Lecture 1 - Neurons
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
what is cell theory?
the body of any animal or human or plants is made up of individual cells
what is reticular theory?
nervous system is made up of a continuous network of connected nerve fibers
what is silver stain?
a technique to selectively stain biological structures, making them visible under a microscope
a prototypical vertebrate neuron has all of the following
dendrites
axon
cell body
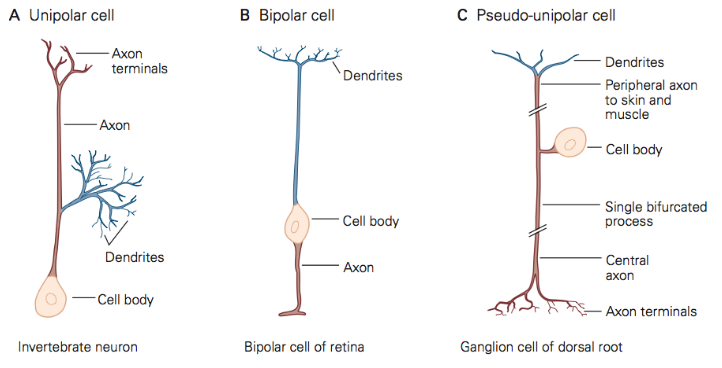
distinguish between unipolar cell, bipolar cell, and pseudo-unipolar cell
unipolar cell: cell body connects to only one direction and that direction connects to both axon and dendrites
bipolar cell: cell body is in the middle, dendrites signal connect to cell body and cell body transfer to axon
pseudo-unipolar cell: cell body is on the side, connecting itself to the axon, which then goes into dendrites and axon terminals
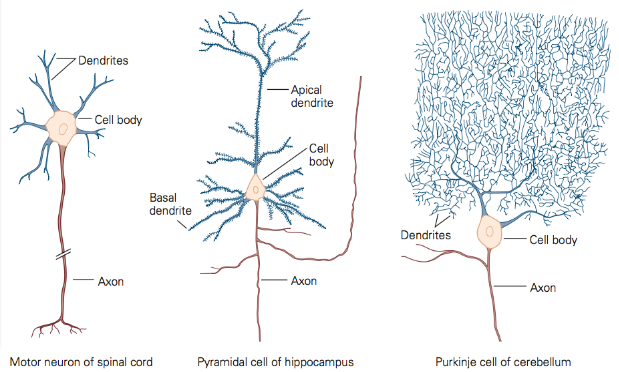
what are the three types of multipolar cells
motor neuron
pyramidal cell
purkinje cell
describe the differences between the three types of multipolar cells
motor neuron: cell body has multiple dendrites
pyramidal cell: cell body has a complex dendrite system
purkinje cell: cell body has a massive complex dendrite system
what is connectome?
the wiring/synaptic connectivity of all neurons
what is the usage of connectomes?
know connectome for a circuit → infer its function
what is an interneuron
A short neuron that facilitates communication between other neurons, usually functions by inhibition
what is the importance of visualizing neurons?
an unprocesses brain image is not useful, however, by visualizing individual neurons of interest, those images become meaningful
what is the golgi stain?
a neuron visualization technique that uses silver to randomly stain a small subset of neurons
what are the pros of the golgi stain
tried and true technique; relatively easy
what is the con of the golgi stain
can only be used on dead tissue
what is the importance of the golgi stain technique?
helps us visualize structural differences in individuals
what is dye filling
a neuron visualization technique that dyes the entire cell through diffusion using a small glass pipette
what are the pros of dye filling
can be performed on both live or dead tissue
can select the exact cells and visually isolate them from others
what is immunohistochemistry?
a neuron visualization technique that uses antibodies (which sticks to specific proteins) to detect specific proteins in cells or tissues. These antibodies have a fluorescent tag so that it shines and when you look under a microscope, the specific ones will be spotted
what is genetically-encoded fluorescent proteins
a neuron visualization technique where special proteins that glow under light called GFP and this is put into the DNA of neurons and the cell reads the GFP gene and builds the glowing protein, therefore when viewed under a microscope it will glow
what is green fluorescent protein?
a naturally glowing protein originally found in jellyfish
what are nodes of ranvier?
small gaps in the myelin sheath that surround axons in the nervous system. These gaps play a crucial role in nerve signal transmission by allowing electrical impulses to "jump" from one node to the next
what is cell differentiation?
the biological process by which a generic, unspecialized cell (like a stem cell) becomes a specific type of cell with a distinct function — such as a neuron, muscle cell, or skin cell.
describe how cell differentiation occurs
start with a stem cell
receive a signal (hormones or hcemical)
some genes are expressed or silent
DNA is read and transcribed into RNA
RNA gets read and create proteins (proteins carry out the jobs of a cell and the identity of a cell is determined by the kind of protein
what are antibodies?
specialized proteins produced by the immune system to identify and neutralize harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, and toxins
describe simply how immunohistochemistry works
Find protein of interest, develop antibodies of interest, get tissue and wash tissues with antibodies, if protein of interest is in the sample, then the antibodies will stick to the proteins
what are the problems with immunohistochemistry?
need to know the specific protein, meaning that you need to know the information of the protein before you can do it
need to create antibodies, meaning tha tyou need to make an immune response in the organism and the organism has to create the antibodies and we need to collect the antibodies
Cells don’t let things inside of them, so proteins of interest needs to be expressed outside of the cell body
describe how genetically-encoded fluorescent proteins work
start with a fluorescent protein gene
attach it to a specific promoter
insert the gene into an organism’s DNA
the cells transcribe and translate the gene
those cells then glow under microscope
what is a promoter
a DNA sequence that controls when and where a gene is turned on
what are the cons of genetically-encoded fluorescent protein?
variable gene expression
costly set up
describe how to express FPs with viruses
Researchers can inject viruses into the brain to deliver fluorescent protein genes to specific cells.
This is flexible, targeted, and avoids breeding transgenic animals, but it does require surgery.
what is the clarity technique
a neuron visualization technique that removes fat from brain tissues so that light can pass through more easily. Making thick brain samples more transparent while keeping the neurons and their fluorescent labels intact
describe why we sometimes use confocal microscope instead of fluorescent microscope to visualize FPs
fluorescent microscope: all light from tissue is reflected to the eye piece, obstructing view
confocal mircoscope: pin-hole eliminates out-of-focus light, allowing single focal plane visualization and can reconstruct images from different focal planes
what is electron microscopy?
a neuron visualization technique that uses a beam of electrons instead of light to visualize very small structure
what is the one pro of electron microscopy?
has the best resolution of all neuron visualization technqiues
what are the cons of electron microscopy?
require an electron microscope (expensive) and a technician
time consuming
need to be done in a vacuum
requires a stable enviornment