DPT 744 Lecture 2
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Cervical vertebrae has how many?
C1-C7 but 8 cervical nerves
Thoracic vertebrae has how many?
T1-T12
Lumbar vertebrae has how many?
L1-L5
Sacral vertebrae has how many?
S2-S5
Palpating (most prominent cervical process)
C7
Palpating(Inferior tip of scapula)
T7
Palpating(Superior aspect of iliac crest; Tuffier’s line
L4
Palpating(Posterior superior iliac crest)
S2
In an adult human what are the degrees on the curvature of the back?
Cervical- 2 degrees
Thoracic- 1 degrees
Lumbar- 2 degrees
Sacral- 1 degree
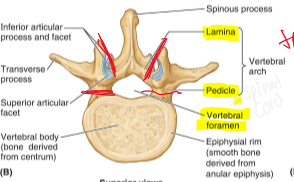
What is the Vertebral Arch?
composed of the pedicles and the laminae
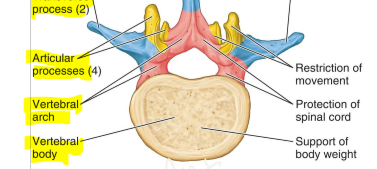
What is the Vertebral foramen
Space created by the body and the vertebral arch
What is the Vertebral canal
contains spinal cord and its coverings; created by successive vertebral foramina
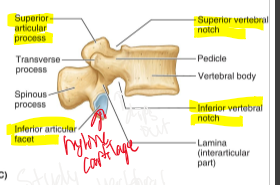
Spinous Process
extension posterior from the meeting of the lamina
Transverse Process
lateral projections originating at junction of the lamina and pedicle
Superior articular process
2 superior projections from the superior portion of the lamina which form synovial joints (facet) with vertebra directly above
Inferior articular process
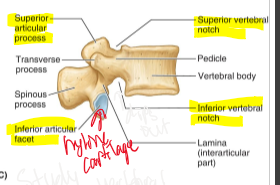
Superior vertebral notch
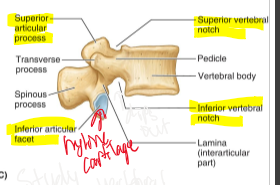
Inferior vertebral notch
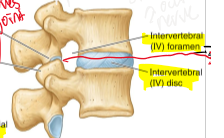
Intervertebral foramen
space created by superior and inferior vertebral notches
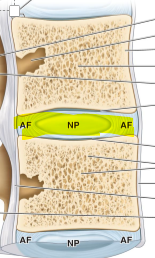
Anulus fibrosus and Nucleus pulposus and if they push out the PLL what happens
between the spinal bones and its called herniated disk.
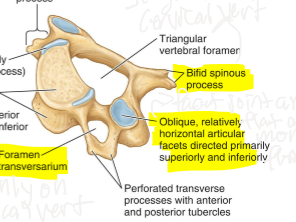
Cervical vertebrae facets are facing which way?
Thoracic vertebra facets which way?
vertical, allow rotation
Lumbar facet are facing which ways
Vertical face each other and allow flexion and extension
C0-C1 is also know as what?
atlantoccipital
C1-C2 is also known as
altantoaxial joint
Transverse ligament of atlas is important why?
Because it keeps the vertebrae in place
The nucleus pulposus and Anulus fibrosus (gel like) are always even in the joint (T or F)
False (because of the Uncinate process which causes upward growth from the superior aspect of each lateral vertebral towards the vertebral body above)
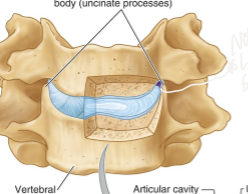
What do the Zygapophysical Joints for the intervertebral disc?
Creates stability by restraining exessive movement protecting the intervertebral disc from torsion (twisting) strain
Thoracic area, the height of body is slightly higher posteriorly and contributes to what?
normal kyphosis
Superior and inferior demi facet form a what
connection of rib
Same level (Rule of ‘threes’
T1-T3
Half a level below (Rule of ‘threes’
T4-T6
One whole level below
T7-T9
One whole level below (Rule of ‘threes’
T10
Half a level below (Rule of ‘threes’
Half a level below
Same Level (Rule of ‘threes’
T12
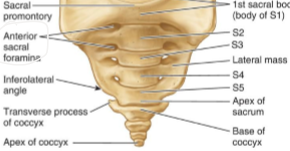
The Sacrum has how many fused vertebrae
5
The base of the sacrum what?
superior facets of S1 articulate with inferior facets of L5
Where does the sacarl nevers come out?
Anterior sacral foramina
What gives the spine stability and strength
Anulus fibrosus of disc 4
What are the ligaments of the spine?
Ligamentum flavum, Posterior longitudinal ligament, Anterior longitudinal ligament
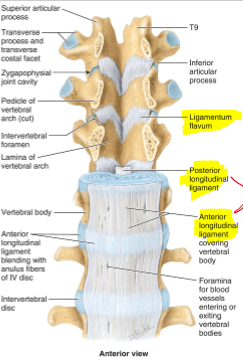
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL) consist of ?
Pain sensitive (stretch too much), Attaches to Post Longitud( PLL), and allows blood to enter
Posterior Longitudinal Lig (PLL)
Very pain sensitive
Ligamentum Flavum
Look at picture

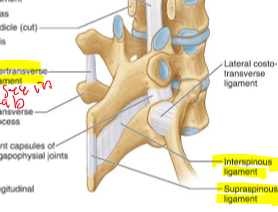
Interspinous ligament
tenses with flexion and pain sensitive
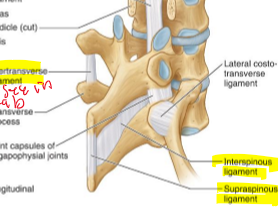
Supraspinous ligament
over the spinous processes and not pain sensitive
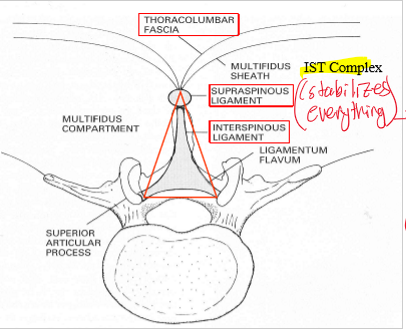
What does the IST complex consist of?
Thoracolumbar fascia, Supraspinous ligament, and Interspinous ligament (stabalizes the trunk and core)
What moves-’fold and unfolds’ with head, neck and trunk movments
Spinal cord
What bounds the Triangle of Auscultation?
Trapezius, Latissimus Dorsi, and Rhomboid major
What landmark is the tip of the spinal cord
Conus Medullaris
Dentate Ligament?
Has fibrous sheets of pua extending midway b/w posterior and anterior rootlets from lateral surface of spinal cored
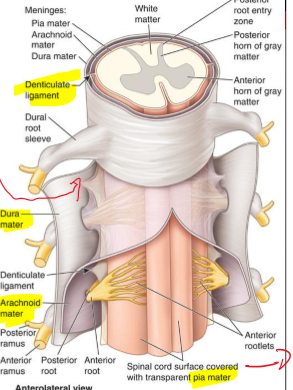
At the Birth the Conus Medullaris is where?
L4/L5 level
At the adulthood the Conus Medullaris is where?
Cord ends at L1/L2 level
What are the loose bundle of lumbar and sacral spinal cords?
Cauda Equina
What is the Lumber cistern?
enlargement of the subarachnoid space between the conus medullaris of spinal cord and inferior end of subarachnoid space and dura mater.
How many Spinal nerves are there?
31!!
Where does the C1 exit?
Between skill(occiput) and atlas
Most Cervical nerves exit where
ABOVE their proper vertebrae (ex. C4 exits out the C3)
Where is the exception with the exiting of the cervical nerves?
The C8 exits below its proper vertebrae because is only 7 cervical vertebrae (Remeber 7up, C8 down)
Where do they usually do epidural shots and why?
in the cauda equina because its hard to hit nerves and the Nerves are like dried spaghetti noodles hanging
Where does the spinal cord stop?
L1 or L2,
If the the spinal cords ends at L1 or L2 what happens to the lower lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal nerves?
They descend as a bunch of nerve roots called cauda equina (horse’s tail)
What does the Filum terminale externum do?
Keeps spinal cord in place
Ventral (anterior) Primary rami
Immediately divide when spinal nerves exit intervertebral foramina
-Travels anterior providing motor and sensory innervation
Dorsal Primary Rami
Travel posterior to innervate structures in the back
What system regards the Brain and spinal cord only?
Central Nervous System (CNS)
What system regards outside the spinal cord?
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
What root of the nerve is in charge of sensory?
Posterior root

What root of the nerve is in charge of motor (movements)
Anterior root
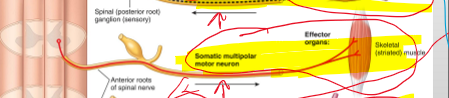
What nervous system is in charge of fight or flight?
Sympathetic nervous system (SNS)- leads to increased alertness
What nervous system is in charge of rest-and-digest?
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS)- slows down most body activities
What nervous system uses “E situations” (exercise, emergency, excitment,embarassment)
SNS
What is SLUDD in the PNS?
Salivation,Lacrimation(tears),Urination,Digestion,Defecation
What are the “3 decreases” in the PNS
-Decerases HR
-Decreased diameter of airways
-Decreased diameter of pupils
Grey matter is inside or outside?
Inside
White matter is outside or inside
outside
What are the effects of spinal flexion?
Elongation and increased tension.
In Complete Spinal Cord injury results in what?
loss of all sensation and voluntary movment inferior to the injuried vertebrae.
Complete Spinal Cord injury (C1-C3)
no function below head level, ventilator is required
Complete Spinal Cord injury (C4-C5)
Quadriplegia (no function of upper and lower libs)
Complete Spinal Cord injury (C6-C8)
loss of lower limb function combined with a loss of hand and variable amount of upper limb function; individual may be able to self feed or propel a wheelchair
Complete Spinal Cord injury (T1-T9)
Paralegia (paralysis of both lower limbs)
Complete Spinal Cord injury (T10-L1)
some thigh muscle function, which may allow walking with long leg braces
Complete Spinal Cord injury (L2-L3)
retention of most leg muscle function; short leg braces may be required for walking
A herniated disc is caused by what?
The Nucleus Pulposus pressing into the posterior longitudinal ligament.
Broken neck at “Scotty dog” indicated what?
Spondyloysis
What are the curves of the spine?
Kyphosis, Lordosis, and Scoliosis
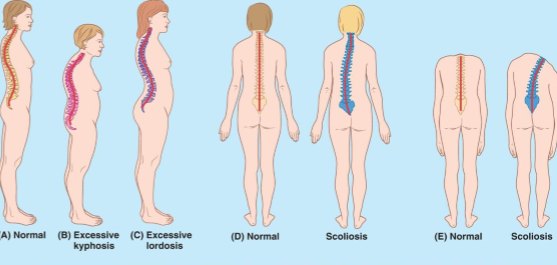
What is the main thing about Lumbar Stenosis?
There is bone growth in the vertebral foramen which causes narrowing of the canal