifferentiated cell type.
Ex: Anaplastic cell division is no longer under DNA control. It is often associated with malignancies and is one of the criteria used to grade the aggressiveness of cancer cells.
What are modifiable risk factors?
These are risk factors such as smoking, lack of exercise, and nutrition, that a person can change to minimize the risk of developing cancer.
Women between the ages of 21-29 should have a PAP test how often?
Every 3 years
For women ages 30–65, screening with both HPV testing and Pap test (preferred) every
5 years or every 3 years with Pap test alone (acceptable).
What is Iron deficiency anemia?
develops when the body’s supply of iron is inadequate for optimal RBC formation. The body cannot synthesize hemoglobin without iron.
What is Folic acid anemia?
is characterized by fragile, megaloblastic (large and immature) cells. Folic acid is found in green leafy vegetables, fruits, cereals, and meats and is absorbed from the intestines.
Maternal folic acid deficiency is strongly associated with
neural tube defects, such as meningomyelocele.
Thalassemia is
is an inherited disorder of hemoglobin synthesis in which either the alpha or beta chains of the hemoglobin molecule are missing or defective.
Ex: Bullseye appearance
Acquired Aplastic Anemia is
rare, the bone marrow fails to produce all three types of blood cells, leading to pancytopenia, a deficiency in both red and white blood cells.
What is Anuria?
is less than 100 mL of urine production per day
What is Oliguria?
is scant urine output, usually less than 400 mL/day or 30 mL/hour for an adult
What is Dysuria?
voiding that is either painful or difficult
What is Polyuria?
is the production of abnormally large amounts of urine by the kidneys—often several liters more than the patient’s usual daily output.
What is Nocturia?
is voiding at night or during usual sleep time
What are signs and symptoms of Thalassemia?
Patients with the major form of thalassemia can develop fractures of the long bones secondary to bone marrow expansion and thinning of bones caused by increased hematopoiesis. Jaundice occurs secondary to hemolysis, and the accumulation of iron in the liver can lead to hepatic failure.
Patients with pernicious anemia present with
pallor; a sore, beefy red tongue; and paresthesia
Clinical manifestations of vitamin B12 anemia include
pallor; weakness; sore, beefy red tongue; paresthesia; and difficulty maintaining balance.
What’s the difference between vitamin b12 deficiency and Pernicious Anemia?
Pernicious Anemia is an autoimmune form of B12 deficiency where the body attacks cells in the stomach that produce intrinsic factor, a protein needed to absorb B12.
B12 deficiency is a condition where the body lacks enough vitamin B12 (cobalamin), which is essential for making red blood cells and maintaining nerve function.
A patient 6 hours postsurgery for a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) complains of symptoms indicating to the nurse that he may be experiencing bladder spasms.
Which medication should the nurse anticipate administering?
Rectal Belladonna and Opiod Suppositories
What are the four core competencies for interprofessional collaborative practice?
Values and Ethics for Interprofessional Practice – Working with individuals of other professions to maintain a climate of mutual respect and shared values.
Roles and Responsibilities – Understanding one’s own role and the roles of other professions to assess and address the healthcare needs of patients and populations.
Interprofessional Communication – Communicating with patients, families, communities, and professionals in health and other fields in a responsive and responsible manner.
Teams and Teamwork – Applying relationship-building values and principles of team dynamics to perform effectively in different team roles.
Four overarching categories of scope of collaboration include are?
Nurse-Patient
Nurse-Nurse
Interprofessional
Interorganizational
6 standards called the nursing process are?
Assessment
Diagnosis
Outcomes identification
Planning
Implementation
Evaluation
Nurse to nurse collaboration examples:
Shift handoff communication
Delegation and supervision
Coordinating patient care
Mentoring
conflict resolution
When a RN delegates what must he or she always do?
Supervise
What are the 5 rights of Delegation?
Right Circumstance
Right Task
Right Person
Right Direction and Communication (clear, concise, correct, and complete)
Right Supervision
Can you name the nursing chain of command?
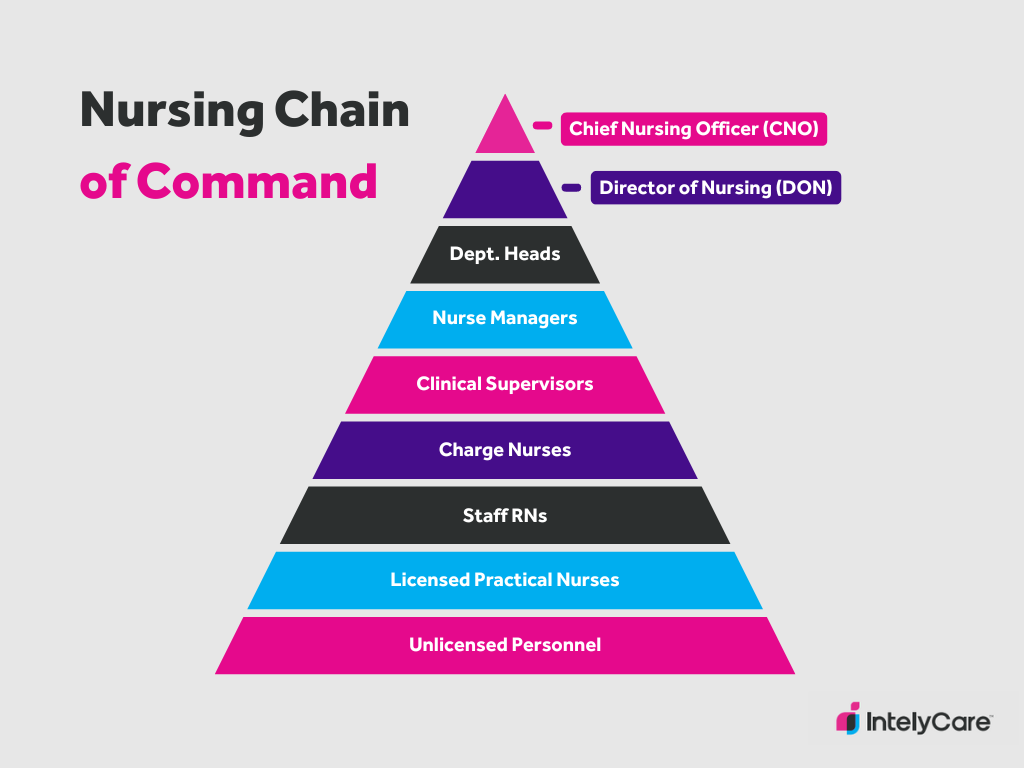
What are the 4 types of Accountability?
Professional Accountability Taking responsibility for maintaining competence, adhering to ethical standards, and upholding the integrity of the profession.
Legal Accountability Following laws, regulations, and institutional policies—like scope of practice and documentation standards—to avoid negligence or malpractice.
Ethical Accountability Making decisions based on moral principles, such as patient autonomy, beneficence, and justice—even when it’s difficult.
Personal Accountability Owning your actions, being honest about mistakes, and striving for continuous improvement in your practice.
what are the Institute of Medicine Core Competencies?
Provide patient centered care
Work in interdisciplinary teams
Employ evidence-based practice
Apply quality improvement
Utilize Informatics
What is Clinical decision support (CDS) when it comes to nursing informatics?
Clinical decision support (CDS) systems provide tools such as alerts, reminders, and guidelines to assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions. An alert about a potential drug interaction is a classic example of CDS.
Which of the following is a key responsibility of a nurse informaticist?
focuses on developing, implementing, and optimizing healthcare technology systems to improve patient care and workflow efficiency.
What are the 4 steps of evidence-based practice?
Pose a question
Gather the best evidence
Evaluate the evidence
Apply the evidence to clinical practice.
4 Consequences of lack of accountability in nursing practice?
Increased risk to patient safety
Increased healthcare costs
poor nurse patient and interprofessional relationships
loss of job or nursing license
Whats the difference between Class 3 and Class 4 Drugs?
Class 3 are combination drugs w/ less than 15mgs of Hydrocodone per dosage unit or products not containing more than 90mgs of codeine per dosage unit. Examples: Tylenol w/ Codeine, Suboxone, and Vicodin
Class 4- These are your sedatives/barbiturates Examples: Xanax, Klonopin, Versed, and Temazepam.
What type of drugs are Class 5?
These are your cough suppressants.
Examples: Robitussin and Phenergan
What’s the difference between the Class 1 and Class 2 drug classes?
Class 1 are substances that have no currently accepted medical use in the United States. EX: LSD, Peyote, Ecstacy, and Marijuana.
Class 2 are substances that have been approved for medical use but have a very high potential for abuse. Ex: Morphine, Hydromorphone, Fentanyl, Adderall, Oxycodone
Name these common Abbreviations
sc
ac
ad lib
hs
pc
tid
sc: Subcutaneous
ac: before meals
ad lib: as desired
hs: hours of sleep
pc: after meals
tid: 3 times a day
What do these common abbreviations mean?
qs
od
os
ou
qs: quantity sufficient
od: right eye
os: Left eye
ou: Both eyes
1 kg = g = lbs.
1 kg = 1000 g = 2.2 lbs.
1 ml of urine weighs how many grams?
1 gram
1t (teaspoon) equals how many ml?
5 ml
Warfarin Therapeutic INR level is?
Antidote?
INR: 2-3.5
Antidote: Vitamin K
Levothyroxine therapeutic level for TSH is?
Antidote?
TSH: 0.4-4
Antidote: none specific, propranolol could be used. (beta blocker)
Digoxin therapeutic level is?
Antidote?
0.5-2
Antidote: Digibind
Therapeutic level for Lithium?
Antidote?
0.5-1.5, shouldnt exceed 2
Antidote: none
Phenytoin therapeutic level?
unbound level?
Antidote?
Total 10-20
Unbound: 1-2
Antidote: None
Theophylline Therapeutic level?
antidote?
10-15, toxicity over 20
antidote: none, can use charcoal.
Lithium signs of toxicity are?
Confusion
drowsiness
slurred speech
uncontrollable shaking
Distinct symptom of Digoxin toxicity is?
Yellow-green visual discoloration
Signs of Phenytoin toxicity is?
Poor muscle control (ataxia)
Side to side eye movement (nystagmus)
Theophylline signs and symptoms of toxicity are?
Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Tremors or seizures
How can you tell if a drug is a controlled substance?
There will be a C with a numerical value inside it on the drug label.
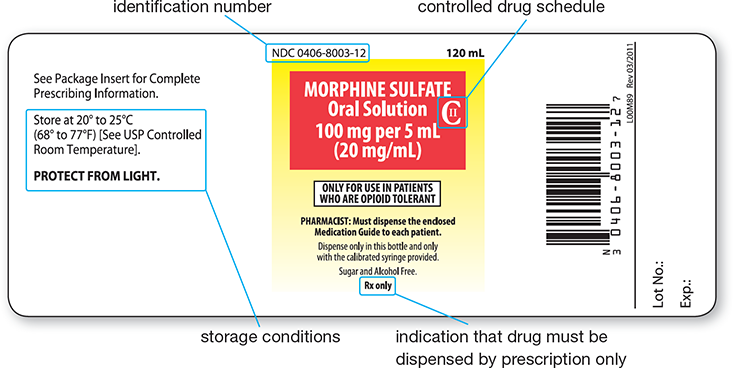
What organ is the primary site for drug metabolism?
Liver
What are some things that can alter the Absorption of medications?
Blood flow
Pain
Stress
Hunger
Fasting
Food
PH
Method of administration
What organ is the most common site of excretion for medications?
Kidneys
Other sites of excretion include:
Bile
Feces
Lungs
Saliva
Sweat
Breast Milk
The four sequential processes of the Pharmacokinetic phase are?
often referred to as ADME, are Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion
Does a low or high therapeutic index range need to be monitored to prevent toxicity?
Low therapeutic index- means that the difference between the minimum effective dose of a medication and the dose that causes toxicity is small.
A drug bound to a protein is an active or inactive drug?
Inactive
The 7 Rights of Medication administration are:
Patient
Drug
Dose
Route
Time
Documentation
Assessment
Most common SubQ sites are:
Back of the upper arm
Abdomen (2 inches away from umbilicus)
Upper thigh
Three common sites for IM injections are:
Vastus Lateralis- the largest muscle of the quadriceps group, located on the outer side of the thigh.
Deltoid- find the acromion process (the bony point of the shoulder), then locate the injection site about 2-3 fingerbreadths (approximately 2 inches) below the acromion, within the central, thickest portion of the deltoid muscle.
Ventrogluteal- Greater trochanter, iliac crest
What is the max ml’s for a deltoid IM?
2 ml
What degree should the needle be at for IM, SubQ, and Intradermal ID?
IM- 90 degrees
Subq-45 degrees
ID- 15 degrees
What route of administration of Insulin is the most common? What about the most rare route and why?
Most common- Subcutaneous route (abdomen)
Most rare- IM, this is because it utilizes concentrated regular insulin
Why is the abdomen the preferred site for subcutaneous insulin?
Because it allows for the fastest and most predictable absorption.
1 oz = ml = T = t
1oz = 30ml= 2T= 6t
T= Tablespoon
t= teaspoon
1qt = pt = cups = oz
1qt = 2 pt = 4cups = 32oz
If 1 quart (32 fluid ounces) is equal to 1 Liter, then 8 fluid ounces is how many milliliters (ml)?
240 ml
If 1 pint (16 fluid ounces) is equal to 500 ml, then how many ml are in 1 fluid ounce?
30 ml
if 1 measuring cup is 8 ounces and 1 ounce equals 2 T (tablespoons), then how many (t) teaspoons are in 8 ounces?
48 teaspoons
1 Tablespoon = 3 teaspoons
If 1-inch equals 2.5 cm and 1cm equals 10mm, then how many mm is 4 inches?
100 mm