aromatic chemistry
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
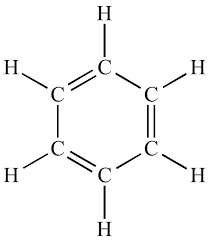
benzene molecular structure and bonding
C6H6
cyclic planar molecule
120 degree bond angle
each carbon has 3 covalent bonds
all C-C bonds are the same length
0.140nm bond length
spare electrons in p orbital overlap to form layers
kekulè structure and bond length
intermediate bond length
why is benzene more stable?
because of ring of delocalised electrons
hydrogenation of benzene and cyclohexatriene
-120×3= -360
-360-(-208)= -152
expected ΔH hydrogenation of cyclohexatriene: -360 kJmol⁻¹
ΔH hydrogenation of benzene is less exothermic by 152kJmol⁻¹
so benzene is more stable than cyclohexatriene
due to ring of delocalised e-
enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexa-1,3-diene and cyclohexa-1,4-diene

benzene vs phenyl naming
Where is the functional group? | Naming approach |
|---|---|
On the alkyl chain (not directly on benzene) | Phenyl- as a substituent
|
Directly on benzene ring | Named as substituted benzene (e.g. benzoic acid, nitrobenzene) |
Reactions of benzene
Benzene does not generally undergo addition reactions because these would involve breaking up the delocalised system
Benzene has a high electron density and so attracts electrophiles
It reactions are usually electrophilic substitutions
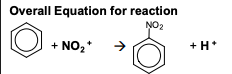
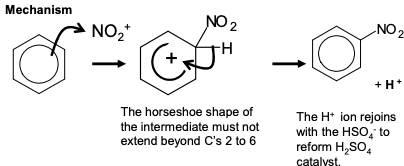
nitration of benzene
change in functional group: benzene —> nitrobenzene
reagents: conc. HNO3 and conc. H2SO4
mechanism: electrophilic substitution
electrophile: NO₂⁺
NOTE: THE + MUST BE ON THE N, NOT THE O2 OR U WILL LOSE MARKS
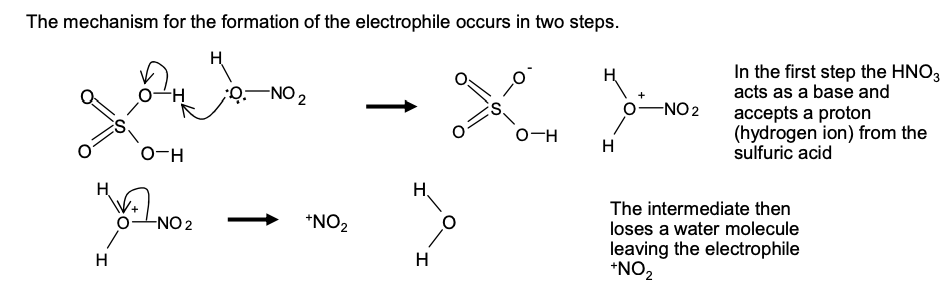
equation for formation of electrophile: HNO₃ + 2H₂SO₄ —> NO₂⁺ + 2HSO₄⁻ + H₃O⁺
The mechanism for the formation of the electrophile
mechanism for nitration of benzene
This reaction with benzene is done at 60 degrees
On using higher temperatures a second nitro group can be substituted.
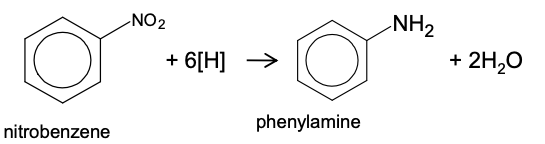
Reducing a nitroarene to aromatic amines
Mechanism: reduction
Reagent: Sn/Fe and HCl
Conditions: Heating
As the reaction is carried out in HCl, the ionic salt C6H5NH3+Cl- will be formed, which is soluble in water
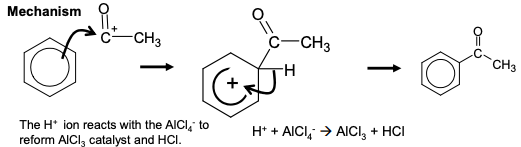
friedel-crafts acylation
Change in functional group: benzene —> phenyl ketone
Reagents: acyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride catalyst
Conditions: heat under reflux
Mechanism: Electrophilic substitution
Equation for Formation of the electrophile:
AlCl₃ + CH₃COCl —> CH₃CO⁺AlCl₄ ⁻
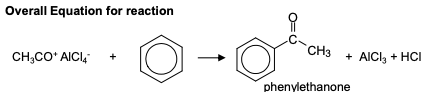
mechanism for friedel-crafts acylation