AQA A-Level Bio (Paper 1) 1: Biological Molecules
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Monomers
Monomers are the smaller units from which larger molecules are made.
Polymers
Polymers are molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together.
Monomer examples
Amino acids/nucleotides/monosaccharides.
A condensation reaction
Joins 2 molecules together with the formation of a chemical bond & involves the elimination of a molecule of water.
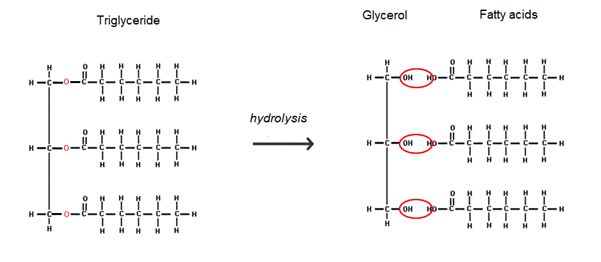
Hydrolysis
A hydrolysis reaction breaks a chemical bond between 2 molecules & involves the use of a water molecule.
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made.
Examples of monosaccharides
Glucose/galactose/fructose
Glycosidic Bond
A condensation reaction between 2 monosaccharides results in a glycosidic bond.
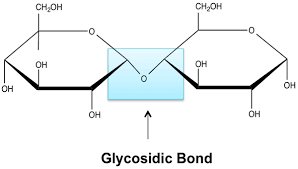
Disaccharides
Disaccharides are formed by the condensation of 2 monosaccharides.
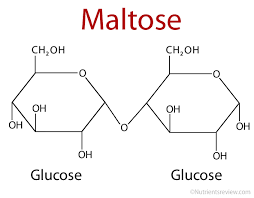
Word eq. to make maltose…
Glucose + Glucose—> Maltose + Water
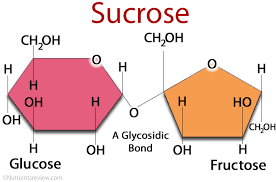
Word eq. to make sucrose…
Glucose + Fructose —> Sucrose + Water
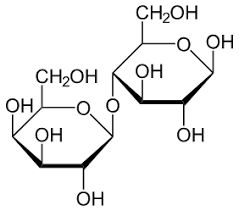
Word eq. to make lactose
Glucose + Galactose —> Lactose + Water
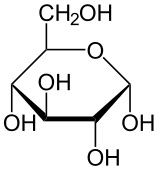
Alpha- Glucose Structure
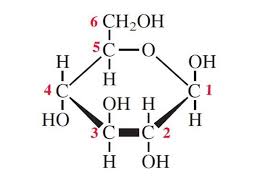
Beta- Glucose Structure
Polysaccharides
Formed by the condensation of many glucose units.
Examples of polysaccharides
Glycogen/starch (alpha glucose units) & cellulose (beta glucose units)
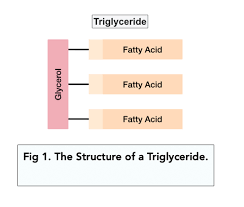
Triglycerides
Formed by the condensation of 1 molecule of glycerol & 3 fatty acids.
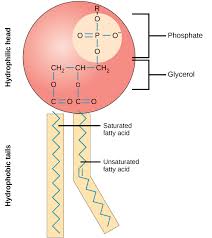
Phospholipids
A fatty acid from the triglyceride is substituted with a phosphate-group.
Isomers
Isomers have the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of atoms in space. (Eg. alpha/beta glucose)
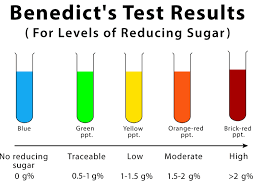
Test for reducing sugars
-Benedict’s solution can be reduced by reducing sugars. It is a clear blue liquid, which changes colour & gives a precipitate depending on how much it is reduced.
1) Place 2ml of the substance (MUST BE LIQUID) in a boiling tube
2) Add 10 drops of Benedict’s solution.
3) Place in a boiling water bath for 3-5 mins
RESULTS:
-Blue solution (no reducing sugar)
-Brick red precipitate (large amounts of reducing sugar)
Sucrose
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar. It is a disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose joined by a glycosidic bond. (Sucrose is common table sugar)
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
A molecule that acts as the energy currency of cells formed from a molecule of ribose, a molecule of adenine and three phosphate groups.
Amino acid
The monomers containing an amino group (NH2 ) , a carboxyl group (COOH) and a variable R group that make up proteins.
Cellulose
A polysaccharide made of beta glucose monomers that is used as a structural polysaccharide which provides strength to plant cell walls.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA
An information storing molecule made up of deoxyribonucleotide monomers joined by phosphodiester bonds to form a double helix.
Dipeptide
Molecules formed by the condensation of two amino acids.
Disaccharide
Molecules formed by the condensation of two monosaccharides.
DNA helicase
An enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds between the two DNA strands in the DNA molecule that is going to be replicated.
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that catalyses the condensation reactions between the new nucleotides in the synthesis of the new DNA strand.
Enzyme
A protein molecule that acts as a biological catalyst and increases the rate of biochemical reactions.
Glycogen
A highly branched polysaccharide made of alpha glucose monomers that is used as the main storage of energy in humans and animals.
Induced-fit model
A model of enzyme action that describes how enzymes undergo subtle conformational changes to better fit the substrate.
Iodine test
A biochemical test used to test for the presence of starch.
Lactose
A disaccharide formed by condensation of a glucose molecule and a galactose molecule.
Latent heat
The amount of energy needed for a substance to change state.
Lipid emulsion test
A biochemical test that produces a cloudy emulsion when performed on lipids.
Maltose
A disaccharide formed by condensation of two glucose molecules.
Metabolite
A molecule formed or used in metabolic reactions.
Phospholipid
A type of lipid formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol, two molecules of fatty acid and a phosphate group.
Primary structure
The individual sequence of amino acids in a protein.
Quaternary structure
A structure only applicable to proteins with multiple polypeptide chains that describes the interactions of the different chains.
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
A relatively short molecule made up of ribonucleotide monomers joined by phosphodiester bonds.
Secondary structure
The local interactions of the amino acids in the polypeptide chain.
Semi conservative replication
The production of two daughter DNA molecules from one DNA molecule which both contain one original DNA strand and one newly synthesised strand.
Starch
A polysaccharide made of alpha glucose monomers that is used as the main storage of energy in plants.
Tertiary structure
The way that the whole protein folds to make a three dimensional structure.
Macromolecule
A molecule containing a very large number of atoms (proteins/nucleic acids)
Carbon Chemistry
All life on Earth depends of the same biochemical basis of life.
The 4 Biological Molecules
Nucleic acids , proteins , lipids , carbohydrates
Macromolecules
A molecule containing a very large number of atoms, such as a protein, nucleic acid, or synthetic polymer.
Hydrophobic
Repels water, non-polar/can’t mix or dissolve into water (phospholipid tails)
Hydrophilic
Attracts water, polar-can dissolve/mix into water (phospholipid heads)
Glycerol Structure
An ester bond
The covalent bond formed by a condensation reaction between the -OH group of a carboxylic acid and the -OH group of an alcohol.
Chylomicrons
A major form of triglycerides, phospholipids, cholesterol, and apolipoproteins.
Micelles
A form of lipids, mainly for intracellular storage of lipids
Theory/explain the lipid “Emulsion test"
Lipids are insoluble in water and soluble in ethanol (an alcohol).
After lipids have been dissolved in ethanol and then added to H2O, they will form tiny dispersed droplets in the water. This is called an emulsion.
These droplets scatter light as it passes through the water so it appears white and cloudy.
results of the Emulsion Test
Possible results:
Confirmation of lipids: a white emulsion floating at or near the top of the water.
Confirmation of the absence of lipids (or levels below the sensitivity of the test): No white emulsion floating at or near the top of the water
Explain the emulsion test
Method
Label the test tubes suitably for the foods to be tested.
Chop solid food on a tile or grind with a pestle and mortar.
Add the food to a labelled test tube to a depth of about 1 cm. For olive oil, add two drops.
Add 3 cm3 of ethanol to each test tube.
Put a clean bung into each test tube and shake carefully at least 10 times. This will help any lipids dissolve in the ethanol.
Allow time for food particles to settle. You may proceed when the ethanol above the food has cleared.
Use the wash bottle to dispense about 3 cm depth of distilled water into the test tubes.
Observe and note any changes in the test tube contents. Record your results in a suitable table.