Surgery EOR: Preoperative/Postoperative Care
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
205 Terms
When can a patient eat prior to a major surgery?
NPO after midnight or at least 8 hours
What risks should be discussed with all patients and documented on the consent form for a surgical procedure?
Risk: Bleeding, infection, anesthesia, scars
If a patient is on anti-HTN meds should the patient take them on the day of the procedure?
Yes
Should a patient who smokes cigarettes stop before an operation?
Yes - improvement is seen in just 2-4 weeks of smoking cessation
What lab test must all women of childbearing age have before entering the OR?
B-Hcg and CBC
What is a preop colon surgery "bowel prep"?
Bowel prep with a colon cathartic (GoLYTELY), oral abx (neomycin, erythromycin), IV antibiotic before incidsion
What must you always order preoperatively for you patient undergoing a major surgery?
1. NPO/IVF
2. Preop abx
3. Type and cross blood (PRBCs)
What electrolyte must you check preoperatively if a patient is on hemodialysis?
Potassium
Who gets a preop EKG?
Patients over 40 or undergoing cardiac procedure
What is the most important preoperative eval performed by the surgical team?
H&P - no documentation exists linking a reduction in mortality and morbidity to routine lab testing in otherwise healthy patients undergoing elective procedures
Detailed H&P prior to surgery including special attention to...
Hx of CVA, heart dz, pulm dz, renal dz, liver dz, GI d/o, DM, prior surgeries, bleeding problems, clotting problems, difficulty w/ anesthesia, nutrition, etoh, illicit drugs
What is an ASA score?
American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) classification system which stratifies the degree of perioperative risk for patients
Describe the ASA classification system
ASA 1: Normal healthy patient
ASA 2: Patient with mild systemic disease
ASA 3: Patient with severe systemic disease
ASA 4: Patient with severe systemic disease with a constant threat to life
ASA 5: Moribound patient who are not expected to survive without an operation
ASA 6: Brain dead patient
Mouth PE important to note
Teeth - if loose worry about intubation
Tongue - think sleep apnea if large
Jaw - TMJ could be difficult intubation
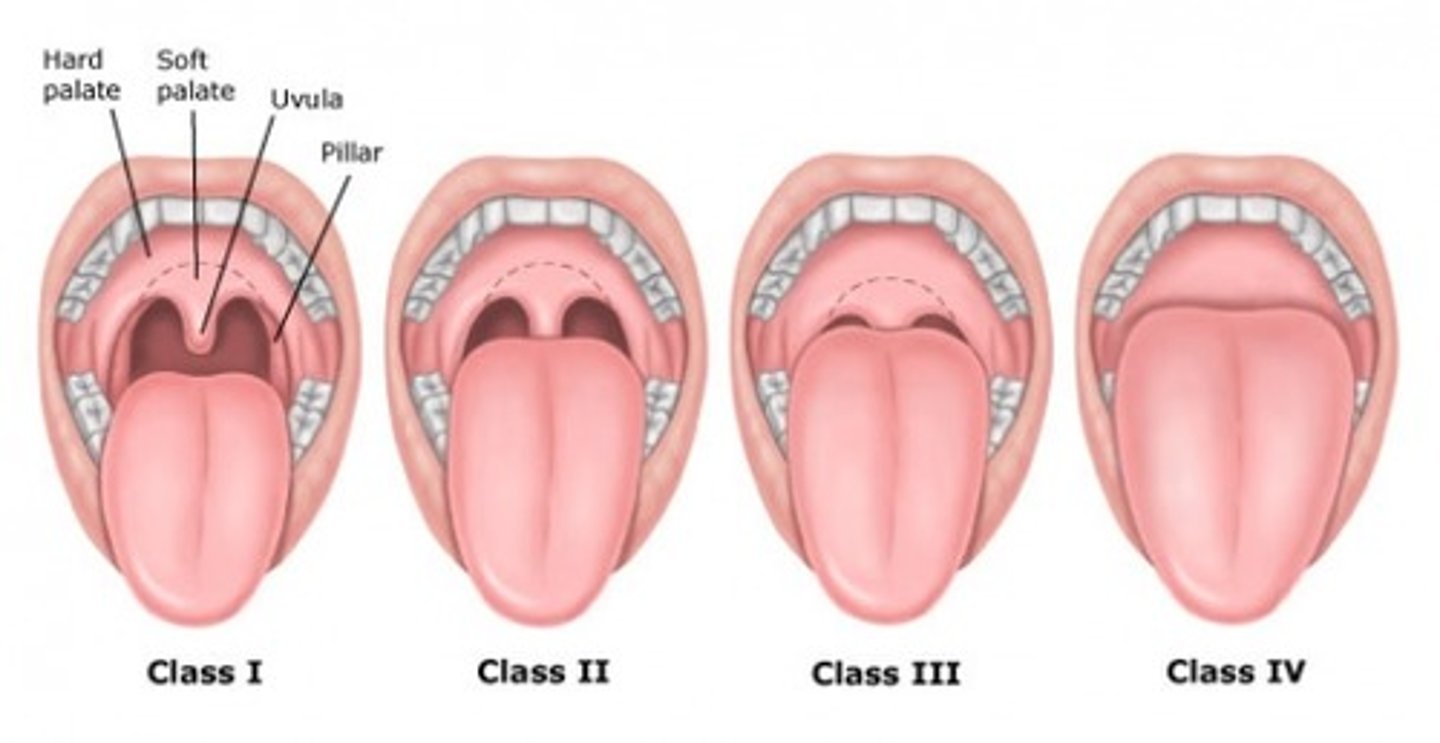
Mallampati score
Airway concerns with surgery
Tracheal deviation - can be issue for maintaining airway during surgery
Neck concerns with surgery
If >17in there is concern for sleep apnea, masses, deformities, ROM
Mallampati score
Classifies how open the airway is
1 - Can see the uvula, no prob w/ intubation
IV- No uvula, hard intubation
Routine preop labs/tests for patients with cardiac disease/vascular disease?
CBC
EKG
What are major cardiac risk factors for surgery?
Unstable coronary syndromes
Recent MI
Severe valvular disease
Ventricular arrhythmias
What are minor cardiac risk factors for surgery?
Hx of CVA
Uncontrolled HTN
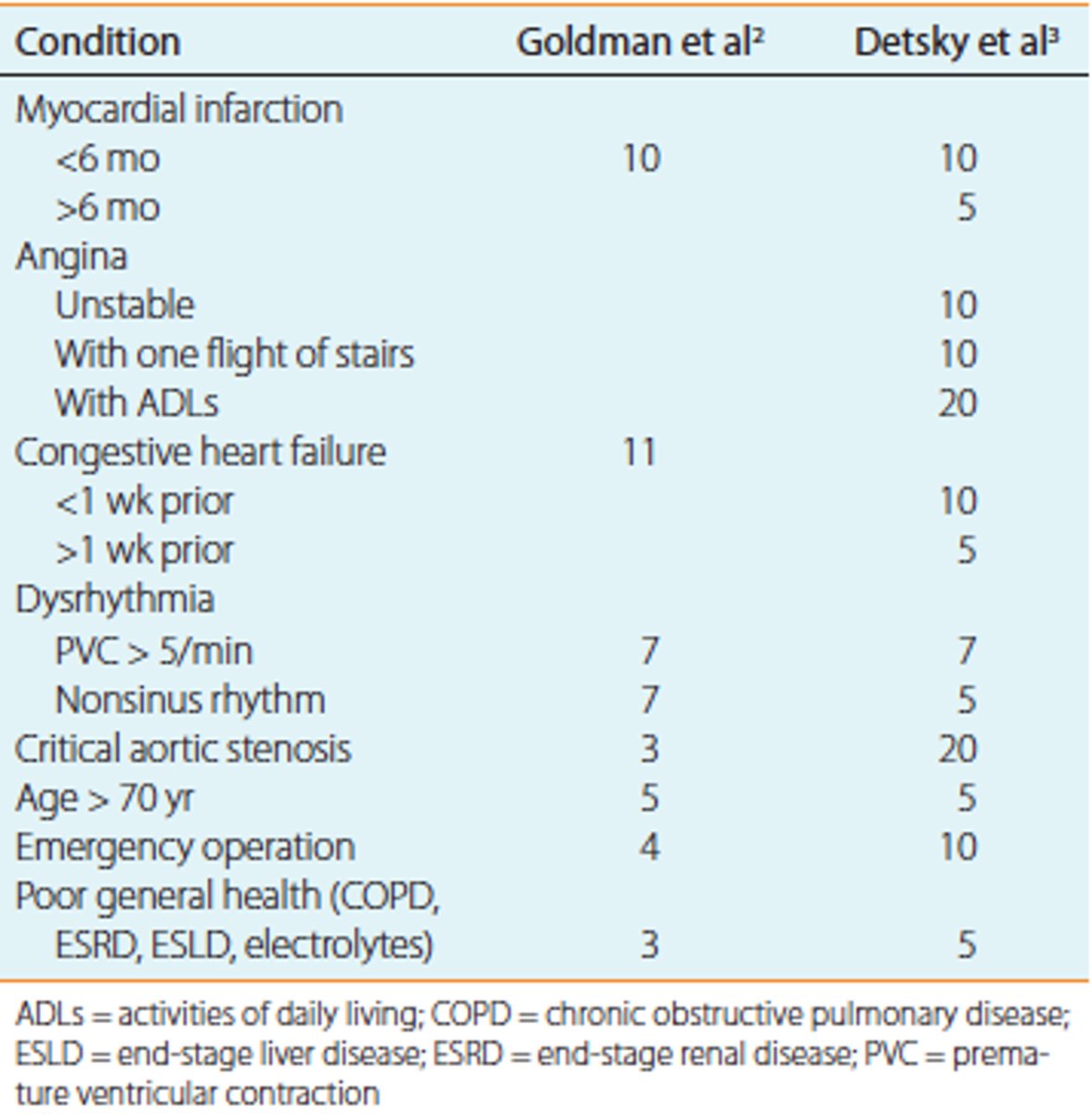
What is the Goldman Criteria for Cardiac Risk?
Assesses risk of perioperative fatal and nonfatal cardiac events. Another used is Detsky's
What are moderate cardiac risk factors for surgery?
Asymptomatic MI
DM
Compensated CHF
What is Lee's revised cardiac risk index?
Validated way to predict risk in patients who undergo elective noncardiac procedures. There are 6 predictors (each get one point):
History of ischemic heart disease
CHF
Hx of CVA
High-risk operation
Preoperative treatment with insulin
Preoperative SCr >2.0 mg/dL
Goldman criteria points
0-5 = Class I
6-12 = Class 2
13-25 = Class 3
>25 = Class 4
Preop lab assessment for cardiac disease?
Resting LV function
Ambulatory EKG monitoring
Exercise stress test or nuclear stress test
Stress echo
Patients with an EF <___% are at greatest risk for complications during surgery
<35%
What are indications for preop coronary angiography?
Patients with suspected left main disease, triple vessel coronary occlusive disease, or unstable coronary syndromes (high risk patients)
What is appropriate medical therapy for CAD prior to surgery?
BB, CCBs, nitrates to ensure myocardial oxygen demand does not exceed supply
What do patients with a history of rheumatic heart disease require prior to surgery?
Prophylactic antibiotics to prevent endocarditis
What should you do if you find your patient to have carotid artery disease?
Endorterectomy prior to surgery - wait 6 months before operation if possible
What are the 2 big things to worry about in surgery w/ a cardiac patient
1. Catecholamine surge which causes an increase in myocardial o2 demand
2. Suppression in the fibrinolytic system which leads to thrombosis
What kind of murmurs are usually benign?
Short, soft, systolic murmurs that are asymptomatic often don't require further investigation
What are risk factors for postop pulmonary complications (PPC)?
Advanced age
Elevated ASA class
CHF
Functional dependence
COPD
Sleep apnea
Smoking status
Low arterial O2 sat
Anemia
Upper abdominal/thoracic operations
Duration of operations over 2 hours
Emergency surgery
Routine preop labs/tests for pulmonary disease?
CBC
EKG
CXR
CXR screening guidelines
All >60
Patients with cardiac/lung disease
Patients undergoing thoracic procedure
Patient education to reduce risk of PPC?
Use of incentive spirometry
Deep inspiration
Coughing
Smoking cessation
Early mobilization
Oral hygiene
Use of CPAP/BiPAP
Clinical features of thrombophlebitis/DVT?
Dull pain
Erythema
Tenderness
Induration of involved vein
Swelling of involved area with heat and redness
Homan's sign (unreliable)
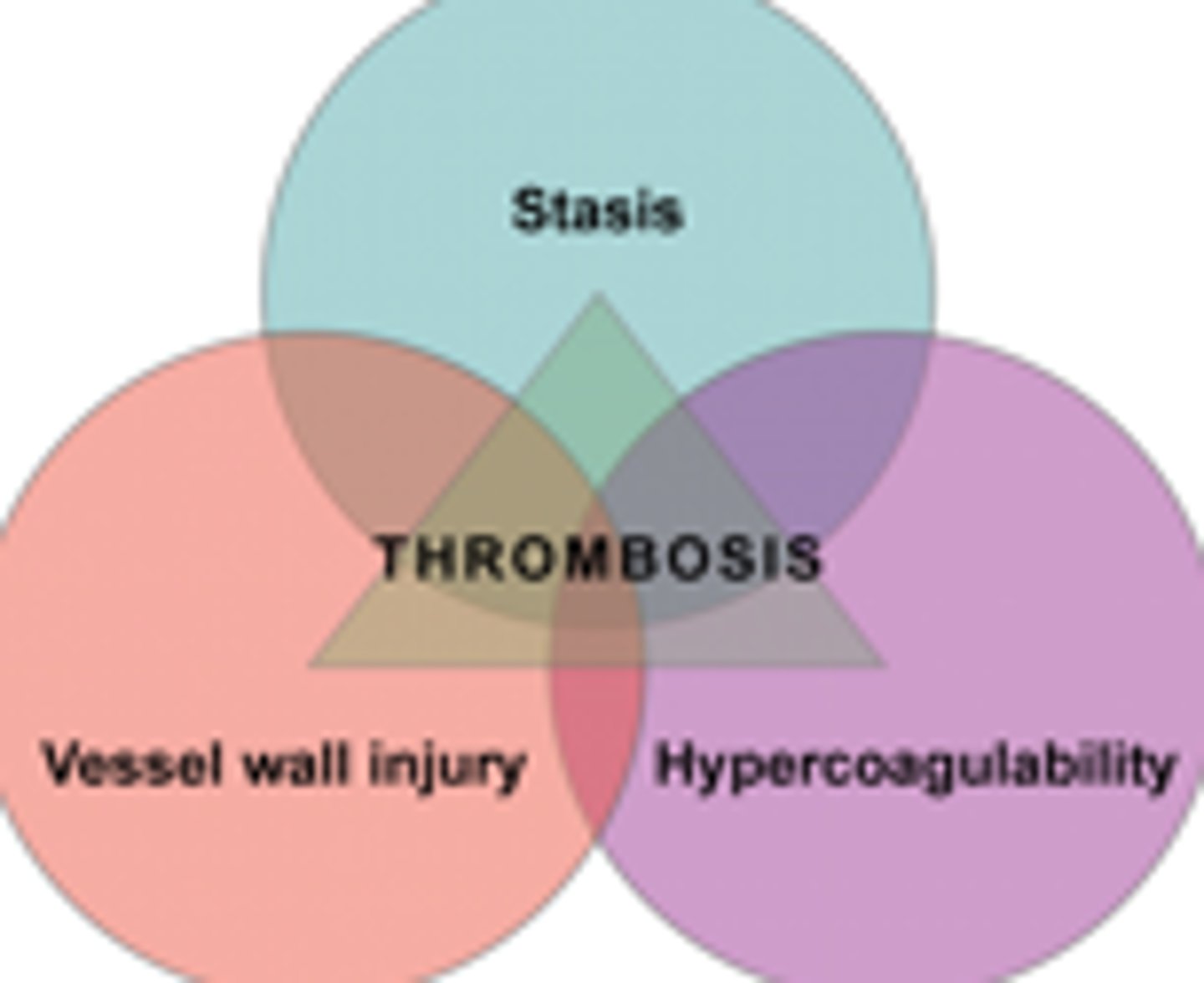
What is Virchow's triad?
Used to identify patients at risk for VTE
Risk factors for DVT?
Prolonged bed rest/immobility
Ortho surgery (total hip replacement)
Long air travel
Malignancy
Nephrotic syndrome
Use of OCPs/HRT
Hypercoagulable state (Pregnancy, Factor V Leiden)
Where does a DVT most commonly occur?
Lower extremities (Long saphenous vein)
Pelvis
Diagnostic test for DVT?
Duplex ultrasound <---preferred study
Venography <--- most accurate study, rarely done
D-dimer (neg is <500)
Spiral CT if PE is suspected (or VQ scan if there is renal impairment)
Treatment for thrombophlebitis/DVT?
Superficial thrombophlebitis is treated with bed rest, local heat, elevation of extremity, NSAIDs
Antibiotics
Surgical intervention if serious
When should DVT prophylaxis be started?
Preoperatively because it is thought that thrombosis starts as early as at the induction of anesthesia
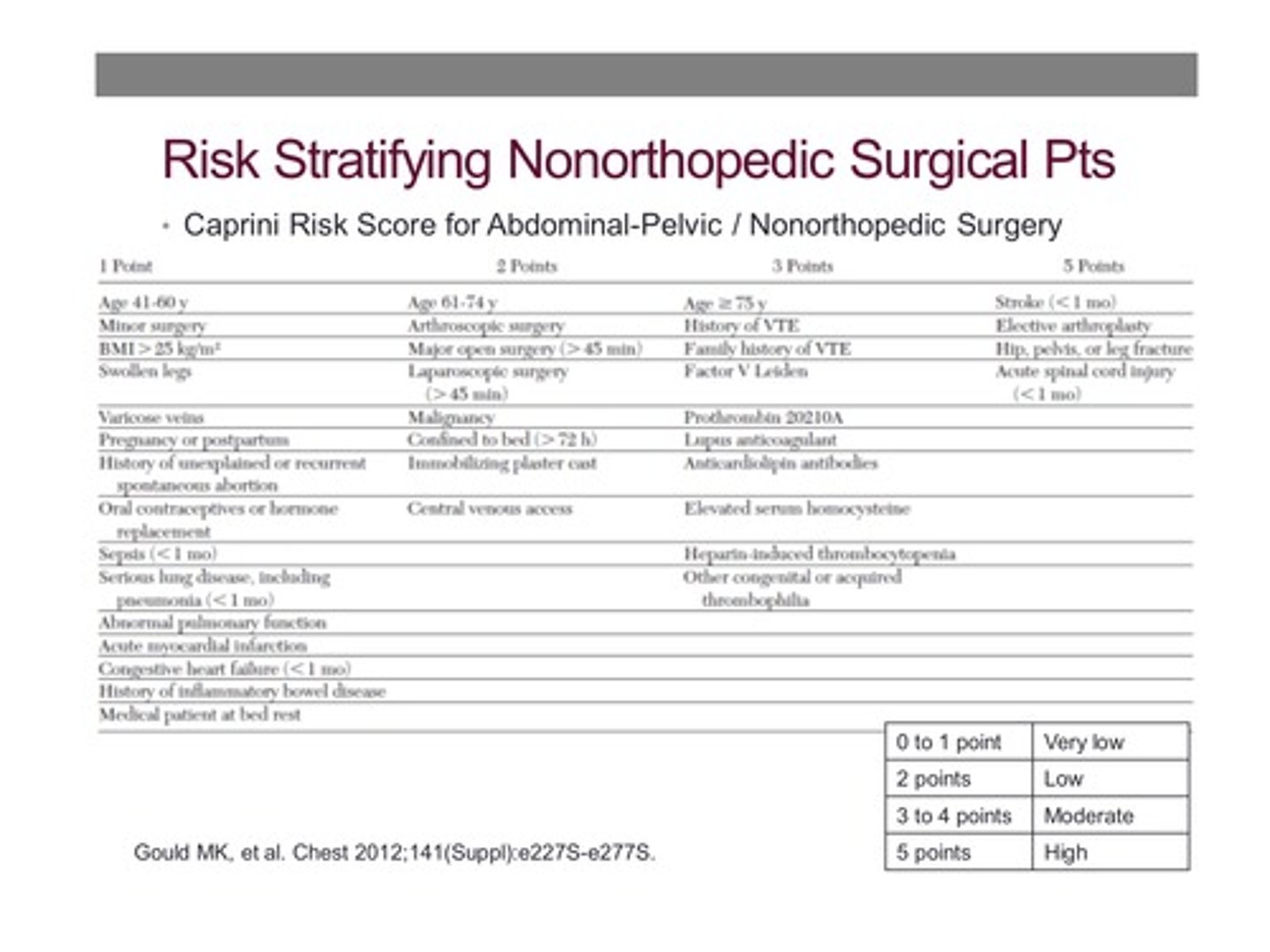
What is the Caprini score?
Elaborate risk factor index for DVT
What is Wells Criteria?
Predicts risk for PE
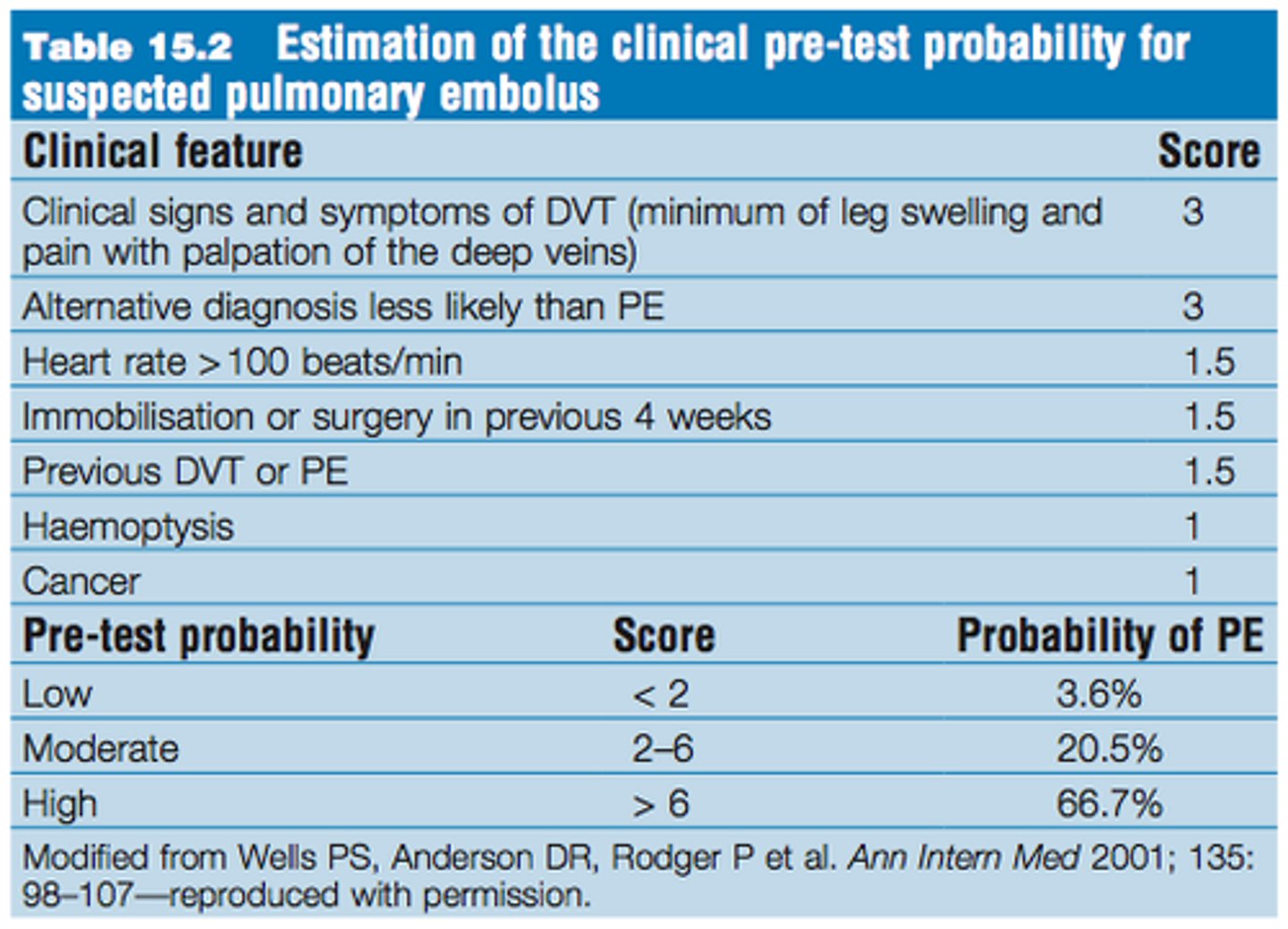
What are VTE prophylaxis options?
Unfractionated heparin
Enoxaparin (low molecular weight heparin)
Warfarin
Fondaparinux
SCDs
Greenfield filter insertion
Dextran
How is unfractionated heparin dosed for DVT prophylaxis?
5000 units given SQ every 8 or 12 hours until patient is fully ambulatory
How is LMWH dosed for DVT prophylaxis?
40mg SQ daily started 12 hours before or soon after the procedure and continued till patient is fully ambulatory or up to 14 days post op
What is the preferred DVT prophylaxis method for trauma patients or those with abdominal or pelvic cancer?
Lovenox
How is Warfarin dosed for DVT prophylaxis?
Will vary from patient to patient. Goal INR is 2-3. Primarily used in ortho patients
How is fondaparinux dosed for DVT prophylaxis?
2.5mg given SQ dialy starting 6 hours post op. Adjustment is needed in patients with renal insufficiency
What should not be used as DVT prophylaxis?
Nonfitted thromboembolic stockings - they can actually promote a tourniquet effect so only fitted stockings should be used (if at all)
Recommended DVT prophylaxis for surgery with Caprini score of 0 (low risk)?
None
Recommended DVT prophylaxis for surgery with Caprini score of 1-2 (low risk)?
LMWH
LDUH (low dose unfractionated heparin)
MP (mechanical prophylaxis)
Recommended DVT prophylaxis for surgery with Caprini score of 3-4 (moderate risk)?
MP
Recommended DVT prophylaxis for surgery with Caprini score of >5 (high risk) and low risk of bleeding?
LMWH
LDUH
MP
Recommended DVT prophylaxis for surgery with Caprini score of >5 (high risk) and high risk of bleeding?
MP
Recommended DVT prophylaxis for surgery with Caprini score of >5 (high risk) and low risk of bleeding but LMWH/LDUH is contraindicated?
Low dose ASA
Fondaparinux
MP
Recommended DVT prophylaxis for abdominal/pelvic surgery for cancer with Caprini score of >5
LMWH for 4 weeks
What is the pathophysiology of hyperglycemia in the post op patient?
Surgical incisions cause increased stress hormones (catecholamines, growth hormone, glucagon, ACTH, and cortisol) and relative insulin deficiency and resistance.
How does hyperglycemia lead to decreased wound healing/increased infection?
Causes decreased neutrophil function
Routine preop labs/tests for patients with DM?
BMP
EKG
Elevated postop blood glucose levels (>140) in diabetic patients are associated with what complications?
Surgical site infections (SSIs)
Prolonged hospital stays
Death
What are current recommendations for glucose ranges in critically ill patients?
120-180
If a patient is on an oral hypoglycemic agent (OHA), should the patient take it on the day of surgery?
Not if the patient is to be NPO on day of surgery
If a patient is taking insulin should they take it on the day of surgery?
In general take only half of a long acting insulin and start D5 NS IV. Check glucose levels pre-op, operatively, and post-op q 6hrs
When should diabetics be scheduled for surgery?
As first case of the day because they will not be eating which will simplify glucose control
How does long term use of steroids cause complications during surgery?
Prolonged use of steroids for any inflammatory disorder can cause suppression of CRH/ACTH so if steroids are stopped suddenly this will lead to decreased production of cortisol and an Addinsonian crisis
How should patients on long term steroids be managed during surgery?
IV drip of hydrocortisone at 10mg/hr or 100-mg q8hr provides adequate replacement
In general when do you consider giving a blood transfusion?
Hemoglobin <7
Why is it important to ask about tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drug use/substance abuse?
It heightens awareness about the possibility of postoperative withdrawal. In general, patients should be advised to refrain from taking illicit drugs for at least a couple of weeks before an operation
What are signs of a wound infection?
Systemic manifestations: fever, chills, malaise/fatigue, tachycardia, tachypnea
Local manifestations: erythema, discharge. heat, pain
Wound dehiscence
What are risk factors for wound infection?
Malnutrition
Advanced age
Immunosuppressive drugs
Prolonged hospitalization
Recent abx use
Obesity
Catheters
Poor tissue perfusion
Steroids
Radiation
What are the 4 classes of wounds?
Clean
Clean contaminated
Contaminated
Dirty
What are examples of clean wounds?
Breast biopsy
Inguinal hernia repair
What are examples of clean-contaminated wounds?
GI, GU, GYN organs entered but no gross contamination
What are examples of contaminated wounds?
Perforated appy
Colectomy for diverticulitis
Perforated bowel/ulcer
Penetrating GI trauma
What are dirty wounds?
Traumatic wounds
Burns older than 72 hours
Free colon perforation
When should antibiotics be administered before incision?
Within 1 hour before incision
What antibiotic is recommended for surgical prophylaxis for the majority of clean surgical procedures? What is an alternative to this?
Cefazolin (Ancef) - can use Vancomycin if there is an allergy to cephalosporins
Which antibiotic should be administered to cover bacteroides?
Metronidazole
Which antibiotics are used for class 1 wounds? Class 2? 3?
1 - 1st gen cephalosporin
2 - 1st, 2nd, 3rd gen cephalosporin depending on procedure
3 - 2nd gen cephalosporin or Zosyn + metronidazole
What are some adjuvant prophylaxis measures besides antibiotics to prevent SSI?
Use of warming blankets to enhance tissue perfusion
Chlorhexidine soap showers
Sterile technique
Removal of hair
What is necrotizing fasciitis?
Life threatening infection that involves different facial layers of the body.
Clinical features of necrotizing fasciitis?
Characterized by discoloration/cyanosis around an incisional site with numbness of the area
MC caused by strep but often polymicrobial
Those at risk are diabetics, immunocompromised, and those with PVD.
How do you treat necrotizing fasciitis?
Debride tissue
Broad spectrum abx (Zosyn+Clinda+Cipro)
IVF
What % of our body is water?
Total body mass is 45%-60% water. The percentage in any individual is influenced by age and lean body mass.
What % of body water is intracellular? Extracelluar?
Two-thirds of total body water (TBW), is intracellular
One-third is extracellular
What % of extracellular fluid is interstitial? Intravascular?
80% is interstitial
20% is intravascular
What is the main intracellular cation? Extracellular?
Intracellular - K
Extracellular - Na
What is the 2nd most plentiful intracellular cation?
Mg
What is the main intracellular anion?
Phosphate
What ions balance K? Na?
K is balanced by PO4
Na is balanced by Cl
What is the main protein in intravascular fluid?
Albumin - it is the main cause of the high colloid osmotic pressure of serum which regulates fluid distribution between two extracellular compartments
What regulates the body's volume status and electrolyte composition? How?
The kidneys - by modulating how much free water and Na+ is reabsorbed from the renal filtrate. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as arginine vasopressin, is the chief regulator of osmolality.
What hormone regulates Na levels?
Aldosterone - increased levels causes increased retention of Na
What causes hypovolemia in the surgical patient?
Loss of isotonic fluids in the setting of hemorrhage, gastrointestinal losses (eg, gastric suctioning, emesis, and diarrhea), sequestration of fluids in the gut lumen (eg, bowel obstruction, ileus, and enteric fistulas), burns, and excessive diuretic therapy
What are some assessments to determine volume status? What is the #1 assessment?
Blood pressure - #1
Pulse
Edema
Skin turgor - (less useful in elderly)
Mucous membranes - (less useful in elderly)
Hematocrit
Fractional excretion of Na
BNP
BUN/Cr ratio (>20)
How do patients clinically present with hypovolemia?
Thirsty
Decreased urinary output
Tachycardia
Fatigue
Muscle cramps
Dizziness
Hypotension
If severe: ischemia, shock, lethargy, AMS
What labs confirm hypovolemia? (4)
Hct - will be high
Serum albumin - high
Urinary Na - decreased
Urea - increased