electrolysis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
dilute sulfuric acid - anode product
oxygen
dilute sulfuric acid - cathode product
hydrogen
dilute sulfuric acid - anode observations
bubbles of oxygen gas
dilute sulfuric acid - cathode observations
bubbles of hydrogen gas
to find products formed in a substance
eg. molten potassium iodide
anode - non metal
cathode - usually metal
anode - iodine
cathode - potassium
Panic mnemonic
Positive is Anode, negative is cathode
electrolysis
when an electric current is directed through a molten or aqueous ionic compound resulting in the compound decomposing or breaking down
electrolyte
the ionic compound in a molten or dissolved solution that can conduct electricity
electrode
the rod used to direct energy
inert so they’re made of platinum (metal) or carbon/graphite (non - metal) so there aren’t any side reactions
why ionic compounds need to be molten or aqueous
mobile ions (solid ionic compounds don’t have free ions to move or carry charge)
why a substance needs to be manufactured through electrolysis
takes too high of a temperature to extract the product
molten lead bromide - anode product
bromine gas
molten lead bromide - cathode product
lead metal
molten lead bromide - anode observations
bromine gas is released
molten lead bromide - cathode observations
lead metal is formed
concentrated aqueous sodium chloride - anode product
chlorine
concentrated aqueous sodium chloride - cathode product
hydrogen
concentrated aqueous sodium chloride - anode observations
chlorine gas is produced
concentrated aqueous sodium chloride - cathode observations
bubbles of hydrogen gas
simple electrolytic cell
remember that cathode is connected to the negative side of the battery and anode is connected to the positive side
electroplating anode
nickel, gold, silver
electroplating cathode
steel, copper, plastic
electroplating
uses electrolysis to coat a thing layer of a metal onto the surface of another metal
inprove appearance and resistance to corrosion
the cathode is the object that needs to be electroplated
the anode is the plating metal
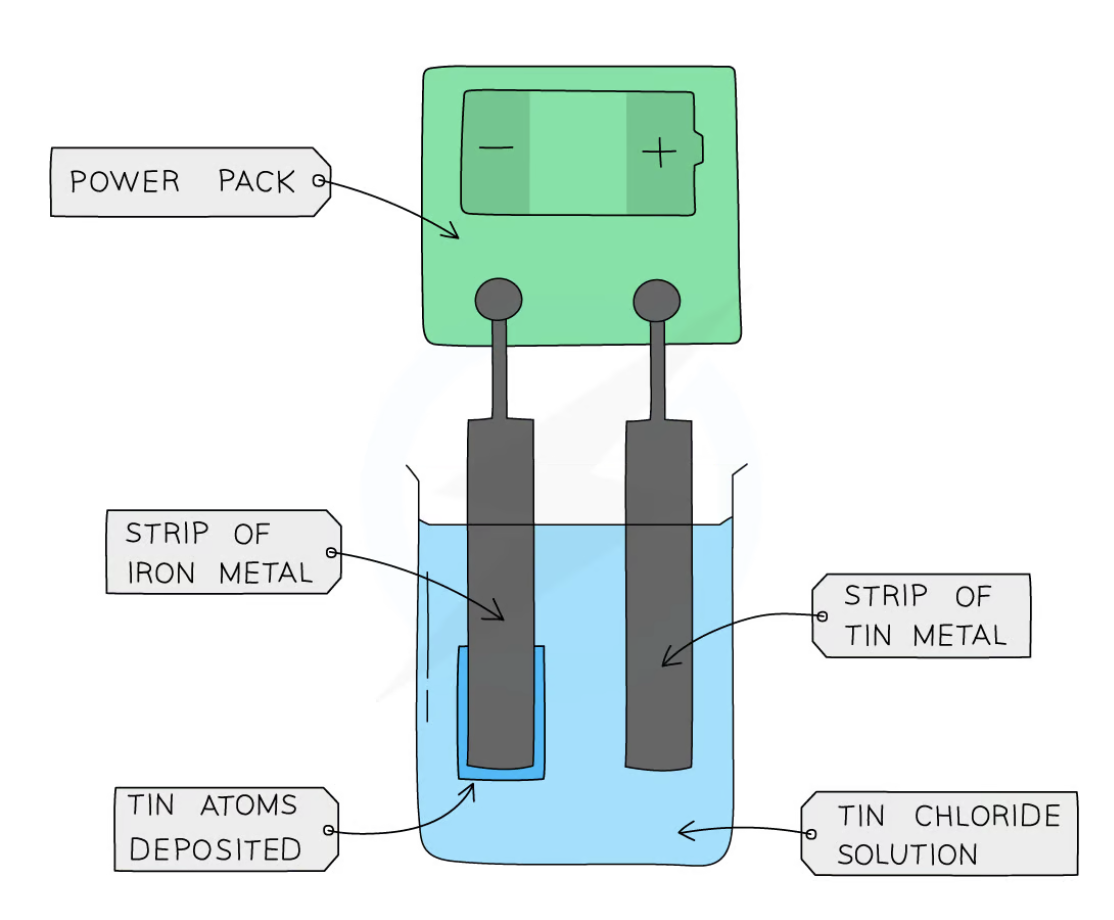
electroplating a strip of iron with tin
At the anode:
Tin atoms lose electrons to form tin ions in solution
The loss of electrons is oxidation
At the cathode:
Tin ions gain electrons to form tin atoms
The gain of electrons is reduction
The tin atoms are deposited on the strip of iron metal, coating it with a layer of tin
halides
compounds formed with halogen elements