5) Depressive Phenotypes
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
why would interruption cause Darwin to forget what he was thinking about?
he had to keep a lot of unrelated facts in his head at the same time
Working Memory
Definition: Keeps information active during ongoing mental tasks.
Darwin needed WM to connect complex ideas — like eye evolution in mollusks.
Had to recall details, compare species, and synthesize insights.
Interruptions caused forgetting — showing WM’s fragile, high-demand nature.
2 types of thinking styles
type 1:
fast, automatic, ituitive
uses heuristics
low effort, often error prone
evolutionaryily impact
type 2:
slow, analytical, deliberate
uses working memory
high effort, attention-demanding
energentically expensive
what was darwin’s thinking style?
Analytical (Type 2) — breaking big problems into smaller ones. - divide and conqcure
→ Required sustained WM and emotional focus.
→ Sad or depressed mood promotes analytical thinking.
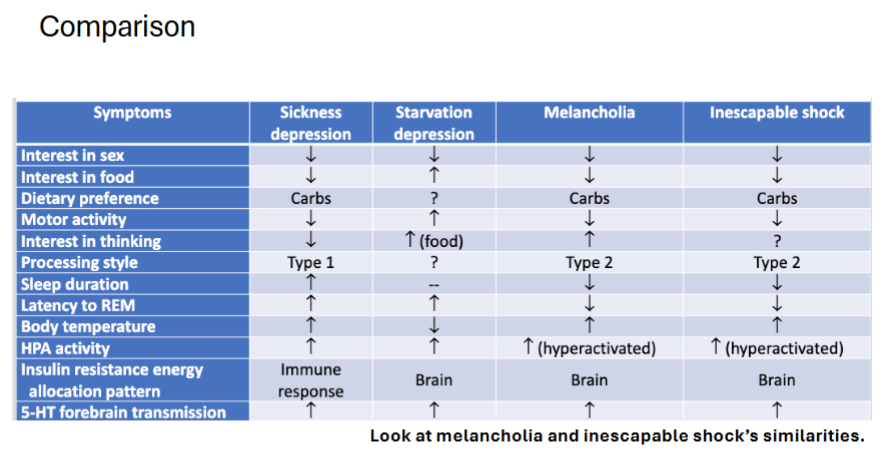
depressive phenotypes
sickenss behaviour - Conserves energy for immune response.
ahedoinna p loss in interst in sex and food → promotes eergy reallocation to immune system in tead of sogntiio soical asn phsycail aocotut, gowth, etc
more fagiuge, less cognitve effort
eat more carbs nad less iron foods
sleep more, less REM sleep
increase core body temp
Insulin resistance (IR) redirects glucose to immune tissues.
starvation depression - Prioritize brain and foraging over reproduction or immunity.
Anhedonia: lost interest in sex/humor, but not food
Fatigue: rest more but still forage actively
Eat less: prefer protein
Low core temp
Weakened immunity
🧠 Adaptive purpose: Prioritize brain and foraging over reproduction or immunity.
Energy reallocated to brain (hypothalamus, mesolimbic reward system).
Insulin sensitivity (IS) increases in brain → fuels foraging cognition.
IR in muscle = energy saving.
Melancholia - deep though
Anhedonia: loss of interest in food/sex, but ↑ interest in thoughts
Sleep less: more REM (memory consolidation)
Fever-like body temp
High cortisol (HPA axis activation)
Shift from social/physical activity → cognitive focus.
→ Promotes rumination (deep analytical thought). - persistant distractino-resistant thoughts
How energy is re-directed to immune tissues
during sickness
Insulin sensitivity (IS) and insulin resistance (IR) reflect how easily glucose (sugar) is taken from the bloodstream. Changes in IS/IR reflect the body’s adaptive metabolic response to (in this case) sickness. Starvation
Insulin resistance helps reallocate energy as the situation demands!