COBCSRG QUIZ 1
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
social responsibility
By `_,' we mean the intelligent and objective concern for the welfare of society that restrains individual and corporate behavior from ultimately destructive activities, no matter how immediately profitable, and leads in the direction of positive contributions to human betterment, variously as the latter may be defined.
CSR
RESPONSIBILITIES that a business has to the society in which it operates.
CSR
A long-term strategy.
Aligns business strategy and operations with universal values.
Leads to a fundamental transformation of strategies, operations, relationships, corporate culture and identity.
A proactive strategic planning, not defensive communication.
Includes philanthropy - but it is much more.
Responsible
1. Reliable or trustworthy.
2. Attributing something as a cause for an event or action.
3. Attributing liability or accountability for some event or action, creating an obligation to make things right again.
accountability
SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
Responsibility as _: Heart of CSR
Actions for which a business can be held accountable.
To be concerned with society's interests that should restrict or bind business's behavior.
What a business should or ought to do for the sake of society, even if this comes with an economic cost

philantropic, ethical, legal, economic
Pyramid of social responsibility
economic view of CSR
Business may also CHOOSE to contribute to social Needs as a matter of philanthropy, but not as a matter of duty or social responsibility
Social Web Model of CSR
business is embedded within a web of social relationships of mutual rights and responsibilities
integrative model of CSR
part or all of the mission of the company is to serve important social goals
Economic
Social Responsibility:
Pursue Profit
Denies social responsibility beyond economic and legal ends
Roots in utilitarian tradition and neoclassical economics
Philanthropic
Narrow csr view: reputational
Reasons and Financial Ends
Free to contribute to social causes; no strict obligation to contribute
Charity work for good public relations, tax deduction, good-will
Social Web
Business as citizen of society
Business to conform to normal ethical duties and obligations
Respect human rights
Approaches:
Kantian Theory -Moral Duties
Stakeholder Theory Decision affects variety of people and groups
Integrative
Non-profit: Pursue social ends as core of their mission
For-profit: Social goals as central part of strategic mission of the organization; social entrepreneurship and sustainability
Reputation management
The practice of attending to the "image" of a firm through CSR activities
Good image for itself, it builds a type of trust bank
Negative image, may stick, regardless of what good the corporation may do.
emotional appeal
products and services
financial performance
social responsibility
workplace environment
vision and leadership
6 dimensions of corporate reputation
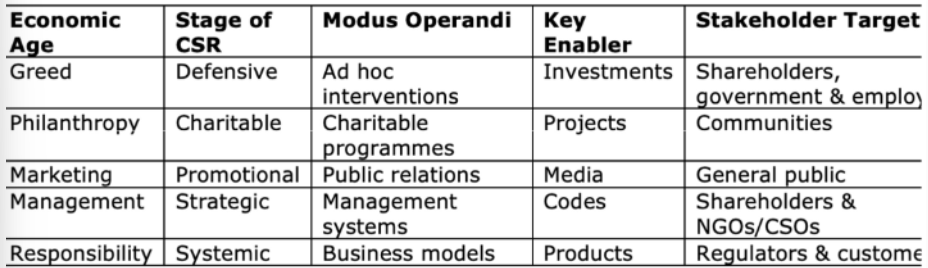
greed - defensive
philantrophy - charitable
marketing - promotional
management - strategic
responsibility - systemic
ages and stages of CSR
Peripheral CSR
Incremental CSR
Uneconomic CSR
failures of CSR
CSR has remained largely restricted to the largest companies, and mostly confined to PR, or other departments, rather than being integrated across the business
CSR has adopted the quality management model, which results in incremental improvements that do not match the scale and urgency of the problems
CSR does not always make economic sense, as the short-term markets still reward companies that externalise their costs to society
ontological shift
CSR as affordable solutions for those who most need quality of life improvements.
Investment in self-sustaining social enterprises will be favored over cheque-book charity.
Supply Chain
Climate change
Involves the transformation of natural resources, raw materials, and components into a finished product that is delivered to the end customer
A network between a company and its suppliers
Produce and distribute a specific product to the final buyer.
Network includes
different activities
People and entities
Information and resources
_ poses a new risk to supply chains and a need to increase their resilience
science of sustainability
Use of auditing and benchmarks to provide a framework for governing sustainable supply chain operations
Clarity around the environmental impact of adjustments to supply chain agility, flexibility, and cost in the supply chain network
Driven by the current climate (in which companies recognize cost savings through green operations as being significant) as well as pushing emerging regulations and standards at both an industry and governmental level
Sustainable supply chain
Business issue affecting an organization's supply chain or logistics network in terms of environmental, risk, and waste costs
Integrating the environmentally sound choices into supply-chain management.
A sustainable supply chain seizes value creation opportunities and offers significant competitive advantages for early adopters and process innovators.
Learning to think sustainably
getting the basics right
The science of sustainability
tiers of sustainable supply chain
TIER _?
Companies begin to realize the need to embed sustainability into supply chain operations
Companies tend to achieve this level when they assess their impact across a local range of operations.
In terms of the supply chain, this could involve supplier management, product design, manufacturing rationalization, and distribution optimization.
Shortening supply chains can be part of a sustainable supply chain strategy.
TIER _?
This is the base level and is the stage in which the majority of organizations are at.
Employing measures such as switching lights and PCs off when left idle, recycling paper, and using greener forms. of travel with
Purpose of reducing the day-to-day carbon footprint
Employ self-service technologies such as centralized procurement and teleconferencing
TIER _?
Uses auditing and benchmarks to provide a framework for governing sustainable supply chain operations.
Clarity around the environmental impact of adjustments to supply chain agility, flexibility, and cost in the supply chain network.
Driven by the current climate (in which companies recognize cost savings through green operations as being significant) as well as pushing emerging regulations and standards at both an industry and governmental level
direct
global
indirect
collective
Approaches to encouraging sustainable practices throughout networks
direct approach
Evaluate first-tier suppliers by using sustainability performance indicators that capture their requirements for lower-tier suppliers
-Survey suppliers on their environmental, health, safety, and labor practices and on their procurement practices
-Work with major first-tier suppliers to map the firm's supply network.
indirect approach
Provide training and foster peer learning among first-tier suppliers to help them improve their procurement practices with lower-tier suppliers.
-Select high-performing suppliers to pilot new sustainability initiatives.
Reward suppliers for cascading sustainability requirements ti lower-tier suppliers.
collective approach
Commit to developing and complying with industrywide sustainability standards, and help suppliers become full members of industry organizations.
Via industry organizations, share resources with competitors and major suppliers to achieve sustainability goals.
Encourage first- and lower-tier suppliers to take advantage of sustainability training programs offered by industry organizations.
global approach
Work closely with relevant NGOs and international institutions interested in improving supply chain sustainability.
Use tools and data that those organizations provide for dealing with suppliers (contracts and scorecards).
-Recognize suppliers that excel in programs sponsored by NGOS and international institutions.
Consequentialist
Focusing on the results of an action
Utilitarian Approach
Egoistic Approach
Common Good Approach
Most common
Concerns large group of people
Weigh the different amounts of good vs bad
Ethics of self-interest
Greatest amount of good for him or herself
General will of the people
Produce the best for people as a whole
Duty-based
Non-consequentialist
Deontological ethics
Duties and obligations we have in a situation
Doing one's duties and doing the right thing
Moral duties regardless of outcome
Can be rigid in applying the notion c duty to everyone regardless of personal situation
Virtue ethics
Agent-centered
Character traits (either + or -) that motivate in certain situations
Ask what sort of person one should be
Emphasizes role models and education to behavior
Sometimes reinforce cultural norms as standard of ethical behavior
ethics of care
Agent-centered
Feminist approach
Experiences of women and other marginalized groups
Anti-consequentialist
Actions highlighting
interpersonal relationships and care or benevolence as virtue
masid danas - see experience
suri nilay - analysis reflection
taya kilos - commitment action
lasallian reflectio framework
course-based
reflection
reciprocity
civic education
Key elements of service learning