Molecular Genetics Lecture 6 - DNA Sequencing II
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Illumina technology uses _____ approach
sequencing by synthesis (SBS)
DNA is sequenced after ___ _______ replicates a DNA fragment
DNA polymerase
Millions of DNA fragments are immobilized on a flow cell and fragments are sequenced in parallel using _____ _____ _____
reversible dye terminators
What does a library (illumina sequencing) contain?
collections of millions of fragments of DNA representing the whole genome
how is the DNA fragmented by?
mechanical or acoustic shearing
what is attached to the DNA fragments during library preparation?
adaptors
what do adaptors bind to?
DNA oligos on the flow cell via complementary base pairing
what is single read sequencing?
sequencing only one end of the fragment
what is paired-end sequencing?
sequencing both ends of a fragment
what are p5 and p7?
adaptor sequences that bind to the flow cell
what are SP (sequencing primers) used for?
used by DNA polymerase for DNA synthesis
what is bar coding/indexing?
allows to index (TAG) and sequence different samples in the same lane (multiplexing of samples)
what are flow cells coated with?
a lawn of oligo pairs that can attach to the DNA fragments by complementary base pairing of adaptors
what is performed on the clusters in the flow cell?
sequencing
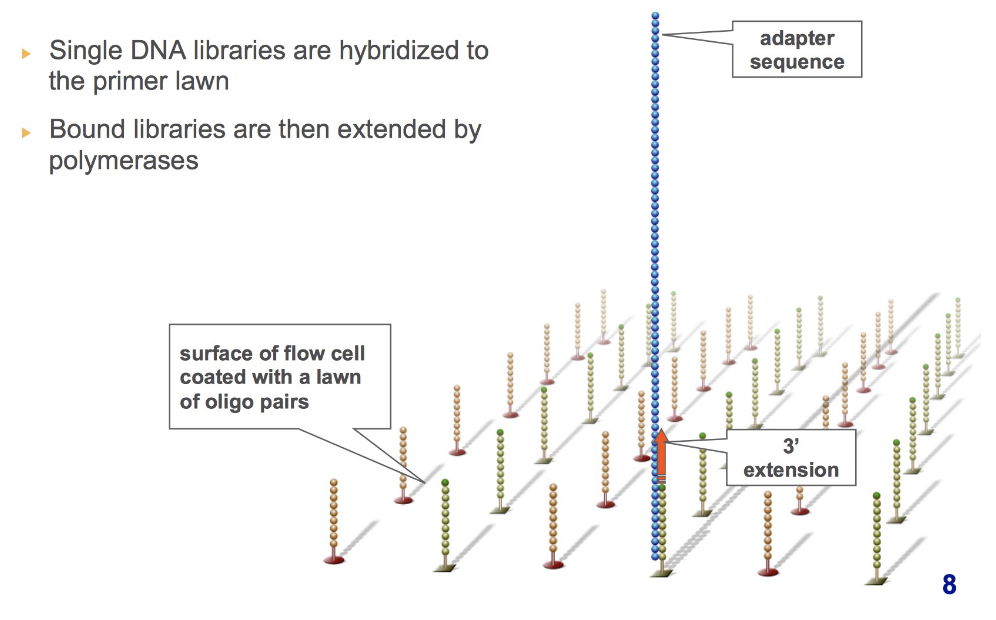
what occurs during the hybridize fragment and extend phase of cluster generation?
single DNA libraries are hybridized to the primer lawn and bound libraries are then extended by polymerases
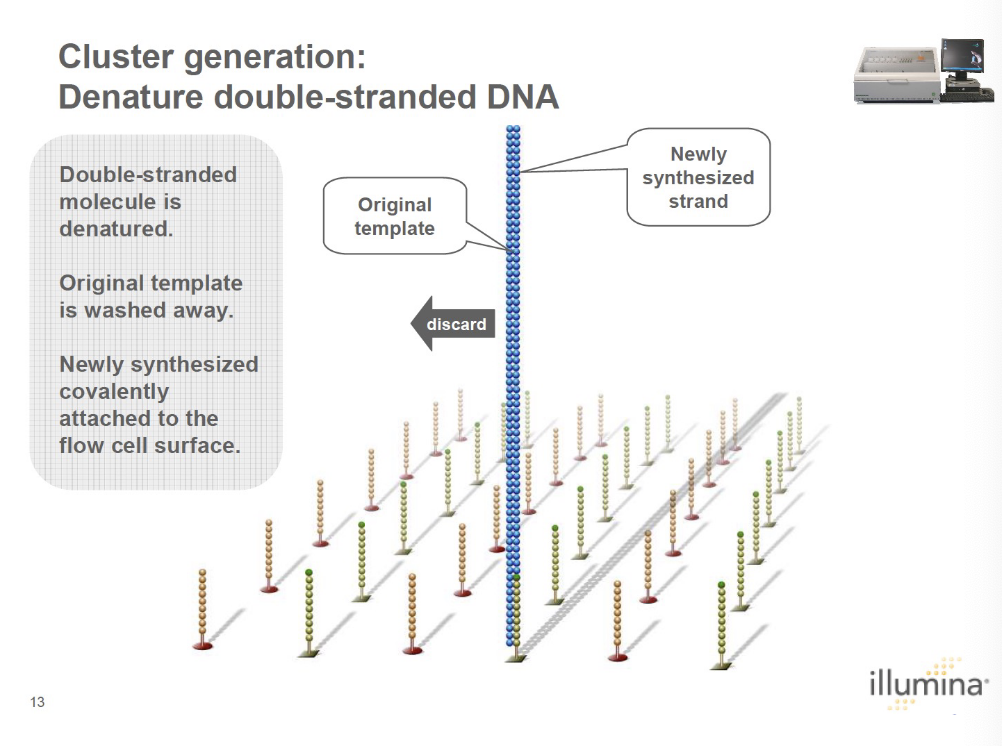
what occurs during the denature double-stranded DNA phase of cluster generation?
double-stranded molecule is denatured and the original template is washed away. the newly synthesized strand is attached to the flow cell surface
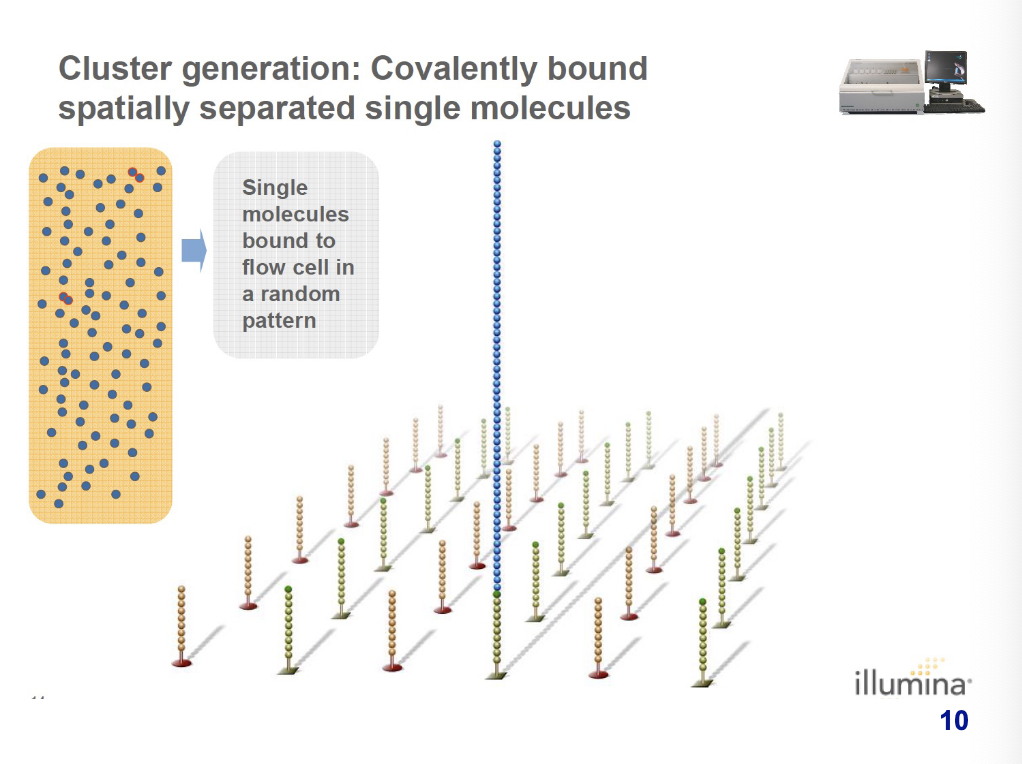
what occurs during the covalently bound spatially separated single molcules phase of cluster generation?
single molecules are bound to the flow cell in a random pattern
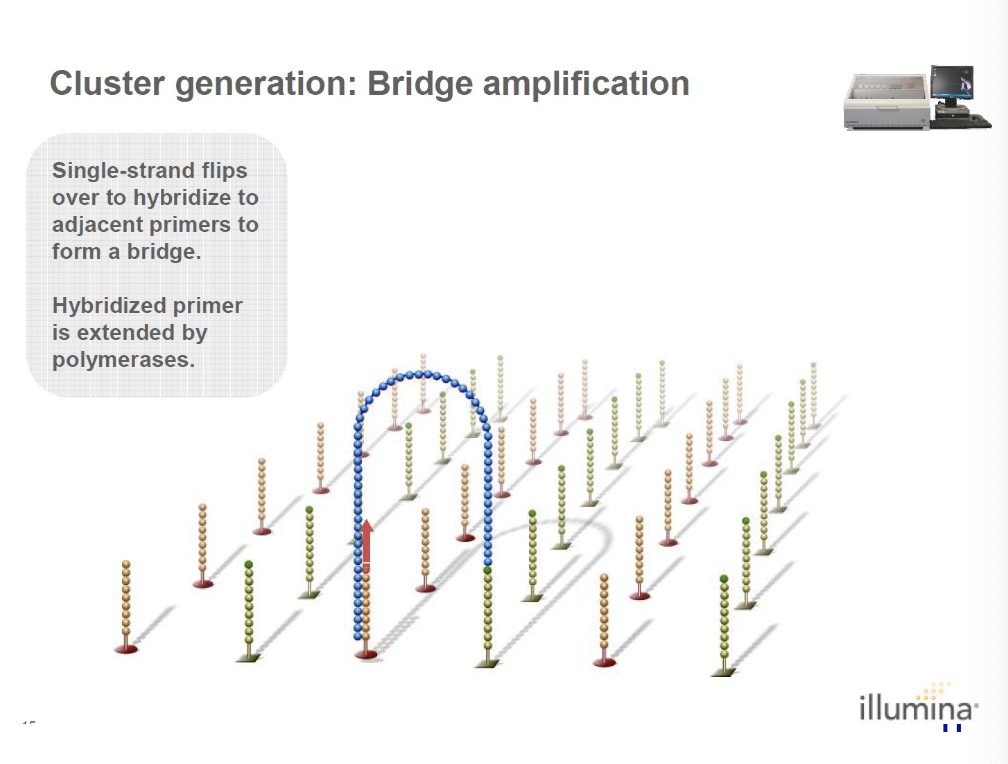
what occurs during bridge amplification?
single strand flips over to hybridize to adjacent primers to form a bridge and the hybridized primer is extended by polymerases which forms a new double-stranded bridge.
what occurs after the new double-stranded bridge is formed during bridge amplification (cluster generation)?
new double-stranded bridge is denatured and there are two copies of covalently bound single-stranded templates
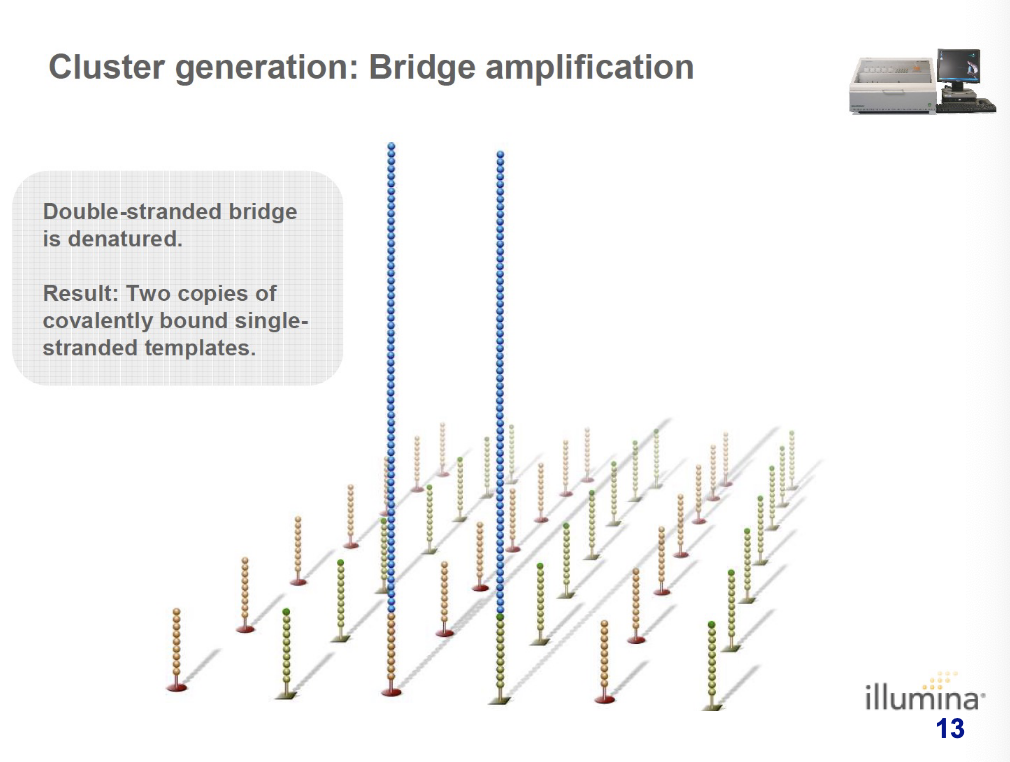
what happens after two copies of covalently bound single-stranded templates have formed during bridge amplification (cluster generation)?
single-strands flip over to hybridize to adjacent primers to form bridges. the hybridized primer is extended by polymerase.
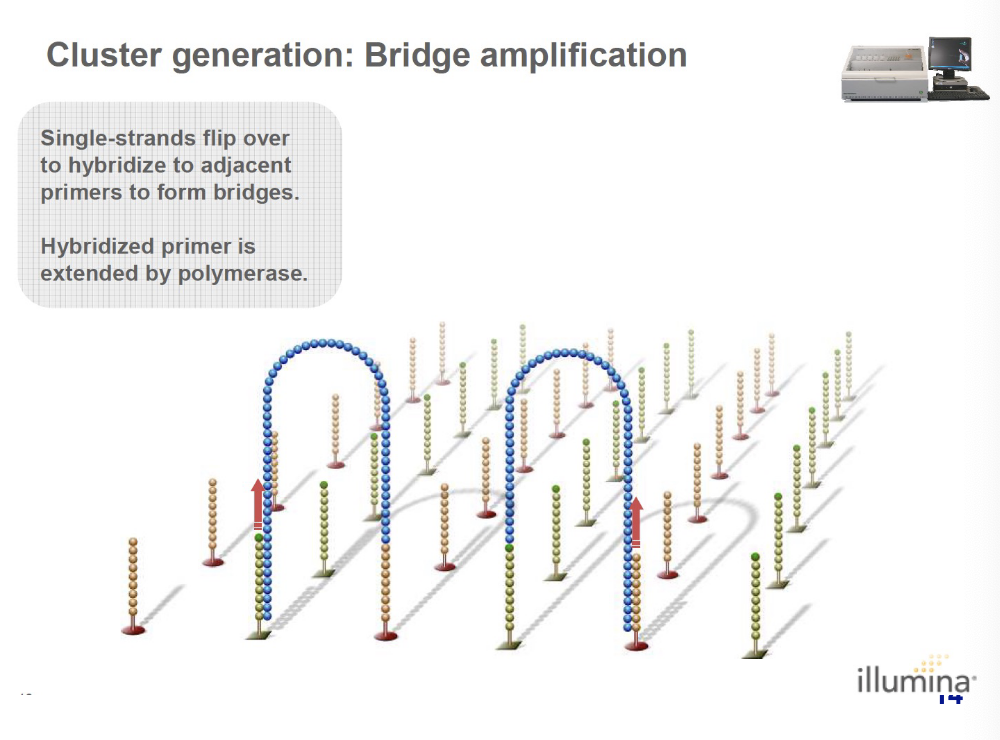
what happens after the hybridized primer is extended by polymerase during bridge amplification (cluster generation)?
bridge amplification cycle is repeated till multiple bridges are formed.
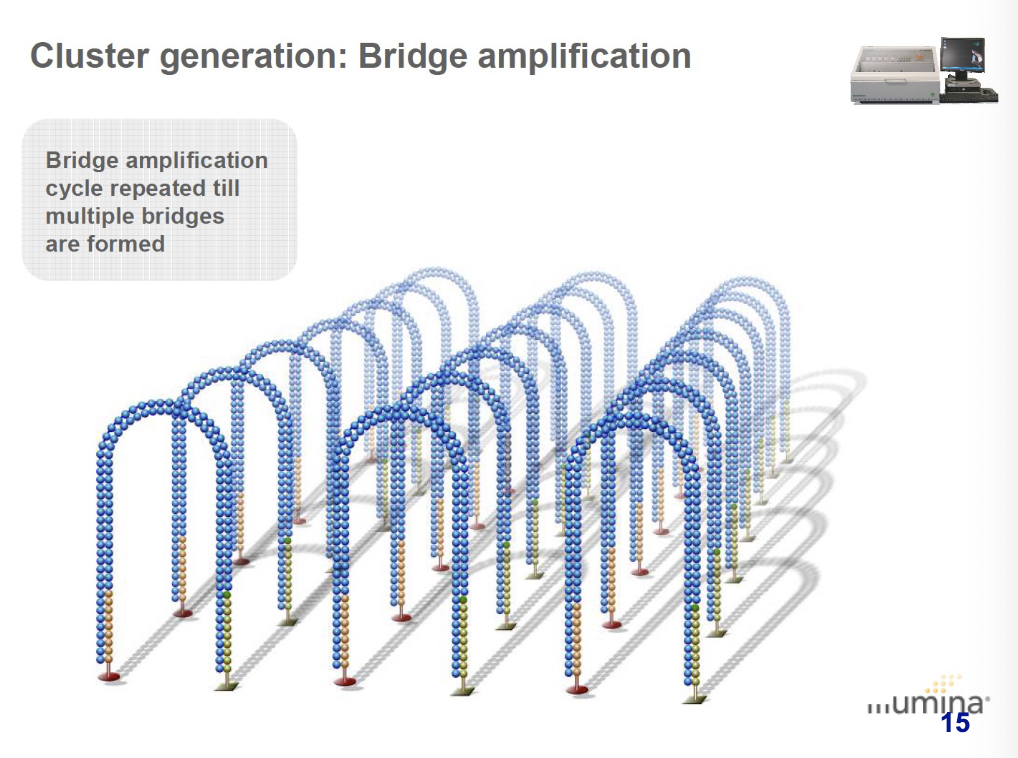
what occurs after the entire bridge amplification process during cluster generation?
dsDNA (double-stranded) bridges are denatured and reverse strands are cleaved and washed away.
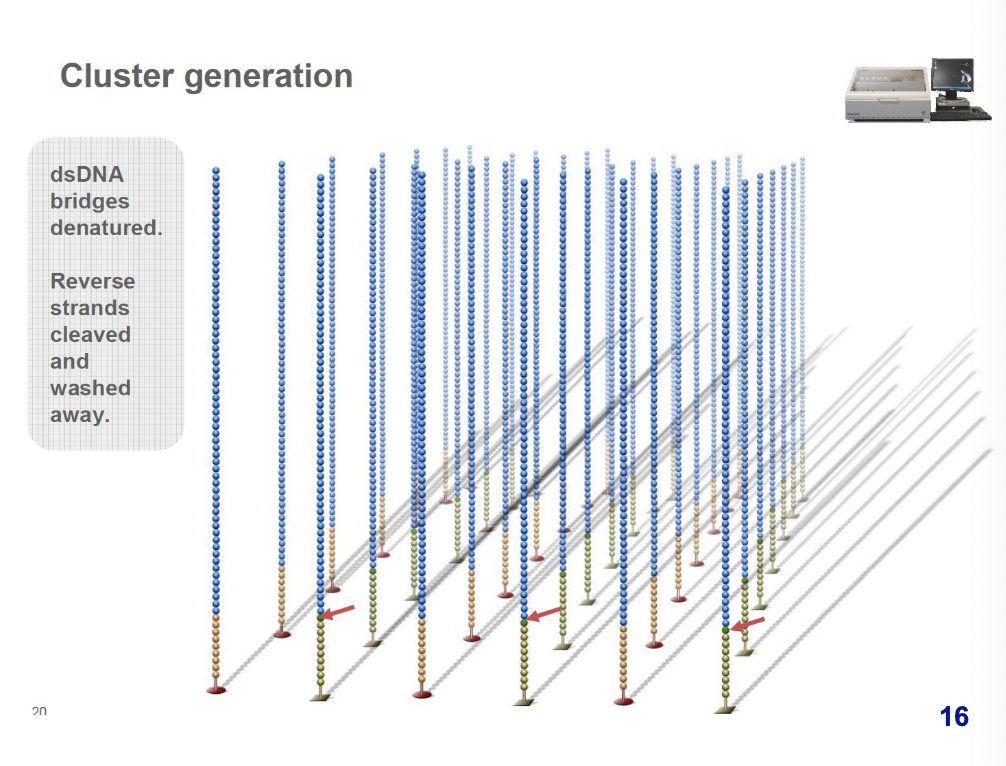
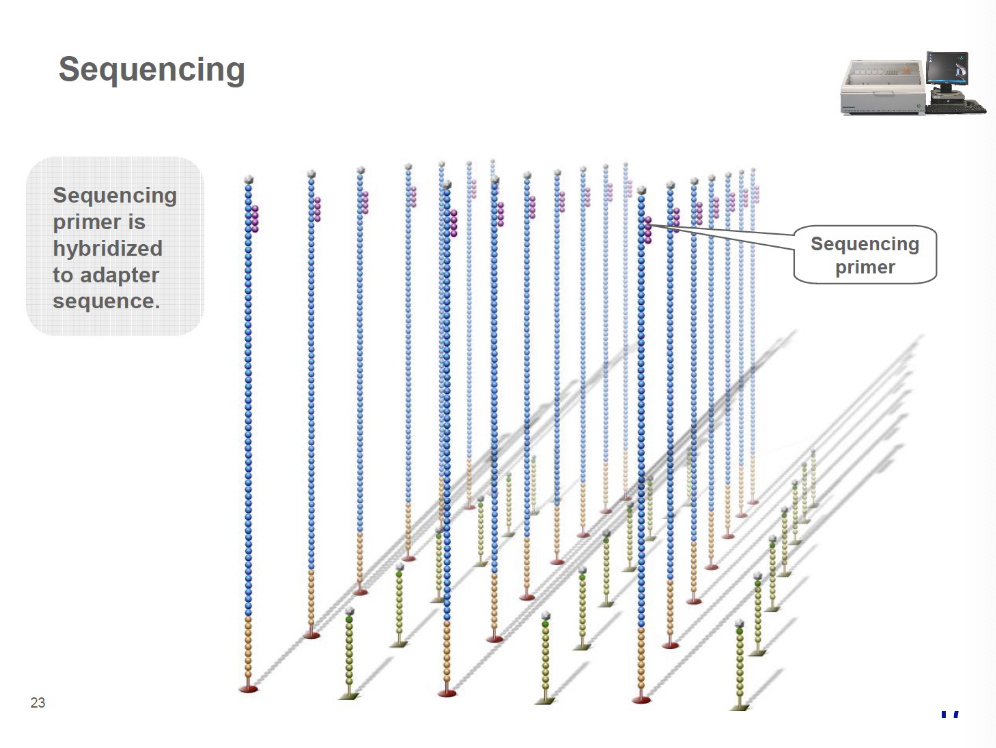
what occurs during sequencing during cluster generation?
sequencing primer is hybridized to adapter sequences
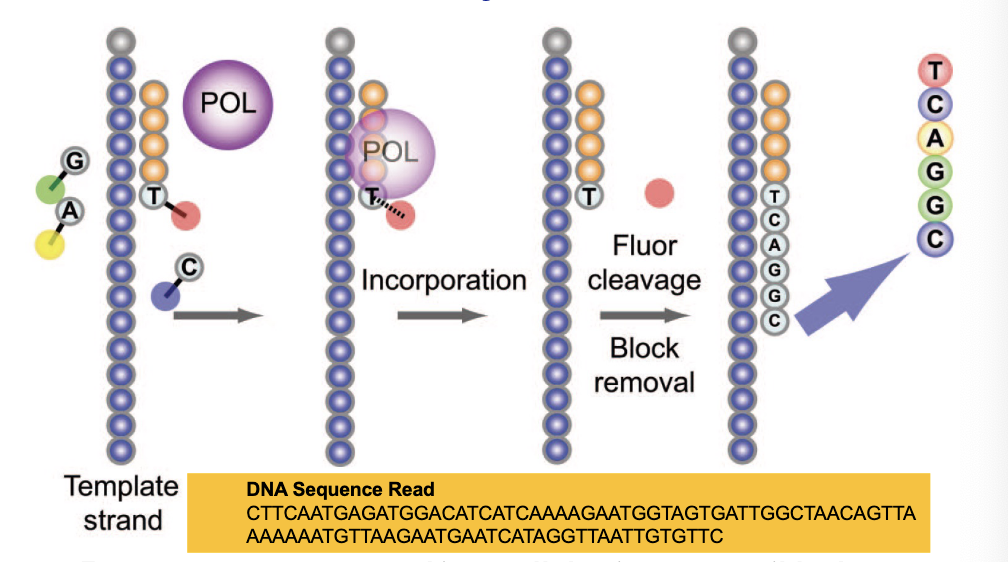
Fragments are sequenced in _______ using reversible dye terminators.
parallel
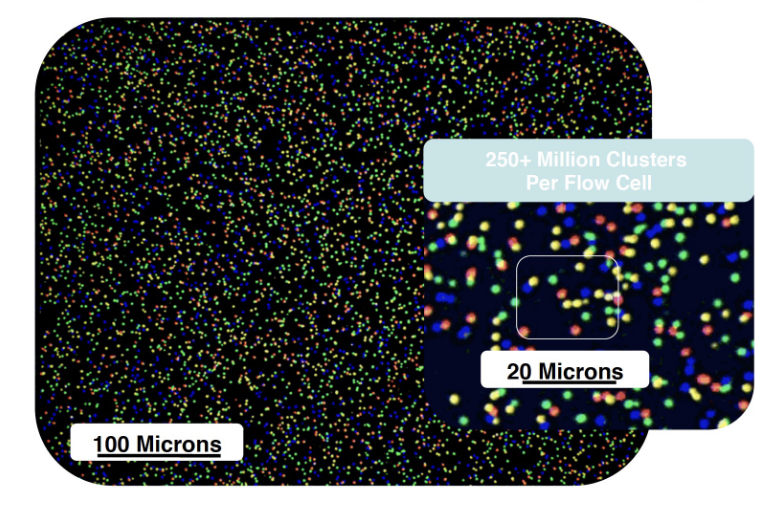
what is this a picture of?
DNA clusters in a flow cell
what are main traits of Illumina technology?
re-sequencing, short reads, low quality, high coverage, high throughput, cheap
what are some applications of illumina technology?
transcriptome (mRNA) sequencing, DNA-protein interactions (ChiP-Seq), DNA methylation (Methyl-seq), small RNA discovery
what are the main traits of Pacific Biosciences Sequencing Technology?
single molecule real time (SMRT), long reads, high quality, low coverage, low throughput, expensive
what is Oxford Nanopore Sequencing Technology?
DNA is sequenced using a nanopore based conductance changes
what are examples of Oxford Nanopore Sequencing Technology?
MinION, GridION, PromethION products
what are the main traits of Oxford Nanopore Sequencing Technology?
very long reads (up to 2 million long reads), high rate (5-15%), useful in genome assembly, sequence RNA directly
what are some applications of NGS (Next Generation Sequencing)?
whole genome sequencing, pathogen detection, study gene function, epigenomics studies
what are some applications of whole genome sequencing?
gene discovery, diagnostic testing to detect alleles/variants, ancestry, identify inference, forensic analysis
how can you study gene function (functional genomics) with NGS?
deducing the protein sequences from DNA sequences, manipulating genes to study its function, mRNA expression, genome-wide protein binding sites
how can you study epigenomics with NGS?
DNA methylation, histone methylation