Physical Assessment Exam 3: Heart Murmurs & Preload Overview
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
Chapter 18
Breast, Axillae, and Regional Lymphatics
What is the lymphatic system
1. Part of the immune system
2. Drains fluids back into the circulatory system
3. Protect against foreign invaders
A way cancer can metastasize through the body is through the
Lymph system
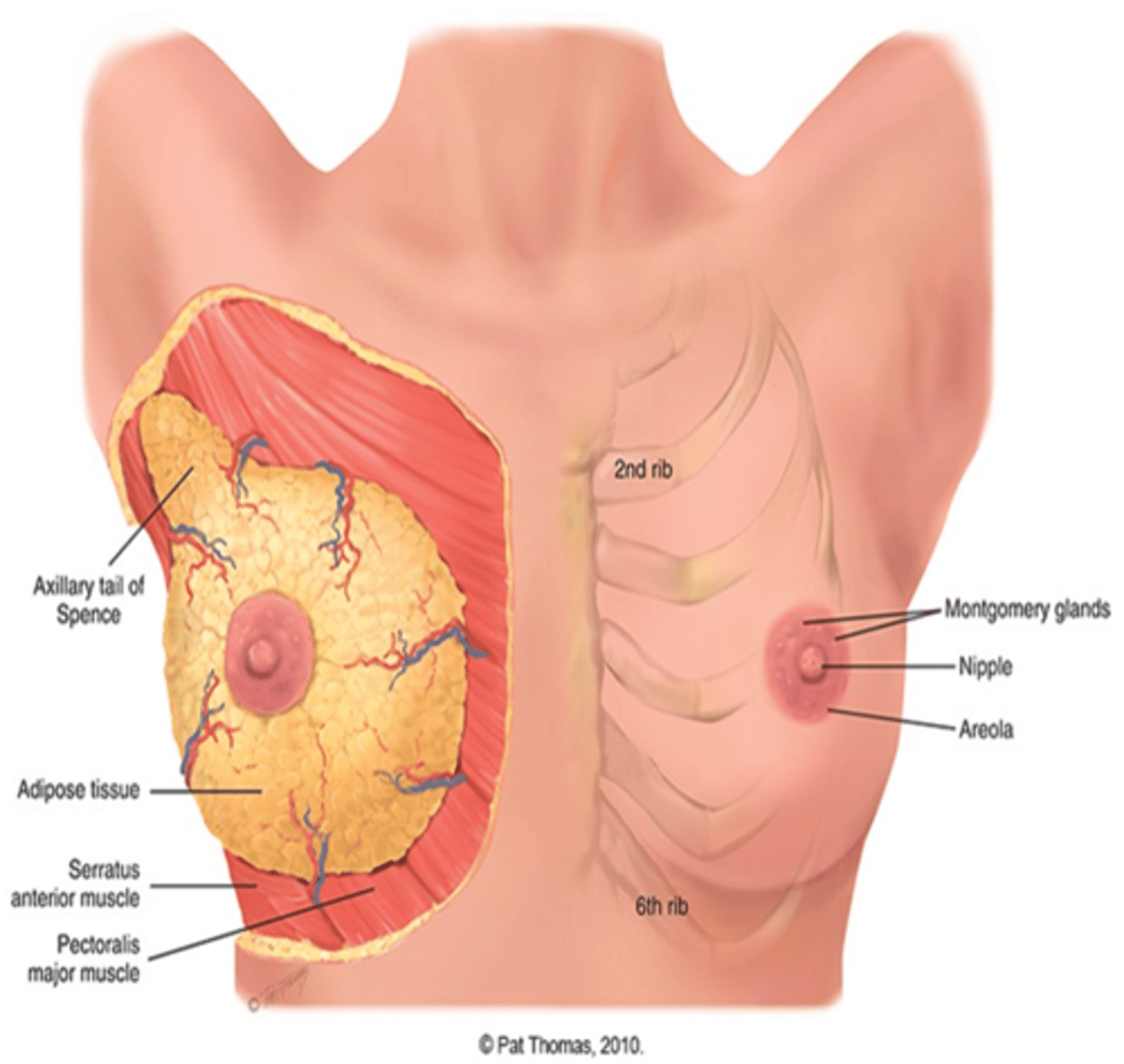
*The breasts are*
Located between second and sixth ribs, extending from side of sternum to midaxillary line
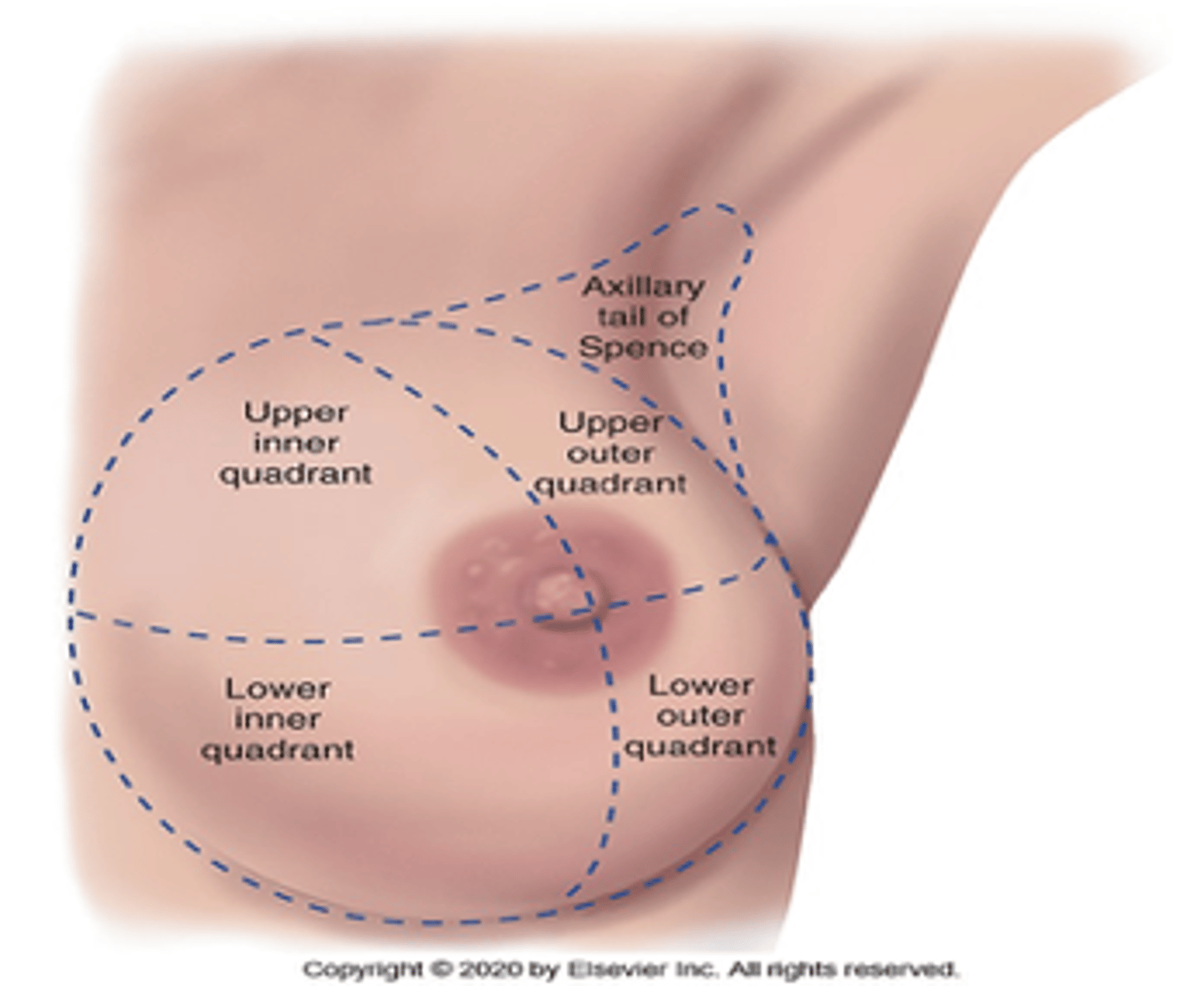
*Where is the site of most of breast tumors?*
Tail of Spence/Upper outer quadrant
*What area does the areola surround?*
Nipples
What lubricates your breast while you are lactating?
Montgomery glands
The breast is composed of?
a. glandular tissue.
b. fibrous tissue, including suspensory ligaments.
c. adipose tissue.
What is the Cooper's ligaments?
Fibrous bands extending vertically from surface to attach on chest wall muscles. Support breast tissue
*Glandular, Fibrous, and adipose breast tissue depend on?*
person's nutritional status
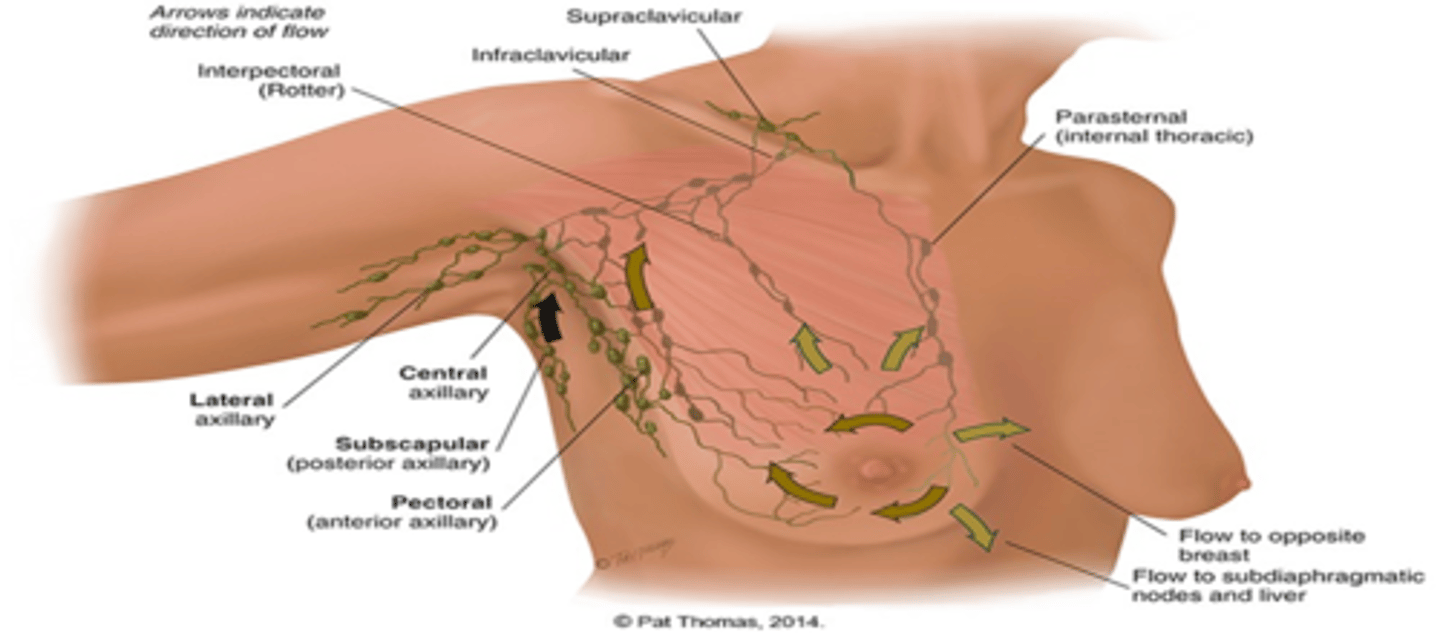
*The four groups of axillary nodes are present* and what is the group of lymph nodes that drains over the three groups of nodes?
a. Central axillary nodes: Drain the other axillary nodes
b. Pectoral (anterior axillary)
c. Subscapular (posterior axillary)
d. Lateral axillary
*From the central axillary nodes, drainage flows up to*
the infraclavicular and supraclavicular nodes.
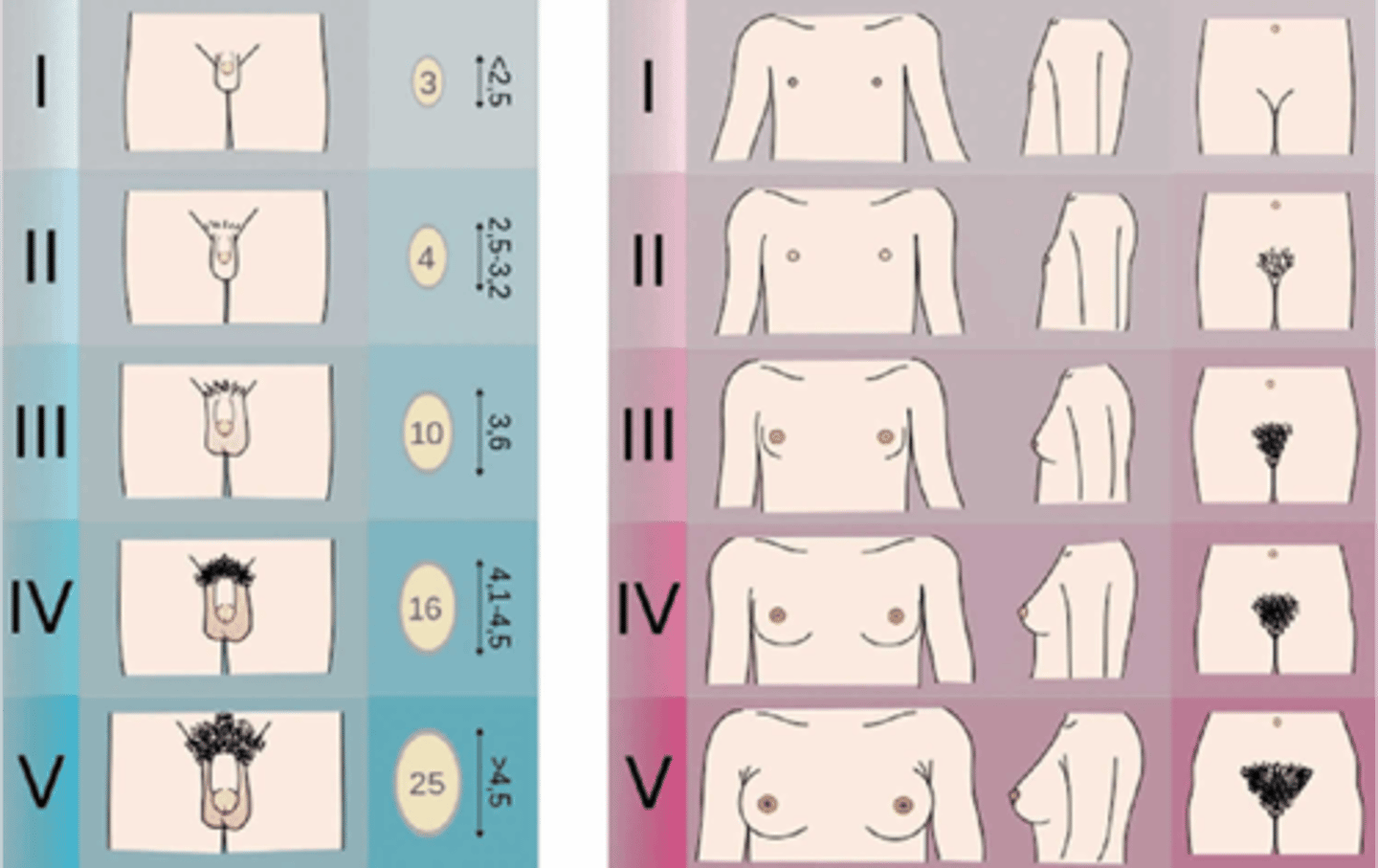
*What is the beginning of breast development?*
Thelarche precedes menarche by two years. Stage 4 (First period arrives)
What is menarche
2 years after thelarche
When do breast buds and pubic hair start to form?
Stage 2. Ages 9-11
When does acne first appear and armpit hair forms; height increases at its fastest rate?
Stage 3. After age 12
Tanner Staging
What month does the breast start to change?
The second month of pregnancy. This is also an early sign for most women.
What is colostrum?
a. May be expressed after the 4th month
b. Thick yellow fluid is precursor for milk, containing same amount of protein and lactose, but practically no fat.
c. Rich in antibodies that protect newborn against infection, so breastfeeding is important.
**This comes first before milk**
What is lactation?
Milk production
Whitish color that begins 1-3 days postpartum
Developmental Competence: Aging Woman
a. Axillary hair decreases.
b. ovarian secretion of estrogen and progesterone decreases, causing breast glandular tissue to atrophy. (Decreased breast size)
c. the lactiferous ducts are more palpable
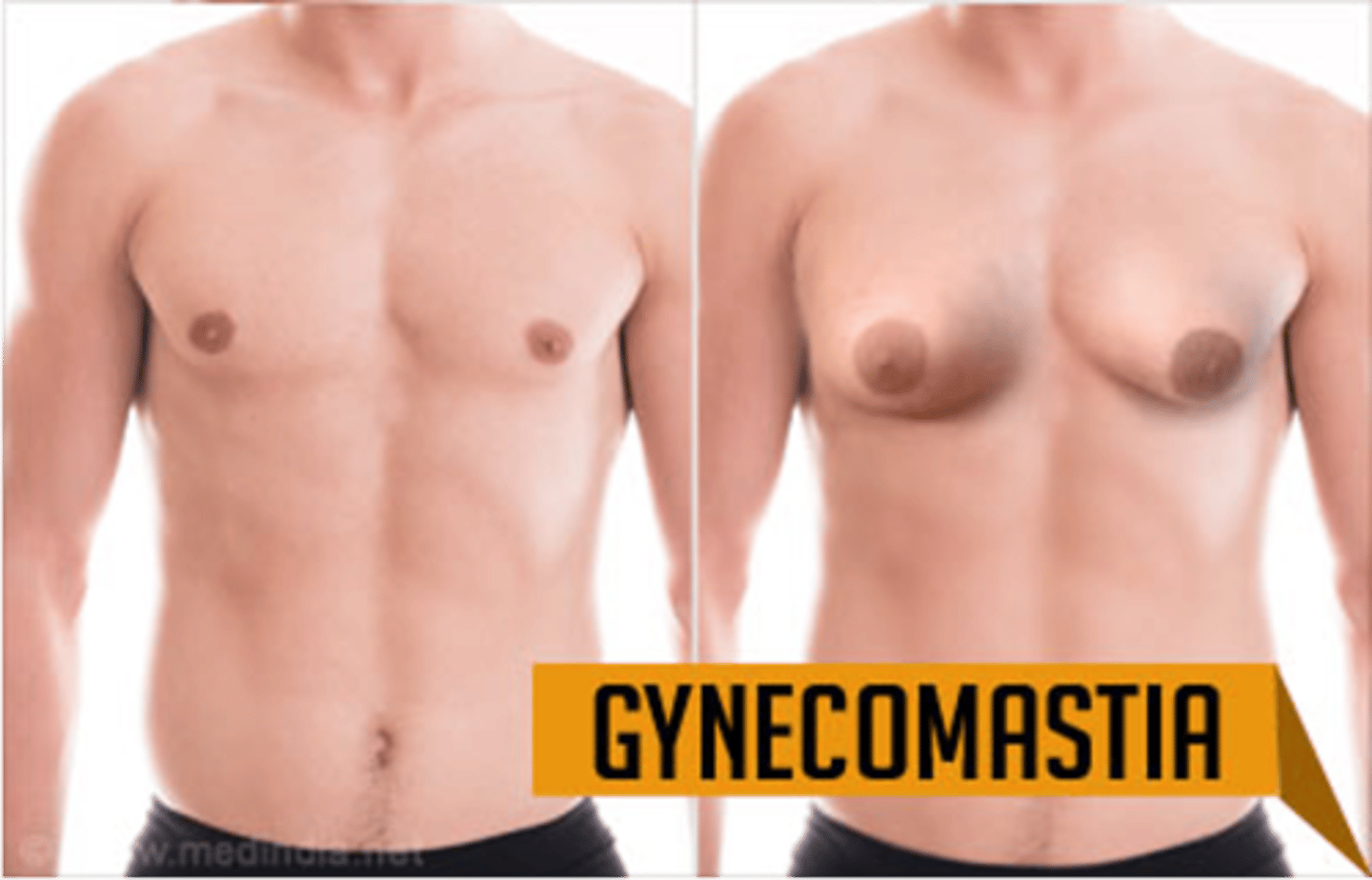
Developmental Competence:Male Breast. What is gynecomastia?
a. During adolescence, it is common for breast tissue to temporarily enlarge.
b. May reappear in aging male and may be due to testosterone deficiency.
c. Reassurance is necessary for adolescent male, whose attention is riveted on his body image.
•Feels like a smooth, firm, movable disk
**Usually temporary**
Breast Cancer: Culture and Women
a. Although many breast lumps are benign, women initially assume worst possible outcome, including cancer, disfigurement, and death.
Breasts can
•Affects body image
•Influenced by society and media response
•Integrated with women’s self-concept
What is the BRCA1 and BRACA2 mutation
If these genes are expressed it can lead to cancer
What can increase your risk of breast cancer?
a. Family history
b. Lifestyle factors (alcohol drinking)
c. Smoking
What is HER2?
is a growth-promoting protein on the outside of all breast cells.
Subjective Data for the breasts and axilla
a. Breast
Pain, lump, and discharge
Rash, swelling, trauma
History of breast disease
Surgery or radiation
Medications
Patient-centered care
Perform breast self-examination/last mammogram
b. Axilla
Tenderness, lump, or swelling
Rash
Subjective Data Questions:Patient-Centered Care
Ask about self-breast exam (SBE)
Teaching moment to review basics of examination. Do this exam about once a month
Objective Data
a. Woman sitting up facing examiner
b. During palpation when woman is supine, cover one breast with gown while examining other
Equipment
-Small pillow
-Ruler marked in centimeters
-Pamphlet or teaching aid for breast self-examination (BSE)
When looking at the characteristics of a lump or mass?
As with clock face, describe distance in centimeters from nipple; or diagram breast in woman’s record and mark in location of lump.
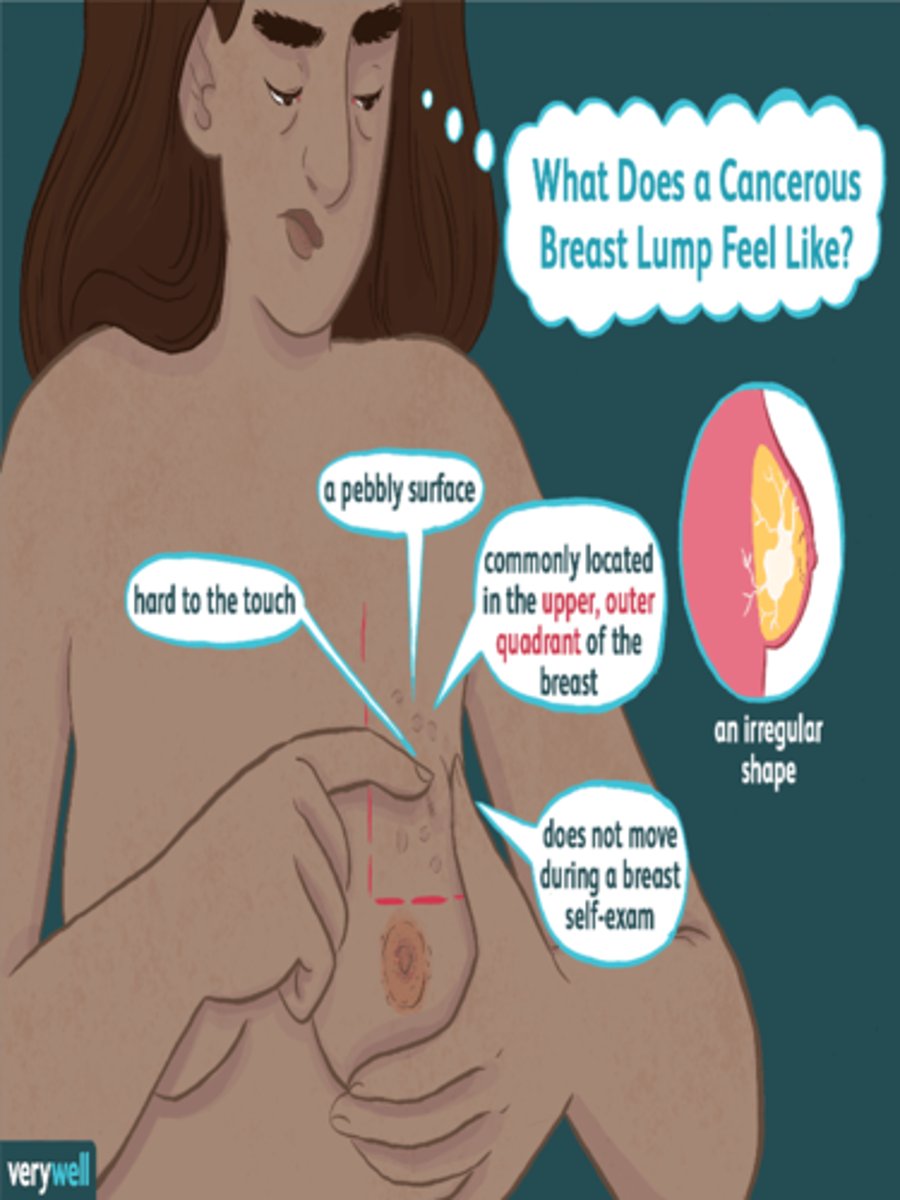
BSE: Keep Teaching Simple
Describe correct technique and rationale and expected findings to note as woman inspects her own breasts.
Women over 50 years old have an increased risk for
breast cancer
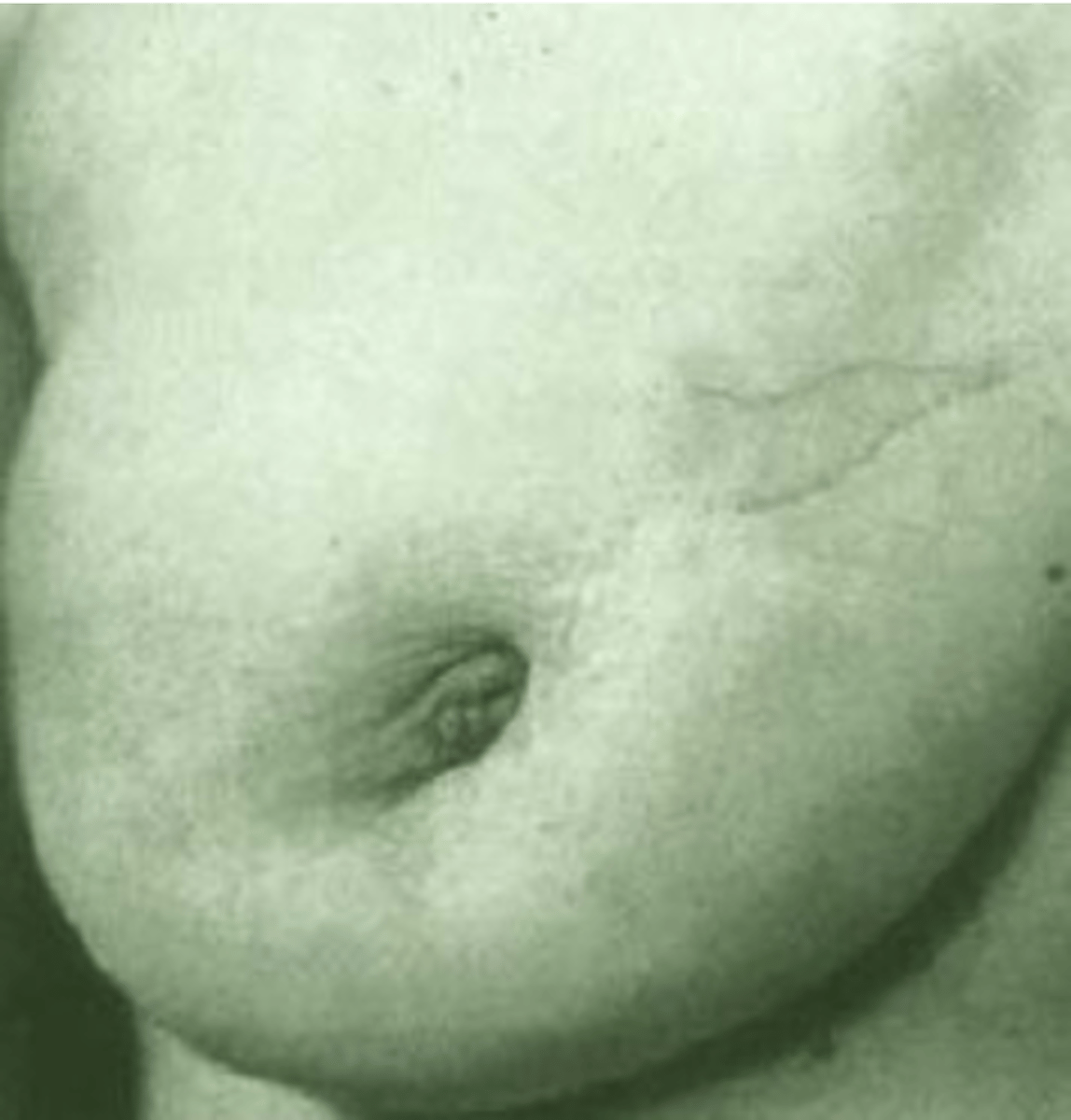
Abnormal Findings:Signs of Retraction and Inflammation
a. Dimpling
-Nipple retraction
b. Edema (peau d'orange)
c. Fixation
d. Deviation in nipple pointing
Chapter 19
The thorax and the lungs
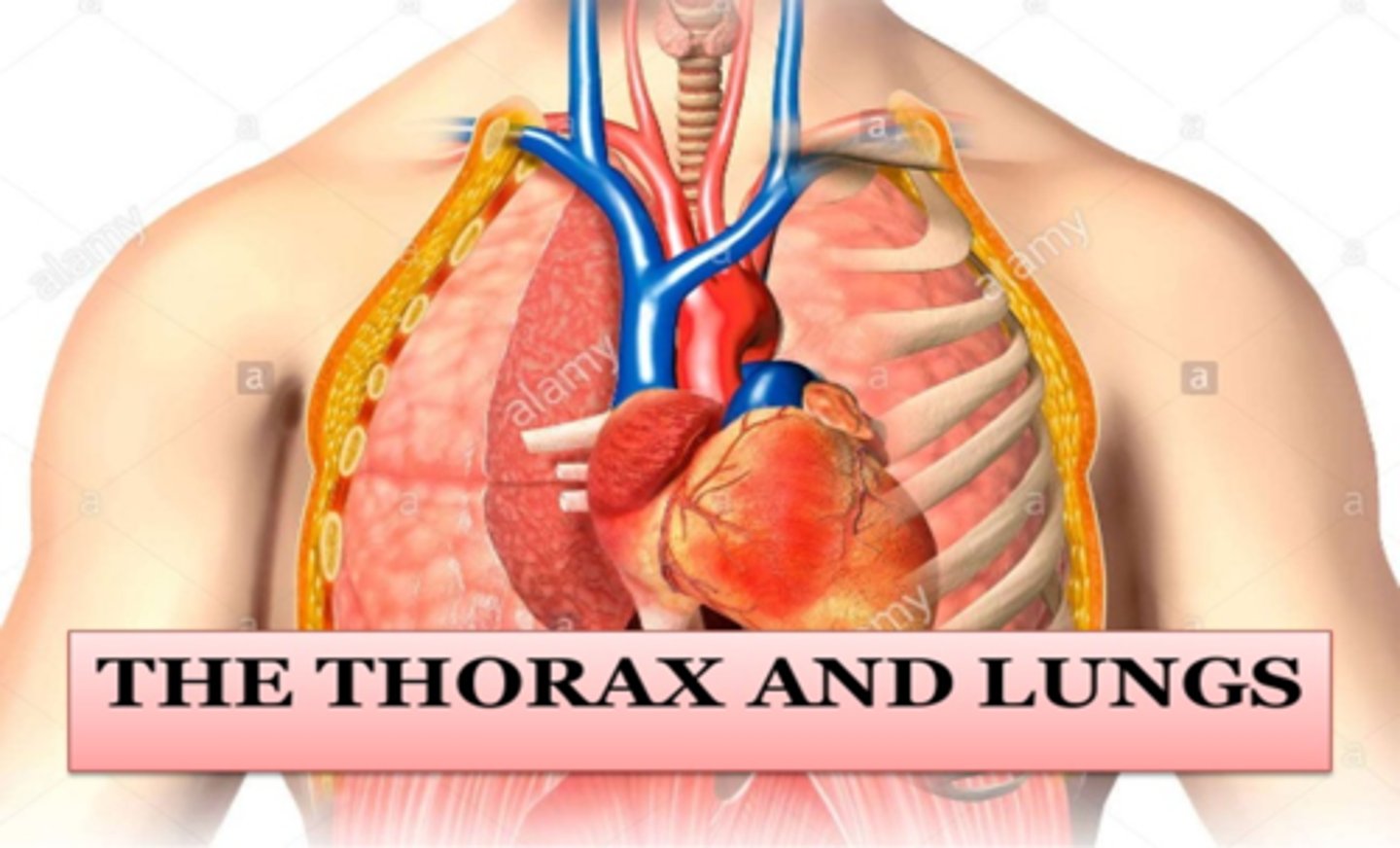
What are the four major functions of the respiratory system?
1. Supplying oxygen to the body for energy production
2. Removing carbon dioxide as a waste product of energy reactions (ATP)
3. Maintaining homeostasis (acid-base balance) of arterial blood
4. Maintaining heat exchanged (less important in humans)
Structures of the Respiratory System
What does the thoracic cage consist of?
Defined by sternum 12 pairs of ribs, and 12 thoracic vertebrae
Which ribs are known as the "floating ribs"?
Ribs 11 and 12 and they have free palpable tips
*What is the manubriosternal angle?*
This is known as the "Angle of Louis" and it is at articulation of manubrium and sternum and continuous with the second rib. The "Angle of Louis" is where your trachea is and when your bronchi start.
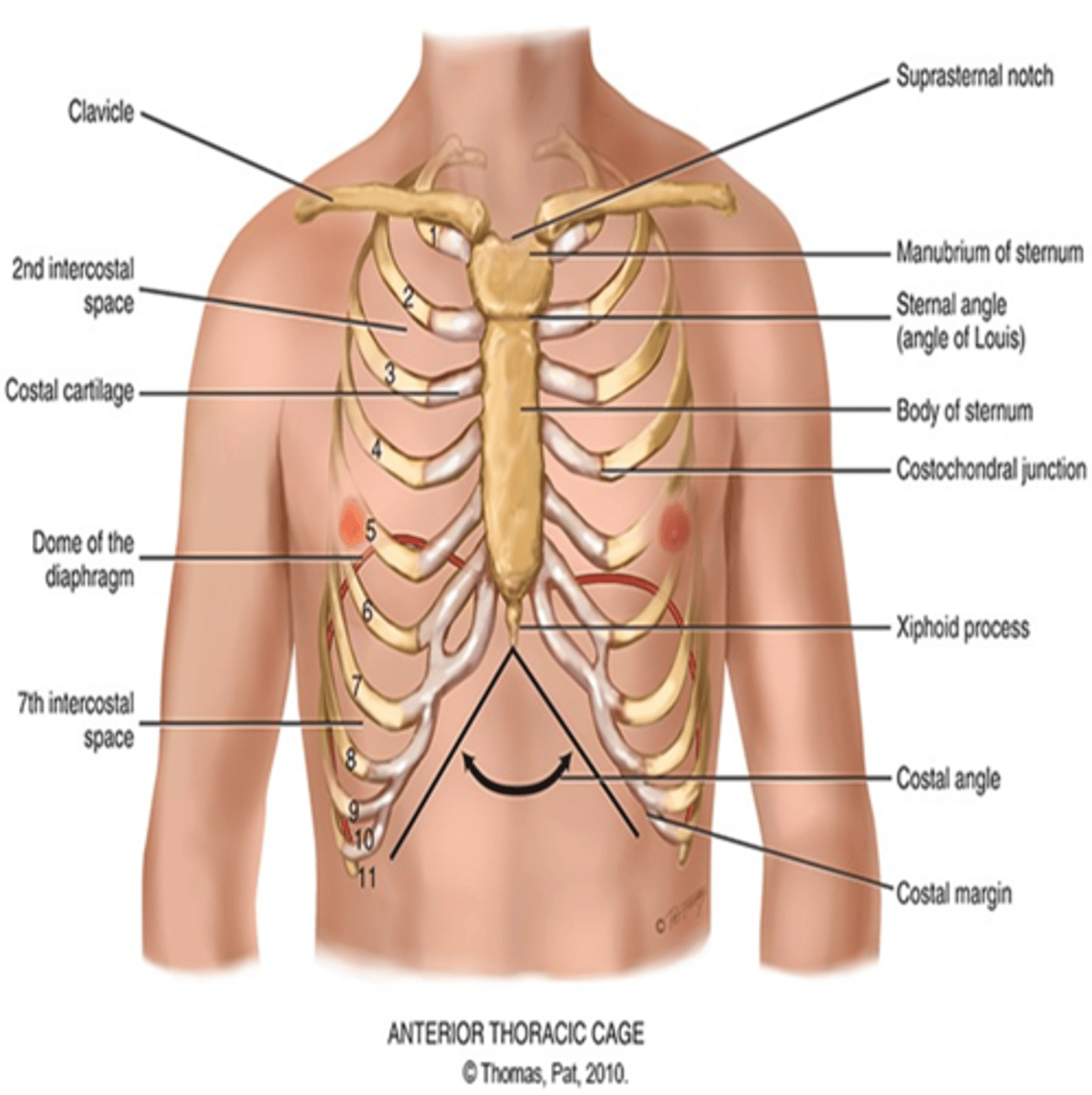
How do we locate the "Angle of Louis"?
a. Identify Angle of Louis, palpate lightly to second rib, and slide down to second intercostal space.
b. Angle of Louis also marks site of tracheal bifurcation into right and left main bronchi
c. Corresponds with upper border of atria of the heart, and it lies above fourth thoracic vertebra on back.
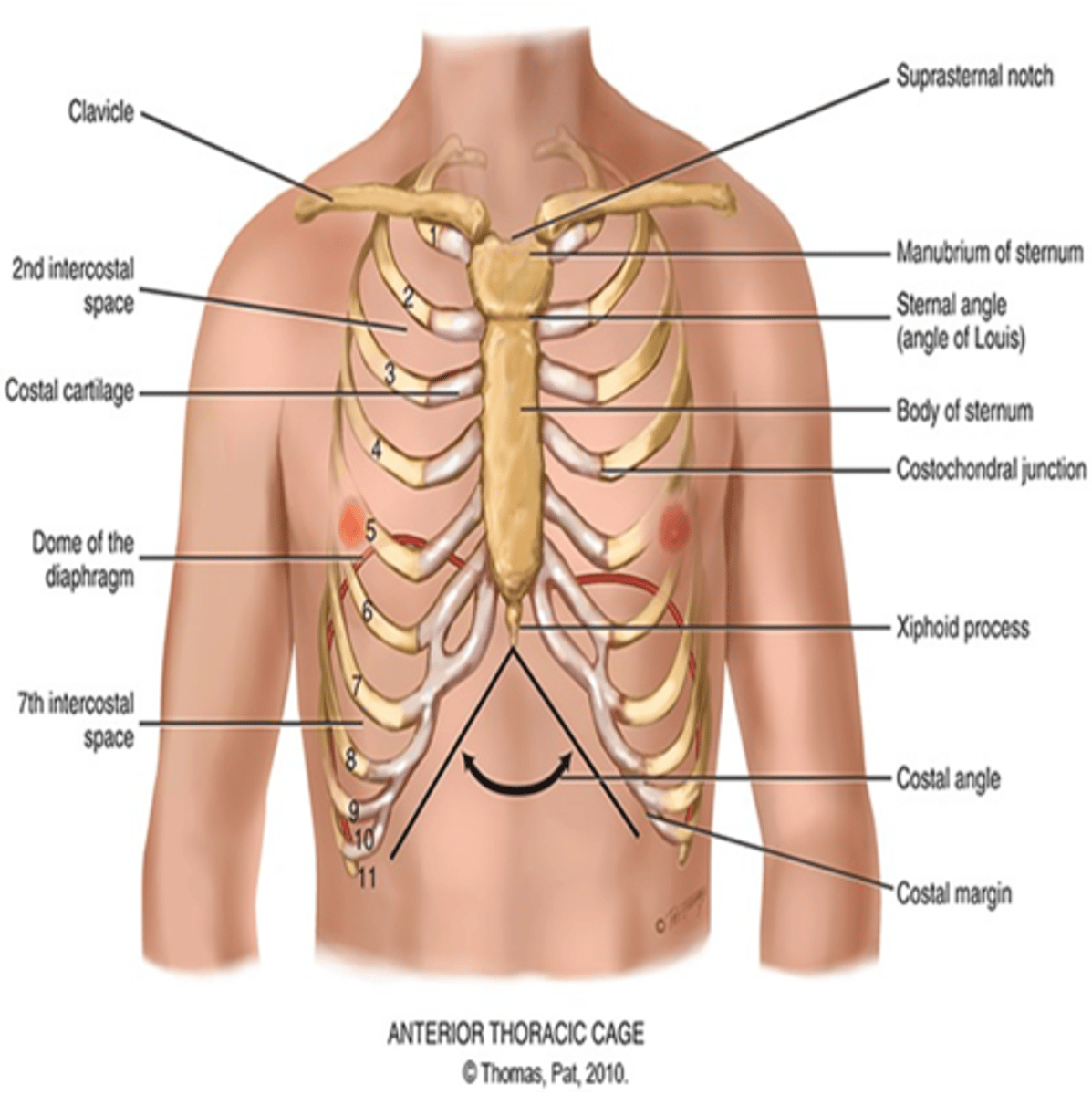
What does the sternum consist of and what is it also known as
The breastbone. It consists of the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process.
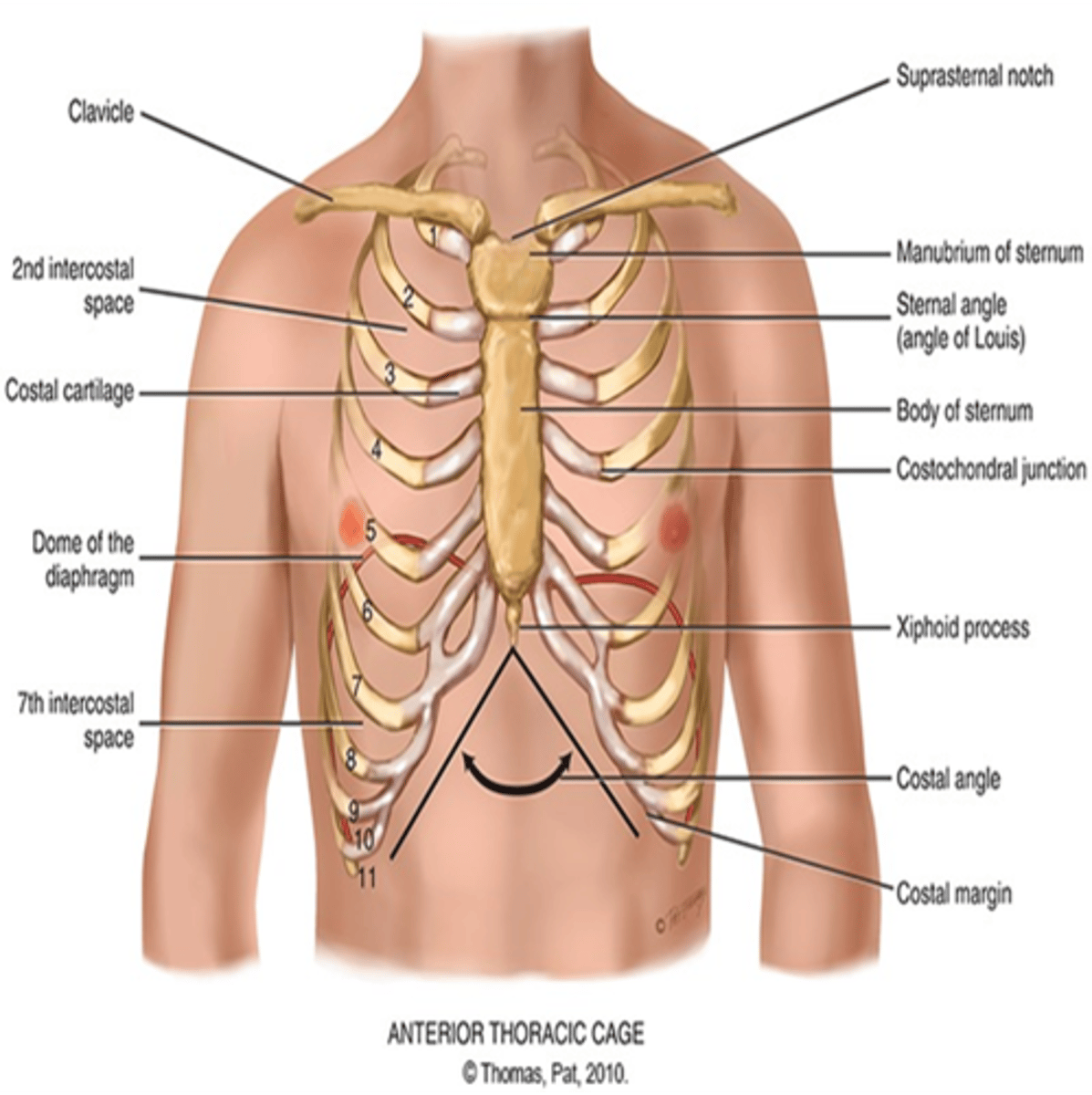
What is the suprasternal notch?
U-shaped depression just above the sternum, between the clavicles
What is between the ribs?
intercostal spaces
What is the costal angle?
the right and left costal margins form an angle where they meet at the xiphoid process
What does the mediastinum contain?
esophagus, trachea, heart, great vessels
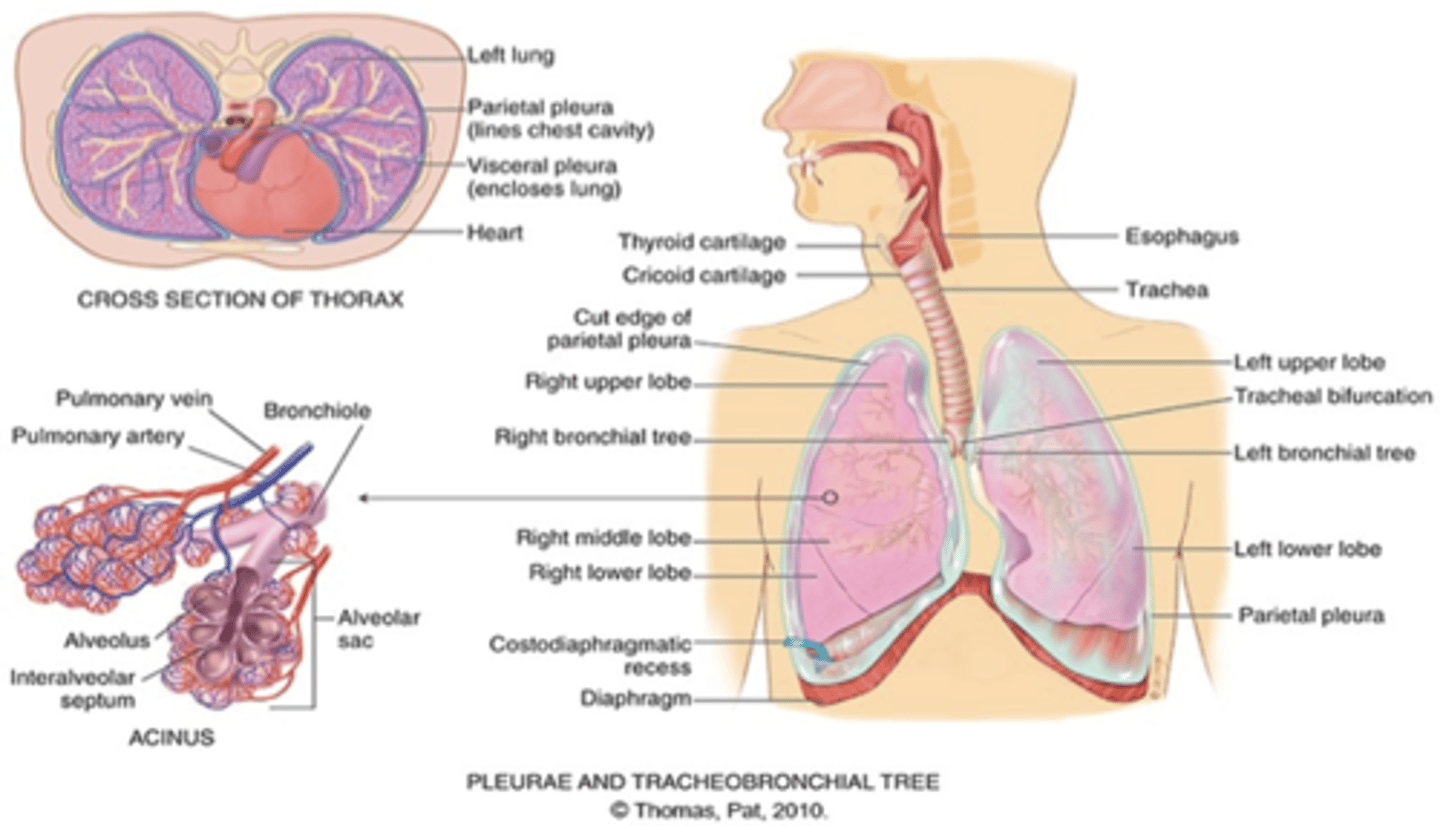
What do the right and left pleural cavities contain? What separates them?
contain the lungs separated by mediastinum
How many lungs do we have?
2 (right and left)
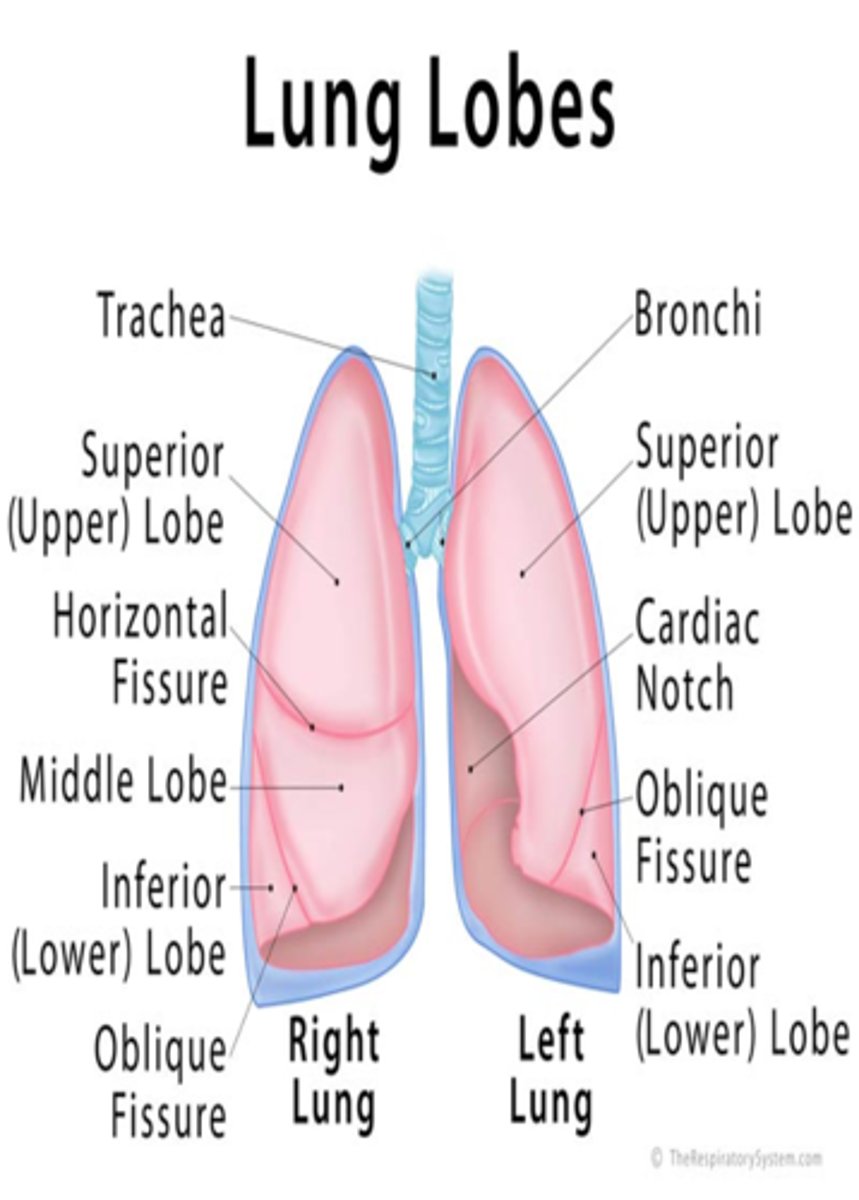
How many lobes does the right lung have?
3 lobes
The right lung is shorter than the left because of the underlying liver
How many lobes does the left lung have?
2 lobes
The left lung is narrower than the right because the heart bulges to the left
Why do you need a right midclavicular line?
To locate the apex of the heart
*What does the left lung contain?*
a. Has no middle lobe
b. The anterior chest contains mostly upper and middle lobes with very lower lobes
c. The posterior chest contains almost all lower lobes
What is pleura effusion of the lungs?
Fluid between the pleural space. A chest tube can help fix this and drain the fluid
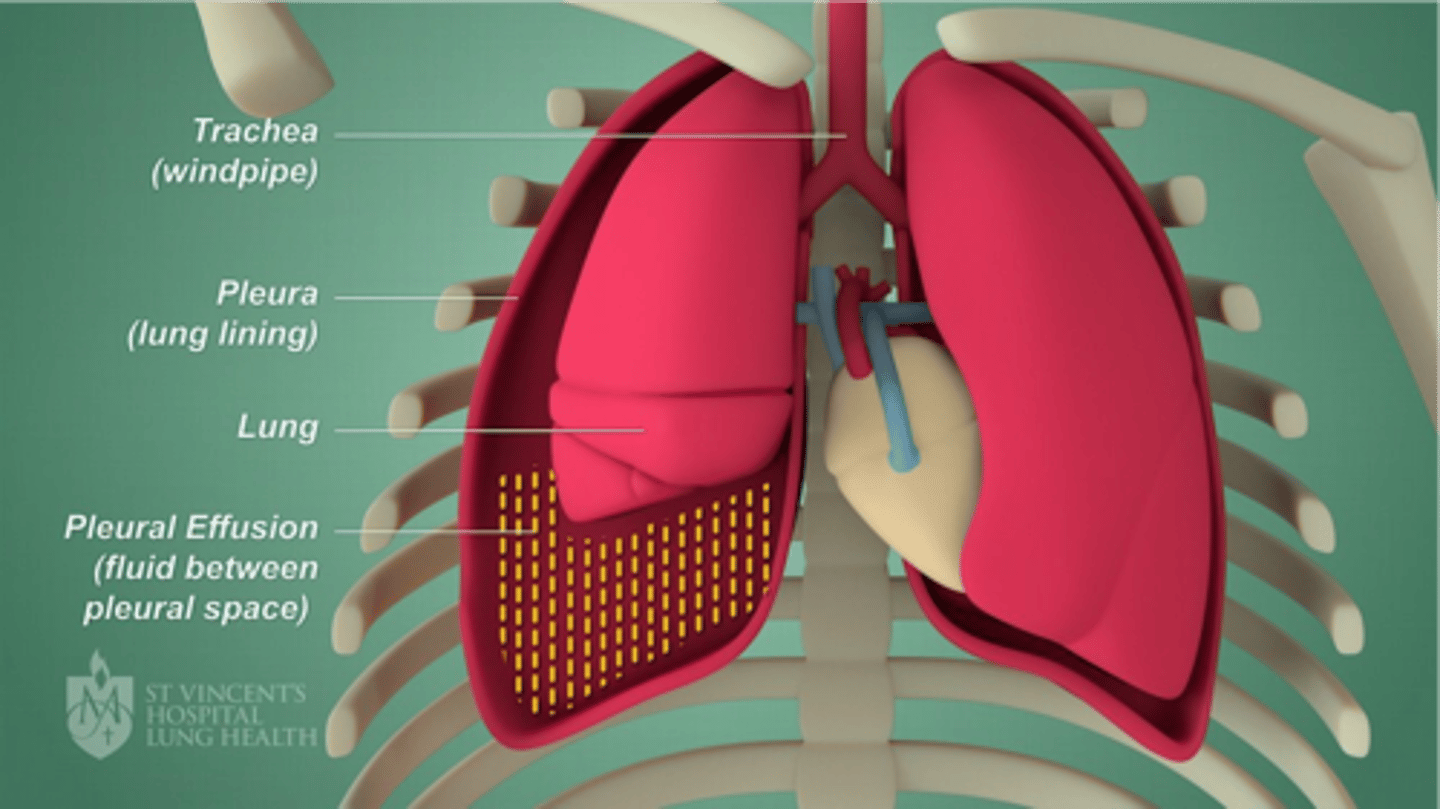
What is the pleurae?
•Visceral pleura lines outside of lungs, Parietal pleura against the ribs. Pleural cavity normally has a vacuum, or negative pressure, which holds lungs tightly against chest wall.
The bronchial tree
Right main bronchus is shorter, wider, and more vertical than the left main bronchus
*What is hypercapnia?*
An increase of carbon dioxide in the blood
What is a decrease of oxygen in blood?
Hypoxemia
What is inspiration?
Air rushing into the lungs and the chest size increases
What is expiration?
Air is expelled from the lungs as the chest recoils
What is surfactant?
A detergent like complex, reduces surface tension and helps keep the alveoli from collapsing. It has a clinical importance in the development in utero.
How does mechanical expansion alter the size of the thoracic container?
Both vertically and anteroposterior
What is associated with environmental tobacco smoke exposure?
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), negative behavioral and cognitive functioning, and increased rates of adolescent smoking
*What is the second most common cancer diagnosed?*
Lung cancer
*What is asthma?*
The most common chronic disease in childhood. It is the highest burden seen in those living at or below the federal level.
Subjective Data
•Cough (How long have you been coughing?)(Gradual or sudden?)
•Shortness of breath (Ever had any shortness of breath or hard-breathing spells)
•Chest pain with breathing (PQRST)
•History of respiratory infections **(COPD, bronchitis, emphysema)** Use Lung Function Questionnaire
•**Smoking history (How long have you been smoking?) (Ask about the 5A's)**
- Ask
-Advise
-Assess
- Assist
-Arrange
•Environmental exposure (Are there any environmental conditions that may affect your breathing? Occupational factors and exposure)
•Patient-centered care (Screening and follow up testing, TB test, Chest x-ray, Pneumonia or influenza immunization

Additional History for Infants and Children
-Has the child had any frequent or very severe colds?
- Is there any history of allergy in family?
-Does child have a cough or seem congested? Does child have noisy breathing or wheezing?
-Are any smokers in home or in car with child?
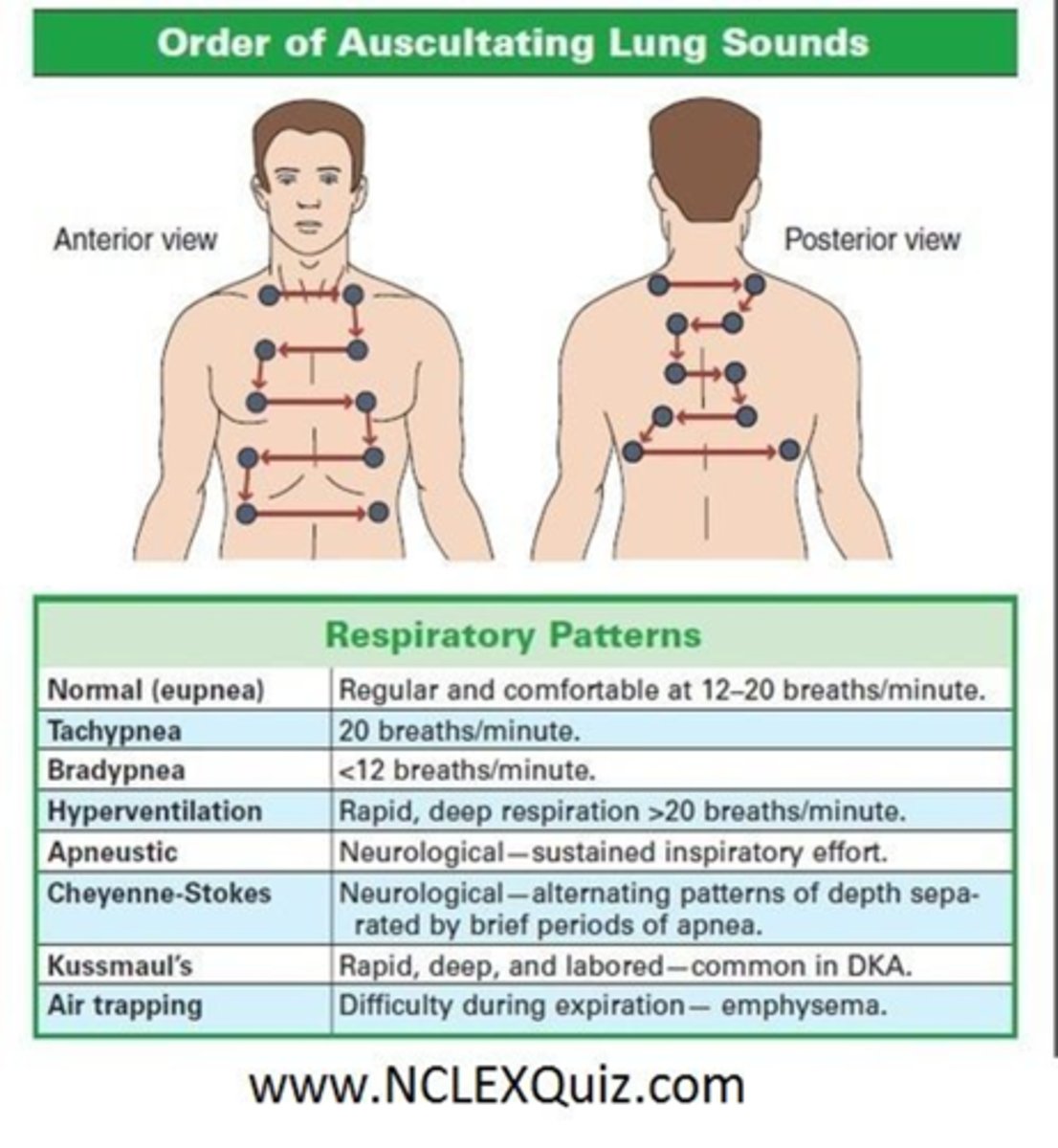
How do we examine the posterior and lateral thorax? What equipment do we ned?
-Perform inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation on posterior and lateral thorax.
-Equipment
a. Stethoscope
b. Small ruler, marked in centimeters
c. Marking pen
d. Alcohol wipe
Normal Respiratory pattern
Rate: 10-20 Breaths per minute
Depth: 500-800 mL
Pattern: Even
The ratio of pulse to respiration is fairly constant about 4:1
Inspection of the Anterior Chest
-Note shape and configuration of chest wall.
-Note patient's facial expression.
-Assess level of consciousness.
-Note skin color and condition.
-Assess quality of respirations.
a. Note respiratory effort.
b. Observe for symmetry.
c. Determine if accessory muscles are being used.
Tactile (or vocal) fremitus
Compare vibrations from one side to other as the person repeats "ninety-nine or "blue moon"
What sound do you hear in a healthy lung>
Resonance is low pitched, clear, hollow sound
What are the three types of breath sounds heard normally in adults and older child?
A. Bronchial
B. Bronchovesicular
C. Vesicular
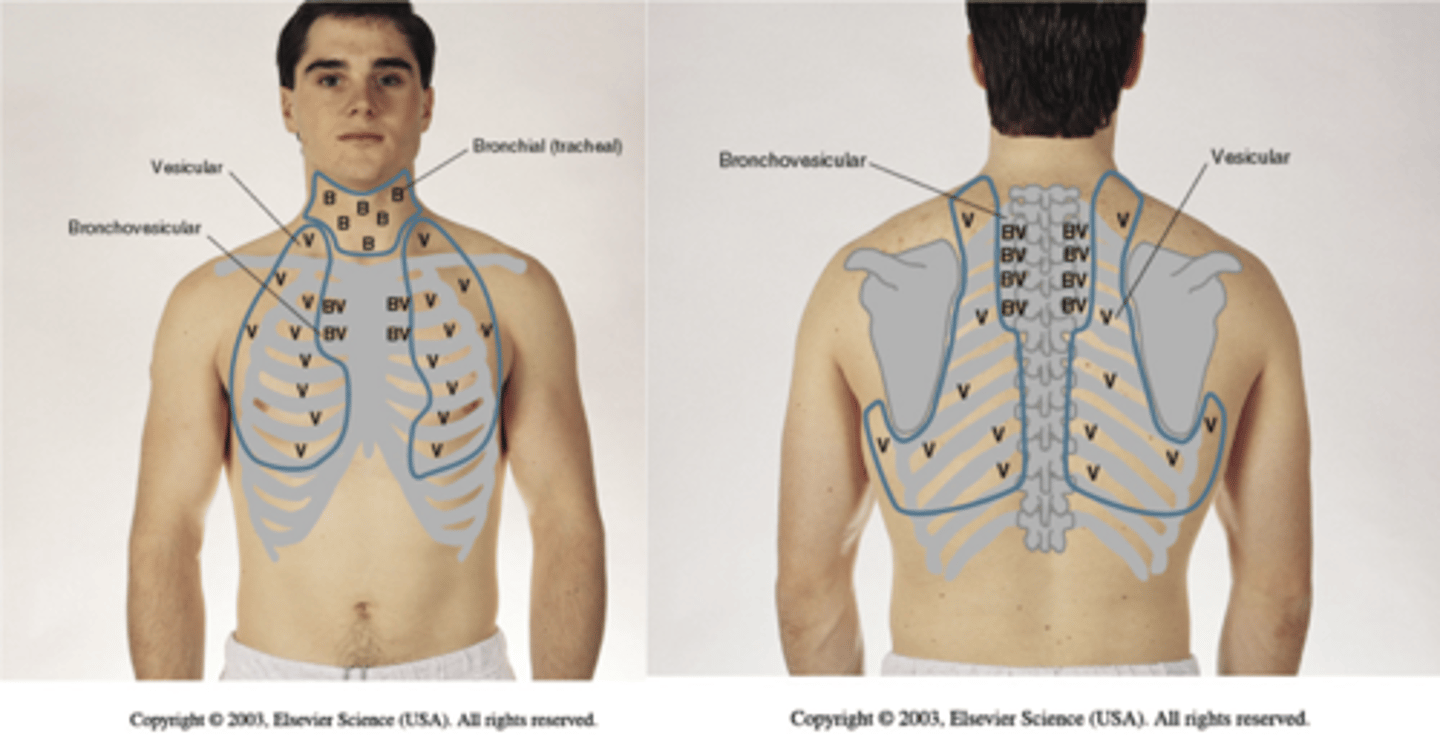
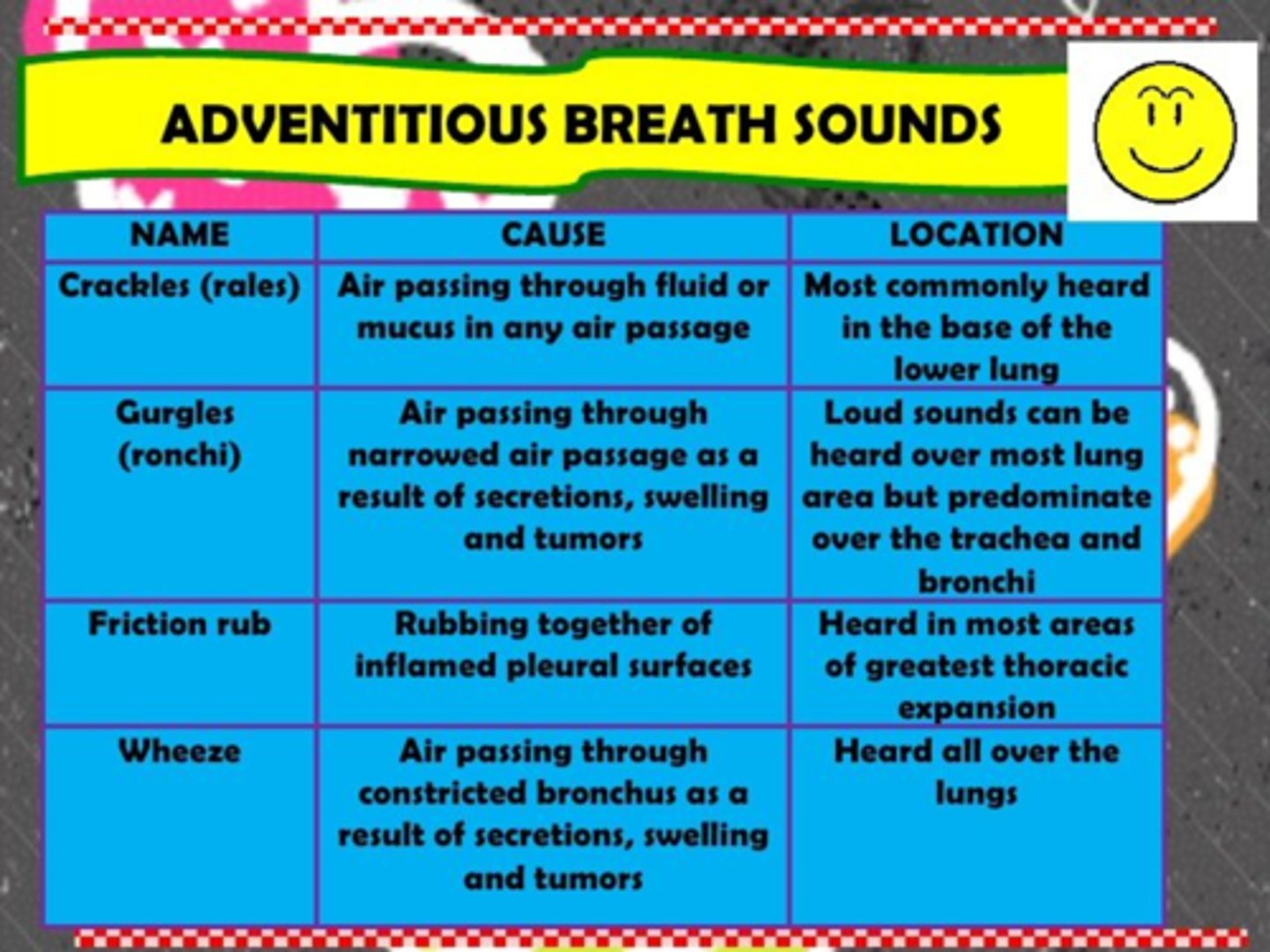
What are abnormal breath sounds?
Adventitious sounds
crackles -- soft high pitched sounds
Wheezes -- musical sounds , produced by constricted airways
*How long do we listen to respirations?*
Use a flat diaphragm of the stethoscope and listen to at least one full respiration in each location.
Perform bilateral comparison
Respiratory Patterns
adventitious breath sounds
*What is the forced expiratory time?*
The number of seconds it takes for the person to exhale from total lung capacity to residual volume
What is the spirometer?
Used in ambulatory care settings to measure lung health
What is the pulse oximeter?
noninvasive method to assess arterial oxygen saturation
What is the 6-minute walk test? (6 MWT)
safer, simple, inexpensive, clinical measure of functional status in aging adults
What is atelectasis?
Closure or collapse of alveoli
Chapter 20
Heart and Neck Vessel
What is automaticity?
The ability of the heart to start and maintain rhythmic activity without the use of the nervous system
What cranial nerve is associated with the central nervous system?
Cranial Nerve 10
*What makes up the cardiovascular system?*
The heart and circulatory system
What does the heart do?
The heart works as a pump that pushes blood to the organs, tissues, and cells of your body
*What is the formula for cardiac output?*
CO = HR x SV
SV= blood volume in each systole
HR= beats per minute
*What is preload?*
venous return that builds during diastole
*What is afterload?*
the opposing pressure the ventricle must generate to open the aortic valve against the higher aortic pressure
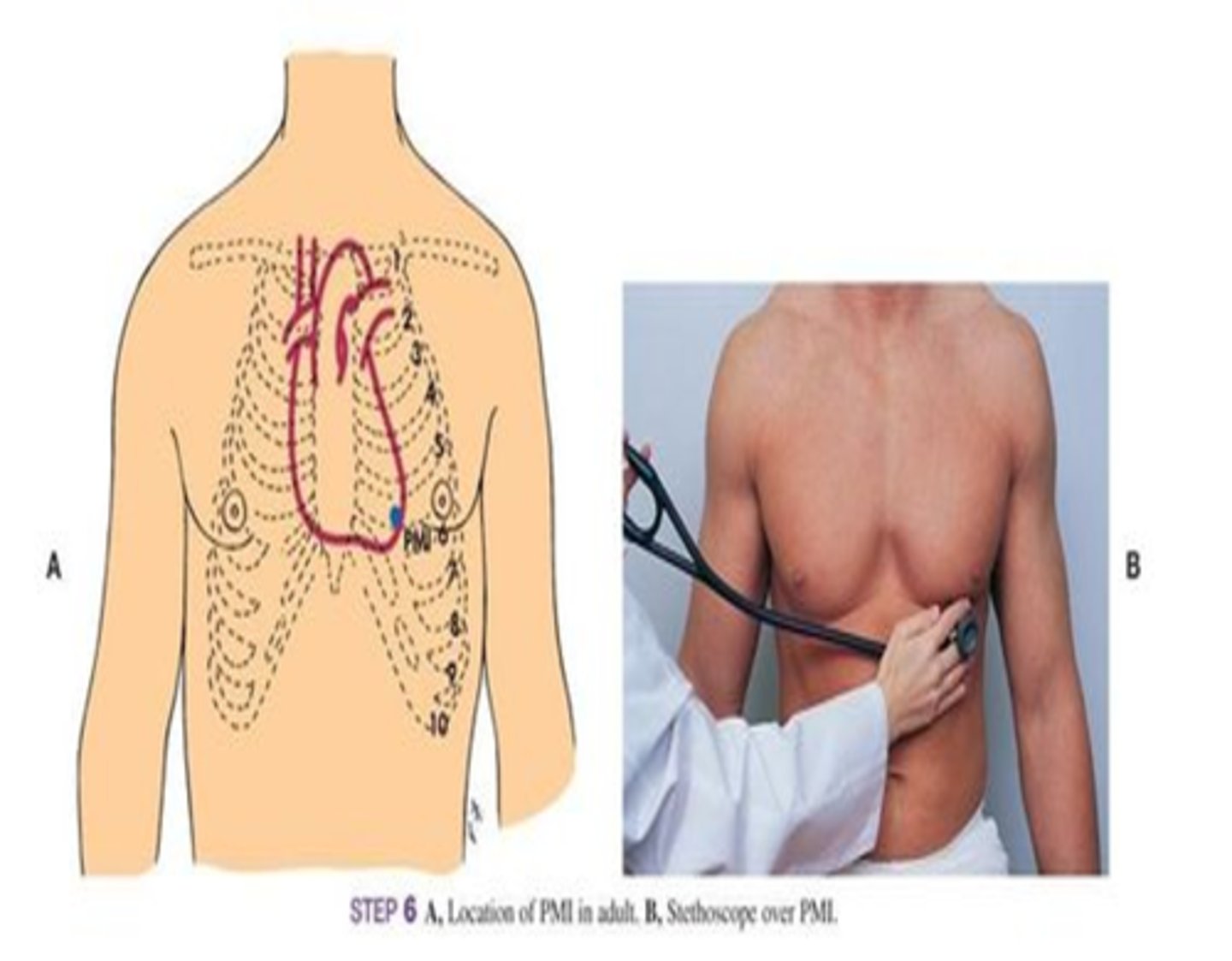
*What is the precordium?*
the area on the anterior chest directly overlying the heart and great vessels
How many chambers does the heart have?
4 (2 atria, 2 ventricles)
What are the great vessels?
major arteries and veins connected to the heart
*The blood vessels arranged in two continuous loops (2 types of circulation in out body)*
Pulmonary circulation
Systemic circulation
When the heart contracts, it pumps blood simultaneously into both loops
The cardiac chambers
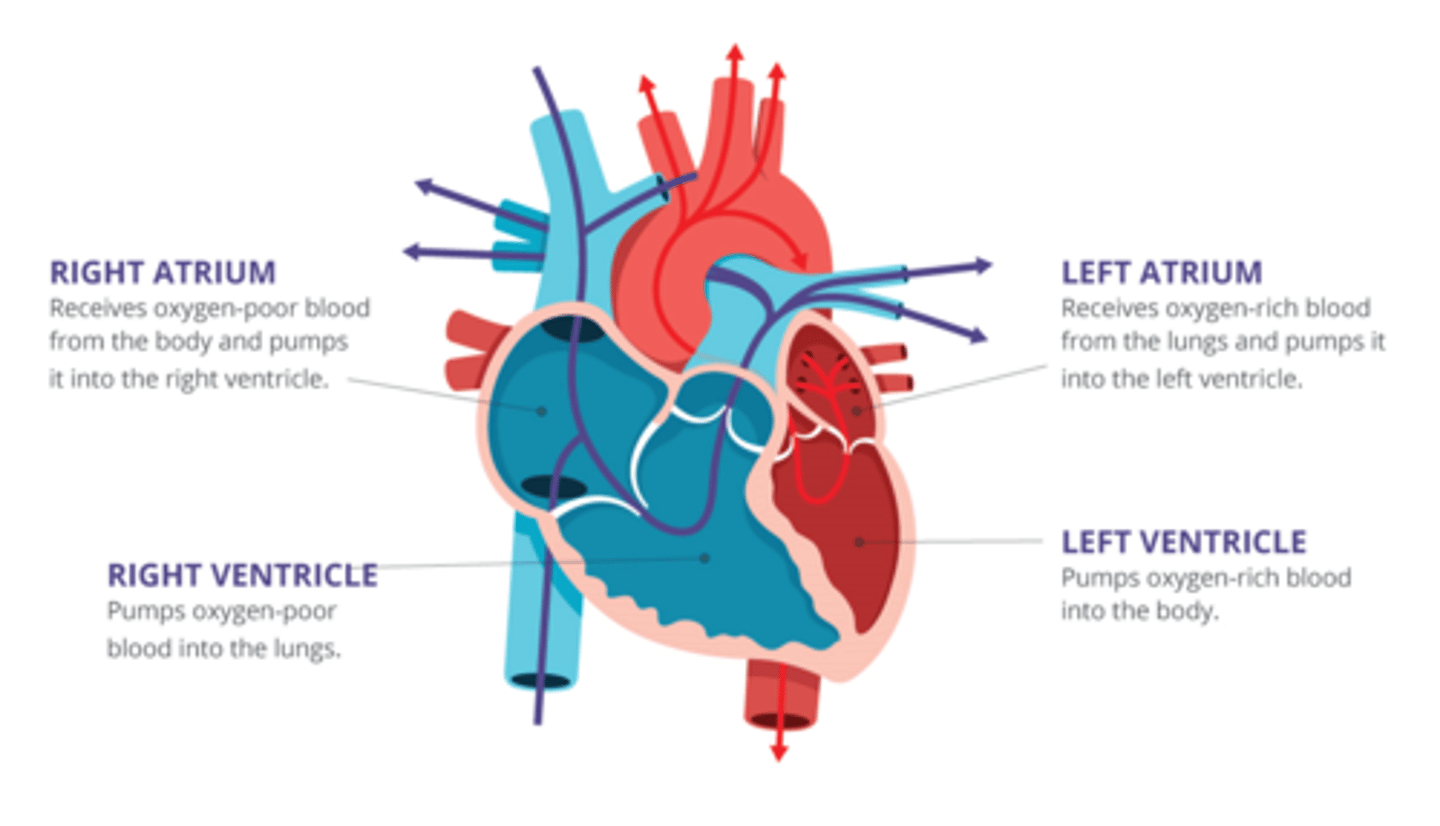
*How does blood flow through the heart?*
1. Inferior and Superior Vena Cava
2. Right Atrium
3. AV tricuspid
4. Right ventricle
5. Pulmonic valve: semilunar
6. Pulmonary artery
7. Lungs
8. Pulmonary vein
9. left atrium
10. AV Bicuspid aka Mitral aka Apical
11. Left Ventricle
12. Aorta
What are the numerous layers of the heart?
A. Pericardium (Tough wall)
B. Myocardium (Muscle)
C. Endocardium (Thin layer)
*Where is S1 heard the loudest?*
apex of the heart
*Where is S2 heard the loudest?*
base of the heart
*What makes an auscultating heart sound at ERB's point?*
S1 and S2 heard equally
*What is the purpose of valves?*
It separates the four chambers and its main purpose is to prevent backflow of the blood. Valves open and close passively in response to pressure gradients,
What are the four valves in the heart?
Two AV valves (Tricuspid and Bicuspid)
Two semilunar valves (Aortic and Pulmonic)