HNM109 Exam Revision
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Complete miscarriage
body has passed all of the pregnancy tissue
Ectopic pregnancy
embryo implants outside of the uterus
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD)
diagnostic term for severe neurodevelopmental impairments that result from brain damage caused by alcohol exposure before birth
Glycosuria
presence of excessive amounts of glucose in the urine, which normally contains little to no glucose
Incomplete miscarriage
some but not all of the pregnancy tissue has passed.
Inevitable miscarriage
miscarriage that has started, pregnancy tissue is still in the uterus
Missed/silent miscarriage
embryo/ fetus has died but remains in the uterus
Placenta previa / abruption
previa: placenta covering the cervix
abruption: placenta (abruptly) separating too early from the uterus
Pre-eclampsia
serious pregnancy disorder that causes high blood pressure and organ damage, particularly to the kidneys, typically after 20 weeks of pregnancy or in the postpartum period
Proteinuria
too much protein in the urine
Stillbirth
death of a baby during pregnancy after 20 weeks of gestation or at a weight of 400 grams or more
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
unexpected and unexplained death of an infant under one year of age, typically during sleep, after a thorough investigation has found no specific cause
Teratogens
an agent that increases the incidence of congenital malformation
Threatened miscarriage
body shows signs that you may miscarry.
Internal os
constriction at the upper end of the isthmus (lower part of uterus that connects to cervix)
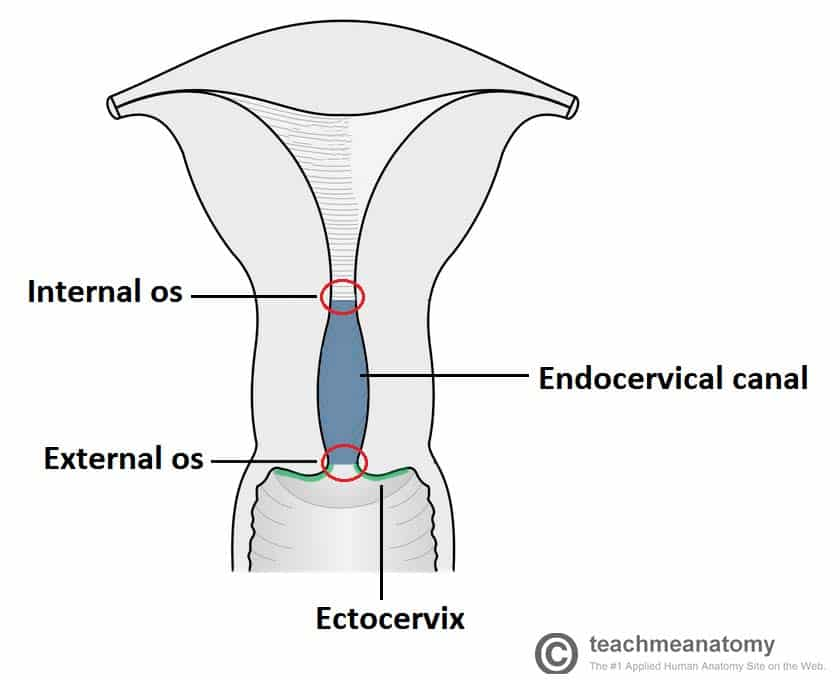
Cornu
junction between each fallopian tube + uterus
Fallopian tubes
functions
capture the egg
facilitate fertilization by transporting sperm to the egg and providing a suitable environment for fertilization
transport the fertilized egg (embryo) from the ovary to the uterus for implantation
Fundus
area above + between uterine tubes (fallopian)
Histological internal os
transition point between the endocervical canal and the uterine body
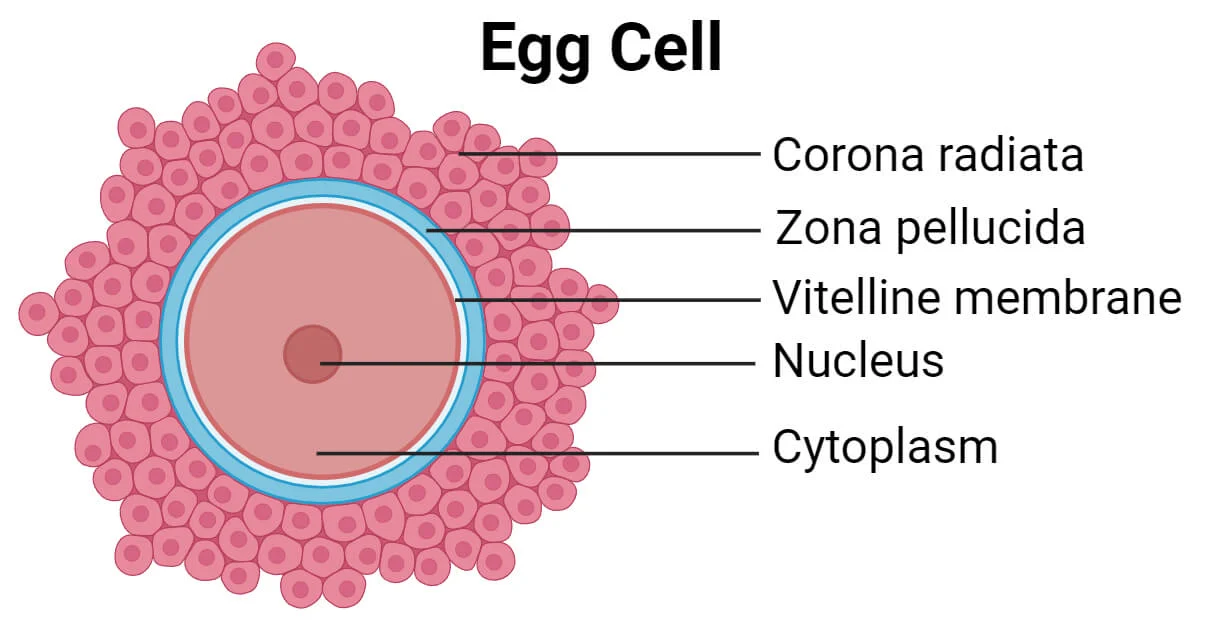
Oocytes
eggs
Supravaginal cervix
upper larger potion of cervix that extends from the internal os to the external os
Aneuploidy
genetic condition where a cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes, either an extra or a missing copy, rather than the typical 46 in humans
Atresia (of oocytes)
physiological process of degeneration and death of oocytes (immature eggs) and their surrounding follicular cells within the ovary
FSH (follicle-stimulating Hormone)
produced by the pituitary gland that regulates the reproductive system. - stimulates egg development in the ovaries and helps maintain the menstrual cycle and ovulation
Gonadotrophin
set of hormones that stimulates the gonads (ovaries and testes) to produce other hormones and gametes
HPO (hypothalamic-Pituitary-Ovarian) axis
key endocrine system that regulates female reproduction by controlling the menstrual cycle and ovulation
hCg - human chorionic gonadotropin
hormone produced during pregnancy, detected by all pregnancy tests and used to monitor pregnancy progression
Menopause
natural end of your reproductive life, marked by 12 consecutive months without a period and a decline in hormone (estrogen) levels
Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI)
loss of ovarian function before age 40, leading to irregular or absent periods and infertility.
Monotrophic rise
refers specifically to the pattern where only one hormone (e.g. follicle-stimulating hormone or FSH) rises while others like estradiol remain relatively unchanged
Oestrogen
female sex hormone produced mainly by the ovaries, responsible for sexual and reproductive development, bone health
uterine hyperplasia, hypertrophy, vascularization, swelling of tissues
Oogenesis
Process of female gamete (egg cell) formation in ovaries - First meiotic division begins before birth but is arrested until post-puberty
Ovulation
Oestrogen increase → LH surge → stimulates prostaglandin release → oestrogen drops → rupture of vesicular follicle (aka egg release)
Progesterone
maintains inactiveness of myometrium
Promote decidual secretions: which promote embryo implantation, nurturing developing placenta, suppresses the immune response to the embryo
lowers smooth muscle excitability - aka relaxes smooth muscles
4Ds
When feeling an urge to smoke:
Delay
Deep breathe
Do something else
Drink water
5 A’s
Steps to intervention:
Ask, Advise, Assess, Assist, Arrange
motivational R’s
Relevance, Risk, Reward, Roadblocks, Repetition
BMI formula
weight/ height^2
Naegele's Rule
add 7 days to the first day of the LMP and subtract 3 months, or add 9 months.
Cardiotocography (CTG)
medical test to monitor a baby's heart rate and uterine contractions
Pulsality index
non-invasive measurement that quantifies the degree of blood flow pulsatility in an artery
fetal middle cerebral artery pulsality index
assesses blood flow resistance in the fetal brain
Embryogenesis
process of forming a fertilized egg (a zygote) into an embryo
Electronic fetal monitoring
use of electronic fetal HR monitoring for evaluation of fetal wellbeing in labour
external FHR monitoring: uses a device to listen to or record fetal HR through mother’s abdomen
internal FHR monitoring: uses an electronic transducer connected directly to fetal scalp
Fertilisation
biological process in sexual reproduction where a male gamete (sperm) and a female gamete (ovum or egg) fuse to form a new single cell called a zygote
Group B Strep
common bacterium that usually causes no problems but can lead to serious infections in newborns.
GBS can be passed to a baby during birth, leading to potentially life-threatening conditions like sepsis, pneumonia, or meningitis.
Preventive antibiotics during labor protect the baby, and if a baby develops GBS, it can be treated with antibiotics after birth.
NST (non-stress test)
safe, non-invasive prenatal test that monitors a baby's heart rate and movement during the third trimester to assess fetal health and well-being
Oral glucose tolerance test
medical test that measures how the body responds to sugar; used to diagnose conditions like diabetes, pre-diabetes, and gestational diabetes
Non-invasive prenatal screening/ prenatal testing (NIPS/ NIPT)
examines cell-free DNA from the placenta circulating in the mother's blood.
It screens for common chromosomal abnormalities, including Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome), Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)
Surfactant
increases lung compliance (can be inflated with less effort) - collapse of alveoli is prevented, absorbs lung fluid after birth
Umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry (DV)
used to assess flow velocity waveforms in the fetal umbilical artery
umbilical vein
takes O2 blood to liver then heart (inferior vena cava)
ductus venosus
allows blood to go through umbilical vein to meet up with inferior vena cava
shortcut through liver
foramen ovale
sends blood from RA → LA
opening between the heart's left and right atria that is essential for fetal circulation
allows oxygenated blood from the placenta to bypass the lungs and enter the systemic circulation
ductus arteriosis
vessel b/w pulmonary artery + aorta
umbilical artery
takes blood back to placenta
“FETUS” acronym:
Foetal movement felt by experienced clinician
Electronic device detects foetal heartbeat
The birth of the baby
Ultrasound detects baby
See visible movements (experienced clinician)
“PROBABLE” acronym:
Positive pregnancy test
Returning of fetus when uterus is palpated - ‘ballotement’
‘Osiander’s sign’ - pelvic congestion - pulsation of fornices
Braxton-Hicks contractions
A softening of the cervix (Goodell’s sign)
Bluish colour of vagina + cervix ‘Chadwick’s sign’
Lower uterine souffle (whistling noise)
Enlarged uterus/ abdomen
Skin changes - pigmentation changes
“PRESUME” acronym
Period absent
Really tired
Enlarged breast
Sore breast
Urination increased
Movements (maybe?)
Emesis (N+V)
Gravidity
the number of times a woman has been pregnant
Parity
number of times that she has given birth to a fetus with a gestational age of ≥20/40
Sepsis
body’s immune system has an extreme response to an infection
Vaginal functions
Escape of menstrual blood flow
Coitus with entry of the male penis
Birth of the fetus, placenta and membranes
role of the midwife
Midwife = professional who works in partnership with women to give necessary
Woman-centred care
Philosophy - work in partnership with the woman
Continuity of care
meeting the same health professional for each antenatal visit + ongoing labour, birth and postnatal care
Opposite = fragmented care (seeing many different healthcare professionals)
Aligned with midwifery primary care
Can be provided under private obstetric care
Effect of smoking on the baby
carbon monoxide replaces some of the oxygen in the blood
→ reducing amount of O2 baby receives via umbilical cord
affects how placenta forms
reduces nutrients crossing placenta to the baby
Associated risks of smoking
increased risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
miscarriage
ectopic pregnancy - embryo implants outside of the uterus
low birthweight
small gestational age, pre-term birth (less than 37 weeks)
weaker immune system
pre-eclampsia
long term damage to lungs/ brain/ blood e.g. asthma or pneumonia
placenta issues
placenta previa: placenta covering the cervix
placental abruption: placenta separating too early from the uterus
What actions should the midwife take thereafter in terms of assessing smoking behaviours?
See if they need written resources or a Quitline referral
Quitline - refer woman if they are smoking during the pregnancy
monitor the baby closely
continue encouraging mother/partner to stop smoking
Effect of alcohol on the baby
No safe level of alcohol consumption during pregnancy/ breastfeeding has been identified
Risk of harm to the fetus increases the higher the amount + frequency the mother drinks
Associated risks of alcohol on baby
lower birth weights
miscarriage
stillbirth
premature birth
birth defects
a range of conditions known as Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD)
Effect of alcohol on breastfeeding
alcohol crosses into the breastmilk and can:
stay there for several hours
reduce the flow of your milk (this can unsettle your baby and cause them to eat and sleep less)
affect how the baby’s brain and spinal cord develops
What sort of support will help women to reduce or cease alcohol use in pregnancy?
Pregnant Pause
support network - e.g. family, partner, friends
What actions should the midwife take thereafter in terms of assessing smoking behaviours?
See if they need written resources or a Quitline referral
Quitline - refer woman if they are smoking during the pregnancy
monitor the baby closely
continue encouraging mother/partner to stop smoking
urge to smoke, 4Ds
Diet changes for nausea/ morning sickness
can be made worse by sugary foods (e.g. ginger stuff)
made better with carbs + proteins (meals + small snacks throughout the day
avoiding refined, fried and spicy foods
eat foods rich in B group vitamins
reduce coffee + tea
Diet changes for constipation
can be helped with increased fibre intake (fruit + veggies, grains, beans + lentils, brown rice, nuts, seeds, dried fruits)
Diet changes for heartburn
avoid fried, fatty, spiced foods
avoid coffee, tea, alcohol, cigarettes (worsen heartburn)
chew food thoroughly + eat slow
eat apple, pineapple, papaya, kiwifruit (have enzymes which speed digestion of food)
eat raw almonds / cashew nuts
How BMI affects where woman gives birth:
low pre-pregnancy BMI: increased risk of
preterm birth, small for gestational age, low birthweight
high pre-pregnancy BMI: increased risk of
large for gestational age, macrosomia, childhood obesity/ overweight
What foods should pregnant women avoid in pregnancy and why?
undercooked or raw meats, fish, and eggs
pate - avoid
very high in vit A, too much may not be good for bebe
blue cheese - avoid
Important micronutrients
folic acid, iron, calcium, iodine, and vitamin D
Role of motivational interviewing
The suggested structure (5Rs) below may assist with discussion on smoking behaviours + other behaviours
Physiological factors affecting fertility
Age + menopause
as a woman grows older, ongoing atresia (death) of oocytes
decrease in quality of oocytes with advancing maternal age
shown by higher incidence of chromosomal anomalies e.g. aneuploidies —> reduce chances of successful fertilisation, implantation and early embryo development
Menopause timing
estimated that natural fertility ceases ~10 years before menopause
primary ovarian insufficiency (POI): menopause before the age of 40 years
aka premature ovarian failure or hypergonadotrophic amenorrhoea
once this condition is established, fertility is usually lost, although spontaneous pregnancies may occur
Epigenetics
changes in gene expression caused by the environment
environmental factors can cause epigenetic changes assoc w DNA methylation + histone proteins
can shorten functional life span of a woman’s ovaries
Pelvic diseases
e.g. endometriosis, neoplasms, infection
may involve surgery
which can lead to early menopause
Body-fat connection
excessive exercise/undernutrition can postpone puberty, reduce fertility, prevent menstruation
Older women and childbirth
women over 35 may have more difficulty conceiving, are more likely to bear twins
declining fertility (may be due to less-frequent ovulation or problems e.g. endometriosis)
risks that increase with age
Miscarriage
chromosomal abnormalities (#1 cause of miscarriage)
hypertensive complications (increase w/ age)
Teenage pregnancy
tend to be poor + relatively socially and economically disadvantaged espec. compared to older mothers
Conception factors + lifetime health
Vaccinations
German measles (Rubella): normally a mild viral disease; however, infection during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy can result in severe abnormalities in an unborn baby.
Chicken pox: in very early pregnancy/ close to the baby’s due date can cause infection in the baby, miscarriage or possible abnormalities. COVID-19 vaccination: The Pfizer vaccine (Cominarty) and Moderna vaccine (Spikevax) are safe and effective at any stage of pregnancy, or if breastfeeding or if planning to get pregnant.
Flu vaccination: Pregnant women can become quite sick with flu and are also at risk of complications.
Whooping cough: Whooping cough (pertussis) vaccination does not last a lifetime.
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD)
important that women don’t drink alcohol until they know whether they’re pregnant
Sperm - not sure how it’s affected by alcohol so it is best for both parents to avoid when trying
alcohol decreases/ inhibits milk production
enters breast milk approx. 30-60 mins after you start drinking
for every standard drink, need to wait at least 2 hours before you can breast feed
avoid drinking for first month post birth
always breastfeed baby before you drink
If there is alcohol in ur system, no amount of pumping and dumping will clear the alcohol
only once bloodstream has cleared of alcohol that breastmilk will clear
Vaping + smoking
Smoking = most common + impo factors affecting follicle maturation due to compounds in tobacco
nicotine from e-cigarettes passes through placenta - same as tobacco
nicotine + other chemicals can interfere with milk supply and pass into breast milk
Pre-conception health
underweight + overweight obesity can impact chance of conception + healthy pregnancy
high BP, diabetes, blood complications
underweight during pregnancy is assoc w/ pre-term birth
Oogenesis process
First meiotic division begins before birth but is arrested until post-puberty
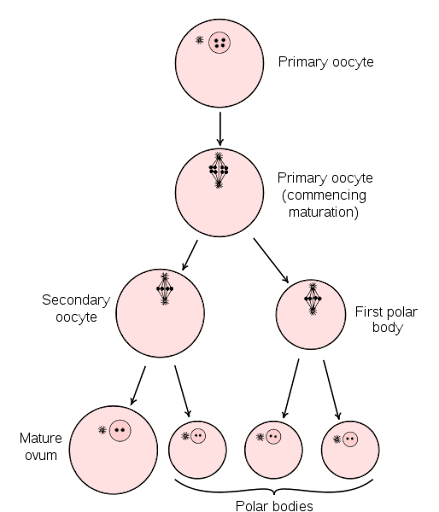
Ovulation process
Begins when oestrogen levels peak; ends when vesicular follicle ruptures
Triggers release of 2ndary oocyte (surrounded by zona pellucida and corona radiata)
Rise in oestrogen levels (~48h before ovulation) triggers LH surge
luteinizing hormone (LH) interacts with LH receptors on granulosa cells (increasing production of oestrogen by dominant follicles)
High level of LH stimulates production of prostaglandins (PGF2a and PGE2)
Allows primary oocyte to complete 1st meiotic division + become secondary oocyte
Simultaneously, oestrogen lvls drop + proteolytic enzymes are synthesis
Breaks down thecal cells + assist rupture of vesicular follicle = egg release
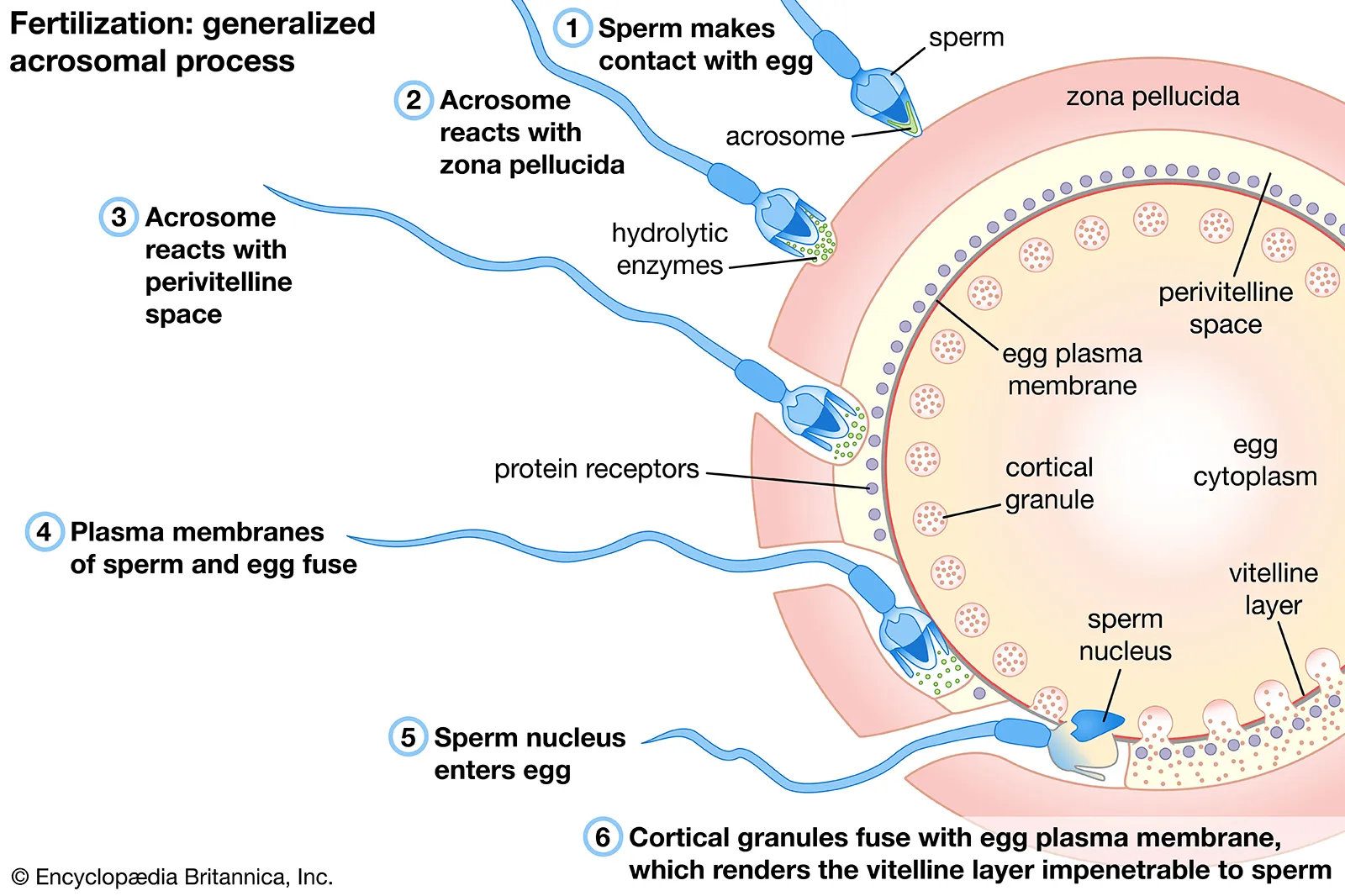
Fertilisation
1. Capacitation
process of maturation enabling a freshly ejaculated sperm to fertilize an ovum
Glycoproteins + seminal plasma proteins removed from acrosome (head of sperm cell)
2. Acrosome reaction= acrosome cap perforates - contents in acrosomal vesicle are released
Lytic enzymes released around oocyte
Digests first physical barrier and corona radiata follicular cells disperse
Sperm makes contact with zona pellucida + binds with glycoproteins on its surface
Enters cytoplasm of the ovum
Cell membranes of oocyte + sperm fuse
Head + tail of sperm enter the oocyte (leaving the sperm’s plasma membrane behind)
***oocyte completes 2nd meiotic division
Describe the changes to the uterus that facilitate growth of the embryo
pear-shaped —> globular (until 20w)
upper part enlarges due to estrogen
pelvic is anteverted —> upright + inclines/ rotates to the right
due to colon in left side of pelvic cavity
uterine wall 10mm —> 25mm
lower uterus 7mm —> softens + elongates to 25mm
differentiation of lower uterine segment
size 7.5cm length 2.5cm wide/deep —> 20cm long, 25cm wide, 22.5 deep
50g weight —> 80 + 1200g
x20 increase
muscle fibres —> early pregnancy: more fibres + more compliant —> term: muscle fibres increase three-fold
due to hyperplasia; due to estrogen
Uterine muscle during pregnancy
(like other smooth muscles) - uterus is spontaneously contractile
Can perform considerable muscular feats to expel its contents (e.g. during menstruation + childbirth)
At other times, it's prevented from contracting
Must remain inactive to allow development + growth of fetus + placenta during pregnancy
Uterus usually follows predicted rate of growth (only a reliable indicator of gestational age in 20/40)
Main part of uterine growth during second half of pregnancy is almost entirely due to hypertrophy (size increase)
Growth of the fetus acts as powerful stimulator for growth of contractile proteins of the myometrium
Hormonal influences on uterus in pregnancy
Oestrogen + progesterone (initially from corpus luteum + placenta) are mainly responsible for influencing uterus
Oestrogen promotes growth of muscle fibres
Progesterone maintains inactiveness of myometrium
Interaction has growth-promoting effect ⇒ increases uterine muscle compliance
Actions of oestrogen + progesterone on target cells
estrogen stimulates RNA synthesis
Progesterone's role is less understood
May be responsible for increasing membrane resting potential in pregnancy (so muscle fibre contractions are less likely to occur)
CVS - physiological changes
- Plasma volume increases by 30%-40% (approx 1,500mL) between weeks 7–34
- Cardiac output increases by 30%-50% (from 5L/min at 10 weeks to 6.5L/min at 25 weeks)
- Stroke volume increases by 30%, heart rate by 15%
- Blood pressure remains same or drops slightly due to decreased total peripheral resistance (via progesterone)
- Vasodilation due to progesterone-induced arterial smooth muscle relaxation
- Relaxation of venous smooth muscle increases venous capacity
- Uterine blood flow rises from 50mL/min (10 weeks) to 500mL/min (term)
- Decreased resistance in renal blood vessels early in pregnancy
- Skin and mucous membrane blood flow increases up to 70% by week 36, causing heat intolerance, sweating, nasal congestion
- Supine position can compress vena cava in late pregnancy, decreasing venous return and cardiac output (left side to supine can decrease cardiac output by 25%-30%)
- Additional blood volume accommodated in uterus, breasts, muscles, kidneys, and skin
Respiratory - physiological changes
- Increased basal metabolic rate leads to 20% rise in O₂ consumption and CO₂ production
- Progesterone increases chemoreceptor sensitivity to CO₂
- Ventilation increases by 40%, mainly via 25%-40% increase in tidal volume
- Hyperventilation from increased ventilatory drive can cause dyspnoea
Genitourinary/ Renal - physiological changes
- Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) increases by 40%-50% in 1st trimester and falls in last few weeks
- Increased renal blood flow caused by reduced vascular resistance
- Reabsorption of electrolytes increases due to RAAS activity (stimulated by estrogen & progesterone)
- Progesterone dilates and may kink ureters from 10 weeks, raising risk of urinary stasis and infection
- Increased urinary frequency in early pregnancy from increased renal plasma flow; later, from fetal/uterine pressure
Endocrine/metabolic - physiological changes
- Human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) prevents corpus luteum degeneration and stimulates estrogen & progesterone
- Human placental lactogen reduces maternal glucose, mobilizes lipid stores, accelerates fetal amino acid transfer
- Estrogens induce uterine hyperplasia, hypertrophy, vascularization, swelling of tissues®
- Progesterone increases decidual secretions, suppresses maternal immunity, lowers smooth muscle excitability
- Anterior pituitary enlarges and increases ACTH secretion
- Placental CRH increases throughout pregnancy, playing a role in initiating labor
- Corticosteroid production (glucocorticoid & aldosterone) rises, cortisol up to 2-3x by term
- Thyroid gland enlarges, T3/T4 increases due to higher iodine clearance
- Parathyroid hormone increases, boosting calcium absorption
GIT - physiological changes
- Progesterone relaxes oesophageal sphincter causing reflux/heartburn
- Decreased stomach tone, motility, and reduced secretion delay gastric emptying
- Nausea/vomiting from decreased peristalsis, increased abdominal pressure, high hCG & sex steroids
- Slower peristalsis improves absorption but causes constipation
- Water reabsorption in colon and uterine compression further aggravates constipation
- Fluid retention in gums, leading to sponginess & bleeding
- Hormonal changes increase vulnerability to dental issues
Integument - physiological changes
- Melanocyte-stimulating hormone increases pigmentation, leading to chloasma and linea nigra
- Areola and perineum darken/toughen
- Collagen stretching causes stretch marks (striae gravidarum), linked to corticosteroids
- Perineum stretches during pregnancy
Musculoskeletal - physiological changes
- Increased laxity of joints (symphysis pubis, sacroiliac, sacrococcygeal) to increase pelvic capacity
- Ligament relaxation due to relaxin & estrogen
- Relaxin-induced symphysis widening begins at 10–12 weeks
- Greater joint mobility allows coccyx movement during labor
- Weight gain, cardiovascular/respiratory changes, and edema contribute to discomfort
Signs of miscarriages (cervix, bleeding, pain)
Cervix | Bleeding | Pain | |
Threatened | Closed | Yes | Some |
Inevitable | Open | Yes | Yes |
Incomplete | Open | Yes - may be heavy | Yes- may be intense |
Complete | Closed | Minimal, decreasing | Yes, ~decreasing |
Missed | Closed | No | No |
What signs would indicate that a pregnancy loss may be occurring or is inevitable?
Miscarriage happens when pregnancy stops growing
Lots of bleeding - enough to fill 2 pads in an hour
Large blood clots - golf ball size
Very bad cramps + stomach pain
Fever/ chills
Dizzy like you'll faint
Unusual smelling vaginal discharge
Ectopic pregnancies cause bleeding