BSCI330: Plasma Membrane and Plant Cell Wall REVIEW
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Which of the following would you expect to diffuse freely through the plasma membrane?
Anything small and nonpolar (ex. steroid hormones) because the inside of the plasma membrane is hydrophobic.
Describe the nature and structure of phospholipids
Amphipathic (polar head and nonpolar tails)
One tail is saturated (no hydrogen bonds) and the other is unsaturated (one cis hydrogen bond creates a kink)—increases membrane fluidity
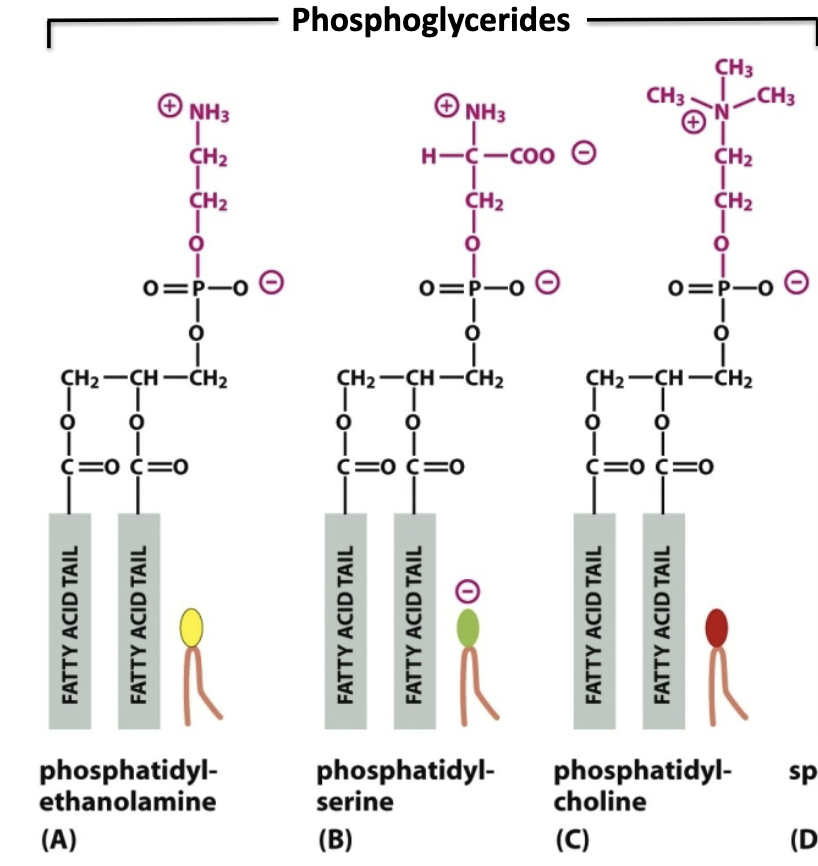
Phosphoglycerides
Two fatty acids + glycerol/glycerine + phosphate + polar head group
THREE TYPES:
Phosphatidylethanolomine: Head is ETHANOL + AMINE; net neutral charge
Phosphatidylserine: Head is AMINO ACID SERINE (amine +, carboxyl -, phosphate - = net - charge)
Phosphatidylcholine: Head is tertiary amine; net neutral charge
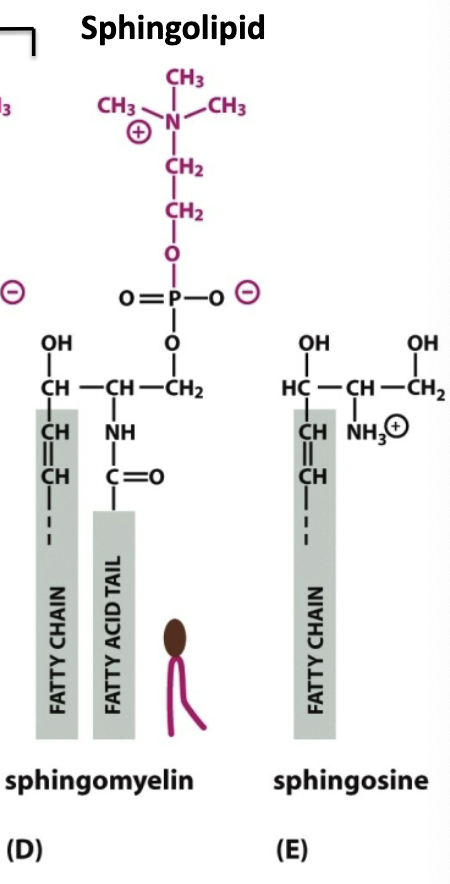
Sphingolipid
Linker molecule sphinoglycine + had its own fatty acid chain (just add 1 more fatty acid with an AMIDE LINKAGE)
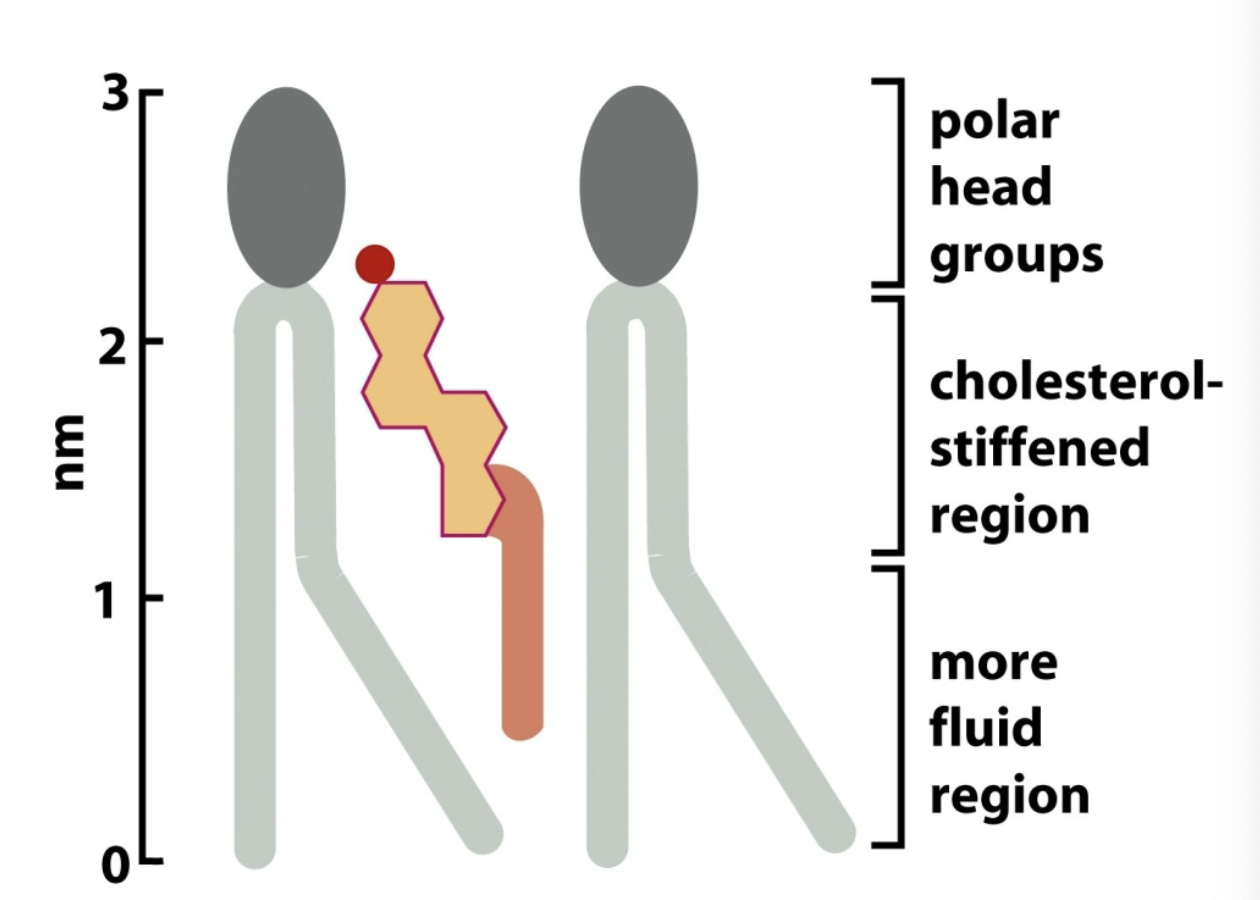
Sterols
Create a RIGID ring structure thru less flexible short bonds; increase stiffness to the membrane by adding more sterol.
HIGH TEMP: prevent from becoming too fluid
LOW TEMP: prevent from freezing solid
What is ergosterol?
Found in fungi!
Most antibiotics that target bacteria target differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Antifungal drugs target ergosterol
nystatin and amphotericin B bind to ergosterol and form pores which allow ions to leak (disrupt function thru osmotic stress → cell dies)
miconazole and lamisil target enzymes that synthesize ergosterol so that cells can’t synthesize new membrane —> stops proliferation
Phospholipids orientation in plasma membrane
Self-assemble into bilayer membrane
NO HYDROPHOBIC FORCE that causes them to cluster
Water molecules are most stable when interacting with hydrophillic heads, which means hydrocarbon tails associate with each other.
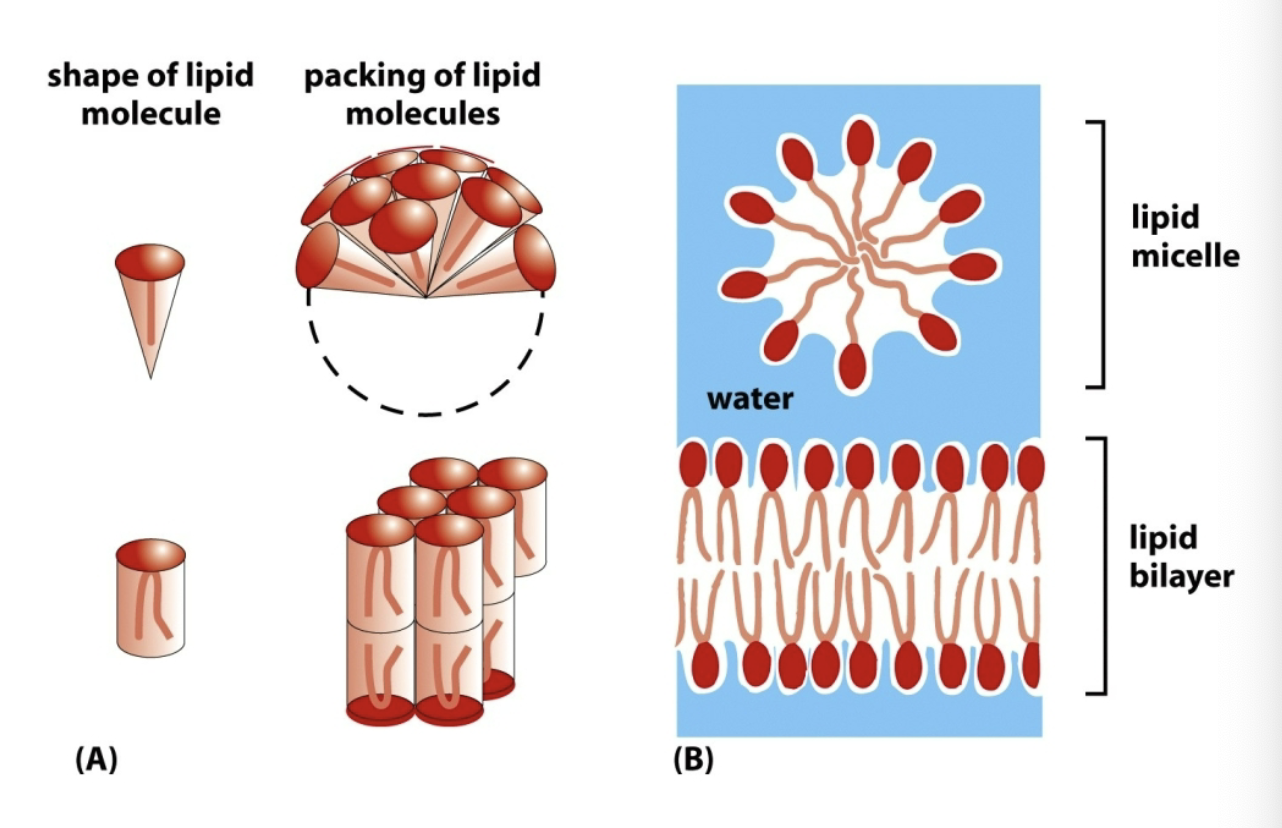
Explain the energetically unfavorable/favorable shape of bilayer
At the edges, water can interact with hydrophobic molecules, so it curls the plane into a sphere to avoid this.
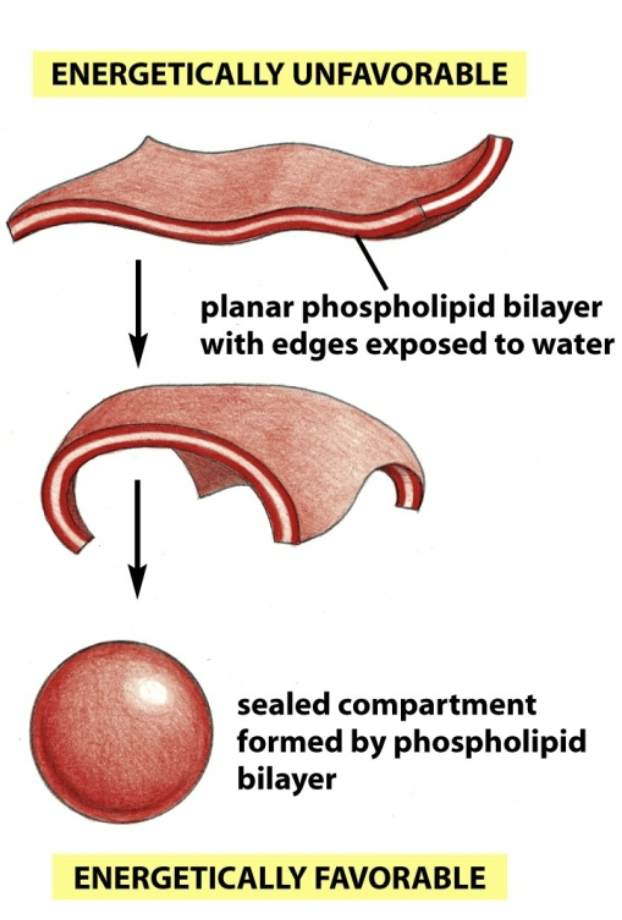
What is the fluid mosaic membrane?
A non-uniform structure:
fluid - constituents can diffuse within lateral constraints
mosaic - not a continuous surface; made of discrete pieces (different lipid composition)
hydrocarbon tails can be different heights
Why is flip-flop rare?
The hydrophilic head would have to push through the center (can’t establish bonds that stabilize it); disorder of water overwhelms the membrane.
Lipid Rafts
Portion of lipid membranes where hydrocarbon tails are longer than the rest, resulting in protruding lipid heads
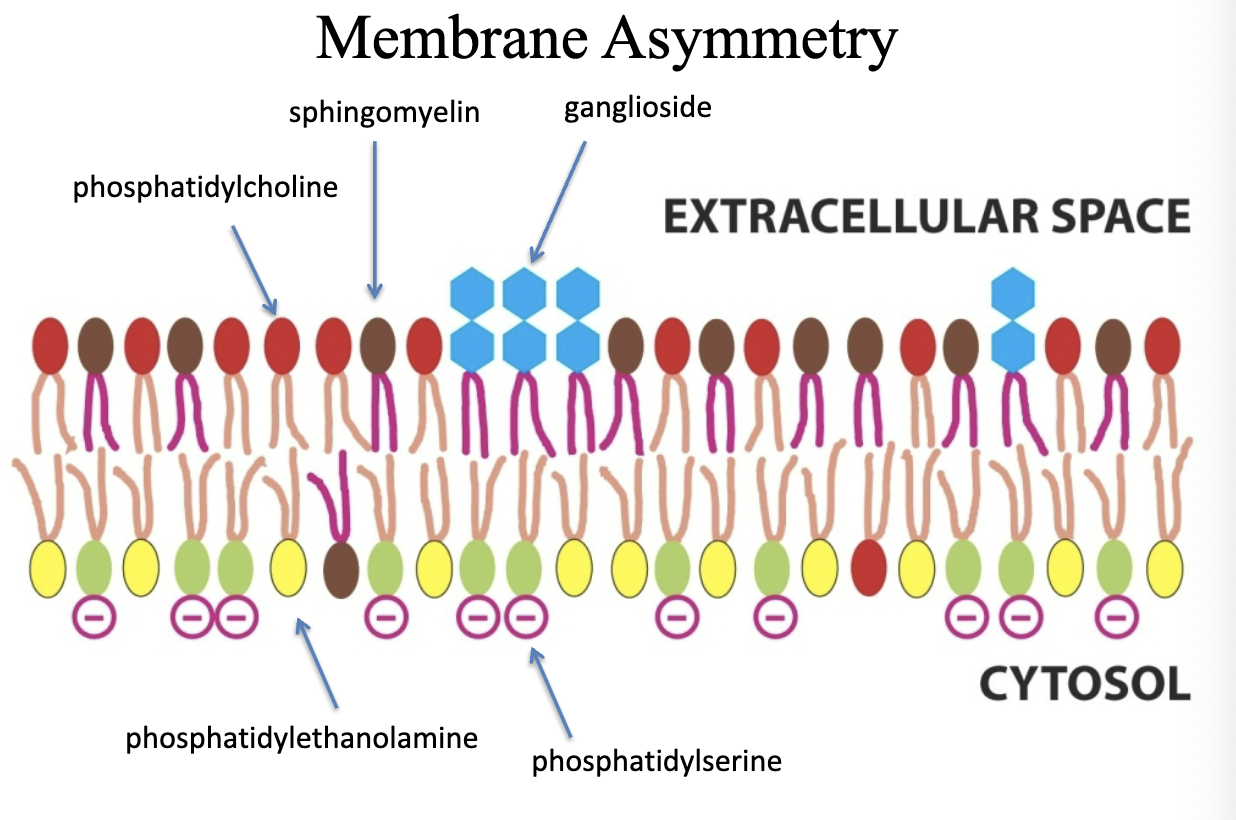
Membrane Asymmetry
The ganglioside is exclusive to the outer leaflet, whereas the phosphatidylserine is exclusive to the inner leaflet!
Voltage can be created on the inner leaflet to do work. ATP is used to maintain asymmetry.
Cell death can be signaled by asymmetry of the cell (phosphatidylserine on the outer leaflet).
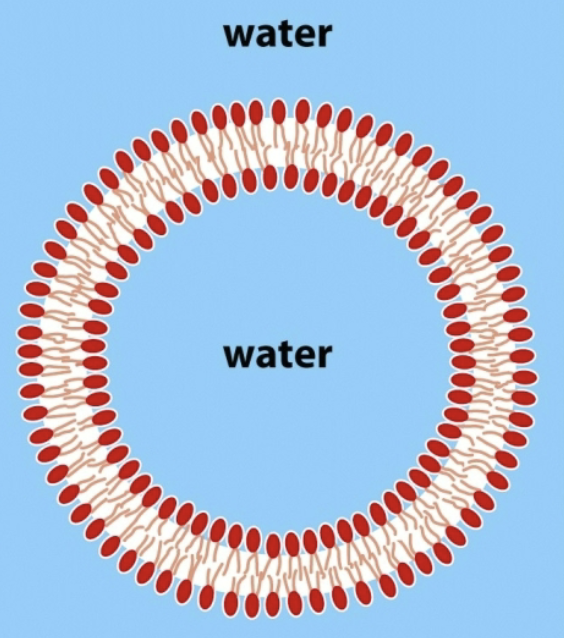
Liposome
Technique used to study lipid membranes; spherical vesicle with a hallow center
Can form the the liposomes with different conditions (inside and outside) and test different membranes
Once liposome is formed, cannot change interior environment!
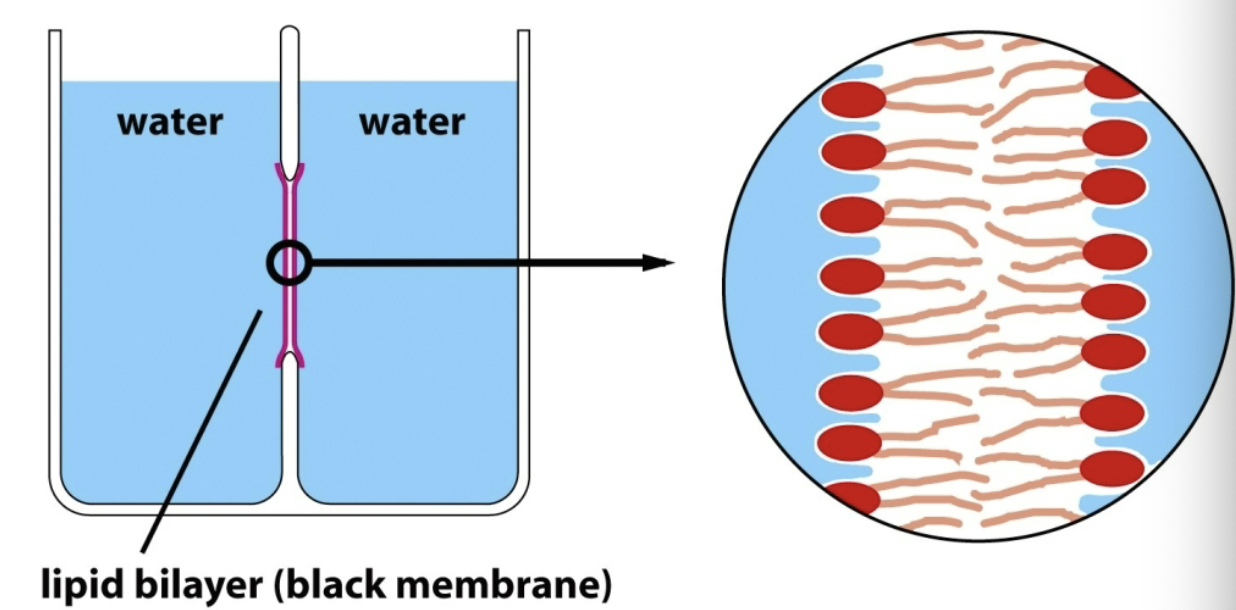
Black Membrane
Technique used to study lipid membranes; consists of a dish with two chambers and a wall between them—the wall has a hole/window
Planar lipid bilayer that is formed across this window
Does not necessarily mimic cellular conditions, but have access to change conditions on either side of the membrane and apply a voltage!
Membrane Proteins (function + types)
Function: molecular transport, signal transduction, structural support, anchorage to cytoskeleton, interactions with other cells
Types:
Peripheral - attached to surface
Integral - embedded into membrane
Transmembrane - crosses the membrane completely via transmembrane region
Plant Cell Wall
Can be separated from the plant cell
Made from carbohydrates (mainly cellulose)
Function of Cellulose
Provide tensil strength; resistance to stretching (one comparable to steel)
Pectin
Second set of complex carbohydrates in cell wall; short chain
Like a gel that resists the compressive force and distributes it
Lignin
Waterproofing agent
Tonicity in animal cells?
Hypotonic: Concentration of water is high outside → cell SWELLS
Hypertonic: Concentration water is low outside → cell SHRIVELS
Isotonic: stable environment
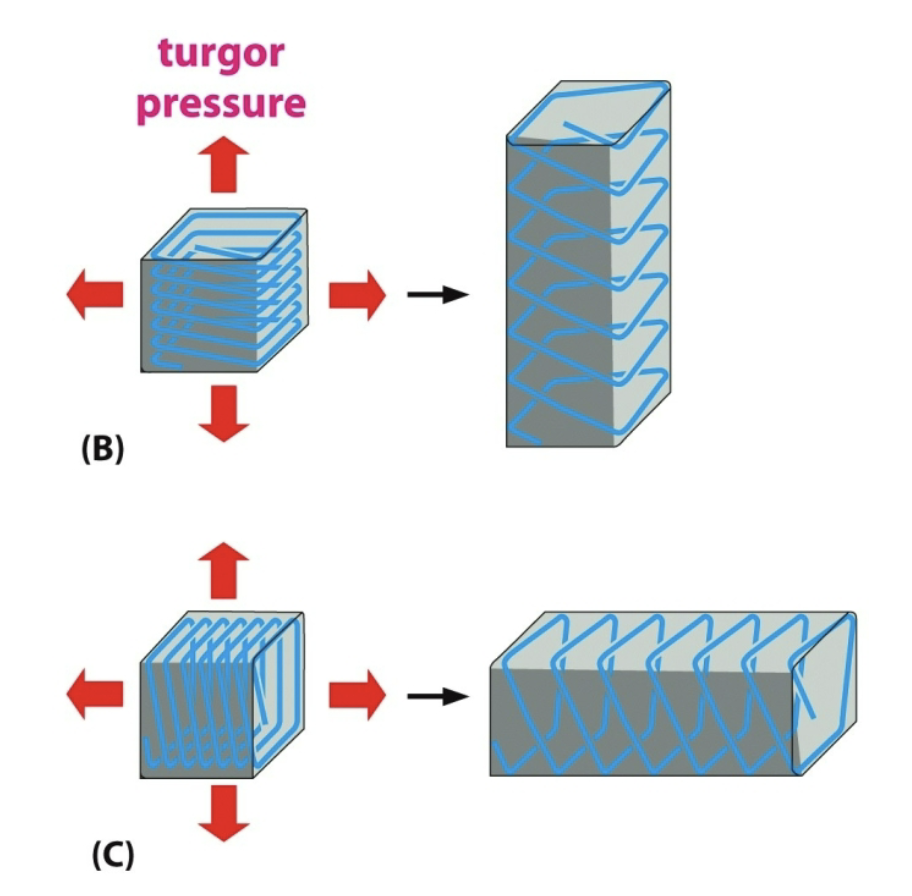
Turgor Pressure
Ability for plant cells to build up pressure from excess water (helps plants to grow)